Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paper 2 Questions Student Book Answers: Answers Extra Information Mark
Uploaded by
saadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paper 2 Questions Student Book Answers: Answers Extra Information Mark
Uploaded by
saadCopyright:
Available Formats
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
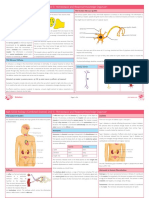
01.1 stimulus 1
central nervous system – brain 1
and spinal cord
effector – a muscle or a gland 1
motor neurone – carries 1
01.2 electrical impulses to a muscle
receptor – detects changes in 1
the environment
synapse – gap between 1
neurones
X – sensory neurone 1
02.1
Y – relay neurone 1
chemical released (from X) do not allow electrical impulse 1
accept neurotransmitter or
named chemical e.g.
02.2 acetylcholine
diffuses 1
across synapse (to Y) 1
allow 1 mark for correct
0.21 / 0.2 / 0.211 substitution or rearrangement
2
provided no subsequent step:
02.3 65.4 = 1.38 / time
or
time = 1.38 / 65.4
seconds / s 1
any two from: 2
• fewer synapses /
neurones involved
02.4
• shorter pathway allow impulse does not travel
to brain
• does not involve a
thought process
02.5 adrenaline accept epinephrine 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 1
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
(stimulates) any two from: 2
• release of glucose into accept breakdown of stored
blood glycogen
• increased heart rate
02.6 • increased breathing rate allow increased amount of
oxygen in blood
(for) increased respiration 1
(to) transfer more energy (to run) 1
any three from: 3
• (both have) 22 pairs of allow 44 chromosomes control
chromosomes that characteristics
control characteristics
• 23rd / another pair of
chromosomes
03.1
determines sex
• females have XX
chromosomes
• males have XY
chromosomes
male and female gametes allow ecf from 3.1 1
correctly written in Punnett
square
03.2
all genotypes correctly derived allow 1 mark for 2 / 3 correctly 2
from their gametes derived genotypes
any one from: allow ecf from their Punnett 1
• 1 in 2 square
• 2
03.3 • 50%
• 1:1
• 2:2
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 2
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
any six from: 6
• mother given FSH / LH /
fertility hormone(s)
• stimulates egg
maturation / release
• eggs collected
• sperm collected
• eggs fertilised (in petri
03.4 dish)
• embryos form
• (cells from embryos
tested to identify sex
• healthiest female
embryo(s) selected
• implanted into woman’s
womb / uterus
any four from: reference to both selection in 4
selection of sex in general general population and if risk
population: of genetic disorder required for
• unethical to select sex of full marks
baby
• would lead to unequal
proportion of males and
females in society
• may lead to ‘designer
babies’
03.5 if risk of serious genetic
disorder:
• reduces stress / upset for
parents
• prevents suffering / early
death of a child
• reduces proportion of
genes for genetic
disorder in population
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 3
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
any three from: 3
• good eyesight to see
prey
• good sense of smell /
hearing to detect prey
04.1
• strong legs to run fast
• sharp teeth to kill / hold
prey
• sharp claws to hold / rip
apart prey
any two from: 2
• new pathogens
04.2 • new predators (of the
fox)
• competition
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 4
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
1 mark for factor and 1 mark 2
for a correctly linked reason
different genes
• as daffodils produced by
sexual reproduction
or
amount of light
• light is needed for
photosynthesis
or
• more light and plants
grow more
or
• less light and plants grow
05.1 taller to find light
or
amount of mineral ions
• more ions and plants will
grow more
or
amount of water
• water is needed for
photosynthesis
or
disease / pests
• can stunt / slow growth
or
• restrict photosynthesis
height is a continuous variable allow the idea of many 1
05.2
different values to be plotted
suitable scales for both axes allow +/- ½ a square 1
with titles allow 1 mark for 3 or 4 correct
05.3 bars 1
bars labelled correctly
bars plotted correctly 2
05.4 25.0 – 29.9 (cm) 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 5
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
05.5 20.0 – 44.9 (cm) 1
06.1 12 1
1 185 600 allow ecf ×98 800 calculated 4
correctly
allow 1 mark for field area of
24 700 (m2)
06.2 and
allow 1 mark for quadrat area
of
0.25 m2
allow 3 marks for 98 800
throw quadrats randomly allow idea of not selecting 1
areas
or
06.3
take more samples / quadrat
and calculate a mean
to reduce effect of high / low 2
06.4
quadrat values
20% 2
allow 1 mark for counting 5
squares
06.5 or
allow 1 mark for (incorrect
number of squares / 25) ×100
correctly calculated
06.6 transect 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 6
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
Question Answers Extra information Mark
idea of damage to plant only
required once
ribwort plantain grows mainly allow answers in terms of 1
away from path / on the field / quadrat number / start and
grass / on area not walked on finish
ignore figures
(because) ribwort plantain has 1
tall leaves / is taller and gets
damaged (more) on path
06.7 greater plantain grows mainly on 1
path / walked on area allow answers in terms of
quadrat number / start and
finish
(because) greater plantain ignore figures 1
grows flatter / lower to ground /
is shorter (so) will be damaged
less by trampling / will not be
pulled out
allow for 1 mark where
number of one plant high,
number of other plant low
07 • pancreas detects blood 1
sugar concentration
• if concentration is high 1
pancreas secretes insulin
• (insulin) stimulates liver 1
and / or muscle cells to
absorb glucose
• and store as glycogen
1
• if concentration low,
pancreas secretes 1
glucagon
• (glucagon ) stimulates
liver and / or muscle cells 1
to convert glycogen to
glucose
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 7
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
select a cow that produces a 1
creamy milk
breed with a bull from a cow that 1
produced creamy milk
08.1
select offspring that produce the 1
most creamy milk to breed from
repeat over several generations 1
until all cows produce creamy
milk
gene for poison is cut from ignore characteristic 1
bacterial DNA / plasmid / accept from Bacillus
chromosome thuringiensis / Bt
08.2 1
using enzyme(s)
and transferred to cotton plant do not allow to cotton plant 1
cells / DNA / chromosome plasmid
increased yield as less eaten by 1
insects
fewer pesticides need to be 1
08.3
used
(so) producer can make more 1
money
Any two from: 2
• gene (for poison) could
be passed onto wild
plants
• may kill useful insects allow named insect e.g. bees
08.4
• ecosystem / food chain
could be affected
allow less variation in cotton
• gene pool of cotton plant population
plants could be reduced
produce hormones 1
09.1
that are released directly into the accept are ductless glands 1
blood
adrenal gland = C 1
pituitary gland = A 1
09.2
thyroid gland = B 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 8
Paper 2
Student book answers questions
(pituitary gland) secretes several 1
different hormones
09.3
which stimulate other glands (to 1
release hormones)
any six from: 6
• FSH causes eggs to
mature in ovary
• FSH stimulates release
of oestrogen from ovary
• oestrogen stimulates
thickening of uterus
lining
• oestrogen inhibits
release of FSH
• oestrogen stimulates
release of LH
• LH causes ovulation /
09.4 release of an egg
• progesterone is released
after ovulation from the
ovary / empty follicle
• progesterone maintains
the uterus lining
• progesterone inhibits
release of FSH and LH
• if egg is not fertilised
levels of all hormones
fall
• (fall in level of hormones)
causes menstruation
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 9
You might also like
- Cells and Organisation Foundation Practice Exam Questions Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCells and Organisation Foundation Practice Exam Questions Mark SchemeVeena PurohitNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkDocument5 pagesStudent Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarksaadNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkDocument6 pagesStudent Book Answers Paper 1 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkEngwarwickNo ratings yet
- C7 Practice AnswersDocument3 pagesC7 Practice AnswersMo KhNo ratings yet
- MScopy Practice 9Document10 pagesMScopy Practice 9Grish coolNo ratings yet
- Nerves ND NeuronsDocument1 pageNerves ND Neurons2yzd7tkryqNo ratings yet
- Kendriyavidyalaya Sangathan, Mumbai Region: Answer KeyDocument5 pagesKendriyavidyalaya Sangathan, Mumbai Region: Answer KeyYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- 9201 92011 International Gcse Biology Mark Scheme v2Document13 pages9201 92011 International Gcse Biology Mark Scheme v2laurelxu33No ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bio End of Topic B1Document13 pagesAQA GCSE Bio End of Topic B1josephNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers Paper 2 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkDocument6 pagesStudent Book Answers Paper 2 Questions: Answers Extra Information MarkEngwarwickNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Unit 4 Mark Scheme Jan21Document19 pagesA Level Biology Unit 4 Mark Scheme Jan21andhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics P12 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Physics P12 Practice AnswersjayakantharushanNo ratings yet
- Delhi - Science - 3 Set PDFDocument21 pagesDelhi - Science - 3 Set PDFAbhinav SharmaNo ratings yet
- KMS-CSECHsbiog-01253020-MayJune2022 Question 6Document3 pagesKMS-CSECHsbiog-01253020-MayJune2022 Question 6Jovanni PeterNo ratings yet
- Answers To Biology Paper 2 STPM Trial Examination 2010 PahangDocument15 pagesAnswers To Biology Paper 2 STPM Trial Examination 2010 PahanglsueyinNo ratings yet
- Additional MCQs - Unit 2Document2 pagesAdditional MCQs - Unit 2Savage TongueNo ratings yet
- As Biololgy Unit 2 Mark Scheme Jan21Document15 pagesAs Biololgy Unit 2 Mark Scheme Jan21andhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- BR Bio 2022 1 enDocument4 pagesBR Bio 2022 1 enZeinab HijaziNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 5 Key by Zta Malappuram - 230212 - 105930 PDFDocument4 pagesHsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 5 Key by Zta Malappuram - 230212 - 105930 PDFഎസ്സാർപി ഊരുചുറ്റൽ തുടരുന്നുNo ratings yet
- Nd-Lesson-3 21 SynapsesDocument22 pagesNd-Lesson-3 21 Synapsesapi-176402481No ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE Combined B2 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Biology GCSE Combined B2 Practice AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response: Homeostasis: The Maintenance of A Constant Internal EnvironmentDocument39 pagesCoordination and Response: Homeostasis: The Maintenance of A Constant Internal EnvironmentKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise And: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument3 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise And: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionHarry LeungNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER EXAM I GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - FEBRUARY 28 2023 - 10 - 00AM 12 - 00PM - General Biology 2 S2 AY22 23 ST12I PDFDocument17 pages3RD QUARTER EXAM I GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - FEBRUARY 28 2023 - 10 - 00AM 12 - 00PM - General Biology 2 S2 AY22 23 ST12I PDFB9 GENE MARVIN S. BORBONNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme P2 Pahang (STPM)Document16 pagesMark Scheme P2 Pahang (STPM)Rozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Human Nervous System 2 MSDocument9 pages5.2 Human Nervous System 2 MSTosyn AriyoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture - Synapse and Receptors - CNS Physiology (2nd Edition)Document16 pages2nd Lecture - Synapse and Receptors - CNS Physiology (2nd Edition)Mihaela Cenușe100% (1)
- AQA Biology GCSE Combined B14 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Biology GCSE Combined B14 Practice AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- 2011 Cell CommunicationDocument22 pages2011 Cell CommunicationFidiya Septi Kusma WardaniNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics GCSE Combined P9 Practice AnswersDocument1 pageAQA Physics GCSE Combined P9 Practice AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Biology 2A03: Introduction To Physiology & HomeostasisDocument409 pagesBiology 2A03: Introduction To Physiology & Homeostasisampedm100% (8)
- SV Bio 2021 1 enDocument7 pagesSV Bio 2021 1 enibrahimantar.25No ratings yet
- 2022 4exp BB WA1 ANSDocument3 pages2022 4exp BB WA1 ANSJoshua NingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Coordination in HumansDocument5 pagesChapter 16 - Coordination in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Samian AQA Biology GCSE Combined B1 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesSamian AQA Biology GCSE Combined B1 Practice AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- 15 Control and Co-OrdinationDocument11 pages15 Control and Co-OrdinationLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System 2 Exam Qs and MsDocument4 pagesThe Nervous System 2 Exam Qs and MsalexNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19-gk-VDocument21 pagesLecture 19-gk-VHusam Abduldaem MohammedNo ratings yet
- New Document 1Document37 pagesNew Document 1lewisandlloydgamingNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Physics Feb 24 Shift 2Document16 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Physics Feb 24 Shift 2B Srinivas.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2Ligaya Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- BM6504 Bio Potential Electrodes: Biopotentials Ms.B.Divya Ap/BmeDocument27 pagesBM6504 Bio Potential Electrodes: Biopotentials Ms.B.Divya Ap/BmePrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C7 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C7 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme 2017Document10 pagesMark Scheme 2017Millie DanceNo ratings yet
- MS Physics Set 55-2-3 2019Document21 pagesMS Physics Set 55-2-3 2019Ankur GhoshNo ratings yet
- Neural System (DPP ALL Part)Document14 pagesNeural System (DPP ALL Part)ShrutheeNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Transport in Cells MSDocument17 pages1.3 Transport in Cells MSMethyl OrangeNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Slides f14Document29 pagesChapter2 Slides f14Julissa GomezNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 2Document28 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 2Phil JacksonNo ratings yet
- 4 Coordination and ControlDocument6 pages4 Coordination and ControlVenant HakizimanaNo ratings yet
- Exam #1 Notes and Potential QuestionsDocument35 pagesExam #1 Notes and Potential QuestionsubahcchabuNo ratings yet
- 9698 w03 MsDocument27 pages9698 w03 Msapi-3718440No ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document21 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022JenNo ratings yet
- AQA Homeostasis and Response Knowledge OrganiserDocument6 pagesAQA Homeostasis and Response Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48: Nervous SystemsDocument14 pagesChapter 48: Nervous Systemskuitang100% (5)
- B2 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesB2 Practice Answerssumitha14dasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document22 pagesLecture 5SudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Part 3-Synapses, Neuromuscular Junction and NeurotransmittersDocument22 pagesUnit 2-Part 3-Synapses, Neuromuscular Junction and Neurotransmittersgdhanoa55No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document105 pagesLecture 1ZarAshyNo ratings yet
- Practical Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxation for ChemistsFrom EverandPractical Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxation for ChemistsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnets Part 2 Yr8Document4 pagesElectromagnets Part 2 Yr8saadNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnthalpyDocument11 pagesLattice EnthalpysaadNo ratings yet
- How Far MSDocument6 pagesHow Far MSsaadNo ratings yet
- How Fast MSDocument5 pagesHow Fast MSsaadNo ratings yet
- Hess Cycle QuestionsDocument1 pageHess Cycle QuestionssaadNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues, Organs - Systems 3 MSDocument5 pagesPlant Tissues, Organs - Systems 3 MSsaadNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Forces and Motion 1 TestDocument7 pages4.5 Forces and Motion 1 TestsaadNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1 QPDocument19 pagesPhotosynthesis 1 QPsaadNo ratings yet
- How Fast QPDocument14 pagesHow Fast QPsaadNo ratings yet
- The Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)Document11 pagesThe Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)saadNo ratings yet
- 1 Powers and RootsDocument4 pages1 Powers and RootssaadNo ratings yet
- Higher Revision 4Document7 pagesHigher Revision 4saadNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras Theorem in 3D ShapesDocument7 pagesPythagoras Theorem in 3D ShapessaadNo ratings yet
- 1 PictogramsansDocument6 pages1 PictogramsanssaadNo ratings yet
- What Is Entropy?Document9 pagesWhat Is Entropy?saadNo ratings yet
- The Second Law: The Availability of EnergyDocument10 pagesThe Second Law: The Availability of EnergysaadNo ratings yet
- Foundation Revision 1Document7 pagesFoundation Revision 1saadNo ratings yet
- Indices Answers MMEDocument2 pagesIndices Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency Questions MMEDocument10 pagesCumulative Frequency Questions MMEAmin Sharif SharifNo ratings yet
- Foundation Revision 3Document7 pagesFoundation Revision 3saadNo ratings yet
- Foundation Revision 4Document7 pagesFoundation Revision 4saadNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles Answers MMEDocument1 pageInterior and Exterior Angles Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Foundation Revision 2Document7 pagesFoundation Revision 2saadNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency Answers MMEDocument4 pagesCumulative Frequency Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Circle Sectors and Arcs Answers MMEDocument1 pageCircle Sectors and Arcs Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Cosine Rule Answers MMEDocument1 pageCosine Rule Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Grouped Frequency Tables Answers MMEDocument2 pagesGrouped Frequency Tables Answers MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Grouped Frequency Tables Questions MMEDocument9 pagesGrouped Frequency Tables Questions MMEsaadNo ratings yet
- Bearings Questions MMEDocument8 pagesBearings Questions MMEewjajajajaNo ratings yet
- Circle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEDocument8 pagesCircle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEAhmed NallaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Growth and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Growth and DevelopmentSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Dysfunction and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Gynecology and Women's HealthDocument7 pagesThyroid Dysfunction and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Gynecology and Women's HealthnandaNo ratings yet
- Enteral Dan ParenteralDocument25 pagesEnteral Dan ParenteralFikaNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University R.N Pelaez Blvd. Carmen, Cagayan deDocument46 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University R.N Pelaez Blvd. Carmen, Cagayan deevanisansNo ratings yet
- USMLE Platinum Notes Step 2, 2e PDFDocument768 pagesUSMLE Platinum Notes Step 2, 2e PDFMohammed Faisal Uddin71% (7)
- Progesterone III: A) Tris (2,2'-Bipyridyl) Ruthenium (II) - Complex (Ru (Bpy) )Document4 pagesProgesterone III: A) Tris (2,2'-Bipyridyl) Ruthenium (II) - Complex (Ru (Bpy) )Jimboreanu György PaulaNo ratings yet
- 9780702072987-Book ChapterDocument2 pages9780702072987-Book ChaptervisiniNo ratings yet
- Primal Hormones Made by Aesthetic Primal 1Document59 pagesPrimal Hormones Made by Aesthetic Primal 1enzopark776No ratings yet
- Circardian RhythmDocument15 pagesCircardian RhythmGopika SNo ratings yet
- Jejunoileal Shunt in Surgical Treatment of Morbid ObesityDocument11 pagesJejunoileal Shunt in Surgical Treatment of Morbid ObesityTiago VieiraNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNo ratings yet
- 1152L - Session 9 - Lab Report SheetDocument5 pages1152L - Session 9 - Lab Report Sheetjoe wycliffeNo ratings yet
- Health Seeking Behaviors and Management Methods For Menstrual Pain Among Female Senior High School Teenagers in AgogoDocument59 pagesHealth Seeking Behaviors and Management Methods For Menstrual Pain Among Female Senior High School Teenagers in AgogoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ashiq Tutorials Krok-1 Question PaperDocument23 pagesAshiq Tutorials Krok-1 Question PaperSk ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- 01 - Blood-Function and CompositionDocument45 pages01 - Blood-Function and Compositionsylvester GelacNo ratings yet
- Dietabajaencarbohidratos Moreno Capponi 2020Document11 pagesDietabajaencarbohidratos Moreno Capponi 2020PerlaNo ratings yet
- Uniece Fennell AutopsyDocument7 pagesUniece Fennell AutopsySarahNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2020 Multiple Myeloma With BMT Leak Resulting in Septic ShockDocument56 pagesCase Study 2020 Multiple Myeloma With BMT Leak Resulting in Septic Shockapi-519485865No ratings yet
- ENDODocument9 pagesENDOJohn denver FloresNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Overgrowth of Cells Within The Ovary: Transvaginal SonogramsDocument3 pagesAbnormal Overgrowth of Cells Within The Ovary: Transvaginal SonogramsMadel AcobNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersDocument76 pagesMetabolic and Endocrine DisordersMika Kresna100% (1)
- Gynecology PDFDocument85 pagesGynecology PDFrachaNo ratings yet
- Revised CGHS Rates For Empanelled Hospitals Under CGHS AhmedabadDocument28 pagesRevised CGHS Rates For Empanelled Hospitals Under CGHS Ahmedabadghazi4uNo ratings yet
- Krok Review: How To Prepare Krok TestDocument84 pagesKrok Review: How To Prepare Krok Testgaurav100% (2)
- Customer Masters - Clinivantage BasicDocument23 pagesCustomer Masters - Clinivantage BasicUNIQUE DIAGNOSTICNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Hormonal Response To ExerciseDocument53 pagesChap 5 Hormonal Response To ExerciseAnnie KhanNo ratings yet
- Smart Test Series: 1. Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Document2 pagesSmart Test Series: 1. Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Adnan mirzaNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument46 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisMedi - LecturesNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Carbohydrates For Soccer: A Focus On Skilled Actions and Half-Time PracticesDocument10 pagesNutrients: Carbohydrates For Soccer: A Focus On Skilled Actions and Half-Time PracticesNut. Ana Gabriela Cruz ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Lectures 1 3 DR - LigonDocument14 pagesEndocrinology Lectures 1 3 DR - LigonJealine Marie BernabeNo ratings yet