Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deep Foundations - Barrette Piles: Tutorial 2 Episode 1
Uploaded by
Abu Hena Mostofa KamalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deep Foundations - Barrette Piles: Tutorial 2 Episode 1
Uploaded by
Abu Hena Mostofa KamalCopyright:
Available Formats
Setec tpi university
#Tutorial #MOOC #Civil Engineering #Structural Engineering
THE NEW
– PARIS
LAW COURT
Tutorial 2 Episode 1
DEEP FOUNDATIONS – BARRETTE PILES
The cores of the tower are based on 2.70mx1.20m barrette piles, which are 50m deep, in
order to be anchored in coarse limestone. They are built on the same principle as the
diaphragm wall, but they are much deeper and therefore there are two peculiarities.
The first is an excavation in two phases with two different tools:
After achieving the low guide walls,
• Excavation is started with a hydraulic mill for pre-drilling tender horizons Auversian
clayey sand. This is the same procedure for the diaphragm walls. This is the same
procedure for the diaphragm walls.
• Next, to cross the hard horizon of Marn and Loos Stones, the excavation is
continued with a hydro perforation cutter.
It comprises two drums with teeth which rotate in opposite directions and grind the ground.
The cuttings are sucked continuously from the bottom panel by a pump located between the
drums, while the recycled slurry is injected at the top, that is the reverse circulation. Here, the
tool never rises to the surface during perforation. Verticality can be assessed by
instrumentation on the fixed frame and into the barrel of the tool. It may be corrected in real
time by operating some hydraulic components present on the mill body.
The second feature due to the length of the barrette piles is that the cages are necessarily
prefabricated in 5 sections, which must be assembled directly in the excavation. Each
segment is held from the top by means of horizontal tubes slipped through the loops. A
second section may then be coupled to the first. The auscultation tubes are nested and
welded. The coating of steel is provided through cable ties. Before each run, concrete
spacers pads are in placed to ensure the concrete cover of 7cm. The elements are coupled
and then step by step down. The last section of the reinforcement cage does not play
structural role but simply serves as hanger. Indeed, the barette piles are not made from the
raft level but from the natural terrain at 32NVP. The last section cage will therefore be torn
during the general excavations.
Finally a concrete column is slided down, in the barrette pile, section by section to the bottom
of the excavation, and we proceed to the concreting from the bottom, through mixer trucks.
During the excavation, the part of the concrete barrette pile that is above raft level is
demolished
Thanks : Solétanche Bachy
Picture: Pierre-Alexandre Chevallier
Text : Audrey Zonco – setec tpi
Voice Over : Audrey Zonco– setec tpi
Edit : Toys film
Translation: Gemma Aubeeluck – setec tpi
You might also like
- Construction Techniques, Equipments & Practice: WelcomeDocument88 pagesConstruction Techniques, Equipments & Practice: WelcomeRON SAMUEL 401935No ratings yet
- Diaghragm Wall 2Document8 pagesDiaghragm Wall 2aramsayed100% (1)
- Breif Explanation Bout Diaphragm WallDocument27 pagesBreif Explanation Bout Diaphragm WallYoussef WaleedNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument9 pagesDocumentea_she3415No ratings yet
- Tunnel Construction Techniques and Their DetailsDocument72 pagesTunnel Construction Techniques and Their DetailsRajesh Khadka100% (1)
- Construction PlanDocument9 pagesConstruction PlanEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- 103 Sce Module 3Document8 pages103 Sce Module 3Joab Gabriel Elegado CalumpianoNo ratings yet
- Execution Paroi MouléeDocument16 pagesExecution Paroi Mouléeel ouarti mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document43 pagesLecture 1aa5419No ratings yet
- Gantry Piling - MethodDocument2 pagesGantry Piling - Methodnaseeb100% (1)
- Tunnel Construction and Tunneling Methods Pipe Jacking Method by Dr. Azealdeen Salih Al-JawadiDocument14 pagesTunnel Construction and Tunneling Methods Pipe Jacking Method by Dr. Azealdeen Salih Al-JawadiAzealdeen AlJawadiNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm WallDocument28 pagesDiaphragm WallTiong V YenNo ratings yet
- Construction Techniques, Equipments & Practice: WelcomeDocument40 pagesConstruction Techniques, Equipments & Practice: WelcomedhanabalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tremie Technique in Concreting of Bottom Plug of WellsDocument16 pagesAnalysis of Tremie Technique in Concreting of Bottom Plug of Wellstangkokhong67% (3)
- Diaphragm WallDocument5 pagesDiaphragm WallChandra Prakash Khatri0% (1)
- Parois Moul Es & Barrettes VaDocument8 pagesParois Moul Es & Barrettes VaBasant Narayan SinghNo ratings yet
- DW 2016Document2 pagesDW 201604BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Ismailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFDocument8 pagesIsmailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFRonald HeijmansNo ratings yet
- Diaphargm Wall Construction DetailsDocument48 pagesDiaphargm Wall Construction DetailsAkshay Joshi100% (1)
- PSC Girder Bridge Construction - Construction of A Bridge-Bridge Construction MethodDocument16 pagesPSC Girder Bridge Construction - Construction of A Bridge-Bridge Construction MethodVinay Raj100% (1)
- Unit 2Document97 pagesUnit 2Sid SNo ratings yet
- What Is Pile Foundation?: Civil CourtDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pile Foundation?: Civil CourtSumeet HulugadeNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Wall ConstructionDocument7 pagesDiaphragm Wall ConstructionHarsha Vardhan MeduriNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Chimney ConstructionDocument10 pagesMethodology For Chimney ConstructionRangan Mitra100% (1)
- Tunnel Boring MachinesDocument58 pagesTunnel Boring MachinesAliArababadiNo ratings yet
- Major Components of FlyoverDocument3 pagesMajor Components of FlyoverSaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls, Cut-Off Walls and Slurry Walls: Implenia Spezialtiefbau GMBHDocument9 pagesDiaphragm Walls, Cut-Off Walls and Slurry Walls: Implenia Spezialtiefbau GMBHNemanja BralovicNo ratings yet
- Nicoll Highway IncidentDocument8 pagesNicoll Highway IncidentAnonymous PeeXLtNsMpNo ratings yet
- Tunnel EngineeringDocument13 pagesTunnel Engineeringbitsj2023071516No ratings yet
- Methodology For Piling WorkDocument5 pagesMethodology For Piling WorkAftab AlamNo ratings yet
- Plugging of Diversion Tunnel - TehriDocument5 pagesPlugging of Diversion Tunnel - Tehriengr_usman04No ratings yet
- Joints in Gravity DamsDocument7 pagesJoints in Gravity DamsTumbaNo ratings yet
- KMC ReportDocument19 pagesKMC ReportBijayNo ratings yet
- BAUER Diaphragm and Cut Off WallsDocument16 pagesBAUER Diaphragm and Cut Off Wallsshahramk80100% (1)
- Tunneling Through Hard Rocks: Full Face MethodDocument5 pagesTunneling Through Hard Rocks: Full Face MethodYoga RajNo ratings yet
- Tugas Tunnel and FoundationDocument18 pagesTugas Tunnel and FoundationNadhifah FairuzNo ratings yet
- Paper Presented at CRRI On Bottom Plug in Well FoundationsDocument11 pagesPaper Presented at CRRI On Bottom Plug in Well FoundationskishoredataNo ratings yet
- Escuela Academica Profesional de Ingenieria de MinasDocument10 pagesEscuela Academica Profesional de Ingenieria de MinascarmenNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Wall Construction SequenceDocument10 pagesDiaphragm Wall Construction Sequencedanzy89100% (2)
- 10B UnderpinningDocument24 pages10B UnderpinningAlma AinaNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Wall ConstructionDocument9 pagesDiaphragm Wall Constructionmeladbelal1234No ratings yet
- Metro InstrumentationDocument20 pagesMetro Instrumentationdafo407No ratings yet
- Draft PPT Pile FoundatationDocument14 pagesDraft PPT Pile FoundatationDwijendra ChanumoluNo ratings yet
- Tunnel MethodsDocument3 pagesTunnel MethodsBabar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Rion Anti Rion BridgeDocument7 pagesRion Anti Rion BridgeNagar NitinNo ratings yet
- TBMDocument26 pagesTBMMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument88 pagesBuilding Constructionmurad_ce100% (5)
- Assignment No 4Document6 pagesAssignment No 4SHELAR GAURINo ratings yet
- Secant Piles: What Are Secant Pile Walls?Document3 pagesSecant Piles: What Are Secant Pile Walls?ulhas_nakashe100% (2)
- 7436 - Tomislav ReportDocument8 pages7436 - Tomislav ReportM SNo ratings yet
- Piling - Contiguous, Interlocking and SecantDocument7 pagesPiling - Contiguous, Interlocking and Secantmudassir2640100% (2)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173No ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The North River Tunnels. Paper No. 1155From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The North River Tunnels. Paper No. 1155No ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Elena Papadopoulos - Design of Column Base PlatesDocument31 pagesElena Papadopoulos - Design of Column Base PlatesNoé InzunzaNo ratings yet
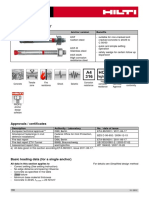
- Technical Bulletin For Kwik BoltDocument3 pagesTechnical Bulletin For Kwik BoltAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Hilti HST FTM 2012-09Document10 pagesHilti HST FTM 2012-09VishalDhimanNo ratings yet
- DiaphragmWalls Barretes PDFDocument4 pagesDiaphragmWalls Barretes PDFAnonymous 6vZfB9pfzaNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations - Barrette Piles: Retaining Wall and Foundations For 36-Storey Property With Four Basement LevelsDocument2 pagesDeep Foundations - Barrette Piles: Retaining Wall and Foundations For 36-Storey Property With Four Basement LevelsAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1544930 PDFDocument73 pagesTechnical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1544930 PDFkmh33403No ratings yet
- Technical Bulletin For Kwik BoltDocument3 pagesTechnical Bulletin For Kwik BoltAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
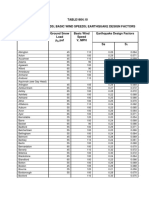
- 16 Table1604Document8 pages16 Table1604Abu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Hilti HST FTM 2012-09Document10 pagesHilti HST FTM 2012-09VishalDhimanNo ratings yet
- Idges 1973Document506 pagesIdges 1973hcabanillaspNo ratings yet
- Joist Joists Joist Girders: Catalogue andDocument104 pagesJoist Joists Joist Girders: Catalogue andAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- 112-High Strength Bolting PDFDocument68 pages112-High Strength Bolting PDFJanesha100% (1)
- Concrete Block Sizes & ShapesDocument12 pagesConcrete Block Sizes & Shapesecruz_yhwhNo ratings yet
- Bolt Shear StrengthDocument2 pagesBolt Shear Strengthmnaziria6612No ratings yet
- To STR PDFDocument1 pageTo STR PDFAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
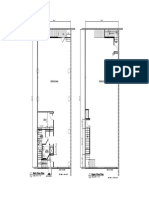
- 61301r2 Floor LayoutDocument1 page61301r2 Floor LayoutAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- 61301r2 Floor LayoutDocument1 page61301r2 Floor LayoutAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- To STRDocument1 pageTo STRAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Footing Detail PDFDocument1 pageFooting Detail PDFAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- TwoTnwo Bitsler Method 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesTwoTnwo Bitsler Method 2016 PDFPutra GarutNo ratings yet
- Laterally Loaded Pile PadDocument9 pagesLaterally Loaded Pile PadAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- TwoTnwo Bitsler Method 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesTwoTnwo Bitsler Method 2016 PDFPutra GarutNo ratings yet
- Rfi 1 - PumpDocument1 pageRfi 1 - PumpAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Footing DetailDocument1 pageFooting DetailAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- M.G - A2.1 2nd Floor PlanDocument1 pageM.G - A2.1 2nd Floor PlanAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Spec 2.3 Steel Building Structural Design CriteriaDocument3 pagesSpec 2.3 Steel Building Structural Design CriteriaAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Circular No. 7, Soil Nail WallsDocument425 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Circular No. 7, Soil Nail WallsJuan SegundoNo ratings yet
- Sure Fire Hedging StrategyDocument3 pagesSure Fire Hedging StrategyAbu Hena Mostofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Helical Foundations What An Engineer Needs To KnowDocument6 pagesHelical Foundations What An Engineer Needs To Knowameensderaj100% (1)
- Advanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- Gold Advanced Progress Test 5Document6 pagesGold Advanced Progress Test 5BernardNo ratings yet
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocument28 pagesHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- EXP1POSTLABDocument13 pagesEXP1POSTLABGiane MagimotNo ratings yet
- ManufactureDocument2 pagesManufactureRahima Akter RakhiNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Dragon FruitDocument6 pagesProduction Technology of Dragon FruitAbhinash MoirangthemNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning: VocabularyDocument9 pagesFood Poisoning: VocabularyHANG WEI MENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Eoi QAMDocument6 pagesEoi QAMPeeyush SachanNo ratings yet
- Sermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)Document1 pageSermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)GeorgesEdouardNo ratings yet
- S.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Document532 pagesS.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Gianpiero Boccato0% (1)
- Double-Outlet Right Ventricle With An An Intact Interventricular Septum and Concurrent Hypoplastic Left Ventricle in A CalfDocument6 pagesDouble-Outlet Right Ventricle With An An Intact Interventricular Septum and Concurrent Hypoplastic Left Ventricle in A CalfYoga RivaldiNo ratings yet
- With EU Stage V Engine Installed: 200 HP (149 KW) / 2,200 RPMDocument4 pagesWith EU Stage V Engine Installed: 200 HP (149 KW) / 2,200 RPMSara Sarmiento EcheverryNo ratings yet
- Visedo FPC-2016Document13 pagesVisedo FPC-2016Probonogoya Erawan SastroredjoNo ratings yet
- Rubber Lined Piping - A Solution To Corrosion ResistanceDocument5 pagesRubber Lined Piping - A Solution To Corrosion ResistanceMohamed AghilaNo ratings yet
- Class 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic WavesDocument33 pagesClass 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic Wavesakirank1No ratings yet
- Cateora2ce IM Ch012Document9 pagesCateora2ce IM Ch012Priya ShiniNo ratings yet
- Menstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalDocument4 pagesMenstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalMy Home KaviNo ratings yet
- Web+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumeDocument57 pagesWeb+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumetranthabinNo ratings yet
- Into The Unknown 21 Doc PDFDocument9 pagesInto The Unknown 21 Doc PDFFernando AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Mercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147Document3 pagesMercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147YB MOTOR Nissan - Datsun SpecialistNo ratings yet
- Leta-Leta CaveDocument5 pagesLeta-Leta CaveToniNo ratings yet
- The Failed Rotator CuffDocument307 pagesThe Failed Rotator Cufforthofitness2017No ratings yet
- Arc 2019-2020Document95 pagesArc 2019-2020AEN HTM DD1 HTM DD1No ratings yet
- IMS Institute BelgradeDocument10 pagesIMS Institute BelgradeBoško JanjuševićNo ratings yet
- Diels-Alder Reaction: MechanismDocument5 pagesDiels-Alder Reaction: MechanismJavier RamirezNo ratings yet
- Art and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaDocument30 pagesArt and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaBen WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Popular CultureDocument6 pagesPopular CultureAmritaNo ratings yet
- EY Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument24 pagesEY Enhanced Oil RecoveryDario Pederiva100% (1)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris X - XiDocument6 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris X - XiBydowie IqbalNo ratings yet
- 2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorDocument19 pages2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorSherifNo ratings yet