Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gene Silencing: How Does It Works?
Uploaded by
Joon Bok Namlee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Gene silencing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesGene Silencing: How Does It Works?
Uploaded by
Joon Bok NamleeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Gene silencing
o Interruption or suppression of the expression of a gene at transcriptional or translational levels.
o A technique that aims to reduce or eliminate the production of a protein from its
corresponding gene.
o Gene silencing occurs when RNA is unable to make a protein during translation.
o Gene silencing is often considered the same as gene knockdown. When genes are silenced, their
expression is reduced. In contrast, when genes are knocked out, they are completely erased from
the organism's genome and, thus, have no expression.
How does it works?
1. This is accomplished by binding of a
specific strand of RNA to an existing
m-RNA strand.
2. The m-RNA creates a copy of DNA
strand.
3. By binding the RNA to the m-RNA,
m-RNA is prevented from the
replicating that portion of the DNA.
4. Specific gene can be targeted and
prevented from replicating in to new
DNA strands.
Types;
1. Transcriptional Gene Silencing - the result of histone modifications, creating an
environment of heterochromatin around a gene that makes it inaccessible to
transcriptional machinery (RNA polymerase, transcription factors, etc.).
2. Post-transcriptional Gene Silencing- the result of mRNA of a particular gene being
destroyed or blocked. The destruction of the mRNA prevents translation to form an
active gene product in most cases, a protein.
Gene silencing methods used in research:
Antisense Oligonucleotides
o Oligonucleotides are short nucleic acid fragments, bind to complementary target
mRNA molecules. Can be composed of single-stranded DNA or RNA and are
generally 13–25 nucleotides long.
o When added to the cell oligonucleotides causes the target mRNA molecules to be
degraded, while steric-blocker oligonucleotides prevent translation of the mRNA
molecule.
Ribozymes
o Are catalytic RNA molecules used to inhibit gene expression.
o These catalytic RNA molecules bind to a specific site and
work by cleaving mRNA molecules, essentially silencing the
genes that produced them.
RNA interference (RNAi)
o A biological response where small pieces of
RNA: Small interfering (siRNA) & MicroRNA
(miRNA) shut down protein translation by
binding to the messenger RNAs that code for
those proteins.
Applications of gene silencing
o In the medical field, the gene silencing technique is used to study genes associated with cancer,
infectious disorders and other genetic disorders.
o RNA interference has been used to silence the overexpression of some genes which causes
cancer.
o Used in plant genetics for creating genetically modified organisms or plants that are economically
important.
o Used in treating infectious diseases like HIV.
o Scientists are now applying the gene silencing method to treat diseases like asthma, cystic
fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, chronic myeloid
leukemia and neurodegenerative disorders.
Resources:
o https://www.slideshare.net/tailorparvez/gene-silencing-56053684
o https://hopes.stanford.edu/gene-silencing/#:~:text=Two%20of%20the%20leading%20and,and
%20antisense%20oligonucleotides%20(ASOs).&text=In%20RNAi%2C%20the%20molecules
%20that,%2Dinterfering%20RNAs%20(siRNAs).
o https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_silencing
o https://www.thermofisher.com/blog/ask-a-scientist/what-is-rnai/
You might also like
- Gene Silencing: An In-Depth Look at Mechanisms and ApplicationsDocument18 pagesGene Silencing: An In-Depth Look at Mechanisms and ApplicationsNAMRA RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Gene Silencing: Presented By: Parvez ShaikhDocument29 pagesGene Silencing: Presented By: Parvez ShaikhsankarNo ratings yet
- 20MSRBT028 GeneSilencingDocument29 pages20MSRBT028 GeneSilencing200409120010No ratings yet
- Gene SilencingDocument29 pagesGene SilencingDaud KhanNo ratings yet
- Gene SileningDocument30 pagesGene SileningSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 AntisenseDocument48 pagesLecture 4 AntisensesankarNo ratings yet
- RNAi in Developmental BiologyDocument7 pagesRNAi in Developmental BiologyAaryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gene SilencingDocument7 pagesGene SilencingMaliha JahanNo ratings yet
- Gene SilencingDocument5 pagesGene SilencingAnjali Anil100% (2)
- Gene Silencing: Presented by Aastha Pal M.Sc. 4 Semester (Biotechnology) Swami Rama Himalayan UniversityDocument22 pagesGene Silencing: Presented by Aastha Pal M.Sc. 4 Semester (Biotechnology) Swami Rama Himalayan UniversityAmit NegiNo ratings yet
- 2019 BTEC 5360 ClassDocument31 pages2019 BTEC 5360 ClassSeayoung LEENo ratings yet
- Regulation of Plant Gene Expression by Antisense RNADocument28 pagesRegulation of Plant Gene Expression by Antisense RNAProject ICTNo ratings yet
- Gene Silencing TechniquesDocument15 pagesGene Silencing TechniquesShaher Bano Mirza100% (2)
- Antisensedrugs 141028044659 Conversion Gate02Document45 pagesAntisensedrugs 141028044659 Conversion Gate02Dalia Ali El EbeedyNo ratings yet
- Antisense Technology 7th SemDocument17 pagesAntisense Technology 7th SemSavita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Transgene SLIENCINGDocument35 pagesTransgene SLIENCINGRajaram Krishnasamy100% (1)
- Gene Silencing - Antisense RNA & SiRNADocument18 pagesGene Silencing - Antisense RNA & SiRNAvenkatsuriyaprakash100% (1)
- Gene Silencing: Presented byDocument23 pagesGene Silencing: Presented byRouf Ahmad100% (1)
- CellbioDocument13 pagesCellbiojafameg801No ratings yet
- Antisense RNA Technology and Its ApplicationsDocument2 pagesAntisense RNA Technology and Its Applicationssomu1No ratings yet
- Gene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Document21 pagesGene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Niranjana KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Que8 Promoter trapping system to study embryogenesisDocument1 pageQue8 Promoter trapping system to study embryogenesisPavan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Antisense OligoDocument40 pagesAntisense OligoinigoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism & FunctionsDocument7 pagesMechanism & FunctionsShaher Bano MirzaNo ratings yet
- Rna InterferenceDocument10 pagesRna InterferencewaktoleNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression: Transcription, Post-Transcription & mRNA Decay (MSBE 802Document39 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression: Transcription, Post-Transcription & mRNA Decay (MSBE 80219740730No ratings yet
- Liquid Waste ManagementDocument28 pagesLiquid Waste ManagementSubhradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing: Sanjeev Sharma, Aarti Bhardwaj, Shalini Jain and Hariom YadavDocument28 pagesPost-Transcriptional Gene Silencing: Sanjeev Sharma, Aarti Bhardwaj, Shalini Jain and Hariom YadavGhayas Muhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Modifications Controlling RNADocument5 pagesModifications Controlling RNADiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR-Cas9 for Genome EditingDocument2 pagesZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR-Cas9 for Genome EditingmuhsinNo ratings yet
- 302 Gene ManipulationDocument25 pages302 Gene ManipulationArisha razaNo ratings yet
- GMFMRTMRDocument27 pagesGMFMRTMRSaverioFortunatoNo ratings yet
- RnaiDocument13 pagesRnaiIrah Jane BadeNo ratings yet
- Antisense Technologies: Improvement Through Novel Chemical ModificationsDocument17 pagesAntisense Technologies: Improvement Through Novel Chemical ModificationsAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- RNAi MphilDocument28 pagesRNAi Mphilrameeshasaleem01No ratings yet
- Final Document Rna TherapyDocument21 pagesFinal Document Rna Therapysumaira saddiqueNo ratings yet
- Antisense RNA TherapyDocument17 pagesAntisense RNA TherapyGuleRia ShiVani100% (1)
- coding &non coding DNADocument31 pagescoding &non coding DNAGiD MOhNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio Part 1 2014Document95 pagesMol Bio Part 1 2014Manish SoniNo ratings yet
- Tanyut Module4 Assignment3Document7 pagesTanyut Module4 Assignment3Tanyut HuidromNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument29 pagesGene Expressionomar khaled العكلNo ratings yet
- Restriction Enzyme DigestionDocument3 pagesRestriction Enzyme DigestionMahathir Mohmed100% (1)
- RNA Interference Class NotesDocument4 pagesRNA Interference Class NotesmanaleepandyaNo ratings yet
- Biological BackgroundDocument15 pagesBiological Backgroundrustyryan77No ratings yet
- R DNA TchnologyDocument32 pagesR DNA TchnologyReena GuptaNo ratings yet
- Life and Times of An Rna L3Document4 pagesLife and Times of An Rna L3katieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biologykris_bt20029241No ratings yet
- DNA Structure & InheritanceDocument9 pagesDNA Structure & Inheritancewakeetha cNo ratings yet
- Polymorphism Introduction AymanDocument39 pagesPolymorphism Introduction AymanBasma Adel KhattabNo ratings yet
- Non-Coding RNADocument2 pagesNon-Coding RNAvanderbroNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The PresentationDocument20 pagesWelcome To The PresentationPervez Imran PrinceNo ratings yet
- MICRORNAs: A REVIEW STUDYDocument10 pagesMICRORNAs: A REVIEW STUDYIOSR Journal of PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Antisense RNA: Example: The Flavr Savr TomatoDocument10 pagesAntisense RNA: Example: The Flavr Savr Tomatomamut343No ratings yet
- Rna InterferenceDocument19 pagesRna InterferencePROFESSORNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Gene ExpressionDocument28 pagesAnalysis of Gene ExpressionfurqanNo ratings yet
- RNA InterferenceDocument26 pagesRNA InterferenceAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1. Blotting TechniquesDocument16 pagesChapter # 1. Blotting TechniquesShahzadAliNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument7 pagesRegulation of Gene ExpressionGodwin UnimashiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Cell Cycle Drugs DNA RegulationDocument2 pagesBiochemistry Cell Cycle Drugs DNA RegulationMarie SantoroNo ratings yet
- The Frankfurt School and The Culture IndustryDocument4 pagesThe Frankfurt School and The Culture IndustryJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Separation of Sulfur, Salt, Iton Fillings and SandDocument3 pagesSeparation of Sulfur, Salt, Iton Fillings and SandJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Theory (Jerome Bruner) : The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) Has Been Defined AsDocument2 pagesConstructivist Theory (Jerome Bruner) : The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) Has Been Defined AsJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang Theory Is The Leading Explanation About How The Universe BeganDocument31 pagesThe Big Bang Theory Is The Leading Explanation About How The Universe BeganJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Test ProtozoanDocument2 pagesTest ProtozoanJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Philippine TaxationDocument4 pagesEvolution of Philippine TaxationJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Bryophytes DiversityFINALDocument6 pagesBryophytes DiversityFINALJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- El Filibusterismo: CharactersDocument2 pagesEl Filibusterismo: CharactersJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Post AssessmentDocument1 pagePost AssessmentJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Causes, Effects and Major PollutantsDocument2 pagesAir Pollution: Causes, Effects and Major PollutantsJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- How Do You Think Human Activities Have Affected The EcosystemDocument1 pageHow Do You Think Human Activities Have Affected The EcosystemJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Education Response To The Needs of The Society and CommunityDocument2 pagesEducation Response To The Needs of The Society and CommunityJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Our Report About Bicol's Superstitious BeliefsDocument1 pageOur Report About Bicol's Superstitious BeliefsJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Article Critique Authors: Robert F. Collison1, Emma C. Raven1, Charles P. Pignon2,3,4 and StephenDocument2 pagesArticle Critique Authors: Robert F. Collison1, Emma C. Raven1, Charles P. Pignon2,3,4 and StephenJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- A. Personal Background of The Psychologists or Advocates in Education (Please Include Picture/s)Document3 pagesA. Personal Background of The Psychologists or Advocates in Education (Please Include Picture/s)Joon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
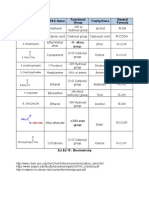
- Chemical Formula Iupac Name Functional Group Family/Class General FormulaDocument1 pageChemical Formula Iupac Name Functional Group Family/Class General FormulaJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Key ConceptsDocument1 pageKey ConceptsJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Key Dimensions of IE in Basic EducationDocument1 pageKey Dimensions of IE in Basic EducationJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Comets, Meteors, and AsteroidDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Comets, Meteors, and AsteroidJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- DLP TemplateDocument2 pagesDLP TemplateJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- DLP TemplateDocument2 pagesDLP TemplateJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- SpiralDocument1 pageSpiralJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Junior High School CurriculumDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Junior High School CurriculumJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Teaching The ConceptDocument3 pagesTeaching The ConceptJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Key ConceptsDocument1 pageKey ConceptsJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- The Emphasis in Learning Should Be On The Development of Meaning and ComprehensionDocument1 pageThe Emphasis in Learning Should Be On The Development of Meaning and ComprehensionJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument6 pagesThe Structure of The AtomJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Pomegranate - Botany, Postharvest Treatment, Biochemical Composition and Health Effects (2014) PDFDocument188 pagesPomegranate - Botany, Postharvest Treatment, Biochemical Composition and Health Effects (2014) PDFAndré Campelo100% (2)
- Asmi 04 0857Document12 pagesAsmi 04 0857Elver SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryDocument90 pages3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry National Board Exam ReviewDocument42 pagesBiochemistry National Board Exam ReviewJulienne Sanchez-Salazar75% (4)
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- Grade 12 Biology Module3Document87 pagesGrade 12 Biology Module3Genevieve MerroNo ratings yet
- BP605T Unit 4-6Document482 pagesBP605T Unit 4-6Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2 Winter 2020Document10 pagesPractice Test 2 Winter 2020proplayer910No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument4 pagesTranscriptionkaiaNo ratings yet
- Protein synthesis steps and genetic codeDocument1 pageProtein synthesis steps and genetic codeZaifel PacillosNo ratings yet
- Phet - Activity 1Document4 pagesPhet - Activity 1api-306913723No ratings yet
- Ribosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeDocument2 pagesRibosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeIs SianNo ratings yet
- SOL Review Answer SheetDocument15 pagesSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL: DNA BIOLOGY and TECHNOLOGY 1. Describe The Biochemical CompositionDocument6 pagesTUTORIAL: DNA BIOLOGY and TECHNOLOGY 1. Describe The Biochemical Compositionaesha89No ratings yet
- Validation Test No. 1 in Grade 10 Science Quarter 3 Week 1-4Document2 pagesValidation Test No. 1 in Grade 10 Science Quarter 3 Week 1-4orlan sisonNo ratings yet
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocument6 pagesDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Review:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachDocument4 pagesReview:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachIndrani GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic TranscriptionDocument16 pagesEukaryotic TranscriptionKunal DuttaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument17 pagesCell Biology BasicsHizzei Caballero100% (3)
- Paper - IV Molecular BiologyDocument236 pagesPaper - IV Molecular BiologyNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- B. Exon: C. Transcription, TranslationDocument5 pagesB. Exon: C. Transcription, TranslationRuhna BaigNo ratings yet
- CH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFDocument93 pagesCH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFasaNo ratings yet
- Essential guide to human histologyDocument315 pagesEssential guide to human histologyJames Mark Magsipoc OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation: The Relationship Between andDocument40 pagesTranscription and Translation: The Relationship Between andAutozer IDNo ratings yet
- BET 2019 Question PaperDocument33 pagesBET 2019 Question PaperRadzNo ratings yet
- CH 12-Brooker Biology-Gene Expression at The Molecular LevelDocument4 pagesCH 12-Brooker Biology-Gene Expression at The Molecular Leveltiffycutie1No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WSDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis WSkatherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Transcription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFDocument131 pagesTranscription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFMuhammad Haris AshfaqNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument70 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument21 pagesMolecular BiologyvaishnaviNo ratings yet