Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modern Management Tools
Uploaded by
Johanna HolzerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modern Management Tools
Uploaded by
Johanna HolzerCopyright:
Available Formats
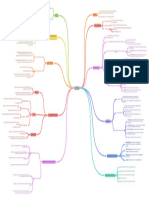
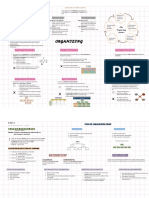
Peter F.
Drucker
management model with aim to improve
agreed on by management & employees by clearly defined objectives
performance of organization
better participation
commitment among employees basic idea: everyone has a say in goal
setting & action plans
alignment of objectives across whole
organization
breaks down the primary operational
"What gets measured gets done" important: measurement
activities of the business into five distinct
segments of the value chain
acronym for criteria to make objective
setting easier
processes relating to the supply of raw
in-bound logistics
materials or inputs
target a specific area for improvement
Specific
actual processes/undertakings that create
What exactly should be achieved?
operations product/service that has value to the
customer
at least indicator of progress
processes necessary for transferring the
When (quantify) will it be achieved? Measurable primary activities:
management by objectives outbound logistics product or delivering the service to the
SMART criteria customer
e.g. when we hit a 3% increase in X coined by George T. Doran Porter's Value Chain Analysis
processes or activities employed to deliver
Who will do it? Assignable marketing & sales
information to potential client
goal CAN be achieved with available processes employed to support product/
Realistic service
resources service following the sale
When should the goal be achieved? Time-related how the firm is organized around the value
organization of firm structure
creation process
most common: Specific, Measurable,
many different alternatives for each letter
Achievable. Relevant, Time-bound discovery, hiring, training, and managing the
HR
employment benefits of internal personnel
because of involvement motivation secondary/support activities:
technological processes necessary to
better communication technology development
support operations
advantages
better coordination acquiring the resources necessary to carry
purchasing (procurement/acquisitions)
out the operations that create value
alignment of objectives clarity of objectives
supervision of employees
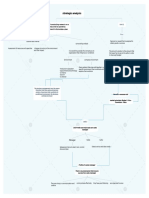
used to analyze an industry on profitability
increased pressure to perform disadvantages
position company where forces are weak
emphasis on quantity rather than quality
exploit changes in forces
used to
e.g. to neutralize supplier power, standardize
most complex instrument reshape forces in one's favour specifications for parts -> switching costs are
lower
added non-financial perf. meas. to financial
metrics ability of new competitors to enter the market
originally: performance measurement Threat of New Entry
concentration on financials only = insufficient low if incumbents seem too powerful (likely
framework
to cut prices, resources to fight back etc.)
gives managers a more balanced view of
organization strategic planning & management system relative strength of suppliers in the industry
Supplier Power
designed to improve communication & high if it's more concentrated than the
against strategic goals
monitor performance industry (e.g. Microsoft), doesn't depend on
Porter's Five Forces the industry, industry faces switching costs
used extensively to align business activities
to vision & strategy of the organization ability of customers to control product prices
developed by Kaplan & Norton Buyer Power high if negotiating leverage -> few buyers,
standardized products, few switching costs,
communicate goals/objectives able to threaten to produce a product
themselves
align day-to-day work with strategy Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
used to ability of other products/services to meet
prioritize projects/products/services wants & needs of customer base
towards strategic targets measure & monitor progress
modern Threat of Substitution
high if attractive price-performance trade-
financial
management tools off, low switching costs for buyers
ability of competitors to increase market
customer share
organization is looked at with regards to
4 perspectives high if numerous competitors (equal in size/
processes
power), slow industry growth, high exit
Competitive Rivalry
barriers, highly-committed rivals
learning/growth
What do we want to achieve? objectives can lead to price competition, especially
when products are nearly identical &
switching costs low, fixed costs are high &
"Messgröße"
marginal costs are low, product is perishable
How can we measure our progress? measures
e.g. change in total revenue
each perspective should be looked at with 4
give figures to measures aspects in mind with respect to business costs & sales
targets measures
e. g. by 3%
proceeds through multiple phases
Which action do we have to take to achieve basic idea: life cycle of a product in the
initiatives
the objective? market requires many skills, tools & processes
involves many professional disciplines
helps to develop BSC
based on biological cycle
connects strategic objectives in cause-and- diagram that describes how an organization
products have a limited life
effect relationships with each other creates value
Strategy Map
connects aspects with each other different challenges, opportunities &
3 assumptions sales pass through distinct stages
problems for seller
better overview created on one page -> graphical
products require different strategies in
different departments in the different stages
chart to analyze business units & products development
used to allocate resources sales: low starts slowly
analytical tool
brand marketing investment: very high
product management competition: low or none
used in introduction
strategic management demand has to be created
advertising: very high
portfolio analysis customers have to be prompted to product
for Boston Consulting Group (BCG) created by Bruce Henderson profit: low makes (almost) no money
units with high market share
sales: high
slow-growing industry mature market
investment: high reduced due to economics of scale
cash cows Product Lifecycle Management
generate cash in excess BCG Matrix (Growth-Share Matrix) growth competition: high a few new players
to be "milked" continuously with as little
as many as possible advertising: high public awareness increases
investment as possible stages
profit: high begins to rise
units with low market share
peaks
mature market
sales: high
dogs (pets) market saturation = reached
generate barely enough cash to maintain
"break even"
market share
production volumes increase -> costs are
investment: low
lowered
don't generate cash for company should be sold off
maturity
competition: very high
units with low market share
four types of elements
advertising: high brand differentiation emphasized
fast-growing industry
profit: high
to determine if they are worth investment to
careful analysis needed
grow market share or not question marks (problem children) sales: low
have potential to become a star and
when market growth slows down investment: low
eventually a cash cow
decline competition: low
can also degenerate into dog if market
growth declines
advertising: low
units with high market share
profit: low
fast-growing industry
stars problem: identifying features of the stages
when market growth slows & they maintain
category leadership
should be next cash cows
otherwise: become dogs
You might also like
- Tiktok Trends 2023Document16 pagesTiktok Trends 2023Magas ValdespinoNo ratings yet
- 3 Steps To 10,000 A Month in Instant Passive Income Streams (J P Clarke)Document78 pages3 Steps To 10,000 A Month in Instant Passive Income Streams (J P Clarke)LuckyNo ratings yet
- TOGAF 9.1 MetamodelDocument1 pageTOGAF 9.1 Metamodelcreamz100% (1)
- Sticky Branding Work BookDocument38 pagesSticky Branding Work BookChjk PinkNo ratings yet
- CEB IT-Building and Putting Your Business Capability Model To WorkDocument27 pagesCEB IT-Building and Putting Your Business Capability Model To WorkOleksandrNo ratings yet
- Marketing Health and WellnessDocument22 pagesMarketing Health and WellnessDexent PrinceNo ratings yet
- HR Consulting - Road - MapDocument1 pageHR Consulting - Road - MapGVS RaoNo ratings yet
- BA - Requirements.cheat Sheet UpdatedDocument2 pagesBA - Requirements.cheat Sheet Updateddorian Adonis Siri Henriquez100% (1)
- OTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationDocument45 pagesOTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationAshish PathaniaNo ratings yet
- ERP Trends Macola 021617Document1 pageERP Trends Macola 021617Tarik MudrovNo ratings yet
- LeanIX An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX enDocument1 pageLeanIX An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX enLarry LarsNo ratings yet
- Operational Plan Template. Assess 2 Part 2Document4 pagesOperational Plan Template. Assess 2 Part 2Milena Maria Sarmiento Perez100% (3)
- S4H - 730 How To Approach Remote Fit-to-Standard Workshops - CloudDocument20 pagesS4H - 730 How To Approach Remote Fit-to-Standard Workshops - Cloudbupesh kNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 Poster 2 - What Drives IT Governance PDFDocument1 pageCOBIT 5 Poster 2 - What Drives IT Governance PDFLuis MessiasNo ratings yet
- 201 Marketing ManagementDocument125 pages201 Marketing ManagementAjay KareNo ratings yet
- 1b Wheelen Hunger Strategic Management ModelDocument3 pages1b Wheelen Hunger Strategic Management ModelMuhd Farid75% (4)
- STP AssignmentDocument22 pagesSTP AssignmentSherine AhmedNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsFrom EverandHandbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsNo ratings yet
- S4H - 074 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - CloudDocument44 pagesS4H - 074 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - CloudRaymundo PiresNo ratings yet
- One Page Plan For PMO MetricsDocument1 pageOne Page Plan For PMO MetricscelogcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document1 pageLesson 4Bùi Thị Vân Anh 06No ratings yet
- (HRM-DH45ISB-1) Nguyễn Minh Thảo - Mindmap Session 9 (Performance Management) - 31191022307Document1 page(HRM-DH45ISB-1) Nguyễn Minh Thảo - Mindmap Session 9 (Performance Management) - 31191022307Ng. Minh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Performance Management SystemDocument9 pagesPerformance Management SystemAditya JhaNo ratings yet
- Bsbops502 1Document7 pagesBsbops502 1shashankthummaNo ratings yet
- Complexity ReductionDocument1 pageComplexity ReductionRASHMI RASHMINo ratings yet
- An Agile Performance ManagementDocument2 pagesAn Agile Performance ManagementadarshrNo ratings yet
- Business Process ManagementDocument4 pagesBusiness Process ManagementASA EKNo ratings yet
- The Analysis and Design of WorkDocument1 pageThe Analysis and Design of WorkPhương NgânNo ratings yet
- Research Papers.: Background and PurposeDocument13 pagesResearch Papers.: Background and Purposeneha BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Aisyah Nabihah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance Evaluation: Core CompetencyDocument2 pagesEmployee Performance Evaluation: Core Competencyjon aeliaNo ratings yet
- Análisis EstratégicoDocument1 pageAnálisis EstratégicoMarlon VelezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Charting A Company S DirectionDocument1 pageChapter 2: Charting A Company S DirectionAlma CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Charting A Company S DirectionDocument1 pageChapter 2: Charting A Company S DirectionAlma CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Za Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicDocument4 pagesZa Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicAgung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Unit 7Document7 pagesPaper 1 Unit 7Ruchi MishraNo ratings yet
- MindMap Cobit 5 Dan Audit Sistem Informa PDFDocument6 pagesMindMap Cobit 5 Dan Audit Sistem Informa PDFMoch IrwanNo ratings yet
- Waode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Document4 pagesWaode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Sri SardiyantiNo ratings yet
- No Nama Peneliti Tahun Judul Variabel Penelitian Obyek Penelitian Hasil PenelitianDocument17 pagesNo Nama Peneliti Tahun Judul Variabel Penelitian Obyek Penelitian Hasil PenelitianNurul NurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Internal Control: Relationship Among ProcessDocument1 pageInternal Control: Relationship Among ProcessVânAnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: People CMM Level 2 Process AreaDocument7 pagesPerformance Management: People CMM Level 2 Process Areaapi-3754364No ratings yet
- Description: Tags: FSASA-2BTIGVisionFramework 200608Document1 pageDescription: Tags: FSASA-2BTIGVisionFramework 200608anon-693594No ratings yet
- Strategic Planning of Socio-Economic Development of Service EnterprisesDocument4 pagesStrategic Planning of Socio-Economic Development of Service EnterprisesCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Cpoo JDDocument4 pagesCpoo JDcasanjaykumarsahNo ratings yet
- Aps Level and Executive Level ClassificationsDocument7 pagesAps Level and Executive Level ClassificationsCJ SNo ratings yet
- 105 165903 HFX2023Roles3Document2 pages105 165903 HFX2023Roles3sujoyNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document24 pagesSession 2vighneshsitaraman2000No ratings yet
- MNT 095 PEP InsertDocument84 pagesMNT 095 PEP InsertWaelNo ratings yet
- Activity Catalog TemplateDocument1 pageActivity Catalog TemplaterhNo ratings yet
- EPC In: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEPC In: Cheat SheetPiotr SenkusNo ratings yet
- BB 50Document6 pagesBB 50Gerson Antonio MocelimNo ratings yet
- Management Process Jean Lea M. AdoremosDocument13 pagesManagement Process Jean Lea M. Adoremosblessed joy silvaNo ratings yet
- Management Process: Jean Lea M. AdoremosDocument13 pagesManagement Process: Jean Lea M. Adoremosblessed joy silvaNo ratings yet
- ManagementDocument3 pagesManagementBhie JaneeNo ratings yet
- Success and Failure of ERPDocument3 pagesSuccess and Failure of ERPmohammed adhilNo ratings yet
- Airtel TargetsandEvaluationDocument2 pagesAirtel TargetsandEvaluationRashi VajaniNo ratings yet
- Erp Implementation Life CycleDocument24 pagesErp Implementation Life CycleSULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Chapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and ProgrammingDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Chapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and ProgrammingNavneet NandaNo ratings yet
- Action Plan HRMDocument2 pagesAction Plan HRMCristelle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- ICAB Lecture 1 & 2 On Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Costing - RCKDocument10 pagesICAB Lecture 1 & 2 On Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Costing - RCKrajeshaisdu009No ratings yet
- Business Plan: Competitor AnalysisDocument1 pageBusiness Plan: Competitor AnalysisAJ AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Article 4th PDFDocument1 pageArticle 4th PDFLe Nguyen SophieNo ratings yet
- Work Study and MeasurementDocument1 pageWork Study and Measurementkrisha mae piamonteNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?Document20 pagesInformation Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?hadouiriNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic Managementayushi gargNo ratings yet
- MD BGMT 110 Learning Activity 1 2Document1 pageMD BGMT 110 Learning Activity 1 2CharlotteNo ratings yet
- Controversial Ads-Ethical AdsDocument17 pagesControversial Ads-Ethical AdsAntonella ConvertinoNo ratings yet
- Proiect MarketingDocument1 pageProiect MarketingMihnea NiculescuNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - Jigyasa AroraDocument1 pageCover Letter - Jigyasa Arorajigyasa aroraNo ratings yet
- Log 2Document107 pagesLog 2KHIEM HUOL GIANo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram Infographic 03Document8 pagesVenn Diagram Infographic 03Hector Tomas Reyes CumpaNo ratings yet
- B2B Markets and CRM NDocument252 pagesB2B Markets and CRM NInfotech Edge100% (1)
- Chapter - 4 Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsDocument19 pagesChapter - 4 Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsAheint MyetNo ratings yet
- References PMKDocument3 pagesReferences PMKhjNo ratings yet
- ML Inter - Text Bank Reading (12 Units) - pp.113-160Document48 pagesML Inter - Text Bank Reading (12 Units) - pp.113-160Hìnn HoànggNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Essay: Traditional Media and Social Media (UCSP)Document2 pagesCompare and Contrast Essay: Traditional Media and Social Media (UCSP)jc nerNo ratings yet
- Lauren Harris Resume (2014.10)Document1 pageLauren Harris Resume (2014.10)LaurenHarris84No ratings yet
- Advertising BlackbookDocument56 pagesAdvertising BlackbookLeena KNo ratings yet
- Sop Durian - RizqiCipta - 325Document5 pagesSop Durian - RizqiCipta - 325RizqiCiptaAnugrahNo ratings yet
- Franchise Business ModelDocument8 pagesFranchise Business Modelmuskaangarg12345No ratings yet
- Business Idea, Business Plan and EnterpriseDocument36 pagesBusiness Idea, Business Plan and EnterpriseJohnny Come Lately100% (1)
- Actividad 4 - Admin IIDocument3 pagesActividad 4 - Admin IIRicardo Javier Marulanda ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Product Management Chap. 1Document11 pagesProduct Management Chap. 1Sean CataliaNo ratings yet
- Deepanshu Negi - 21mba2993 - MKT-4 - Imc.Document6 pagesDeepanshu Negi - 21mba2993 - MKT-4 - Imc.Shubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Affiliate MarketingDocument9 pagesAffiliate Marketingj2d8jgrhkfNo ratings yet
- Product Marketing Manager ResumeDocument6 pagesProduct Marketing Manager Resumenemyzyvudut3100% (2)
- Marketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsDocument2 pagesMarketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsAyush MundNo ratings yet
- Problem Faced by Amway in BriefDocument9 pagesProblem Faced by Amway in BriefDebabrata Sahana0% (1)
- Advert Is NGDocument21 pagesAdvert Is NGCharlesNo ratings yet