Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Steam Engine 1
Uploaded by
Aiman SherdilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Steam Engine 1
Uploaded by
Aiman SherdilCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # 6
“Demonstration of steam engine”
Objective:
To understand the working and controlling of steam engine.
To understand how the performance of steam engine is measured.
Literature review:
Steam engine:
It is the external combustion engine in which heat energy is converted into mechanical work.
OR
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.
Classification of Steam Engines
Based on axis of engine Orientation of cylinder axis
1. Horizontal steam engine
2. Vertical steam engine
3. Inclined steam engine
Based on speed of engine:
1. High speed engine- speed of 250rpm and above
2. Medium speed engine- speed 100 to 250 rpm
3. Slow speed engine- speed 100rpm and below
Based on type of steam action:
1. Double acting steam engine
2. Single acting steam engine
Based on type of exhaust from engine:
1. Condensing engine
2. Non-condensing engine
Based on number of cylinders:
1. Simple steam engine: one cylinder
2. Compound steam engine: more than one cylinder
Based on type of governing:
1. Throttle governed engine
2. Cut-off governed engine
Based on type of application:
1. Stationary engine
2. Moveable engine
Based on type of valve used:
1. slide valve engine
2. Corliss valve engine
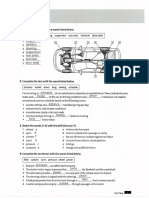
MAIN PARTS OF SIMPLE STEAM ENGINE
Cylinder:
This is the chamber in which the piston moves to and fro due to the action of steam.
Steam Chest:
This is generally cast integral with the cylinder. There are two ports called inlet port and outlet
port made in the casting for connecting the steam chest to he cylinder.
Piston:
This is made of cast iron and moves to & fro in the cylinder by the action of steam.
Piston Rings:
The function of piston rings is to prevent the leakage of steam and any wear and tear taking place
in the cylinder.
Piston Rod:
The piston rod connects the piston and cross head and is made of mild steel.
Cross head:
It connects the piston rod and connecting rod and moves between guides.
Connecting rod:
It is made of forged steel. One end of connecting rod is connected to the cross head by gudgeon
pin and other end is connected to the crank.
Crank shaft:
It is made of alloy steel. The crank shaft is main part of steam engine which serves the purpose
of converting the force applied by the connecting rod into a rotational force.
Valve:
It reciprocates over the valve seat in the steam chest by the eccentric so located on the crank
shaft relative to crank so as to admit or exhaust steam to & from the cylinder at the proper time
through the port.
Eccentric rod:
The valve rod connects the valve and the eccentric rod through a valve rod guide which prevents
the bending of the valve rod while the eccentric rod connects the valve rod and eccentric.
Governor:
The function of governor is to maintain the speed of engine fairly constant irrespective of the
load.
Main Bearings:
Generally two main bearings are provided at each end of the crank shaft to support it, the
bearings are attached to the frame.
Working of Steam Engine:
Steam from the boiler enters the steam chest and is admitted to the front end of the cylinder
by the valve slide. The high-pressure steam presses the piston backward, driving the engine
wheels around one-half turn
At the end of the piston stroke the valve shifts, allowing the expended steam to escape through
the exhaust port.
At the end of the forward stroke, the steam is released from the rear portion of the cylinder
At the same time, the valve slide begins admitting high pressure steam to the back end of the
cylinder.
This presses the piston forward, pulling the engine wheels around another half turn.
Brake power or shaft power:
The power available at crankshaft is known as brake power or shaft power
Indicated power:
The power actually obtained in piston is known as indicated power
Formula for shaft power:
P=τ×ω
=F×R×ω
=(W-T)×R×ω
=(W-T)×R×2πN60
Advantages:
1. Steam engine (or external combustion engine) could be located anywhere because water
is heated in a separate boiler to produce steam
2. A steam engine (or external combustion engine) can be used at any time because steam
can be produced at any time.
3. A steam engine (or external combustion engine) can be used to run trains for going from
one place to another.
4. A steam engine (or external combustion engine) is much more powerful than a windmill
or water-mill.
5. A steam engine (or external combustion engine) can use virtually any combustible
material for fuel-wood, coal, oil, old furniture, …anything that can be put into the
firebox.
Disadvantages:
1. A steam engine does not start at once
2. A steam engine is unsafe to use.
3. A steam engine has low efficiency
4. Giving too much pollution
***************************************************
You might also like
- Experiment-5 Aim-Apparatus UsedDocument3 pagesExperiment-5 Aim-Apparatus UsedPradyot DeoliaNo ratings yet
- Steam Engine: Presented By: P - Deepak KumarDocument46 pagesSteam Engine: Presented By: P - Deepak KumarAccount PhoneNo ratings yet
- Growth of The STEAM-ENGINEDocument76 pagesGrowth of The STEAM-ENGINENauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes ON Internal Combustion Engine: Course Code: Me 4101Document10 pagesLecture Notes ON Internal Combustion Engine: Course Code: Me 4101MahiNo ratings yet
- Introduction IC EnginesDocument8 pagesIntroduction IC EnginesSarmad Altaf Hafiz Altaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Bme NotesDocument34 pagesBme NotesAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDocument49 pagesThermodynamics Lab Reportjawad60% (5)
- English Task 6: Machine and Motors: Author: Nazhmi FadhilaDocument4 pagesEnglish Task 6: Machine and Motors: Author: Nazhmi FadhilaNazhmi FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Practical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineDocument9 pagesPractical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document35 pagesLab 1Mamoon KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Construction and Operation: External Combustion EngineDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Construction and Operation: External Combustion Enginekrishna samNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Diesel EngineDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Word - Diesel EngineprasadNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument44 pagesIC EnginesIbrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Ibrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Objective:: Power Plant Lab (Me-223L) Experiment No: 6 Title: Demonistration of Steam EngineDocument5 pagesObjective:: Power Plant Lab (Me-223L) Experiment No: 6 Title: Demonistration of Steam EngineMuhammad Nouman RashidNo ratings yet
- Prime Mover Refers To A Machine or Device That ConvertsDocument8 pagesPrime Mover Refers To A Machine or Device That ConvertsАбдельнасир АбдельрахманNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument9 pages4 Stroke Petrol EngineZahid MughalNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockMr. Jerome Nithin GladsonNo ratings yet
- Basics of EnginesDocument7 pagesBasics of EnginesMian AsimNo ratings yet
- Experiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument6 pagesExperiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineHafeez AliNo ratings yet
- Marine EngineDocument26 pagesMarine EngineNeil Stephen GuiaoNo ratings yet
- Thermo Ex.1Document10 pagesThermo Ex.1Hafeez AliNo ratings yet
- EME Notes Unit 1Document11 pagesEME Notes Unit 1SumanranuNo ratings yet
- Wankel EngineDocument15 pagesWankel EngineMuhammad Bin RiazNo ratings yet
- Turbine GuidelineDocument104 pagesTurbine GuidelineArnab Mukherjee100% (9)
- Steam EngineDocument13 pagesSteam EngineMuhammad Bin RiazNo ratings yet
- SteamDocument24 pagesSteamsanju_17No ratings yet
- PPD Pasgt Marlaw Reviewer Material For MidtermDocument6 pagesPPD Pasgt Marlaw Reviewer Material For MidtermJimmy C. Enojo Jr.No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 5 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inKanwarlal KharolNo ratings yet
- Boat Ship Fundamentals of Naval Science Marine Propulsion Systems Including Steam PDFDocument63 pagesBoat Ship Fundamentals of Naval Science Marine Propulsion Systems Including Steam PDFtoshugoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document11 pagesLab Report 3Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument49 pagesSteam EngineUsman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1Shivajee YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 12Document8 pagesLab Report 12mamoona noreenNo ratings yet
- Thermo NotesDocument18 pagesThermo NotesPavan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument3 pagesSteam TurbineErAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument19 pagesSteam TurbineMahadev KovalliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Ic EngineDocument54 pagesChapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Ic Engineavanish SinghNo ratings yet
- Wankel EngineDocument8 pagesWankel EngineMuhammad Qasim JameelNo ratings yet
- Engine Part IDocument39 pagesEngine Part Iaashish koiralaNo ratings yet
- Meg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesDocument36 pagesMeg 5-LF-37 Aux Steam TurbinesAkash KandwalNo ratings yet
- Study of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelDocument11 pagesStudy of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelFaisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Pusa Institute of Technology Industrial Visit At: WectinDocument17 pagesPusa Institute of Technology Industrial Visit At: WectinNavneet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-3: Diesel Power Plant LayoutDocument12 pagesUnit-3: Diesel Power Plant LayoutPavankumar PavankumarpvNo ratings yet
- Steam and Gas TurbineDocument28 pagesSteam and Gas TurbineMahmoud Mohammed100% (1)
- Ic Engines& Gas TurbineDocument10 pagesIc Engines& Gas TurbineBhairab BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Ci Engine Book ModifyDocument167 pagesCi Engine Book ModifyARUMUGA NAINARNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine TopicDocument66 pagesIc Engine TopicSubodh DanaoNo ratings yet
- MEC-Unit 02 NotesDocument30 pagesMEC-Unit 02 NotesNivashini VindhyaNo ratings yet
- Ee Assignment 5Document7 pagesEe Assignment 5Himanshu AryaNo ratings yet
- SME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyDocument29 pagesSME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine Terminologykishan24812No ratings yet
- Experiment 3 ThermoDocument11 pagesExperiment 3 ThermoMuneeb NaveedNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines OverviewDocument21 pagesInternal Combustion Engines OverviewRex SabersonNo ratings yet
- Vehicle EngineDocument31 pagesVehicle EnginenoahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document29 pagesLecture 2khalid mustafaNo ratings yet
- Unit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Document17 pagesUnit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 7 "Demonstration of Steam Turbine" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- L&TDocument35 pagesL&Tramesh2184No ratings yet
- Part Catalog Es22d5 Es28d5 X3engineDocument96 pagesPart Catalog Es22d5 Es28d5 X3engineSugeng Ariyadi100% (1)
- Cylinder Head Valve & Cylinder Piston MotoDocument23 pagesCylinder Head Valve & Cylinder Piston MotoDeysi CardenasNo ratings yet
- (VESPA) Manual de Taller Vespa SDocument144 pages(VESPA) Manual de Taller Vespa SBairon PeñaNo ratings yet
- 80 RT Flex Service OperationDocument102 pages80 RT Flex Service OperationEu Ursanu100% (1)
- RAV Engine ManualDocument24 pagesRAV Engine ManualIsaac Okorie zakuNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Timing - Check: Testing and AdjustingDocument5 pagesFuel Injection Timing - Check: Testing and AdjustingDiego Catari100% (3)
- 00 Hyundai XG 3.5 Dohc 2005Document81 pages00 Hyundai XG 3.5 Dohc 2005Ferran Alfonso100% (1)
- 300-Foundations & Equipment MountingDocument32 pages300-Foundations & Equipment MountingStephen KokoNo ratings yet
- 4607 17705 Rep ManualDocument46 pages4607 17705 Rep Manualjosit31415No ratings yet
- Electro Tyfon ManualDocument4 pagesElectro Tyfon ManualAmit ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Mazda CX-7 Modelo 2007Document19 pagesMazda CX-7 Modelo 2007gerber damianNo ratings yet
- Engine Gearbox Steering Suspension Rear Axles Fuel Tank Drive ShaftDocument4 pagesEngine Gearbox Steering Suspension Rear Axles Fuel Tank Drive ShaftFabio ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- Ek9.9dmh'12 Ek15dmh'12 Ek9.9jmh'12 Ek15pmh'12: (6B79) (6B89) (6B99) (6C09)Document41 pagesEk9.9dmh'12 Ek15dmh'12 Ek9.9jmh'12 Ek15pmh'12: (6B79) (6B89) (6B99) (6C09)Muhammad hardaniNo ratings yet
- Двигатель 1.4 8vDocument46 pagesДвигатель 1.4 8vAlexandr MonastirschiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Crank and RodDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 - Crank and Rodalextty75% (12)
- 1998 Seadoo Shop ManualDocument426 pages1998 Seadoo Shop Manualvudka100% (1)
- 1106D Training PresentationDocument64 pages1106D Training Presentationbagus100% (7)
- CV (Sr. QA QC Engineer)Document5 pagesCV (Sr. QA QC Engineer)mansih457100% (1)
- Doosan DX140LC-3 Excavator Parts ManualDocument778 pagesDoosan DX140LC-3 Excavator Parts ManualDjalmaNo ratings yet
- Ecotech Engine Handbook PDFDocument26 pagesEcotech Engine Handbook PDFJameel KhanNo ratings yet
- F150A FL150A: Service ManualDocument313 pagesF150A FL150A: Service Manualusaez2No ratings yet
- 4BY2-150, YanmarDocument2 pages4BY2-150, YanmarArul muuklisinNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Test DesignDocument5 pagesFatigue Test Designamir_homNo ratings yet
- Description and Operation: Engine - 2.5L Duratec-ST (VI5) - EngineDocument13 pagesDescription and Operation: Engine - 2.5L Duratec-ST (VI5) - EngineAlejandro BrionesNo ratings yet
- S70MC-C8 2 PDFDocument348 pagesS70MC-C8 2 PDFVuich ToanNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Yzf r15 v2.0.Tdf - Final.kkDocument13 pagesYamaha Yzf r15 v2.0.Tdf - Final.kkAchinKaliaNo ratings yet
- Motor Daewoo Lanos Mecanica ElectricidadDocument615 pagesMotor Daewoo Lanos Mecanica Electricidadenriqu33sNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Use ManualDocument41 pagesMechanical Use ManualthrewawayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Classifications, Termonolgy and Components PDFDocument79 pagesLecture 2 Classifications, Termonolgy and Components PDFMemo KhalidNo ratings yet