Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extension Worksheet - Option H
Uploaded by
Hellö PëachOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extension Worksheet - Option H
Uploaded by
Hellö PëachCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma
Extension worksheet – Option H
1 a Gastric juices are secreted as a result of stimuli and responses. State two stimuli that
initiate these responses. (2)
b Describe the role of each of the following in the control of digestive secretions.
i the nervous system (2)
ii the endocrine system (2)
c Explain what is meant by a ‘hormone’. (2)
d What is the main difference between an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland? (2)
e With reference to the production of ADH, explain what is meant by ‘negative feedback’.
(3)
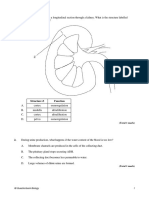
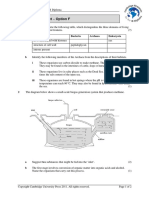
2 The diagram below shows cells of the ileum that are concerned with absorption of digested
materials.
a What is the significance of:
i the folded membrane at the top of the cells
ii the large numbers of mitochondria in the cell
iii the tight junctions between the cells?
(3)
b List three ways in which materials may be taken into these cells. (3)
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2011. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 2
Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma
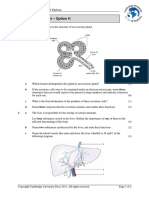
c The capillary at the bottom of the diagram receives absorbed nutrients. What larger
vessel does this capillary eventually become and what is the destination of the blood that
it carries? (2)
d Name three substances that are not absorbed by the intestine and leave the body in
faeces. (3)
3 At high altitude, a person may suffer headache, insomnia and nausea due to the low partial
pressure of oxygen in the air.
a Outline what is meant by the partial pressure of oxygen. (1)
b Several physiological changes occur after a person has spent time at high altitude. Below,
match each change in response to altitude with the approximate time for the adjustment
to occur, from the list that follows.
i increase in red blood cell production
ii increase in breathing
iii increase in capillary density
iv increased heart rate (4)
Approximate time taken for change
A several weeks
B a week
C a few minutes
D over a period of days
c Llamas, which live in the high Andes, have high blood cell counts and their red blood
cells live for far longer than those of humans. How does this adaptation help them
survive at altitude? (2)
d Llama hemoglobin collects and offloads oxygen more efficiently than human
hemoglobin. Sketch, on the same axes, the likely dissociation curves for human and
llama hemoglobin. (2)
e Why might an athlete choose to train at high altitude for an event that is held at sea level?
(2)
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2011. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Kendriya Vidyalaya SangathanDocument4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya SangathanAdi KumarNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2021-22 Class XII Term 2 Subject: BiologyDocument9 pagesPractice Questions 2021-22 Class XII Term 2 Subject: BiologySadaf RafiqNo ratings yet
- Answers For Extension Worksheet - Option HDocument2 pagesAnswers For Extension Worksheet - Option HHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Bio MCDocument9 pagesBio MCJames ChauNo ratings yet
- Biology exam questions on key topicsDocument7 pagesBiology exam questions on key topicsUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- UFP Biology for Life Sciences Exam B PRACTICE QUESTIONSDocument109 pagesUFP Biology for Life Sciences Exam B PRACTICE QUESTIONSbayigamellisaNo ratings yet
- St. Peter's Biology ExamDocument5 pagesSt. Peter's Biology ExamHasna Hena SarkerNo ratings yet
- Xi See Bio 2022 QP Set 1 Surender SharmaDocument4 pagesXi See Bio 2022 QP Set 1 Surender SharmaJoshua ZongteNo ratings yet
- Class XI Annual - 2022-23Document6 pagesClass XI Annual - 2022-23Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2023 Xe Biology WorksheetDocument5 pages2023 Xe Biology Worksheetsomeonehalp12No ratings yet
- S3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Document5 pagesS3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Zna101No ratings yet
- XI Biology Sample PapersDocument6 pagesXI Biology Sample Papersprem TNo ratings yet
- Biology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Document8 pagesBiology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Mutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- 2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQDocument180 pages2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQArthur ChoiNo ratings yet
- XI_Biology_Model Paper_24Document5 pagesXI_Biology_Model Paper_24mitrasupratik42No ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY EXAMDocument9 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY EXAMShradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology MCQ Scoring GuideDocument21 pagesAP Biology MCQ Scoring Guideghalia massoudNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response 3 QP PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination & Response 3 QP PDFJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Master Cells and Nutrition RevisionDocument3 pagesMaster Cells and Nutrition RevisionBushraNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2Document7 pages9 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2agarwalnoni5No ratings yet
- Doe. Practice SheetDocument38 pagesDoe. Practice Sheetshaikhrameez818No ratings yet
- CLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Document4 pagesCLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Lawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Scindia Kanya Vidyalaya: BIOLOGY (044) M.M.:35 Time: 90 MinutesDocument2 pagesScindia Kanya Vidyalaya: BIOLOGY (044) M.M.:35 Time: 90 Minutesrea agarwalNo ratings yet
- Bio Level 2 July 22Document4 pagesBio Level 2 July 22John GachuhiNo ratings yet
- D3.3 HomeostasisDocument5 pagesD3.3 HomeostasisParidhi BhandariNo ratings yet
- No. of Printed Pages: 4Document4 pagesNo. of Printed Pages: 4Mehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- HL Paper 2: One Greenhouse GasDocument17 pagesHL Paper 2: One Greenhouse GasIrksomeApple788 GamerNo ratings yet
- Biology Holiday PackageDocument7 pagesBiology Holiday PackagechogoNo ratings yet
- Support Worksheet - Chapter 2Document3 pagesSupport Worksheet - Chapter 2Hellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology Cells Practice TestcamNo ratings yet
- Topic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Document26 pagesTopic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Novanolo Christovori ZebuaNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 S3 AE AnswersDocument12 pages2021-2022 S3 AE AnswersEndi WongNo ratings yet
- HKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2000 BiologyDocument6 pagesHKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2000 BiologyKathy WongNo ratings yet
- Biology (2)Document2 pagesBiology (2)Swara BatheNo ratings yet
- Biology - Paper 1 - Marking SchemeDocument13 pagesBiology - Paper 1 - Marking SchemeNZURE NJOKANo ratings yet
- Bio Question 1Document9 pagesBio Question 1James ChauNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 3Rd Edition Dunford Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesNutrition For Sport and Exercise 3Rd Edition Dunford Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdaviddulcieagt6100% (9)
- Env QuestionsDocument216 pagesEnv QuestionsAnil JainNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyGlennNo ratings yet
- Suprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Document7 pagesSuprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Yumna Sa'diyyahNo ratings yet
- Aceiteika Joint Mock Examination Board 2023 Biology S.4Document11 pagesAceiteika Joint Mock Examination Board 2023 Biology S.4sharifkakooza252No ratings yet
- MB Biology MorningDocument7 pagesMB Biology MorningSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- File 2Document8 pagesFile 2angela.ok.auNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Yearly Examination 2022 - Paper 1-1-1Document17 pagesYear 11 Yearly Examination 2022 - Paper 1-1-1Hadi BeydounNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Question PapersDocument72 pagesAnalysis of Past Question PapersShamaNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Science - First Preliminary Examination - QP - Set ADocument5 pagesClass - X - Science - First Preliminary Examination - QP - Set ALaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Iveexo TQIJkr 5 J1 Z 2 SVMDocument8 pagesIveexo TQIJkr 5 J1 Z 2 SVMPreeti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Kibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 FinalDocument15 pagesKibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 Finalmins.succesorNo ratings yet
- GCSE Cell Structure & Transport Question BookletDocument14 pagesGCSE Cell Structure & Transport Question BookletMN NgọcNo ratings yet
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Document22 pages2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS XI BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesKENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS XI BIOLOGYYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 3rd Edition Dunford Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesNutrition For Sport and Exercise 3rd Edition Dunford Solutions Manualnancyruizftycjqbnip100% (32)
- Document (48)Document7 pagesDocument (48)TanuNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument5 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 11.3 KidneyDocument6 pagesHL Topic 11.3 KidneyPraveenNo ratings yet
- Teaching Ideas For Option H, Further Human Physiology: Practical ActivitiesDocument2 pagesTeaching Ideas For Option H, Further Human Physiology: Practical ActivitiesHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Support Worksheet - Option HDocument2 pagesSupport Worksheet - Option HHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology G Planning SchemeDocument2 pagesIB Biology G Planning SchemeHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Support Worksheet - Option HDocument2 pagesAnswers For Support Worksheet - Option HHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work For Option H, Further Human Physiology: Cambridge Biology For The IB DiplomaDocument2 pagesScheme of Work For Option H, Further Human Physiology: Cambridge Biology For The IB DiplomaHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology G Assess WSSDocument3 pagesIB Biology G Assess WSSHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology F Planning TIDocument2 pagesIB Biology F Planning TIHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology F Planning SchemeDocument3 pagesIB Biology F Planning SchemeHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Extension Worksheet - Option FDocument2 pagesAnswers For Extension Worksheet - Option FHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Support Worksheet - Option F: 1 A Feature Bacteria Archaea EukaryotaDocument1 pageAnswers For Support Worksheet - Option F: 1 A Feature Bacteria Archaea EukaryotaHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Extension Worksheet - Option GDocument2 pagesAnswers For Extension Worksheet - Option GHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Extension Worksheet - Option GDocument3 pagesExtension Worksheet - Option GHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology G Planning TIDocument2 pagesIB Biology G Planning TIHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Extension Worksheet - Chapter 2: 1 A B C DDocument2 pagesAnswers For Extension Worksheet - Chapter 2: 1 A B C DHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology F Assess WSSDocument2 pagesIB Biology F Assess WSSHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Support Worksheet - Option GDocument2 pagesAnswers For Support Worksheet - Option GHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Teaching Ideas For Chapter 1, Statistical Analysis: Practical ActivitiesDocument1 pageTeaching Ideas For Chapter 1, Statistical Analysis: Practical ActivitiesHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- IB Biology 1 Assess WSSDocument2 pagesIB Biology 1 Assess WSSNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- Extension Worksheet - Option F: Chlamydia, Which Is One of The Most Common Sexually Transmitted Infections in Humans, IsDocument2 pagesExtension Worksheet - Option F: Chlamydia, Which Is One of The Most Common Sexually Transmitted Infections in Humans, IsHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Support Worksheet - Chapter 1: 1 A B C D 2 A BDocument1 pageAnswers For Support Worksheet - Chapter 1: 1 A B C D 2 A BHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Exemplar Exam Question - Chapter 2, Cells: Structured QuestionsDocument2 pagesExemplar Exam Question - Chapter 2, Cells: Structured QuestionsHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work For Chapter 1, Statistical Analysis: Cambridge Biology For The IB DiplomaDocument1 pageScheme of Work For Chapter 1, Statistical Analysis: Cambridge Biology For The IB DiplomaHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Extension Worksheet - Chapter 2Document2 pagesExtension Worksheet - Chapter 2Hellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Support Worksheet - Chapter 2Document3 pagesSupport Worksheet - Chapter 2Hellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Exemplar Exam Questions - Chapter 1, Statistical AnalysisDocument1 pageExemplar Exam Questions - Chapter 1, Statistical AnalysisHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Answers For Support Worksheet - Chapter 2: 1 A B C 100 DDocument2 pagesAnswers For Support Worksheet - Chapter 2: 1 A B C 100 DHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Lean Canvas Template PDF 0isorxDocument4 pagesLean Canvas Template PDF 0isorxMJ KuhneNo ratings yet
- Evolution Introduc QnsDocument2 pagesEvolution Introduc QnsHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- PankreatitisDocument107 pagesPankreatitisIlmiah BagusNo ratings yet
- How To Use Your Symbicort Inhaler (Budesonide/formoterol) : 80mcg/4.5mcg, 160mcg/4.5 MCGDocument3 pagesHow To Use Your Symbicort Inhaler (Budesonide/formoterol) : 80mcg/4.5mcg, 160mcg/4.5 MCGDanielNo ratings yet
- Odds Ratio Calculations for Disease ExposureDocument4 pagesOdds Ratio Calculations for Disease ExposureJoshMatthewsNo ratings yet
- Smt. B. K. Shah Medical Institute & Research Centre 1st Year Post Graduate Students Record - 2015-2016Document4 pagesSmt. B. K. Shah Medical Institute & Research Centre 1st Year Post Graduate Students Record - 2015-2016TRH RECRUITMENTNo ratings yet
- Pathology REP FinalDocument15 pagesPathology REP Finalswerelloxsthe3rdNo ratings yet
- 2-Shortness of Breath by Dr.hananDocument49 pages2-Shortness of Breath by Dr.hananSoon SheedNo ratings yet
- Microanatomy of GIT 1Document64 pagesMicroanatomy of GIT 1MEHJABINHAQNo ratings yet
- DVT PreventionDocument8 pagesDVT PreventionRonald ThakorNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Surgery An Interdisciplinary ApproachDocument1,004 pagesCosmetic Surgery An Interdisciplinary ApproachDaniel FilizzolaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Video Assisted Teaching on Post-Op ExercisesDocument36 pagesEffectiveness of Video Assisted Teaching on Post-Op ExercisesGEORGE HONNALLINo ratings yet
- CDC - AV Fistula Graft Can Decannulation Observations ATDocument2 pagesCDC - AV Fistula Graft Can Decannulation Observations ATDewi Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular ProblemDocument52 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular ProblemWARREN WILLIAM PERAN100% (3)
- Transport of OxygenDocument41 pagesTransport of OxygenEsther DeepikaNo ratings yet
- O Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inDocument2 pagesO Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- SJT Practice Paper Large Print PDFDocument83 pagesSJT Practice Paper Large Print PDFRumaisha Nuha ZNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Odontogenic Cysts: ArticleDocument5 pagesPathogenesis of Odontogenic Cysts: ArticleHusnul KhatimahNo ratings yet
- Big Pharma's Worst NightmareDocument51 pagesBig Pharma's Worst NightmaredjoleNo ratings yet
- Other Amoebae - Free Living Nov 2019Document32 pagesOther Amoebae - Free Living Nov 2019Ntobi ThomasNo ratings yet
- TEACHING PLAN FOR Varicose VeinsDocument5 pagesTEACHING PLAN FOR Varicose Veinscertified_maharot_ako2828No ratings yet
- PSN Endometriosis Nov 15 SD Feb 19Document56 pagesPSN Endometriosis Nov 15 SD Feb 19lili mursidaNo ratings yet
- Virchow's TriadDocument3 pagesVirchow's TriadQuốc Vinh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Country Presentation MaldivesDocument11 pagesCountry Presentation MaldivesEndah PutriNo ratings yet
- HRCT FinalDocument156 pagesHRCT Finaldrqazi777No ratings yet
- Case Study On Acute Gastroenteritis and Acid Peptic-2Document15 pagesCase Study On Acute Gastroenteritis and Acid Peptic-2FHAMITHANo ratings yet
- Impression Techniques For Dental ImplantDocument48 pagesImpression Techniques For Dental ImplantAli AlmakramiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Parasitology Discussion on Plasmodium Species MalariaDocument29 pagesMidterm Parasitology Discussion on Plasmodium Species MalariaEran Mark RojasNo ratings yet
- Cerumen ImpactionDocument9 pagesCerumen Impactionnnennachidera2002No ratings yet
- Hervita - Depression and Anxiety Disorder Management in IndonesiaDocument30 pagesHervita - Depression and Anxiety Disorder Management in IndonesiaPrissilma TaniaNo ratings yet
- Invasive Cervical Traction Gardner Wells TongsDocument3 pagesInvasive Cervical Traction Gardner Wells TongsErvan Hartanto ErvanNo ratings yet
- TMDDocument170 pagesTMDVinaya Srinivasan100% (2)