Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proteins & Enzymes: Biochemistry
Uploaded by
Princess RonsableOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proteins & Enzymes: Biochemistry
Uploaded by
Princess RonsableCopyright:
Available Formats
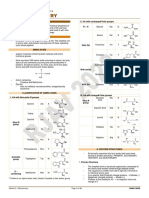
BIOCHEMISTRY
I. PROTEINS & ENZYMES
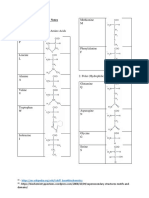
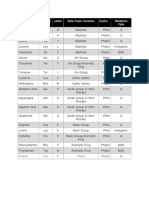
A. AMINO ACIDS
Classification by R-Group
A. NON-POLAR (Hydrocarbons) VILFAG MWP
▪ smallest BRANCHED CHAIN AMINO ACIDS VIL
▪ achiral
Glycine Gly G
▪ starting material of Valine Val V
heme synthesis
▪ one of the commonly
Alanine Ala A transaminated amino Isoleucine Ile I
acid
▪ aromatic amino acid
Xanthoproteic test
Phenylalanine Phe F Leucine Leu L
Rgt. HNO3
(+) yellow/orange
▪ only 2˚ amine
▪ sulfur-containing
“imino acid”
Methionine Met M
Lead-acetate test
(+) black ppt Proline Pro P Ninhydrin test
▪ aromatic General test for amino acid
▪ indole-containing (+) violet (1˚ amino acid)
▪ precursor of except Proline (yellow)
Serotonin (5-HT)
Tryptophan Trp W
Hopkins-Cole
Rgt. glyoxylic acid
(+) Violet-ring
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
B. POLAR (OH,SH,NH) QNSTCY (Cute ni Stacey)
Asparagine Asn N ▪ amidic Glutamine Gln Q ▪ amidic
Serine Ser S ▪ precursor of choline Threonine Thr T
▪ aromatic
▪ phenolic
▪ thiol-containing
▪ precursor of
▪ part of glutathione
cathecolamine
Cysteine Cys C Tyrosine Tyr Y
(Epi, NorEpi, Dopa)
Millon’s Test
Nitroprusside
Rgt. Hg+2 sol’n.
(+) red
(+) pink / rose
C. ACIDIC (2nd COOH) AG
Glutamate /
Aspartate /
Asp D Glutamic Glu E
Aspartic Acid
Acid
D. BASE (2nd NH2) LAH
▪ guanadino -containing
▪ starting material for
Lysine Lys K synthesis of Arginine Arg R Sakaguchi test
Tranexamic acid Rgt. α napthol
(+) red
▪ imidazole –containig
Histidine His H Pauly test
Rgt. Diazotized sulfanilic acid
(+) red
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
BY METABOLISM BY NEED (ESSENTIAL)
Ketogenic LL Leucine, Lysine P Phenylalanine H Histidine Needed in diet,
Glucogenic The Rest V Valine A Arginine cannot be
Both TWIFY Phenylalanine, Isoleucine, T Threonine L Leucine synthesized
Tryptophan, Threonine, Tyrosine L Lysine Non-essential (the
T Tryptophan rest)
I Isoleucine Can be
* NO TYROSINE
M Methionine synthesize
B. PEPTIDE STRUCTURE
Hydrolysis Break Biuret test – for presence of Peptide bonds;
Condensation Connect use Cu++ ions (+)violet / (-) hydrolysed
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
Primary Peptide bonds Sequencing rgts. (Sanger rgt. & Edman rgt.)
Secondary H bonds between amide atoms α & β helix
Tertiary 3D arrangements of peptide chains
Quarternary Multiple interacting peptide chains/subunits *subunits = cooperative bonding
CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEINS
By Shape 1. Globular Water soluble; plasma proteins 2. Fibrous Water insoluble, structural proteins
By Composition 1. Simple Amino acid only 2. Conjugated Amino acid + Non Amino Acid
1. Structural Collage, keratin, eslastin Hypothalamic, Pituitary and Pancreatic
4. Regulatory
2. Transport Hgb (O2), Ceruplasmin (Cu) Hormones
By Function
3. Storage Myoglobin 5. Defense Immunoglobulins
6. Catalytic Enzymes
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
C. ENZYMES
THEORIES OF BINDING
Lock & Key theory Only 1 substrate; Rigid active site
Induce fit Active site can change conformation (flexible)
Enzymes rarely work alone need assistance of co-factor
Entire Enzyme (holoenzyme) a. Inorganic – Metal ions b. Organic – come from B vitamins
Protein (apoenzyme) Zn+2 Carbonic anhydrase B2 NAD+
Fe+2 Catalase B3 FAD+ / FMN+
Nonprotein (cofactor) Mg+2 Hexokinase B5 CoA “coenzymes”
CLASSIFICATIONS OTH LIL
Oxidase, Reductase, Lyase
EC #1 Oxidoreductase
Dehydrogenase Deaminase removes NH2
*heterogenous
EC #4 Decarboxylase remove COOH (as CO2)
EC #2 Transferase Kinase - transfers PO4 * usually removes
Anhydrase/Dehydratase remove H2O
fxnal grp
Hydrolase Urea, Lipase, Protease,
EC #5 Isomerase Isomerase, Epimerase, Mutase, Racemase
EC #3 *usually L word Nuclease, L-asparaginase,
enzyme Acetylcholinesterase Ligase
EC #6 Synthase, Syntethase, Carboxylase
(condensation)
ENZYME KINETICS
Michaelis Menten plot Enzyme Inhibition
Km required to reach ½ max Km Vmax
Reflects the affinity o the enzyme Competitive Same
Factors affecting Enzyme Kinetics: Noncompetitive Same
1. Temperature 2. pH Uncompetitive
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
II. CARBOHYDRATES
Aldehyde Ketone
RCHO RCOR
*end *middle
CLASSIFICATIONS
1-unit Monosaccharide 2-unit Oligosaccharide
a. Functional grp: i. Aldose (ex. ribose) ii. Ketose (ex.ribulose) Maltose Glucose + Glucose
b. # of carbons Aldose Ketose Sucrose Glucose + Fructose
3 Trioses Glyceraldehyde Triulose Dihydroxyacetone Lactose Glucose + Galactose
4 Tetrose Erythrose Tetrulose Erythrulose >10 units Polysaccharide often structural / storage
5 Pentose Ribose Pentulose Ribulose Plant - Plant -
6 Hexose Glucose Hexulose Fructose Structural cellulose Storage starch
▪ Linear = Fischer projection ▪ Cyclic = Hayworth projection - cell wall - stored
Fungi - Animal -
*penultimate – 2 to the last Carbon
nd
*involves attachment of the penultimate components energy
chitin glycogen
O to the Carbonyl C
ISOMERISM QUALITATIVE TESTS
Epimers Differ only 1 chiral carbon Test for Reagent Result
Enantiomers All chiral carbons are inverted Molisch test General test α-napthol (+) violet
Diastereomers Etc./ between Epi & Enantiomer Seliwanoff test Ketoses Resorsinol (+) cherry red
Anomer Differ @ carbon #1 only (α & β) Iodine test Starch I2 solution (+) blue/violet
Lac, Mal/Suc,
REACTIONS: Osazone test Phenylhydratazone (+) crystals
Glu/Fru/Man
Oxidation Condensation Bial’s test Pentoses Orcinol (+) green
Reduction Mucic acid test Galactose HNO3 (+) crystals
Tollen’s test Reducing sugars Ammoniacal AgNO3 (+) Silver Mirror
Most common sugars are reducing Fehling’s test
(+) brick red
except Sucrose & Trehalose Benedict’s test Reducing sugars CuSO4
ppt.
Also differentiates mono (fast) & di (slow) Barfoed’s test
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
III. LIPIDS
FATTY ACIDS SAPONIFIABLE LIPIDS
Saturated No C=C Unsaturated C=C
Caproic 6 Palmitic 16 Palmitoleic 16 1. Triacylglyecrol
Caprilic 8 Stearic 18 Oleic 18
Capric 10 Arachidic 20 Linoleic 18 X=
Lauric 12 Behemic 22 Linolenic 18 H Phosphatidic acid
Myristic 14 Lignoceric 24 Arachidonic 20 Phosphatidylcholine
Choline
Reaction of Lipid 2. Phospholipids “Lecithin”
1. Saponification 2. Auto-oxidation/ Phosphatidylethanolamine
Ethanolamine
3. Hydrogenation/Reduction Rancidification “Cephalin”
QUALITATIVE TESTS Inositol Phosphatidylinositol
Test for Reagent Result X=
H2SO4 + H Ceramide
Lieberman-
Sterols Acetic (+) green Glu or Gal Cerebroside
Burchard Glyco-
Anhydride Oligosacch Globoside
sphingo-
(+) burnt fat 3. Sphingolipids Oligosacch w/
Acrolein Test Glycerol KHSO3, ∆ Ganglioside lipids
odor sialic acid
Ammonium (+) yellow Sphingo-
Phosphate Choline + PA Sphingomyelin
molybdate ppt phospholipid
4. Waxes
NON-SAPONIFIABLE LIPIDS
1. Fat Soluble A Eyesight E antioxidant
vitamins D Not true vit. K Coagulation
10 Monoterpene 30 Triterpene
2. Terpenes
15 Sesquiterpene 40 Tetraterpene
1Terpene = 10C
20 Diterpene
C27 compound; contains CPPP nucleus
CHOLESTEROL
CycloPentanoPerhydroPhenanthrene
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
IV. NUCLEIC ACIDS
Replication Transcriptions Translation
Central Dogma DNA DNA RNA PROTEINS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
NUCLEOTIDE STRUCTURES Sequence of
Primary
nucleotide; linear
Purine Involves pairing via
Adenine Guanine
(PurGA) the H-bonds *coiling
Secondary
INTERstrand (DNA)
INTRAstrand (RNA)
Pyrimidine Further organization
Cytosine Uracil Thymine
(PyrCUT) Tertiary Ex. Supercoiling,
plasmid
REPLICATION Involves
▪ DNA Synthesis ▪ Bidirectional unwind double stranded- Quartenary nucleoprotein complex
Helicases Ex. Histones
▪ Semi-conservative ▪ Has high fidelity /accuracy DNA
▪ Semi-discontinous ▪ DNA DNA relieve super coiling DOUBLE HELIX
Steps: Topoisomerase prevent the breaking of
1. DNA double helix is opened by DNA 1. Complementary base-pairing
helicases required in the synthesis AT (2bonds) CG (3bonds)
Initiation Primase
2. Primase creates a temporay RNA of the RNA primers 2. Helical/handed
primer for each DNA strand DNA polymerase CW = right handed (A-DNA,B-DNA)
Elongation I only one to remove DNA primers CCW = left handed (Z-DNA)
3. DNA polymerase at the replication fork II involve in DNA repair 3. Antiparallel (5’ 3’) (3’5’)
synthesize DNA in 5’ to 3’ direction. There are responsible for the synthesis of Okazaki
III
two strands, the leading & lagging strands. fragment
4. DNA polymerase removes RNA primer & fills the DNA ligase connect the okazaki fragments
gaps between the Okazaki fragments
5. DNA ligase joins DNA fragments of the lagging
strand, creating a single DNA molecules
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
TRANSCRIPTION
▪ RNA synthesis C = G A=U ▪ Unidirectional main enzyme; has 2 subunits: sigma & core
RNA Polymerase
▪ synthesis of DNA mRNA ▪ Lower fidelity can initiate polymerization
act as template for translation (synthesis of protein)
▪ process by which the genetic messages contained mRNA
carrier of codons
in DNA are “read”, or transcribed, & carried out of
adaptor molecule of amino acid
nucleus to parts of the cell called ribosomes where
tRNA carrier of anticodon
protein synthesis occurs
Types: (2) Charged (w/ AA), Uncharged (w/o AA)
Steps: rRNA together w/ other proteins make up the ribosomes
1. Initiation: Once RNA polymerase binds with +1, POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL MODIFICATIONS
process of unwinding starts and sigma subunit is
released
2. Elongation (by core subunit)
Template Strand Antisense
Non-Template / Information Strand Sense
3. Termination:
Rho-dependent Termination sequence
Rho-independent Palindrome sequence then
hairpin loop
Product: pre-mRNA
TRANSLATION
▪ protein synthesis ▪ mRNA protein RULES OF THE GENETIC CODE
3 bases : 1 amino acid 1. Universal
UUU – Phe 1 Amino acid ~ many codons
2. Degenerate/ redundant
Codons UUC – Phe except Methionine (AUG), Tryptophan (UGG)
AUG – Met (start) 3. Non-ambigous 1 codon = 1 amino acid
64 codons 61 coding (amino acid)
4. Non-overlapping
3 non coding (stop)
UAG, UGA, UAA 5. Coma less, no skips 5’- UUU | AAA | GGG - 3’
AAA anticodon UUU codon
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
POST TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATION
Interactions toward the protein’s native state
1. Folding
Sometimes requires use of chaperone proteins
2. Side chain modificaiton Removal of AA’s or addition of fxnal grps
By glycosylation
3. Targeting
In ER / golgi apparatus
By proteasomes
4. Degradation
Common: Ubiquination
MUTATIONS
alteration in the gene sequence often lead to disease
SMALL MUTATIONS:
due to substitution of a single base
Point Mutation Transition Pur Pur ; Pyr Pyr
Transversion Pur Pyr ; Pyr Pur
Frameshift Mutation Due to addition or removal of base
Classification base Silent No AA change New stop
Non-sense
on effect Missense AA change codon
REPAIR MECHANISM
Excess UV mutation photolyase – Xeroderma pigmentosa
Depurination/ Depyrimidation Result to AP site Repair: excision repair
Due to reactive O
Prevention: Anti-oxidants
Oxidative stress species (ROS)
Endogenous glutathione
Uncontrolled death
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
IDENTIFICATION TEST
Identification of Reagent Positive result
PROTEINS
Xanthoproteic test Phenylalanine HNO3 Yellow / Orange
Lead acetate test Methionine Thioether Black
Hopkin’s Cole Tryptophan Glyoxylic acid Violet ring
Ninhydrin Proline Violet 1˚ except proline 2˚
Nitroprusside Cysteine Red
Millon’s test Tyrosine Hg2+ Pink / rose
Pauly test Histidine Diazotized sulfanilic acid Red
Sakaguchi test Arginine α-napthol Red
Molisch test Carbohydrates (general) α-napthol Violet
Iodine test Starch I2 sol’n Blue/Violet
Bials test Pentoses Orcinol Green
Seliwanoff’s test Ketoses Resorcinol Cherry red
Osazone test Lac/ Mal/ Suc/ Glu/ Fru/Man Phenylhydrazine Crystals
Mucic test Galactose HNO3 Crystals
Tollen’s test Reducing sugar Ammoniacal AgNO3 Silver mirror
Fehling’s
Benedict’s Reducing sugar Cu+2 SO4 Brick red ppt
Barfoed’s
Barfoed’s Differentiate mono & di Mono (fast), Di (slow)
*Most common sugars are REDUCING SUGARS except Sucrose & Trehalose
LIPIDS
Lieberman-Burchard Sterols H2SO4 + acetic anhydride Green
Acrolein test Glycerol KHSO3 Burnt fat odor
PO4 Ammonium molybdate Yellow ppt
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Additional Notes
INSULIN GLUCAGON AMINOACIDOPATHIES
End effect BS BS Phenylketonuria Deficiency on phenylalanine hydroxylase (Phe-Tyr)
Timing Fed Fasted Branched chain alpha keto acid dehydrogenase
Maple Syrup Disease
Glycolysis (increase L,I,V)
Gluconeogenesis Alkaptonuria Hemogentisate oxidase (AKA Black urine disease)
Glycogenesis Albinism Tyrosinase (decrease melanin)
Glycogenolysis METABOLISM
Processes occurs at: Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis
Carbohydrate Glycogenesis Glycogenolysis
Mitochondria TCA, ETC, B-oxidation, Ketogenesis
Kreb’s Cycle Electron transport chain
Glycolysis, Glycogen metabolism, Fatty Acid Synthesis Fatty Acid Oxidation
Cytosol PPP, FA synthesis, Cholesterol Lipid Mevalonate Pathway (MEV) Methylerythriol Pathway (MEP)
synthesis Ketogenesis
BOTH Heme synthesis, Urea cycle, TERPENES
“HUG takes 2” Gluconeogenesis Name #C # of isoprene Example
Most volatile oils
RATE LIMITING STEPS
Monoterpene 10 2 e.g. geraniol, citral, menthol
Glycolysis Phosphofructokinase Limonene Most common
Gluconeogenesis Fructose 1,6-Biphosphatase Parthenolide Serotonin antagonist
Sesquiterpene 15 3
Kreb’s cycle Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Quinghaosu Artemisia annua
Glycogenesis Glycogen synthase Paclitaxel Taxus brevifolia
Glycogenolysis Glycogen phosphorylase Diterpene 20 4 Forksolin
Pentose Phosphate Glucose-6-Phosphate Zingiberol
Pathway dehydrogenase Triterpene 30 6 Neem Azadirachta indica
Fatty Acid Synthesis Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Retinol
Tetraterpenes 40 8
B-oxidation Carnitine acyl transferase Lycopene
Ketogenesis HMG CoA Reductase
Urea cycle Carbamoyl-P-Synthethase
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
DEFICIENT ENZYMES
GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS
Type Name Enzyme Type Name Deficient Enzyme
O Glycogen Synthase IH Hurler
Glucose-6- IS (Formerly V) Scheie α-L iduronase
Ia Von Gierke Von GP
Phosphatase IH/S Hurler-Scheie
Glucose-6- II Hunter Iduronate sulfatase
Ib
Ptranslocase IIIA Heparan Sulfatase
Lysosomal α (1,4) IIIB San Filippo N-acetylglucosaminidase
II Pompe PomLy
glucosidase IIIC Syndrome Glucosamine-N-acetyltransferase
III Cori Debranching enzyme CD IIID N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase
IV Andersen Branching enzyme AB IVA N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase
Marquio Syndrome
Muscle glycogen Muscleman IVB B-galactosidase
V McArdle
phosphorylase = McArdle VI Maroteaux-Lamy N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase
Hepatic glycogen VII Sly Syndrome B-glucuronidase
VI Hers HeHe
phosphorylase IX Natowicks Syndrome Hyaluronidase
VII Tarui Phosphofructokinase-1 TauFru LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE
AMINO-ACID DERIVATIVE PRODUCTS Tay-Sachs Hexosaminidase A TaySax
Catecholamine Thyroid hormones Sandhoff Hexosaminidase A & B A&B
Tyrosine
Melanin Fabry α-galactosidase A Fabulous Alpha-Gal
Tryptophan Serotonin Melatonin Krabbe β-galactosidase ab
Histidine Histamine Gaucher Β-glucosidase U
Serine Choline Metachromatic
Arylsulfatase
Glutamate GABA Leukodistrophy
Glycine Heme synthesis No man pick’s his
Nieman-Pick Sphingomyelinase
Argine Nitrous Oxide nose w/ his finger
Glycine Heme synthesis Farber Ceraminidase Cerafarber
Argine Nitrous Oxide
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
PHARMACOGNOSY
Plant Family CARBOHYDRATES SUGARS
Old Name New Name MONOSACCHARIDE Test: Benedict’s & Barfoed’s = (+) Brick red ppt
Labitae Lamiaceae #C Aldose (-ose) Ketose (-ulose)
Compositae Asteriaceae Astra composes 2 Diose Hydroxyacetaldehyde
Unbelliferae Apiaceae Unbeliaple 3 Triose Glyceraldehyde Dihydroxyacetone
Leguminaseae Fabaceae LegumFaba? 4 Tetrose Erythrose Erythrulose
Crussiferae Brassicaceae CB Ribose, Xylose, Arabinose
5 Pentose Ribulose, Xylulose
Graminae Poaceae Poe wins grami Test: Bials, Benzidine
Guttiferae Glussiaceae GG Glucose, Galactose Fructose
6 Hexose
Palmae Arecaceae PalmAre Test: Mucic & Phenylhydrazine Test: Seliwanoff
MILK PRODUCTS 7 Heptose Sedoheptulose
8 Octase D-glycero-D-mannoctulose
9 Nanose Neurominic (Salic acid)
DISACCHARIDE
Non-reducing Reducing
Sucrose Gluc + Fruc α 1,2 Maltose Glucose + Glucose α 1,4
Trehalose Gluc + Gluc α 1,1 Lactose Glucose + Galactose β 1,4
Lactulose Fructose + Galactose β 1,4
OLIGOSACCHARIDE
TAXONOMY 1. Maltotriose Gluc + Gluc + Gluc 4. Raffinose Gluc + Galac + Fruc
Domain Order 2. Dextrin 5. Stachylose Gluc + Galac + Galac + Fruc
“Dumb Over Kids Fancy
Kingdom Family 3. Gentianose Gluc + Gluc + Fruc
Prefer Green Candies
Phylum Genus POLYSACCHARIDE
Salads”
Class Species HOMOGLYCAN
Amylose Amylopectin Corn Zea mays Hair seeds Gossypium
2. Cellulose
β-amylose α-amylose Wheat Triticum aestivum of Cotton hirsutum
Structure Linear/helical Branched Potato Solanum tuberosum Chicorium
250-300 units (α 1,4) 1000 or more (α 1,6,α 1,4) 1. Starch 3. Inulin Chicory root
Rice Oryza sativa intybus
Sol in H2O Insoluble Soluble Arrow
Maranta arundincea
Iodine test Deep/dark blue Blue violet/Purple Root
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
HETEROGLYCAN
GUMS & MUCILAGES GLYCOSIDE FlaPheIsoCLaSa AlAnAlCaT
Other Name Botanical Origin ▪ CARDIAC ApAdBlaCoCaDiSquiStro
▪ SHRUB & TREE EXUDATES Ka-GhAT Unsaturated steroidal aglycone tests 2-deoxysugar glycone test
Karaya Sterculia Gum Sterculia urens Liebermann-Burchard Salkowski Keller-Killiani reddish brown
Ghatti Indian Gum Anogiessus latifolia (+) blue-green (+) red ring Baljets
Acacia Gum Arabic Acacia senegal (unsaturated) at junction Legal’s
Tragacanth Gum Tragacanth Astralagus gummifer (-) yellow (saturated)
▪ MARINE GUM ACADs Constituent Other Name Botanical Origin
Gelidium cartilageneum Dogbane/ Black Apocynum
Agar Japanese Isinglass Apocynum Cymarine
Gracilaria confervoides Indian Hemp cannabinum
Irish moss Gigartina mamillosa Adonis Adonitoxin Pheasant’s eye Adonis vernaliz
Carageenan
Red algae Chrondrus crispus Black
Hellebrin Christmas Rose Helleborus niger
Algin Brown seaweed Macrocystis pyrifera Hellebore
Danish Agar Furcellaran Furcellaria fastigiata Convallaria Convallotoxin Lily of the Valley Convallaria majalis
▪ SEED GUM PiCyLo-Guar Cactus Queen of the Night blooming Selenereus
Plantago psyllium Grandiflorus Night cereus grandiflorus
Psyllium
Plantago ovata Digitalis Digitoxin Fox glove Digitalis purpurea
Cydonium Quince seed Cydonia vulgaris Digoxin Grecian foxglove Digitalis lanata
Locust Bean Carob Pulp Mediterranean/
Ceratonia siligua Urginea maritima
Gum St. John’s Bread Squil bulb Sullarenin White
Guar gum Guaran Cyamopsis tetragonolobus Indian Urginea indica
▪ MICROBIAL GUM XD Strophantus
Xanthan Gum Xanthomonas campestris kambe
Dextran Leuconostoc mesenteroides Strophantus
▪ PLANT EXUDATE Pectin Strophantus hispidus
Pomelo Citrus grandis Calamansi C.microcarpa Strophantus gratus
Orange C. aurantum Grape fruit C. paradise Acokanthera
Dalanghita C. nobilis Lemon C.limon shimpera
Ponkan C. sinensis Apple Pyrus malus Maroon – notes as source
▪ STARCH & CELLULOSE DERIVATIVES Additional from other source
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
▪ ANTHRAQUINONE AnFRaCChrynoneS ▪ SAPONIN GlyGiDi AgSiSt
(+) Borntrager’s test Aglycone: Anthracene *catharthics Hemolysis Test Aglycone: Sapogenin
(+) Froth Test
Constituent Other Name Botanical Origin Capillary Test Lieberman-Burchard Test
Aloe barbadensis Constituent Botanical Origin
Barbaloin, Curacao Aloe
Aloe vera Spanish Glycirrhiza glabra
Aloe / Isobarbaloin, Glycirrhiza / Glycyrrhizin,
Aloe ferox Russian Glycirrhiza glabra
Sabila Aloin, Aloe Licorice Glycirrhizic acid
Cape Aloe Aloe africana v.glandulifera
emodin
Aloe spicata Panaxoside, American Panax quinquefolus
Frangula Buckthorn bark Rhamnus frangula Ginseng Gensenoside Asian Panax ginseng
Rheum officinale Chikuse/ Susaponin
Chinese
Rheum palmatum Diosgenin, Botogenin, Dioscorea spiculifora
Rhein Dioscorea
Rhubarb Rheum emodi Hecogenin Dioscorea floribunda
anthrones Indian
Rheum webbianatum Fiber, Hecagenin Agave cantalla
Ornamental Rheum rhaponatum Agave Manogenin
Chrysarobin Andira araroba Gifogenin
Cascara Cascaroside Similax Smilagenin Smilax aspera
Rhamnus purshianus
sagrada A,B,C,D Strophantus Sarmantogenin * See cardiac gly
Sennoside Alexandria Cassia acutifolia ▪ FLAVONOL Aglycone: Flavonoids Gink Milk to Elin
Senna
A,B,C,D Tinnevelly Cassia angustifolia Abundant in: Polygoneceae, Rutaceae,Umbelliferae
▪ CYANOPHORIC (+)Guignard Test = Brick red Constituents Botanical Origin
Wild Cherry Prunus serotina Apricots Prunus armeniaca Citrus fruits
Bioflavonoids from Rutin & Hisperidin;
Bitter almond Prunus amygdalus Barley Hordeum vulgare Glycine max
Citrus and Soya Hesperitin; Diosmin;
▪ ISOTHIOCYANATE Isothiomustard Glycine soja
Constituent Botanical Origin Gingko Ginkolides, Bilobalides Gingko biloba
Black mustard Allyl Sinapis nigra Populus spp. Milk Thistle Silibinin,Silymarin Silybinum marianum
White mustard Acrinyl Sinapis alba Elin Quercitin
▪ ALCOHOL Aglycone: Saligenin Drink Alcohol to WiPo ▪ ALDEHYDE Vanillaldehyde
Salix purpurea Mexican vera cruz
Willow bark Vanilla plantifolia
Salix fragilis Vanilla Bourbon vanilla
Poplar bark Populus spp. Tanitian vanilla Vanilla tanitensis
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
▪ PHENOL PUP ▪ LACTONE CoCaP
Other Name Constituent Botanical Origin Constituent Botanical Origin
Uva ursi Bearberry Arbutin Archostaphylo uva ursi Warfarin, Dicoumarol,
Coumarin Dipterix odorata
Rhus radicans Bishydroxycoumarin,
Poison Ivy Oak Uroshiol
Rhus toxicodendron Cantharides Cantharidin Cantharis vesicatoria
Psoralens Methoxsalen, Trioxalen Ammi majus
▪ TANNINS TaNutHam Gapple
Tests HYDROLYZABLE NONHYDROLYZABLE Constituents Botanical Origin
PHLOBAPHENES, Hammamelis leaf /
PYROGALLOTANNINS Hammamelitonin Hammamelis Virginia
CONDENSED Witch Hazel leaf
Goldbeater’s (+) Blooms Leather (+) Tanners Red Nutgall Tannic acid Quercus infectoria
Ferric Chloride Blue-black ppt Green-black ppt Insect Cynips tinctoria
Bromine Test (-) (+) Japanese &
Gallic acid Rhus chinensis
KMnO4 Decolorize Do not decolorize Chinese Galls
Hydrolysis Polymerize Apple Pyrus mallus
Phenolic acid, sugars, Phlobaphenes (red
Pyrogallol polymers, insoluble)
True tannins Can convert to leather Christmas-themed
Pseudotannins Can’t convert to leather non-hydrolyzable
tannins
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
LIPIDS
FIXED OILS FATS WAXES FIXED OILS
Esters of Fatty Esters of Fatty Esters of Fatty acid + Cottonseed oil Gossypol 0.6% Gossypium hirsutum
Acid + Glycerol Acid + Glycerol MW alcohol Sesame/Teel/Benne oil Sesamol Sesamum indicum
LIQUID except SOLID except Coconut oil Lauric, Myristic Cocus nucifera
Solid, Semisolid, Liquid
Theobroma oils Cod Liver Oil Peanut oil Arachis hypogaea
Unsaturated FA Saturated FA Saturated, Unsaturated FA Castor oil Ricinoleic acid Ricinus communis
Plants Animals Plants & Animals Soybean oil Lecithin Glycine soja
Energy Storage Energy storage Protection Corn oil Linoleic, Oleic Zea mays
FATTY ACIDS Safflower oil Linoleic Carthamus tinctorius
Saturated Unsaturated Sunflower oil Linoleic, Oleic Helianthus annuus
Caproic 6 Palmitic 16 Palmitic 16 Ethiodized oil Papaver somniferum
Caprilic 8 Stearic 18 Oleic 18 Olive oil Oleic Olwa europea
Capric 10 Arachidic 20 Linoleic 18 Almond oil Oleic Prunus amygdalus
Lauric 12 Behemic 22 Linolenic 18 Apricot: Prunus armeniaca
Persic oil Oleic
Myristic 14 Lignoceric 24 Arachidonic 20 Peach: Prunus persiaca
Reaction of Lipid Hydrogenation Sulfation Palm Kernel oil Lauric, Myristic Elalis guaneensis
FATS TheoLaCoUA Linseed/ Flav seed oil Linoleic Linum usitatissimum
Theobroma Theobroma cacao Lard Sus scrofa Theobroma oil Theobroma cacao
Anhydrous Lanolin Ovis aries Butterfat Bos Taurus Hydrogenated Veg. oil Stearic, Palmitic
Cod Liver oil Gadus morrhua COLOR REACTION
Undecylenic acid Pyrolysis Cotton seed oil Halphen’s test
Ricinus communis NagHaCot ng SeBo sa
Azelaic acid Ozonalysis Sesame oil Boudoin’s test
Vegetable si Ser Millon
Beef Tallow Bos Taurus Vegetable oil Serger rxn
Suet para kay Olive
Mutton Tallow Ovis aries Olive oil Millon’s test
WAXES SperJoBeCa IODINE VALUE
Physeter Non-drying <100 Olive, Almond NOA
Spermaceti macrocephalus Beeswax Apis mellifera
Semi-drying 100-120 Cottonseed, Sesame SeCotSe
Drying >120 Linseed, Cod Liver LiCod
Simmondia Carnauba Copernicia
Jojoba oil
chinensis wax punifera
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
PHOSPHOLIPIDS FIXED OILS VOLATILE OILS
Lecithin Cephalin Composition Ester of FA + Glycerol Terpenes, Aromatic cmpds.
VOLATILE OILS Rancidity
Lamiaceae Mint Family Grandular hair or trichomes Resinity = auto-oxidation
Piperaceae Pepper family Modified parenchymal cells Grease spot + -
Apiaceae Dillweed family Oil tubules or vittae Distilled
Pinaceae Pine Family Lysigenous & Schizogenous Saponified
Rutaceae Citrus Family passage COMPONENTS OF VOLATILE OILS
Methods: solid oxidized liquid hydrocarbon
Stereoptene Eleoptene
Water distillation Turpentine hydrocarbon portion portion
Water & steam Distillation Clove, Cinnamon M Menthol M Methylsalicylate
Steam Distillation Peppermint, Spearmint A Anethole E Eucalyptol
Dry distillation Pinaceae T Thymol E Eugenol
Destructive Cupressiaceae 2 BROAD CLASSES OF VOLATILE OILS
Expression/ Eaile a piquer Citrus fruits Acetate-Mevalonate pathway
Glycosidic VO 1. Terpenoids Monoterpene Most commonly found VO
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Benzene, Petroleum Ether Sesquiterpene Largest class of Terpenoids
Enfleurage Use of cold fat : ethanol extract 2. Aromatic Shikimic acid pathway Use: Perfumes
Ecuelle Rolling fruit Lemon
Most Volatile; leaves
Clavenger apparatus Top Notes tLAL Anise Oil
the skin readily
TERPENES Lavender
Name # C Iso # Example Thyme
Most volatile oils. Middle notes intermediate ThRoNes Rose Oil
Monoterpene 10 2
Limonene Most common Nerole
Sesquiterpene 15 3 Parthenolide 5-HT antagonist
Base notes Low, fixative & staying power
Diterpene Paclitaxel Taxus brevifolia
20 4
Forksolin Zingiberol Musk Male dusk deer of Asia Muscone Muscus spp
Triterpene 30 6 Neem Azadirachta indica Discharging pockets of Parodoxus
Civet Civetone
Retinol Civet cats hermaphoditus
Tetraterpenes 40 8 Most valuable base
Lycopene Ambergris Ambrein
note
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
VOLATILE OILS ▪ PHENOL Thy in Clove & Creo taste like Juni Myr
▪ HYDROCARBON HydroTur Thyme oil Thymol Thymus vulgaris
Turpentine oil α & β pinene Pinus palustris Clove oil Eugenol Eugenia caryophillus
▪ ALCOHOL CoCaRoNeJuPiPe Creosote oil Creosole, guiacol Fagus grandiflorus
Coriander oil Linalool Coriandrum sativum Juniper tar Cadinene Juniperus oxycedrus
Cardamom oil Cineole Eletaria cardamomum Myricia oil Eugenol Pimenta racemosa
Geranoil, Nerol, nagCamp sa Car si Buchu with
Rose oil
Citronellol
Rosa gallica ▪ KETONE
Spear & Cedar may Worm!)
Neroli oil (Orange Camphor Carvone Cinnamomum camphora
Linalool Citrus aurantium
Flower oil) Caraway oil Carvone Carum carvi
Juniperus oil Borneol Juniperus communis Buchu oil Diosphenol Berosma betulina
Pine oil Pinus palustris Spearmint oil Carvone Mentha spicata
Menthol American Mentha piperita Cedar leaf oil Thujone, Fenchone Thuja accidentalis
Peppermint oil
Terpineol Japanese Mentha arvensis Wormwood/ Absinthe/ Quinghaosu Absinthe absinthum
▪ ALDEHYDE CitCin Or LeHa ▪ PHENOLIC-ETHER Nut FeAnise
Cymbopogon Nutmeg Myristicin, Safrole Myristica fragrans
Citronella,
winterianus Fennel Trans-anethole, Fenchone Foenicilum vulgare
Citronella oil 2-hexanal/
Cymbopogon nardus Anise oil Trans-anethole, Anisaldehyde Pimpinilla anisum
Acetaldehyde
Cymbopogon citrated Trans-anethole, Illicium verum
Chinese
Ceylon Cinnamon zeylanicum Star Anise Estragole
Cinnamon oil Saigon Cinnamaldehyde Cinnamon laureirii Japanese Hananomin
Cassia Cinnamon cassia ▪ OXIDATIVE OEu
Sweet Decanal, Citrus sinensis Eucalyptus/Cajuput oil Cineole Eucalyptus globulus
Orange oil Limonene ▪ ESTER EGa LaPinMu
Lemon peel 3:1 Geraniol, Citrus limon Gaultheria/ Wintergreen/
Cineole Gaultheria procumbens
oil Neral Betula/ Sweet Birch oil
Hammamelis Witch α-ionone / β- Plants parts where volatile oils are obtained
Hammamelis virginia
oil Hazel terpinol Cinnamon oil Dried bark Oregano Leaf & Flowering Tops
Clove oil Flower buds Cardamon oil Fruit
Mustard Seeds Sandal wood Heart wood
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
RESIN
Complex mixture of: ▪ OLEORESIN TurCapWhite Ginger Bal
Resin acid Oxyacid Esters Acid + alcohol Turpentine Pinus Palustris
Resin alcohols Resinols Resenes Hydrocarbon African (Labuyo) Capsicum frutescens
Resinotannols Give color w/ FeCl3 Capsicum Capsaicin Lousiana long C.anuum v.longum
Resin combination Irish/ tabasco C. anuum v.conoides
Oxyacids White pine Pinus strobus
Oleoresin Volatile oil + Resin Resin acid
(-COOH +phenol) Ginger Bisabolene
Zingiber officinale
Oleo-gum-resin V.O + Gum + Resin Glycoresin Resin + CHO Zingeberol
May Kava si Rosin, Jalap (Hanap) Balsam of
▪ RESIN ni Santa si Podo Mastic nag Pot Copaiba
Capaifera spp
Kava-kava
Mehysticin,
Piper methysticum
▪ OLEO-GUM-RESIN MAgor
Yangonin, Kawain Myrrh Commiphora molnol
Abretic acid, Sylvic Asafetida Asaresinotannol, ferulic acid Ferula foetida
Rosin/ Colophony Pinus palustris
acid, Rescene ▪ BALSAM STPB
Jalap Jalapin, Purganol Exogonium purge Storax Storesin Liquidambar orientalis
Yerba Santa/ Eriodyction Eriodyctn californium Tolu balsam Myroxylan balsamum
Podophyllin, Peruvian balsam Myroxylan pereirae
Podophyllum Podophyllum peltatum
Peltatin Benzoin Styrax benzoin
Mastic α-resin, masticin Pisracia lentiscus BENZOIN TINCTURE “STAB”
Cannabis/ Indian hemp/ THC, Cannabidiol, Storax Aloe
Cannabis sativa
Marijuana/ Pot Nabilone Tolu Benzoin
STEROIDS - Mevalonic acid pathway
Cholesterol Animal Cardiac Glycoside
Sterol Ergosterol Fungi Glucocorticoid Cortisol CHO metab
Phytosterol Plants Mineralocorticoid Aldosterone H2O metab
Hormones
Primary Cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid Sex Male Androgen, testosterone
Bile acid
Secondary Deoxycholic acid, litocholic acid Hormones Female Estrogen, Progestin
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
ALKALOIDS
All alkaloids are SOLID EXCEPT: ▪ TROPANE AA: Ornithine HyoSCEM BeDuWi
Conine Poison hemlock Comium maculatum Hyoscyamine Hyoscyamus niger
Hyoscyamus Henbane
Arecoline Scopolamine
Nicotine Tobacco leaves Nicotania tabacum Dimsonweed Scopolamine
Datura
Scotch Broom Cystisus scoparius Stramonium Jamestown
Spartein Lupin Lupinus mutabilis weed
Hyoscyamine stramomium
ALKALOIDAL REAGENT Huanuco coca Erythroxylan coca
Wagner’s rgt Iodine in KI WIKI Coca Truxillo coca Erythroxylan
Mayer’s rgt K Mercuric Iodide MaMeKI Crack, Coke truxillense
Valser’s rgt Mercuric Iodide VaMI Egyptian Egyptian Hyoscyamine Hyocyamus
Dragendorff’s rgt K Bi Iodide DraBiKI Hyocyamus Hyocyamus Scopolamine muticus
Bouchard rgt Iodine in KI BIKI Mandragora
Mandragora Satan’s apple Mandragorin
Marme’s rgt K Cadmium Iodide MarCaKI officinarum
Sonnencheim’s rgt Phosphomolybdic Belladona Atropine Atropa belladona
Syllables
Scheibler’s rgt Phosphotungstic Duboisa
Duboisa
Hager’s rgt Picric acid myoporoides
Gold cmpds Withania
Withania
Tannic acid somnifera
▪ PYRIDINE-PIPERIDINE AA: Ornithine
Nicotiana Tabacco leaves Nicotine Nicotiana tabaccum ▪ ISOQUINOLINE AA: Tyrosine ISOT
Arecoline, Emetine, Brazillian: Cephaelis
Areca Betel Nut Areca catechu
Catechin, Tannin Ipecac Psychotrine ipecachuanhua
Indian Tobacco Cephaeline Panama: C. acuminate
Lobelia Lobeline Lobelia inflata
leaves Sanguinaria Blood root Sanguinarine Sanguinaria candensis
Leucaena OPIATES OPIOIDS
Ipil-ipil
leucocephala Morphine Papaverine Heroin Apomorphine
Opium
▪ QUINOLINE AA: Tryptophan CC Codeine Thebaine Hydrocodone
Cinchona Cinchonine Cinchona succirubra Noscapine Hydromorphine
Thalleioquine:identify quinine Cinchonidine Cinchona calisaya South America Strychnus castelanaei,
Tubocurarine
Cuprea Cuprea bark Remijia purdiena Arrow poison S. toxifera,
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
▪ IMIDAZOLE AA: Histidine Pimidazole ENZYMES
Pilocarpine Pilocarpus jaborandi Enzyme + vitamins
▪ STEROIDAL CPPP nucleus Stebore Coenzyme (organic & inorganic substances)
Green Hellebore American Germidine Germetrine Veratrum viride *cofactor = non enzyme part of enzyme
White Hellebore European Protoveratine A & B Varatrum album Zymogen or Protein part of
Proenzyme Inactive factor Apoenzyme enzyme
AA: Phenylethylamine,
▪ ALKALOIDAL AMINE PPECK
Tryptophan CARBOHYDRATE
Peyote Mescal buttons Mescaline Lophophora williamsii Amylase +
Salivary gland Zymase
Psilocybe Psilocybin Psilocybe mexicana Diastase
Ephedrine Ma Huang Ephedrine Ephedra sinica Amygdalase +
Amylosin Emulsin
Colchicum Colchicine Colchicum automnale Prunase
Khat Abysinian Tea Cathenone Catha edulis Ivertase Myrosin
▪ INDOLE AA: L-tryptophan VEsPReN ESTERASE
Madagascar Lipase Urase
Vinblastine,
Vinca alkaloids periwinkle, Catharantus roseous PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES
Vincristine
Chichira Pepsin Convert proteins to protease & peptones
Parasitic: Claviceps Trypsin Converts protease & peptones to
Rennin
Ergonovine Ergot purpurea polypeptides and amino acids
Saphrotic: C.paspanii SOURCES OF ENZYME
Calabar, Physostigma Pepsin Sus scrofa *proteolytic enzyme
Physostigmine
Ordeal venenosum Sus scrofa or Bos Taurus
Pancreatin
Reserpine Snakeroot Rauwolfia Rauwolfia serpentina *amylase, lipase & protease
Nux Vomica Strychnine Strychnus ignatii Anonas comosus
Bromolains
▪ PURINE AA: Glycine, Glutamine, aspartic acid *mixture of protein digesting & milk clotting
Coffea arabica, Purified bacterial protein elaborated by Group C
Coffee Caffeine Streptokinase
C.robusta, C.liberica β-hemolytic streprococci
Theophylline Tea Aminophylline Cammela sinensis Papain Carica papaya Clostridium
Collagenase
Theobromine Theobroma cacao From urine or histolyticum
Urokinase
Cola Kola nuts Kola catechin Cola nitida kidney cells
L-
Caffeine, Bacillus subtilis E.Coli
Guarana Paulliana cupana Sustilains asparaginase
Cathecolamine *proteolytic enzyme
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
VITAMINS 10 HALAMANG GAMOT BABY PLANTS
▪ FAT SOLUBLE ADEK Common Scientific Family Use
Vit.A Retinol Tretinoin, Isotretinoin Bawang Allium sativum Lilaceae Anti-HTN
Sunshine D3 Cholecalciferol-7-dehydrocholesterol Akapulko Cassia alata Fabaceae Anti-Fungal
Vit.D
Vitamin D2 Ergocalciferol, Ergosterol Bayabas Psidium guajava Myrtaceae Antiseptic
Vit.E α-tocopherol Mentha cordifolia
Yerba Buena Lamiaceae Analgesic
Vit.K1 Phytomenadione Vit.K3 Menadione Clinopodium douglasi
Vit.K
Vit.K2 Phenylmenaquinone Vit.K4 Menadiol Pansit-pansitan Peperomia pellucida Piperaceae Uric acid
▪ WATER SOLUBLE TaRaNaPaPy BFCo Lagundi Vitex negundo Lamiaceae Cough prep.
1. Vitamin B Complex Ampalaya Momordica charantia Cucurbitaceae Anti-DM
B1 Thiamine B5 Pantothenic acid B9 Folic acid Combretum indicum
Niyog-niyogan Combretaceae Anthelmintic
B2 Riboflavin B6 Pyridoxine B12 Cobalamin Quiqualis indica
B3 Niacin B7 Biotin
Carmona retusa
Saccharamyces Tsaang-gubat Boraginaceae Antidiarrheal
Sugar = Alcohol Brewer’s yeast Erretia microphylla
2. Yeast cerevisiae
+ CO2
Tarula yeast Candida utilis Sambong Blumea balsimifera Asteraceae Diuretic
3. Vit.C Ascorbic acid
4. Vit. H Biotin
VITAMIN FUNCTION DISEASE VITAMIN FUNCTION DISEASE
B1 Thiamine Aldehyde transfer Beri-beri, Wernicke-Korsakoff C Collagen synthesis
B2 Riboflavin REDOX (FAD, FMN) Cheliosis, Angular stomatitis Clotting Factors
Pellagra 3D Dermatitis, K δ-carboxylation of Glu
B3 Niacin REDOX (NAD,NADP)
Diarrhea, Dementia residues in CF
Panthothenic CoA Burning Foot Syndrome Nyctalopia
B5
Acid Transamination Peripheral Neuropathy (night blindness)
A
B6 Pyridoxine Carboxylation Xeropthalmia
Transfer of 1C (dry eyes)
B7 Biotin
component Ricketts
Transfer of 1C (kids)
B9 Folic Acid D
component Osteomalacia
B12 Cyanocobalamin (adults)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
Module 2 All-around Pharmacist (@GapangPharma)
You might also like
- Biochem IndexDocument8 pagesBiochem IndexShekinah Kaye SiegaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ProteinsRegine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Scia Reviewer UpdatedDocument7 pagesScia Reviewer UpdatedJm AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test Test For: Reagent +result: University of Santo Tomas-Legazpi James G. Terrenal 2BSMT-1Document1 pageQualitative Test Test For: Reagent +result: University of Santo Tomas-Legazpi James G. Terrenal 2BSMT-1James TerrenalNo ratings yet
- Gati NotesDocument19 pagesGati NotesjiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24 11-29-22Document21 pagesLecture 24 11-29-22Caleb HeNo ratings yet
- Key To Amino Acids of Phygaris (Student Version) - 1Document1 pageKey To Amino Acids of Phygaris (Student Version) - 1Jeremiah MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chart of Aminoacids Names and Abbreviations and CodonsDocument1 pageChart of Aminoacids Names and Abbreviations and Codonsstlcajun55No ratings yet
- Start Here: Gold Pink White EDTA W/ Plasma SeparatorDocument1 pageStart Here: Gold Pink White EDTA W/ Plasma SeparatorfdsfdsfNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Amino Acid Polar Hydrophobic Amino AcidDocument2 pagesNonpolar Amino Acid Polar Hydrophobic Amino AcidAciel CruzNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument3 pagesProteintrial.shreyasNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidDocument24 pagesAmino AcidAgung PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chem 145: Amino Acid Notes and PropertiesDocument12 pagesChem 145: Amino Acid Notes and PropertiesjlngnNo ratings yet
- Proteinlipid ReviewerfinaleDocument3 pagesProteinlipid ReviewerfinaleNora GamiNo ratings yet
- Amines 3Document15 pagesAmines 3Ansh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide DDocument90 pagesNucleotide DJulie ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Lab DNAReplication Bio1Document6 pagesUnit3 Lab DNAReplication Bio1DuckyRoblox YTNo ratings yet
- Proteins: An OverviewDocument6 pagesProteins: An OverviewDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Ser Sa Thursday GG Ata CystDocument3 pagesAmino Acids: Ser Sa Thursday GG Ata CystYholzManioNo ratings yet
- CheatSheet - Amino AcidsDocument1 pageCheatSheet - Amino AcidsHermenegildo GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2: Amino Acids: M123 Biochemistry, 2 SEMESTER, 2018Document47 pagesLecture # 2: Amino Acids: M123 Biochemistry, 2 SEMESTER, 2018A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid PropertiesDocument2 pagesAmino Acid PropertiesJustine Marie AguilarNo ratings yet
- תרשיםDocument1 pageתרשיםliaorNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle Illustration AtfDocument1 pageUrea Cycle Illustration Atfkecixa7414No ratings yet
- SGL Technical Info SIGRATHERM Chemical Resistance ENDocument13 pagesSGL Technical Info SIGRATHERM Chemical Resistance ENTushar LateNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Biochemistry Free For AllDocument45 pagesAmino Acids: Biochemistry Free For AllAffan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Stereochemistry and ClassificationDocument3 pagesAmino Acid Stereochemistry and ClassificationGio RiveraNo ratings yet
- DiaSystem Scandinavia AB Reagent PerformanceDocument4 pagesDiaSystem Scandinavia AB Reagent PerformancePaulo VictorNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document10 pagesTest 3mathieulaid1No ratings yet
- Amino Acids, PeptideDocument4 pagesAmino Acids, PeptideBronnNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesAmino AcidsAlkadafeNo ratings yet
- AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES CHEMISTRY Pharm - BMLS.NURS - PHEDocument42 pagesAMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES CHEMISTRY Pharm - BMLS.NURS - PHEidokofavour2015No ratings yet
- Mutagenesis AB PAB ALAZ AHMDocument5 pagesMutagenesis AB PAB ALAZ AHMAsdada Adsad CdfdsfNo ratings yet
- LD Atellica Solution Ous Menu Oct 2019-07128017 1800000007128017Document2 pagesLD Atellica Solution Ous Menu Oct 2019-07128017 1800000007128017Xương RồngNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid FlashcardsDocument3 pagesAmino Acid Flashcardsmdsay09No ratings yet
- Amino Acid CodesDocument1 pageAmino Acid Codesmorzan ortizNo ratings yet
- MCAT Quizles AA PropertiesDocument1 pageMCAT Quizles AA PropertiesAnjali PradhanNo ratings yet
- Phytoblend TIPS LEAFLET 20060619Document2 pagesPhytoblend TIPS LEAFLET 20060619Saowalak PhonseeNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Abbreviations, Properties & Memory TricksDocument3 pagesAmino Acid Abbreviations, Properties & Memory TricksAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- LEC 03 - Amino Acids & PeptidesDocument90 pagesLEC 03 - Amino Acids & Peptideseliza makNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 CNPBDocument63 pagesUnit-3 CNPBRinkal ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of AnionsDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Anionsjanrheb delapenaNo ratings yet
- Lansoprazole 2Document1 pageLansoprazole 2Ilham AchtzehnNo ratings yet
- Lyphochek Assayed Chemistry Control: Bio-Rad LaboratoriesDocument2 pagesLyphochek Assayed Chemistry Control: Bio-Rad LaboratoriesTarunNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSE AND RELATED TESTSDocument3 pagesGLUCOSE AND RELATED TESTSAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Protein Structure and FunctionDocument91 pagesLesson 2 - Protein Structure and Functionoddish615No ratings yet
- Dimension Information MenuDocument2 pagesDimension Information MenuArchi ArcherNo ratings yet
- Characterization of P-Menthanols and P-Menthanyl Acetates: David H. DDocument7 pagesCharacterization of P-Menthanols and P-Menthanyl Acetates: David H. DРусланNo ratings yet
- 10 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENDocument62 pages10 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENanthony.johNo ratings yet
- BC Review - IDocument11 pagesBC Review - IFlorangNo ratings yet
- Edengate AMINOACIDSDocument1 pageEdengate AMINOACIDSapi-3708784No ratings yet
- Soal USM STAN 2014 Kunci JawabanDocument51 pagesSoal USM STAN 2014 Kunci JawabanAnding NdingNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesAmino AcidsJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesColor Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsMhaycelle InsertapilyedohereNo ratings yet
- 2.1 BiochemistryDocument19 pages2.1 BiochemistryPaul Darrel MenesesNo ratings yet
- Dr. H. Bambang Ermanadji, MM, AkupunkturisDocument19 pagesDr. H. Bambang Ermanadji, MM, AkupunkturisImam AzharNo ratings yet
- Codon Chart: U C A G UDocument3 pagesCodon Chart: U C A G UyesNo ratings yet
- N-Metabolism AA III 2018 HandoutDocument48 pagesN-Metabolism AA III 2018 HandoutlinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Types of ReceptorsDocument25 pagesPharmacology: Types of ReceptorsPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Juris: All-Around Pharmacist (@gapangpharma)Document9 pagesJuris: All-Around Pharmacist (@gapangpharma)Princess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Juris: All-Around Pharmacist (@gapangpharma)Document9 pagesJuris: All-Around Pharmacist (@gapangpharma)Princess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Qa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog SheeparinDocument19 pagesQa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog Sheeparinlorenjoy19No ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Types of ReceptorsDocument25 pagesPharmacology: Types of ReceptorsPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Qa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog SheeparinDocument19 pagesQa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog Sheeparinlorenjoy19No ratings yet
- Organic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationDocument25 pagesOrganic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Dispensing AnsDocument197 pagesDispensing AnsPrincess Ronsable100% (1)
- Crash Cart Check ListDocument2 pagesCrash Cart Check ListPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Answer Key-GREEN PACOP PDFDocument23 pagesClinical Pharmacy Answer Key-GREEN PACOP PDFOdy100% (3)
- Dispensing ModulesDocument14 pagesDispensing ModulesPrincess Ronsable100% (2)
- CombinepdfDocument177 pagesCombinepdfPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- WHO PharmacovigalenceDocument110 pagesWHO PharmacovigalenceWFreeNo ratings yet
- PharmacotherapyDocument15 pagesPharmacotherapyPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- CPP Modules MidtermDocument58 pagesCPP Modules MidtermPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- CPP ReportDocument1 pageCPP ReportPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Drug Discovery and Development: Lead CompoundsDocument18 pagesDrug Discovery and Development: Lead CompoundsPrincess Ronsable100% (1)
- Act3 Hospharm #1Document1 pageAct3 Hospharm #1Princess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Clinical AbbreviationDocument1 pageClinical AbbreviationPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Basic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYDocument17 pagesBasic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- DR QuizDocument9 pagesDR QuizPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- ContextDocument3 pagesContextPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- RNA ExtractionDocument2 pagesRNA ExtractionSaba IkhlaqNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - RNA Protein Synthesis BIO WORKSHEETDocument7 pagesGizmo - RNA Protein Synthesis BIO WORKSHEEThenry bhoneNo ratings yet
- Master Students Lecture 2 Transcription and TranslationDocument28 pagesMaster Students Lecture 2 Transcription and Translationha88ial88No ratings yet
- BT1010 Mid Semester Exam QnsDocument1 pageBT1010 Mid Semester Exam QnsAmar dattaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic TranscriptionDocument16 pagesEukaryotic TranscriptionKunal DuttaNo ratings yet
- Tips 11-20Document43 pagesTips 11-20Kenneth DayritNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument24 pagesIlovepdf MergedabskNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetJeff Nelson100% (2)
- Nuclear ReceptorsDocument28 pagesNuclear ReceptorsDr. Lehrasip AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationsDocument73 pagesLecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationskibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- Class XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionDocument10 pagesClass XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionMohamad Qulam Zaki100% (1)
- Dna Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDna Replication, Transcription and TranslationJenna PretalNo ratings yet
- Biomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiDocument15 pagesBiomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiKurniah TunnisaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Simulation ActivityDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Simulation ActivitySHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Slides Week 10 Classes35-38 Bio200 Win16 1Document44 pagesSlides Week 10 Classes35-38 Bio200 Win16 1api-272470922No ratings yet
- Targeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesDocument21 pagesTargeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesSabranth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shrestha Et Al. (2018) - Molecular PlantDocument13 pagesShrestha Et Al. (2018) - Molecular PlantAna Luiza Atella de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Practice McqsDocument13 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance: Practice McqsKaviya NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 XamideaDocument64 pagesChapter 6 Xamideakeren spamzNo ratings yet
- Is Junk DNA Bunk? A Critique of ENCODE: PerspectiveDocument7 pagesIs Junk DNA Bunk? A Critique of ENCODE: PerspectivemilithebillyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology I:: Introduction To The CellDocument33 pagesCell Biology I:: Introduction To The CellNaomi Berthi YonindhiNo ratings yet
- SOI2013FinalNew PDFDocument227 pagesSOI2013FinalNew PDFabhijit1729100% (2)
- Stanier Ingraham 5th EditionDocument704 pagesStanier Ingraham 5th EditionChristopher Antony Kannamthara100% (1)
- Microbiology 1.04 Basic Concepts 2 - Microbial GeneticsDocument11 pagesMicrobiology 1.04 Basic Concepts 2 - Microbial GeneticsCamila BarzagaNo ratings yet
- PHT AnswerDocument44 pagesPHT AnswerHebron OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- 2024 Human Biology ATAR Program - Unit 1 and 2Document16 pages2024 Human Biology ATAR Program - Unit 1 and 2aayesha.fatima.rajaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma and Protein StructureDocument50 pagesCentral Dogma and Protein StructureJuanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Application - 0060257852 PDFDocument297 pagesUnited States Patent Application - 0060257852 PDFMatt OusleyNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument20 pagesTranscriptionlordniklausNo ratings yet
- Types of MutationsDocument64 pagesTypes of MutationsI'm Cracked100% (1)