0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesSoil Stress Total Stress, Pore Pressure, U Effective Stress, '
The document discusses the concepts of total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress in soils. Total stress is the stress generated by the weight of the soil and increases with depth and unit weight. Pore water pressure is related to the depth and unit weight of water. Effective stress is defined as the total stress minus the pore water pressure. It provides examples of calculating total stress, pore pressure, and effective stress at different depths for layered soil profiles.
Uploaded by
Nala A.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesSoil Stress Total Stress, Pore Pressure, U Effective Stress, '
The document discusses the concepts of total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress in soils. Total stress is the stress generated by the weight of the soil and increases with depth and unit weight. Pore water pressure is related to the depth and unit weight of water. Effective stress is defined as the total stress minus the pore water pressure. It provides examples of calculating total stress, pore pressure, and effective stress at different depths for layered soil profiles.
Uploaded by
Nala A.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
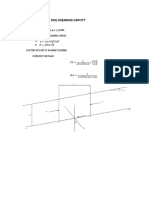
- Introduction to Soil Stress
- Total Normal Stress
- Pore Pressure
- Example Problems
- Effective Stress