Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Null 2
Uploaded by
JB MangunduOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Null 2
Uploaded by
JB MangunduCopyright:
Available Formats
H.M.
MULONDA
Page | 1
TEACHERS’ GUIDING NOTES FOR LEARNERS
ELEMENTARY AGRICULTURE
GRADE 7
REVISED CURRICULUM
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
This handout is not an official textbook, but the summarised notes based on
100% syllabus coverage of the revised curriculum of the Grade 7 Elementary
Agriculture 2015. Therefore the handout should be used together with other
necessary resources at your disposal. In other words they should be viewed
Page | 2
as a complementary source of information to ensure effective teaching and
learning in our lessons.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
THEME: 1 GENERAL AGRICULTURE
TOPIC 1: THE ROLE OF AGRICULTURE IN NAMIBIA.
Page | 3
1. The definition of Agriculture.
Involves cultivation of land and keeping or raising of animals
2. The role of agriculture in Namibia
it provides food for people and animals.
It provides jobs and income
It Provides raw materials
3. Why agriculture is seen as provider of work opportunities in Namibia.
The Majority of our people depend on agricultural related activities.
Large numbers of people earn a living as farm worker.
Creation of jobs along the processing chain, from the farm to the product.
Commercial farming occupies about 44% of our land.
4. Examples of jobs in Agriculture
Farm manager
Engineers
Teacher
Laboratory technicians
Farm land
Store manager
Picker or processor
Sales person
5. Proportion of the local population who are directly and indirectly depend
on agriculture for survival.
a. People who directly depend on agriculture.
Driver of machines on farm.
Cattle headers
Gardeners
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
b. People who depends indirectly on agriculture
They are people who do not live on the farm and are not paid a salary by
farmers.
Teachers
Page | 4
Small enterprises in town.
Agricultural extension officers
Veterinary officers
6. Possible business opportunities based on different agricultural
products or activities.
Butcheries
Sugar refineries
Cotton processing
Mahangu or Maize Milling
Cooking oil processing
TOPIC 2: CONSERVATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
1. Poor or Wrong agricultural practices
Monoculture
Over cropping
Overstocking
Overgrazing
Ploughing down the slope or up the slope
Indiscriminating cutting down trees
2. The danger of wrong agricultural practices on the soil and land.
Monoculture increases the population of pests on land. And soil
becomes less fertile.
Soil erosion caused by overstocking.
Deforestation removes plant cover and the soil is easily eroded.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
3. Soil erosion Note: in the syllabus but very important
a. Causes of soil erosion
Overstocking
Cutting down trees
Page | 5
Overgrazing burning of grass
b. Consequences of soil erosion
Siltation
Desertification
Formation of gullies
High cost of growing crops
4. Suggest ways of preventing wrong farming practices from lowering the
productivity of the soil.
Early planting
Crop rotation
Reforestation
Terracing
Use organic matter
Optimum plant growth
Strip cropping
Avoid bush burning
Avoid overstocking
Avoid overgrazing
GLOSSARY
1. Conservation: the preservation and protecting of our limited natural
resources.
2. Crop Rotation: the planting different crops on the same land each year.
3. Deforestation: the cutting down of trees faster than they can be replaces or
regrows.
4. Monoculture: The planting of the same crop on the same land repeatedly.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
5. Mulching: the covering of the soil with materials such as decaying leaves or
compost to increase soil fertility.
6. Organic fertilisers: refers to compost manure and animal dropping.
7. Overgrazing: allowing livestock to feed on grassland so heavily that the
Page | 6
vegetation is damaged and the soil becomes exposed to erosion.
8. Soil erosion: the removal of top soil by wind or water.
9. Strip cropping: a method of reducing soil erosion
TOPIC 3 HIV AND AT THE WORK PLACE
1. Safety measures applied by local farmers to mitigate the impact of HIV
and AIDS at work places.
Hold regular HIV and AIDS awareness programmes
Encourage voluntary testing
Provide counselling and other forms of social support
Promote safe sex.
2. Actions that local government can take to reduce the spread of HIV and
AIDS.
Awareness campaigns
Encourage citizens to go for voluntary testing.
Provide free condoms for people.
Provide milk to infected mothers so that they do not breast feed their
children.
3. Effects of HIV and AIDS on a family’s Agricultural production.
Reduction in food production.
Loss of income
Loss of skills and knowledge.
4. Problems encountered by local farmers trying to reduce the spread of
HIV and AIDS.
Lack of funding.
Cultural practices
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Resistance to change
Stigma
Page | 7
THEME: 2 PLANT PRODUCTIONS
2.1. GROWING PLANTS FOR DECORATION
a. The importance of growing decorative plants within the school ground.
For beauty
For shelter
For food
For medicine
For financial reasons
To control dust around the area.
b. Different types of decorative plants suitable for their area and
surroundings.
Climbers
Grass /lawn
Rose
Aloe
Fen
Asparagus
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
2.2. PREPARING AND CARING OF DECORATIVE PLANTS.
a. Tools to be used in planting trees, shrubs, and flowers.
Tools Functions
Spade Used for digging
Page | 8
Hoe Cultivating between the rows when weeding
Rake Levelling the soil
Garden line Make a straight line furrow for planting seeds.
Watering can Watering small plants
Fork Break up hard clods
Garden trowel Transplanting small seedlings
Wheelbarrow To transport flowers and manure
b. Determining the best method of preparing seedbeds for planting
different trees, shrubs, and flowers.
Choose area with arable soil.
Mark out the size of the piece of land where the seed bed will be
prepared.
Dig the soil over in this area, using spade and fork.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Apply manure or compost into the soil.
Mix the manure or fertiliser into the soil.
Rake of any stones or plants residue.
Water the seed bed.
Page | 9
c. Alternative medium for growing smaller plants such as containers in
the absence of suitable soil or space.
Growing medium: are temporal places where seeds are planted or sown to
germinate before they are moved to a permanent growing.
Some examples of growing media
Flower pot Seed box Seed tray •Coconut fibres •Old tires
2.3. PLANTING AND CARING OF DECORATIVE PLANTS.
a. Plants and flowers growing in their regions at different seasons
Common name Description Region found
Aloe, Orange red flowers; thick, Waxy leaves; Etosha and Kalkveld
succulent
Quiver tree Smooth yellowish back; yellow flowers; Namib and southern
attracting birds and bees; Succulent.
Bottle tree Thick stem; large white flowers, poisonous Kunene , Erongo
Euphorbia tree Short twisted stem; leafless, Thony Erongo, Kunene
branches
Hoodia/ Xhoba Leafless, spiny plant, succulent stem, red Namib and Kalahari
flowers, which smell very bad. desert
African Moringa Succulent stem, bottle-shaped main trunk. Northern and central
tree regions
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
b. Different types of flowers such as annuals, biennials and perennials
Types of decorative flowers.
Annuals-live foe one year .e.g. daisy
Biennials-live foe two seasons. .e.g. farsley
Page | 10
Perennials-live for many seasons e.g. Aloe
c. The two categories of decorative plant
Flowering plants: plants with flowers.
Rose
Aloe
Non-flowering plants: plants that do not flower.
Fern
Asparagus
d. Classification of decorative plants.
Life span
Plant body
Growth habit
e. Ways of collecting seeds
Hand-pick seeds and put them into envelopes or small container
labelled with name of the plant and the date collected.
Shake branches that carry the seed heads and put them into a cloth or
envelopes.
Cut the seeds heads using secateurs and put them into container.
Some seeds can be hand-picked from the ground although its not
advisable.
f. Ways of sowing plant seeds and seedling using different mediums such
as seedbeds, trays and boxes.
Sowing is process of placing seeds in the soil.
o Seedbed; Seeds can be sown directly in the seedbed and then
receives special attention by giving compost, controlling pest, diseases
and watering every day so that strong, healthy seedlings can be grown.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
o Seed boxes: can be made of wood or plastic. They must have holes in
the bottom for water to drain out. Put soil and manure in the box and
water. Then sow the seeds followed giving special attention.
Page | 11
o Seed trays: seed trays are made of plastic. Each one is divided into
6,12 or more compartments. Two seeds can be sown in each
compartment. The seedlings that develop can be thinned out later.
2.4 BASIC STRUCTURES OF PLANTS
a. Basic structures of trees, shrubs and flowers
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Parts of plants Functions
Roots Absorb water
Anchor the plant
To transport water and nutrients
Page | 12
To store nutrients
Stem/trunk To give shape/ support and strength
Branches Transport nutrients and support
Leaves For photosynthesis (make food)
Flowers For pollination ( reproduction )
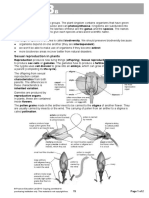
b. Sketched and labelled different parts of the flowers.
2.5. PLANT REQUIREMENTS FOR GROWTH.
a. The need of watering plants.
Caring nutrients to every part of the plant.
For photosynthesis in plants.
Supporting the structure of the plant.
Cooling the plants.
b. Costs involved in watering plants
Water bills: we must have money to pay for water we use.
Power: we must have power to pump water.e.g diesel.
Labour: farm workers must be paid for watering of plants.
Maintenance cost
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
c. Sources of water.
Rainwater.
Underground water
Municipal water
Page | 13
Water from the river
d. Sources and needs of plant nutrients such as organic and inorganic
sources.
Macro-Elements:--the major elements.
Micro-Elements-- minor or trace elements
Macro-Elements ( Inorganic fertilisers) Micro-Elements (Organic fertilisers)
Nitrogen (N) Iron
Phosphorus (P) Boron
Potassium (k) Manganese
Calcium (Ca) Magnesium
Sulphur
Copper
Zinc
Organic fertiliser:: comes from natural sources (animals and plants), for example,
kitchen waste, compost and manure from animals
Advantages of organic fertilisers
Helping soil to hold water better.
Improving drainage.
Allows heavy soils to contain more air.
Improves soil structure.
Long term soil fertility
Disadvantages of organic fertilisers
Does not contain all or more nutrients.
Nutrients are not available immediately or they do not work faster.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Inorganic sources: they are plant nutrients, which are man-made chemical made
from factories.
Advantages of inorganic fertiliser s
Contains more nutrients than organic fertilisers.
Page | 14
They work faster than organic fertilisers.
Disadvantages of inorganic fertilisers.
Short term soil fertility
Does not improve soil structures.
Water does not hold.
2.6. PLANT REPRODCUTION
a. Distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction in plant.
Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction
Involves two sex cells and fertilisations Does not involve any sex cells and fertilisation.
Only one parent involved
Offspring are not genetically identical. Offspring are genetically identical.
There is variation the offspring. There is no variation.
They are able to adapt to their Does not need a partner.
surrounding and evolve. Saves time.
Very quick bacteria can produce an offspring in
few minutes.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Page | 15
2.7. PLANT DIEASES AND PESTS
a. Common plant diseases.
Leaf blight
Brown rust
Down mildew
Mosaic
Damping off
Plant disease Examples of each disease Symptoms of each disease
Bacterial Black rot, black leg, bacterial Appear leaf spots,
Caused by bacteria canker, bacterial soft, bacterial wilt, Cankers
bacterial blight, bacterial speck. Scabs or wilt
Fungal Damping off, white blister, white Fruiting bodies on affected parts
Caused by fungi rust, powdery mildew, downy Birds-eye spot
mildew, club root, Pythium. Damping off of seedlings
Yellow leaves
Viral Crinkled and curled leaves, Yellow Crinkled and curled leaves
Caused by viruses leaves, reduced and stunted plant Yellow leaves
growth, mosaic leaf patterns. Reduced and stunted plant
growth
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
b. Common pests that attack flowers and garden plants..
Cutworms
CMR beetles
Aphids
Page | 16
Bagrada stink bugs
Cabbage caterpillars
Nematodes
Thrips
Spider mites.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
c. Ways to control plant diseases and pest.
Use resistant varieties of plants.
Treating seed
Spray infected plants Page | 17
Hand-picking big insects
Use other animals to feed on other insects e.g. chickens
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) which include the use good hygiene, use
of good cultural practises etc.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
THEME: 3 ANIMAL PRODUCTIONS
3.2 SHEEP AND GOATS
3.2.1. TYPES OF SHEEP/ GOATS Page | 18
a. Pictures of types of goats/Sheep.
…
Angora Goat Boer Goat Saanen goat
Pictures of types of Sheep. …
Merino Doper Karakul sheep Damara ram
Van Rooy sheep
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Types of sheep Types of goats
Merino sheep Boer goat
Dorper sheep Angora goat
Karakul sheep Saanen goat
Page | 19
Damara ram
Van Rooy sheep
NB: This can be given to learners as Practical Investigation: have learners collect
pictures or draw pictures of types of goats/sheep on a poster and bring to class.
b. Products obtained from different breeds of sheep/goats on pictures.
Sheep Goats
Wool Daily products (Milk)
Pelt Mutton
Mutton Mohair
3.2.2. FEEDING SHEEP/GOATS.
a. Why sheep/goat need food.
For growth
To produce or to be productive
To reproduce
To stay healthy
b. Different types of feed required by sheep/goats.
Ground Lucerne hay
Maize cobs
Grass hay
Lick block
Dry veld concentrate lick
Phosphate lick mixed with salt
Clean drinking water every day
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
3.2.3. DISEASES AND PESTS (PARASITE)
a. Common diseases and Pests that attack sheep/goat.
Diseases
Causes of diseases Examples of Diseases that attack goats/sheep Page | 20
Fungi Anthrax
Bacteria Foot and mouth
Bacterium Pulpy kidney disease
Symptoms of Anthrax Symptoms of Foot and Mouth disease
High fever Lameness
Sudden dearth Salivation & foaming at the mouth
Blisters on the feet
PARASITE
Parasite: an animal that gets its food by living on or inside another animal.
Internal parasite: a parasite that lives inside the body of another animal. .
External parasite: a parasite that lives outside of the body of another animal
Internal Parasite External parasite
Round worms Tick
Liver flukes Flea
Tape worms Lice
Mites
Some of the external parasites.
Lice Flea Tick Red Spider
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Some of the internal parasites
Page | 21
b. Signs of an animal that has been affected by diseases and pests
(parasite).
High body fever: sheep and goats have a normal body temperature of 39,4◦c
Unusual behaviour: listless or overactive, unsteady gait, nervousness or
lameness.
Dull eyes: The animal’s eyes are not bright and alert.
Unhealthy looking coat: the animal coat is dull and may have bare patches
Poor appetite: animal does not want to eat.
3.2.4. HANDLING OF SHEEP/GOATS.
a. Identify the external parts of the animal body.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
b. Procedure of handling animals during.
Dosing: is the application of a liquid via the mouth into the digestive system of an
animal: to dose the animal one person must squeeze the standing animal between
his or her legs and use his hands to lift the animal’s head. The second person must
Page | 22
put the nozzle of the dosing gun into the side of the animal’s mouth next to the
throat. Then dosing gun is trigger is pressed to release the required dosage.
Vaccination: is the injection of a vaccine under an animal skin. To vaccinate the
animal, one person must squeeze his or her legs and use his or her hands to hold
the head still. The person with the syringe pulls the loose neck skin away from the
neck and at the same time insert the needle at 45◦.
Marking: involves applying the farmer’s unique identification mark to an animal. The
animal is held in the same way as described under dosing and vaccination.
Castration: is removing the testes or cutting the vas deferens to prevent undesirable
mating. Place it on a table in a sitting position with its back pushed against his or her
stomach. Hold the front legs with one hand and the hind legs with the other hand.
Shearing: is the removal of wool by using sheep shears or electric clippers. The
animal is held in a sitting position between the two legs to shear the belly. It is then
laid on its sides to shear the flanks.
3.2.5. Marketing of sheep/goats.
a. Ways of marketing sheep/goats in their regions in the form of meat or live
animals.
Selling directly to interested buyers.
Taking the animals to the nearest auction on auction day.
Selling animals directly to an abattoir or a butcher.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
b. How quality of animal products influences the sales price and profit of
products.
The age of the animal customers will be willing to pay higher prices for meat from
animals with young age than with old age because meat is tenderer and less fatty.
Page | 23
The size of the animal: determine the total price. The bigger the animal, the higher
the price it will fetch.
The condition of the animal (fat or over fattened/ lean) Most consumers prefer
meat with less fat and more meat.
Healthy of the animal: disease animals receive higher prices than animals infected
with micro-organisms or parasites.
3.3 FISH FARMING IN NAMIBIA
3.3.1 TYPES OF FISH FOUND IN NAMIBIA
a. Relate the different types of fresh water and salt water fish.
Fresh fish: live only in fresh water such as inland dams, ponds, rivers and they
cannot survive in salty seawater.
Salt water fish: refers to fish that only lives or survive in salty seawater.
b. Recognise and obtain pictures and samples of fish found in fresh water
and in salt water.
EXAMPLES OF FRESH WATER FISH
.
Cat fish Tilapia Tiger fish
Carp fish Rainbow trout Large mouth bass
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
EXAMPLES OF SALT WATER FISH
Page | 24
Pilchard Red snapper fish Tuna fish
King mackerel Angel fish Crayfish
Hake Snoek Alfonsino fish
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
3.3.2 EXTERNAL PARTS OF THE FISH.
a. Sketch / diagram of the fish and its different external parts
Page | 25
b. Explain the functions of different parts of the fish.
Part of Fish Function
Eyes To see clearly.
Nostrils Smelling.
Lateral line To detect movement of water.
Mouth Taking food and breathing.
Gill cover To protect the gill slit.
Dorsal fin It helps the fish to stay upright in the water.
Scales Protects the body of the fish
Tail fin It helps the fish to swim .
Pectoral fins To steer and balance the fish.
Pelvic fins Also used to steer and balance the fish.
Ventral fin It helps the fish to
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
3.3.3 FEEDING OF FISH.
a. Reasons for feeding fish.
Growth,
Production
Page | 26
Reproduction
b. Discuss how floating or sinking pellets can feed fish.
Dry feeding: Dried pellets can be scattered on the surface of the water
and fish will eat them from surface.
Wet feeding: The pellets can also be soaked in water before feeding
and when they are scattered onto the water they will sink because they
are heavy.
c. Find pictures or samples of different kinds of fish feed e.g. bread
crumbs, fish meal, oats, and pellets.
3.3.4 DISEASES, PARASITES AND PREDATORS.
a. Types of parasites that affect fish.
Fish lice.
Tape worm.
Anchor worm.
Gill flukes
Flat worm
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Page | 27
b. Types of diseases that affect fish.
Gill rot
Furunculosis
Fin rot
Fungus
c. Common signs of fish infected with a diseases
Gasping for air on the surface
Rubbing the body
Ragged fins, and fish not feeding
Sores on the body
d. Different predators that can destroy eggs, small and large fish.
Birds.
Frogs.
Snakes.
Turtles (tortoise)
Crocodiles
People
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Page | 28
Turtles (tortoise) Frog Snake
Crocodile Fish Eagle People
e. Ways of preventing and controlling diseases and parasites.
Using chemicals such as formalin, acra Flavin, and potassium
permanganate.
Including regular cleaning
Keep fish of the same age in the pods.
Keep compatible breeds of fish in the same pond.
f. Methods of controlling predators.
Cover the pond with wire netting against birds.
Put up a strong fence around the pond to keep out crocodiles.
Use flashlight and net at night to catch predators.
Kill all the predators when the pond is drained once or twice a
year.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
3.3.5 HANDLING OF FISH.
a. Ways of catching fish with a small net and put the fish being
caught in a separate bowl of water.
Put the net into the water and approach the fish slowly.
Page | 29
When the fish is half way in the net scoop the fish into the net
with a quick upwards movement
Fish can also be caught by pressing the net against the side of
the container, trapping the fish.
Pull the net slowly upwards out of the water.
Put the container slowly and gently in the other pond and allow
the fish to swim out by themselves.
b. Methods to be followed in cleaning the aquarium.
Remove the fish, handling them correctly and put them
temporally in a bucket filled with clean water.
Hold the fish properly.
Empty the aquarium, removing stones and shells and any other
decorations.
Scrub the sides9 walls) and the bottom of the aquarium with a
brush to remove all the green algae.
After cleaning, refill the aquarium with fresh, clean water. Or add
lime to neutralize water.
Finally, replace the making sure the temperature of the
aquarium water is the same as the water in the bucket.
3.3.6 HARVESTING, PRESERVATION AND MARKETING OF FISH.
a. Suggest ways of harvesting fish.
Draining of water.
Basket traps.
Fishing nets.
Hook and line.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Page | 30
Fishing nets Hand Net Hook and line. Basket traps
b. Evaluate different ways of preserving fish.
Sun drying.
Salting.
Smoking
Cooking.
Canning.
Chilling or refrigerating.
Salting Chilling, refrigerating Canning
Sun drying Smoking Freezing
c. Suggest ways of marketing fish.
Creating a direct marketing campaign by target your local community by using
also your friends and family become effective marketing tools for your fish.
Make sure that your fish is fresh.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
Make sure that your fish is clean.
Make sure that your fish is affordable to your customers.
The place where you plan to sell must be clean.
Selling directly to consumers.
Page | 31
Selling to open markets.
Selling to restaurants in your areas.
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
THEME 4: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
2.5 PRODUCTION DECISIONS
Page | 32
a. Estimate possible number of customers to purchase specific agricultural
products
As a farmer find out as much as possible about consumers who may buy
your product(s) by asking the following questions.
What products are your potential consumers buying?
Where are they buying, and when are these products available?
Who are the consumers of your produce and where do these
consumers live?
How many people live within your marketing area?
What are they currently buying related to what you are producing?
How much of the product(s) do your potential customers currently
use?
What prices are consumers paying for high-quality products?
Are consumers adequately served at present?
b. Deduce how knowing the customers’ needs may influence decisions on
agricultural production.
Understanding your customers will help you to:
Helps you to decide on the best price to set your products or goods.
Helps builds relationships with your customers
Helps increase your sales and profit.
Helps decrease the costs of attracting new customers.
Helps you to improve customer service.
Helps you predict what they will buy, and estimate how much stock you
need.
END OF NOTES
Elementary Agriculture Senior Primary Phase Grade 7 Notes
Compiled by Mr Hector M Mulonda (TEACHER) 2019 KAVANGO WEST REGION
You might also like
- From Seed to Harvest : Expert Insights into Gardening TechniquesFrom EverandFrom Seed to Harvest : Expert Insights into Gardening TechniquesNo ratings yet
- 2 Agriculture PDFDocument25 pages2 Agriculture PDFRamjeeNagarajanNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 (Basic Concepts in Agri. Crops Production)Document5 pagesActivity No. 1 (Basic Concepts in Agri. Crops Production)Alan BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Ag AgDocument13 pagesAg AgJP MishraNo ratings yet
- Agri Fishery Art 2Document5 pagesAgri Fishery Art 2Angel Rose AnongNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: I. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesAgriculture: I. Answer The Following QuestionsTulshiram NerkarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For AgricultureDocument26 pagesQuestion Bank For Agriculturepatel_monil0% (1)
- Conservation Agriculture CF Handbook For Hoe Farmers Zambia PDFDocument60 pagesConservation Agriculture CF Handbook For Hoe Farmers Zambia PDFPaquissaNo ratings yet
- Crop Production PracticesDocument15 pagesCrop Production PracticesJocelyn Dacillo LozañesNo ratings yet
- 8 - Geog - L-4 AgricultureDocument3 pages8 - Geog - L-4 AgricultureAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Ch22-From Field To Plate - Notebook WorkDocument3 pagesCh22-From Field To Plate - Notebook WorkanikaNo ratings yet
- Notes Geo CH 4 AgricultureDocument8 pagesNotes Geo CH 4 AgricultureDipti GargNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Lesson 3 Nature of FarmingDocument12 pagesModule1 - Lesson 3 Nature of FarmingRowel Arangis PeñoraNo ratings yet
- Conservation Agriculture CF Handbook For Hoe Farmers ZambiaDocument60 pagesConservation Agriculture CF Handbook For Hoe Farmers ZambiaZoran H. VukchichNo ratings yet
- 400 Must Have Words For TOEFLDocument4 pages400 Must Have Words For TOEFLMichelle CillieNo ratings yet
- Ag Eng 311: Banana (Document19 pagesAg Eng 311: Banana (Rocelyn NaborNo ratings yet
- TLE6AG0a-1 - 2023-2024 - Day 3Document3 pagesTLE6AG0a-1 - 2023-2024 - Day 3Ma. Feliza SaliganNo ratings yet
- STD 8-Ch 1 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSTD 8-Ch 1 Lesson PlanHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Abe 165 Module 1Document14 pagesAbe 165 Module 1Michael Christian TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 (Agriculture) Ncert Q/A: 1. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter - 4 (Agriculture) Ncert Q/A: 1. Multiple Choice QuestionsVipul BullaNo ratings yet
- Agri MS 2012Document19 pagesAgri MS 2012Andrew ArahaNo ratings yet
- Tle Afa Org Agriculture9 Las2 (Checked by Sir Leo)Document10 pagesTle Afa Org Agriculture9 Las2 (Checked by Sir Leo)Yves Kim Casido CabantingNo ratings yet
- Cultural Management PracticesDocument13 pagesCultural Management PracticesFebz Canutab67% (12)
- Agriculture NotesDocument1 pageAgriculture Noteshetv031013No ratings yet
- E Agri Covid Booklet 7Document6 pagesE Agri Covid Booklet 7Ndapa ShoneNo ratings yet
- Yhrl Yieshua Igdalino - 11 Andromeda - EarthScience (q1-m11)Document5 pagesYhrl Yieshua Igdalino - 11 Andromeda - EarthScience (q1-m11)Yhrl Yieshua IgdalinoNo ratings yet
- Soal ToeflDocument4 pagesSoal ToeflStovany Ayu ValentineNo ratings yet
- Soil ScienceDocument7 pagesSoil ScienceNeil Jhon TampipiNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 Quarter 2Document29 pagesTle 6 Quarter 2Joseph Corales100% (3)
- Lesson 4 CULTURAL PRACTICES IN CROP OPERATION AT101Document6 pagesLesson 4 CULTURAL PRACTICES IN CROP OPERATION AT101Gerardo AgunatNo ratings yet
- 4.SS 3 Lesson 16Document10 pages4.SS 3 Lesson 16lisahane20No ratings yet
- Social Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture - Learn CBSEDocument15 pagesSocial Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture - Learn CBSESHARANYA SAHANo ratings yet
- Geography Notes 2059/2: O Level O LevelDocument61 pagesGeography Notes 2059/2: O Level O LevelFatima DanishNo ratings yet
- A Exercise 8Document7 pagesA Exercise 8Khent TermoorNo ratings yet
- 11 Keys To Successful Maize ProductionDocument2 pages11 Keys To Successful Maize ProductionMwai Esther100% (1)
- LP 9-10 TLE Lesson 2Document3 pagesLP 9-10 TLE Lesson 2Jan - Brian AsioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingDocument6 pagesChapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument14 pagesGeographyPranav (GRADE IX)No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Waste Generation and ManagementDocument6 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Waste Generation and ManagementLeanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AGR 101 Fundamentals of AgronomyDocument68 pagesAGR 101 Fundamentals of Agronomyjanani queenNo ratings yet
- Cause of Low Productivity of Irish PotatoesDocument16 pagesCause of Low Productivity of Irish PotatoesDennis Onchieku OnyandoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Earth ScienceDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Earth ScienceCian TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Agriculture AssignmentDocument13 pagesAgriculture AssignmentRisa BeharryNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Sustainable Agricultureduc 264Document26 pagesConventional and Sustainable Agricultureduc 264Rizza Donna Gulpan100% (1)
- Problems in My CommunityDocument2 pagesProblems in My CommunityAldrich Francis Ortiz PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Bing WorksheetDocument3 pagesBing WorksheetFrutti MataniNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Establishment and Determining The Yields of Beans in A 3M by 4M Piece of Land at Eldoret National PolytechnicDocument12 pagesProject Report: Establishment and Determining The Yields of Beans in A 3M by 4M Piece of Land at Eldoret National PolytechnicvinalNo ratings yet
- Govardhan Eco Village Newsletter January 2011Document5 pagesGovardhan Eco Village Newsletter January 2011Tushar VoraNo ratings yet
- NArrative Report in Agr-Fishery 1Document5 pagesNArrative Report in Agr-Fishery 1Gelaica joy AbrenillaNo ratings yet
- Inset Test TqsDocument3 pagesInset Test TqsdomniesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AGRICULTUREDocument17 pagesIntroduction To AGRICULTUREVan SweetingNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Ag@School!Document6 pagesWelcome To Ag@School!joan annie abraganNo ratings yet
- Form Two NotesDocument20 pagesForm Two NotesLloydNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Forestry & Environment PDFDocument11 pagesModule 4 - Forestry & Environment PDFManoa Nagatalevu TupouNo ratings yet
- Words For TOEFL Lesson 1Document4 pagesWords For TOEFL Lesson 1Nelly ElizondoENo ratings yet
- Form 3 Week 7 Lesson 1 Study PackDocument12 pagesForm 3 Week 7 Lesson 1 Study PackIss MeNo ratings yet
- WWW - CBSE123.CO - CC: Chapter 1 - Class Viii Crop Production and ManagementDocument5 pagesWWW - CBSE123.CO - CC: Chapter 1 - Class Viii Crop Production and ManagementgunjantiggaNo ratings yet
- Crop Production and Management - Class 8 - NotesDocument15 pagesCrop Production and Management - Class 8 - NotesNelsonNo ratings yet
- Geography Development of Agriculture in The WorldDocument155 pagesGeography Development of Agriculture in The WorldHasifa KonsoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Interpret Farm Plans and Lay OutsDocument37 pagesLesson 7 Interpret Farm Plans and Lay Outsget.famoussxNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Notes For 2020Document51 pagesGrade 6 Notes For 2020JB MangunduNo ratings yet
- MR Joseph K Mangundu Karupu POBOX2467 Rundu: Iphst6 004700Document1 pageMR Joseph K Mangundu Karupu POBOX2467 Rundu: Iphst6 004700JB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Notes For 2020Document38 pagesGrade 4 Notes For 2020JB MangunduNo ratings yet
- NSHE GRADE 7 NotesDocument78 pagesNSHE GRADE 7 NotesJB Mangundu100% (2)
- Elementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentDocument14 pagesElementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionDocument27 pagesElementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Elementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentDocument14 pagesElementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Elementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentDocument14 pagesElementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Agric (2019) + AnswersDocument299 pagesGrade 7 Agric (2019) + AnswersKundai100% (11)
- Grade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteDocument32 pagesGrade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteJB Mangundu100% (1)
- Null 2Document32 pagesNull 2JB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionDocument27 pagesElementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Grade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteDocument32 pagesGrade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteJB Mangundu100% (1)
- Elementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentDocument14 pagesElementary Agriculture Grade 5 Teachers Guiding Notes: Professional DevelopmentJB MangunduNo ratings yet
- Grade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteDocument32 pagesGrade 6: Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S NoteJB Mangundu100% (1)
- Christopher Columbus and BahamasDocument3 pagesChristopher Columbus and BahamasdonkeytoeNo ratings yet
- History of NarraDocument4 pagesHistory of NarraArmand Caleb Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Princeton - 0928Document20 pagesPrinceton - 0928elauwitNo ratings yet
- Fish Farming IELTS Listening Answers With Audio, Transcript, and ExplanationDocument6 pagesFish Farming IELTS Listening Answers With Audio, Transcript, and ExplanationQuocbinhNo ratings yet
- Foods of The ProphetDocument10 pagesFoods of The ProphetZalina AliNo ratings yet
- Coriolis Firm Dairy 03 0909 Fonterra Options Going Forward 101aDocument103 pagesCoriolis Firm Dairy 03 0909 Fonterra Options Going Forward 101acoriolisresearchNo ratings yet
- Directory Sugar Refineries 2021 2022Document2 pagesDirectory Sugar Refineries 2021 2022J Paul VarelaNo ratings yet
- 2019031999Document52 pages2019031999Vinodhanan SNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management in WatermelonDocument42 pagesIntegrated Pest Management in WatermelonGuruPrasadNo ratings yet
- DENR Administrative Order No. 96-29 (DENR-DAO 1996-29) - October 10, 1996Document30 pagesDENR Administrative Order No. 96-29 (DENR-DAO 1996-29) - October 10, 1996Carmencita B. Calilan100% (1)
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomAreeba Inam RaoNo ratings yet
- French Tarragon For Iha PageDocument11 pagesFrench Tarragon For Iha PageAgatheDumenilNo ratings yet
- Organic FarmDocument2 pagesOrganic FarmAlexander QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Yeast FertilizersDocument19 pagesYeast FertilizersPrasadNo ratings yet
- Swaraj 744 XM (ICT) PDFDocument8 pagesSwaraj 744 XM (ICT) PDFManinder Singh SainiNo ratings yet
- Paten Sulfur Mixer PDFDocument7 pagesPaten Sulfur Mixer PDFLily DianaNo ratings yet
- Legal Considerations in Urban Planning OnlineDocument13 pagesLegal Considerations in Urban Planning OnlineRosaleo TolibasNo ratings yet
- Program (MANGO, Litchi & Hogpalm)Document5 pagesProgram (MANGO, Litchi & Hogpalm)PrachuriyaNo ratings yet
- Pestle Analysis of Indian AgricultureDocument32 pagesPestle Analysis of Indian Agriculturesheikhtalha94% (33)
- Internship Report Bank of BarodaDocument101 pagesInternship Report Bank of Barodakundankumarsharma100% (3)
- Familia Acanthaceae en PanamáDocument8 pagesFamilia Acanthaceae en PanamáMario Junior Zegarra VásquezNo ratings yet
- Rencana Reklamasi Pada Lahan Bekas Tambang Pasir Dan Batu Di Desa Nglumut, Kecamatan Srumbung, Kabupaten Magelang, Provinsi Jawa TengahDocument6 pagesRencana Reklamasi Pada Lahan Bekas Tambang Pasir Dan Batu Di Desa Nglumut, Kecamatan Srumbung, Kabupaten Magelang, Provinsi Jawa Tengahriki ramandaNo ratings yet
- Porcine BrucellosisDocument35 pagesPorcine BrucellosisCharlotte AcayanNo ratings yet
- Topography NotesDocument3 pagesTopography Noteszainab billalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of MetalDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of MetalChari Mae Tamayo PanganibanNo ratings yet
- List of Pesticides Currently Approved For Use On Cocoa Farms in NigeriaDocument2 pagesList of Pesticides Currently Approved For Use On Cocoa Farms in NigeriaLivy HaoNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report 2016Document7 pagesAccomplishment Report 2016Radel LlagasNo ratings yet
- Conquer Today Equipment The Fuel Grid 1 PDFDocument5 pagesConquer Today Equipment The Fuel Grid 1 PDFRusu TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Different Types of EcosystemsDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of EcosystemsCherry BrutasNo ratings yet
- Coding DecodingDocument56 pagesCoding DecodingdddfeNo ratings yet