Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FE-3 Basic AC Theory Open Sec1-11
FE-3 Basic AC Theory Open Sec1-11
Uploaded by
Vanesa JeronimoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FE-3 Basic AC Theory Open Sec1-11
FE-3 Basic AC Theory Open Sec1-11
Uploaded by
Vanesa JeronimoCopyright:
Available Formats
Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory Kuphaldt
For other considerations, peak or peak-to-peak measurements may be the best to employ.
For example, when rating insulators for service in high-voltage AC applications, peak
voltage measurements are the most appropriate, because the principal concern here is
insulator "flashover" caused by brief spikes of voltage, irrespective of time.
For "pure" waveforms, simple conversion coefficients can be calculated which equate
Peak, Peak-to-Peak, Average, and RMS measurements.
Bear in mind that the conversion constants shown above for RMS and average
measurements hold true only for pure waveshapes. The RMS and average values of
distorted waveshapes are not related by the same multiplier values:
Section Review:
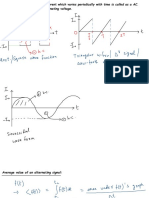
• The amplitude of an AC waveform is its peak as depicted on a graph over time.
• Peak-to-peak measurement is the total height of an AC waveform as measured from
maximum positive to maximum negative peaks on a graph.
• The Average measurement is the mathematical "mean" of all positive or all negative
points on a waveform graph.
• "RMS" stands for Root Mean Square, and is a way of expressing an AC quantity of
voltage or current in terms functionally equivalent to DC.
11
You might also like
- Lecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsDocument21 pagesLecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsShuvodip Das100% (1)
- Alternating Current Investigatory Project 12th Isc 2017Document39 pagesAlternating Current Investigatory Project 12th Isc 2017mayank kashyap77% (22)
- Ac WaveformsDocument4 pagesAc WaveformssrinivasNo ratings yet
- RMS Value, Average Value, Peak Value, Peak Factor and Form Factor in ACDocument4 pagesRMS Value, Average Value, Peak Value, Peak Factor and Form Factor in ACHosam Aldin JabrallahNo ratings yet
- RMS Voltage of A Sinusoidal AC WaveformDocument8 pagesRMS Voltage of A Sinusoidal AC WaveformRoboconDKNo ratings yet
- RMS and Ave VoltageDocument17 pagesRMS and Ave VoltageIroha IsshikiNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Electrical CircuitsDocument57 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Electrical CircuitsHari Krishna MusunooriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Alternating CurrentDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Alternating CurrentSarojBankawatNo ratings yet
- Experiment 02Document5 pagesExperiment 02Aayan ShahNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Ac Circuits: Unit-IiDocument41 pagesFundamental of Ac Circuits: Unit-IiChandra bhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument9 pagesRoot Mean Squarebauro mikaereNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms: Alternating Current and VoltageDocument7 pagesDefinition of Terms: Alternating Current and VoltageExan JohnNo ratings yet
- RMSDocument11 pagesRMSRsuneelNo ratings yet
- The RMS Voltage of An AC WaveformDocument4 pagesThe RMS Voltage of An AC WaveformXhaNo ratings yet
- Below: Peak Voltage of A WaveformDocument7 pagesBelow: Peak Voltage of A WaveformParulian Poltak HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current Relation and Value of SinusoidDocument4 pagesVoltage and Current Relation and Value of SinusoidGlerommie CastroNo ratings yet
- EECKT230 - Course Material 1Document35 pagesEECKT230 - Course Material 1reasjames0No ratings yet
- Root Mean Square ValueDocument2 pagesRoot Mean Square ValueProximo DvNo ratings yet
- Final Viva (Iec)Document13 pagesFinal Viva (Iec)Shaian IslamNo ratings yet
- AC ConceptDocument17 pagesAC ConceptFalguni MathurNo ratings yet
- Make Better AC RMS Measurements With Your Digital MultimeterDocument8 pagesMake Better AC RMS Measurements With Your Digital MultimeterJack_bookNo ratings yet
- Phasor RMSDocument15 pagesPhasor RMSjennethpaima0No ratings yet
- ACFDocument29 pagesACFBhairavi MNo ratings yet
- Average Electrical PowerDocument3 pagesAverage Electrical PowersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits LectureDocument30 pagesAC Circuits LectureYash MehraNo ratings yet
- AC CIRCUITS ReviewerDocument7 pagesAC CIRCUITS ReviewerKyle Joshua BunhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 2 Lab1Document6 pagesElectric Circuits 2 Lab1Hesham Ben aliNo ratings yet
- What Does An AC Voltmeter Measure?: Why Use RMS?Document35 pagesWhat Does An AC Voltmeter Measure?: Why Use RMS?Kelly BerryNo ratings yet
- Root Mean Square: VerificationDocument11 pagesRoot Mean Square: VerificationNick JohnNo ratings yet
- Waveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesDocument10 pagesWaveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Measurements: Application NoteDocument12 pagesPower Supply Measurements: Application NoteFrew FrewNo ratings yet
- ES Unit-2Document55 pagesES Unit-2Mazin VoraNo ratings yet
- LEC - 1 (AC Fundamentals)Document31 pagesLEC - 1 (AC Fundamentals)Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- BEEE (Alternating-Current Circuits)Document6 pagesBEEE (Alternating-Current Circuits)Vedu KadamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument3 pagesRoot Mean SquaresenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Cont..Document50 pagesUnit-1 Cont..mitparikh1046No ratings yet
- Module 5Document71 pagesModule 5Gabriel Carl AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Crest FactorDocument3 pagesCrest FactorAN.ADAMMSNo ratings yet
- What Is R.M.S (Root Mean Square) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is R.M.S (Root Mean Square) ?Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Alat Ukur Dan PengukuranDocument26 pagesAlat Ukur Dan PengukuranriaNo ratings yet
- 2.07 Ripple Factor, PIV, TUF, Form Factor, Peak FactorDocument1 page2.07 Ripple Factor, PIV, TUF, Form Factor, Peak FactorVamsiMadupu100% (2)
- WattsDocument1 pageWattsSanthi SriNo ratings yet
- Module 2A (AC Fundamentals)Document102 pagesModule 2A (AC Fundamentals)vipin10thj.27828No ratings yet
- EIE2100 AC CircuitsDocument91 pagesEIE2100 AC CircuitsP ChiNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanDocument30 pagesAC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanRehnuma NoorNo ratings yet
- NEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Document16 pagesNEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Ricelle Ann ParaleNo ratings yet
- Peak-to-Peak, RMS Voltage, and Power: Where's My Notes From Last Week!Document9 pagesPeak-to-Peak, RMS Voltage, and Power: Where's My Notes From Last Week!WillFonsecaNo ratings yet
- AC Waveforms TheoryDocument129 pagesAC Waveforms TheoryMuhammad Asif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- WattsDocument1 pageWattsrfengineersNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 2 - AC Circuits FE SEM-I 2020-21Document149 pagesBEE Module 2 - AC Circuits FE SEM-I 2020-21THE GR8 HUBNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument31 pagesAC Fundamentals19M647 - SRIRAM ANo ratings yet
- Digital Multimeter Basics and PriceDocument5 pagesDigital Multimeter Basics and PriceIshank PuriNo ratings yet
- Digital MultimeterDocument5 pagesDigital MultimeterVishnu JainNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ac CircuitsDocument17 pagesUnit Ii Ac CircuitsBalu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Power Calculations: - Effective Values: RmsDocument18 pagesPower Calculations: - Effective Values: Rmsرغد كنعانNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instruments: Working of D'Arsonval MeterDocument30 pagesElectronic Instruments: Working of D'Arsonval MeterKarthik VNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument21 pagesAC FundamentalsSaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pagesFoundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Section Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pagesSection Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Section Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument1 pageSection Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Simple AC Circuit Calculations: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pages1.4 Simple AC Circuit Calculations: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument1 pageFoundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- PDF Sinewavechokes 1 3Document3 pagesPDF Sinewavechokes 1 3Vanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: (This Material Relates Predominantly To Module ELP032)Document1 pageAlternating Current: (This Material Relates Predominantly To Module ELP032)Vanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Section Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pagesSection Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument1 pageFoundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet