Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subjective Data: Goal: Independent Intervention:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Data: Goal: Independent Intervention:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Xy-nique De Leon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesSubjective Data: Goal: Independent Intervention:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Data: Goal: Independent Intervention:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Xy-nique De LeonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
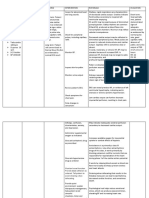
Patient B is a 67 years old male and has been diagnosed with Pneumothorax secondary to Vehicular
Accident. With CTT connected to water seal drainage.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective After 8 hours Independent
Data: Ineffective of shift: Intervention: >Changes may Goal met:
“Nahihirapan breathing 1. Monitor rate, indicate onset The patient’s
ako huminga… pattern related Goal: rhythm, and depth of pulmonary respiratory rate
Tumusok kasi to airway The patient of respiration. Note complications. is increased
yung sarili kong obstruction will be able breathing (RR: 18 bpm)
buto sa baga ko, secondary to to establish a irregularities, for
>Ability to The patient is
kaya eto inaalis Pneumothorax. normal, example, apneustic, mobilize or able to
nila yung effective ataxic, or cluster clear demonstrate
namuong dugo respiratory breathing. secretions is breathing
sa baga ko” pattern as 2. Note competence important to exercises.
As manifested evidenced by of gag and swallow
airway
by the patient. increase reflexes and maintenance. And the patient
respiratory client’s ability to Loss of is able to
Objective rate. The protect own swallow or verbalize his
Data: patient will airway. cough reflex understanding of
With chest verbalize the
may indicate smoking free
thoracostomy understanding
3. Elevate head of need for lifestyle.
connected to of smoking
artificial
water seal free lifestyle. bed as permitted
and position on airway or
chamber at
Objective: sides, as indicated. intubation.
Right,
Bradypnea The patient
> Facilitates
will be able 4. Encourage deep
breathing if client lung expansion
Temp: 36.7’C to
and
RR: 14 bpm demonstrate is conscious
5. Auscultate breath ventilation,
BP: 130/90 breathing
sounds, noting and reduces
mm/Hg exercises to
risk of airway
PR: 79 cpm promote lung areas of
hypoventilation and obstruction by
expansion.
presence of tongue.
adventitious > Prevents or
sounds. reduces
atelectasis.
6. Monitor use of
respiratory >Identifies
depressant drugs, pulmonary
such as sedatives. problems such
7. Instruct the as atelectasis,
patient to avoid congestion,
over-eating and gas and airway
forming foods. obstruction,
8. Maintain calm which may
attitude while jeopardize
dealing with the cerebral
patient oxygenation.
>Can increase
Dependent respiratory
Intervention: embarrassment
Administer pain and
killer/sedative/anti- complications.
pyretic as
prescribed by the >To avoid
doctor. abdominal
distension
Collaborative
intervention: >To limit
Assist in level of
Reclogging of the anxiety
CTT
Assist the patient in
>To Follow
developing plan of
patient’s
smoking cessation
therapeutic
(Inform the patient
regimen to
about the adverse
stabilize her
and side effects of
wellness of
smoking.
health.
>To promote
maximum
inspiration.
>To promote
faster healing
and to promote
patient’s
optimal health.
You might also like
- Clinical Nutrition - A Functional PerspectiveDocument324 pagesClinical Nutrition - A Functional Perspectivelena100% (1)
- Case Study 1 Mrs. Hogan AsthmaDocument4 pagesCase Study 1 Mrs. Hogan Asthmaissaiahnicolle100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic81% (16)
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- MD1187 Recruit Vaccination Form E-Version 13Document2 pagesMD1187 Recruit Vaccination Form E-Version 13Isara Nimcharoen100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismPui_Yee_Siow_6303100% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealCyrus De Asis67% (6)
- NCP GunshotDocument13 pagesNCP GunshotMichael John F. Natividad0% (1)
- Chemotherapy Care PlanDocument5 pagesChemotherapy Care PlanAaLona Robinson50% (2)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan For "HEMOTHORAX PNEUMOTHORAX"jhonroks78% (9)
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- NCP - Hypovolemic ShockDocument7 pagesNCP - Hypovolemic ShockDominique Excelsis J. Degamo71% (7)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- NCP For HemothoraxDocument12 pagesNCP For Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (1)
- Oxygenation - NCPDocument5 pagesOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- 7 NCPDocument7 pages7 NCPVina EmpialesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care Planmcd7r883% (6)
- NCP - Patient With Chest TubeDocument2 pagesNCP - Patient With Chest TubeSelwynVillamorPatente0% (1)
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- ThyroidectomyDocument2 pagesThyroidectomyYenyen Legas100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- Garbage Disposal Teaching Plan PDFDocument3 pagesGarbage Disposal Teaching Plan PDFJanine Joy Orpilla100% (1)
- Shaken Baby Syndrome A Review of 20 CasesDocument4 pagesShaken Baby Syndrome A Review of 20 Casestamis1982No ratings yet
- Ch01 Medical Surgical NursingDocument8 pagesCh01 Medical Surgical Nursingmicky1121100% (1)
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesNursing Care PlanjamNo ratings yet
- Prioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument3 pagesPrioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Pneumothorax'Harold Mark Borja100% (2)
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Asthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageAsthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceWdy Tanakht Sparrow100% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanJayalakshmi David50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeKM67% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- NCP For FrostbiteDocument2 pagesNCP For FrostbiteRommar RomeroNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumothoraxDocument9 pagesCase Study PneumothoraxLee_Cabral_693967% (3)
- NCP For TBDocument3 pagesNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP (Pulmonary Embolism)Document3 pagesNCP (Pulmonary Embolism)Nica Respondo75% (12)
- NCP Increased IcpDocument2 pagesNCP Increased IcphelloaNo ratings yet
- Breast Ca NCPDocument3 pagesBreast Ca NCPThirdy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNo ratings yet
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- NCP Difficulty in BreathingDocument3 pagesNCP Difficulty in BreathingEllyza Grace Tejada75% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Oxy Act 2Document5 pagesOxy Act 2Joshua DauzNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument18 pagesARDSChurrizo IslamiNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPD and Acute PainDocument7 pagesNCP For COPD and Acute PainLenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Mechanical VentilationDocument77 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Mechanical Ventilationrojina poudel0% (1)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisKrizzia CarlosNo ratings yet
- WeaningDocument24 pagesWeaningEko YeppiNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis or TBDocument1 pageTuberculosis or TBJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Mycoplasma PneumoniaDocument1 pageMycoplasma PneumoniaJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug StudyJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug StudyJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- Module 2 The Evolution of Management Thoughts PDFDocument9 pagesModule 2 The Evolution of Management Thoughts PDFJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- The Durie Salmon Staging System PDFDocument2 pagesThe Durie Salmon Staging System PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Cobalt PDFDocument6 pagesCobalt PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Organizing PDFDocument4 pagesModule 4 Organizing PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Merchandising Business ACG 2021 Module 5Document45 pagesAccounting For Merchandising Business ACG 2021 Module 5Janine Joy Orpilla50% (2)
- Module 5 - Staffing PDFDocument15 pagesModule 5 - Staffing PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Leadership Theory and Practice PDFDocument10 pagesModule 8 Leadership Theory and Practice PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- K12 Sa Pilipinas, Solusyon Ba?: Barbie Forteza Bea Binene Elmo Magalona Derick Monasterio Lexi Fernandez Kristofer MartinDocument8 pagesK12 Sa Pilipinas, Solusyon Ba?: Barbie Forteza Bea Binene Elmo Magalona Derick Monasterio Lexi Fernandez Kristofer MartinJanine Joy OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Literature Search: BmeezykgDocument15 pagesLesson 1: Literature Search: BmeezykgERIKA ANNE CADAWANNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between House Environment Factor andDocument13 pagesThe Correlation Between House Environment Factor andinaNo ratings yet
- Flex UK - April 2017Document148 pagesFlex UK - April 2017安建平 澳门南湖区100% (3)
- Lot Testing QC Report Result FormDocument5 pagesLot Testing QC Report Result FormPooja KolugadeNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument3 pagesMyasthenia GravisTee EnnNo ratings yet
- Water Requirements, Impinging Factors, and Recommended IntakesDocument27 pagesWater Requirements, Impinging Factors, and Recommended IntakesAnanda DewaNo ratings yet
- Uganda MOH SMC Quality Assessment Tool FINAL DRAFTDocument52 pagesUganda MOH SMC Quality Assessment Tool FINAL DRAFTOkullu123No ratings yet
- VCI Code of Ethics Regulations 1992Document12 pagesVCI Code of Ethics Regulations 1992deepakvrNo ratings yet
- Use or Ornament?: The Social Impact of Participation in The ArtsDocument111 pagesUse or Ornament?: The Social Impact of Participation in The Artsgerardo anselmo villegasNo ratings yet
- Who Mbhss 2010 Full WebDocument110 pagesWho Mbhss 2010 Full WebalmoslatNo ratings yet
- Western Pennsylvania Guide To Good Health - Winter 2013Document52 pagesWestern Pennsylvania Guide To Good Health - Winter 2013GuideToGoodHealthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Ethical Issues in Stopping The Global Spread of Infectious Diseases - AIDS, Ebola, and ZikaDocument5 pagesChapter 16 - Ethical Issues in Stopping The Global Spread of Infectious Diseases - AIDS, Ebola, and ZikaMahima SikdarNo ratings yet
- 7775 22226 1 PBDocument6 pages7775 22226 1 PBdriveamadeaNo ratings yet
- Stress and ImuneDocument13 pagesStress and ImunePhiNo LupHt DindudNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Nursing CareDocument14 pagesIntraoperative Nursing CareMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Body Circadian Rhythm and Sleep CycleDocument14 pagesBody Circadian Rhythm and Sleep CycleSi sielNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Kinds of Stress That Each Take A Toll On The BodyDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Kinds of Stress That Each Take A Toll On The BodyMd. Rakibul Islam RanaNo ratings yet
- Akash Synopsis EDITEDDocument15 pagesAkash Synopsis EDITEDjagvirNo ratings yet
- Wissow 2017Document20 pagesWissow 2017Mhd. izzan naserNo ratings yet
- Rnpedia MCHNDocument27 pagesRnpedia MCHNlykanotmatroNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Music, Arts, Physical Education, Health (Mapeh) 2Document5 pagesBudget of Work in Music, Arts, Physical Education, Health (Mapeh) 2KeyrenNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of Family PlanningDocument24 pagesModern Methods of Family PlanningGeneen GelvoleoNo ratings yet
- JO - 16 - Renault Follow-Up Plan Audit HSE InternshipDocument2 pagesJO - 16 - Renault Follow-Up Plan Audit HSE InternshipudbarryNo ratings yet
- Cold Stress PDFDocument2 pagesCold Stress PDFfriends_nalla100% (1)
- COSHDocument22 pagesCOSHMaricca U. HagitanNo ratings yet
- Entomology Item6,7Document69 pagesEntomology Item6,7Barat NiloyNo ratings yet