Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Why Is The Lower Terminal of V Is Connected at Top of R ?: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 01
Uploaded by
Syed Afzal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views28 pagesThe lower terminal of V2 is connected to the top of R1 because during the turn-off process of a BJT, excess minority carrier charges are stored in the base region. These charges need to be removed during turn-off, which takes a storage time ts for the collector current to decrease and the base-emitter junction polarity to change. Connecting V2 above R1 allows the stored charges in the base region to dissipate through R1 during turn-off.
Original Description:
Original Title
PE_04_EE17
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe lower terminal of V2 is connected to the top of R1 because during the turn-off process of a BJT, excess minority carrier charges are stored in the base region. These charges need to be removed during turn-off, which takes a storage time ts for the collector current to decrease and the base-emitter junction polarity to change. Connecting V2 above R1 allows the stored charges in the base region to dissipate through R1 during turn-off.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views28 pagesWhy Is The Lower Terminal of V Is Connected at Top of R ?: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 01
Uploaded by
Syed AfzalThe lower terminal of V2 is connected to the top of R1 because during the turn-off process of a BJT, excess minority carrier charges are stored in the base region. These charges need to be removed during turn-off, which takes a storage time ts for the collector current to decrease and the base-emitter junction polarity to change. Connecting V2 above R1 allows the stored charges in the base region to dissipate through R1 during turn-off.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
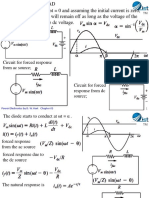
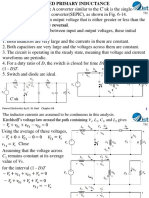
Why is the lower terminal of
V2 is connected at top of R1?
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 01 1
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 2
3
4
5
For turning off the BJT, polarity
of the base voltage is reversed
and thus the base current.
Excess minority carrier charges
are stored in the base region
which needs to be removed
during the turn-off process.
The time required to nullify this
charge is the storage time, ts.
Collector current remains at the
same value for this time.
After this, collector current starts
decreasing and base-to-emitter
junction changes to the negative
polarity; base current also get
reduced.
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 6
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 7
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 8
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 9
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 10
RJC
RCS RSA
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 11
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 12
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 13
Power Electronics by Muhammad H. Rashid 3rd Ed Chap 01-04 14
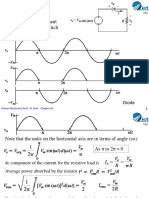
Power Computations
Energy or work
Passive sign convention
Periodic voltage and current functions p(t)>0 indicates power is
being absorbed;
produce a periodic instantaneous power
function. Average power is the time average
of p(t) over one or more periods.
Average Power
Power is also computed from
energy per period. Average power is sometimes
called real power or active
power, especially in ac circuits.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 15
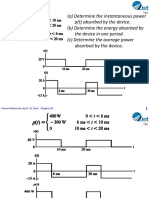
EXAMPLE 2-1
(a) Determine the instantaneous power
p(t) absorbed by the device.
(b) Determine the energy absorbed by
A the device in one period.
(c) Determine the average power
absorbed by the device.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 16
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 17
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 18
A special case that is frequently encountered
in power electronics is the power absorbed or
supplied by a dc source.
Average power absorbed by a
dc voltage source is the
product of the voltage and the
average current.
Similarly, average power absorbed
by a dc source i(t) = Idc is
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 19
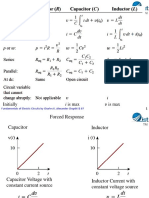
INDUCTORS AND CAPACITORS
For an inductor, the
stored energy is
No net energy transfer indicates that the average power absorbed
by an inductor is zero for steady-state periodic operation.
The voltage-current relationship for the inductor
Multiplying by L/T yields an expression equivalent to the average
voltage across the inductor over one period.
Therefore, for periodic currents, the average voltage across an inductor is
zero. This is very important and will be used in the analysis of many
circuits, including dc-dc converters and dc power supplies.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 20
For a capacitor, stored energy is
If the capacitor voltage is periodic, the stored energy is the same at the
end of a period as at the beginning.
Therefore, the average power absorbed by the capacitor is zero for
steady state periodic operation.
Starting and ending values are the same for periodic voltages
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 21
Multiplying by C/T yields an expression for average current in
the capacitor over one period.
Therefore, for periodic voltages, the average current in a capacitor
is zero.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 22
-
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 23
-
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 24
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 25
-
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 26
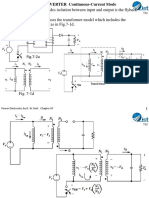
Average power supplied by the dc source during the switching
period is
The average power absorbed by the inductor is zero, and power
absorbed by the ideal transistor and diode is zero.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 27
Another way to approach the problem is to determine the peak
energy stored in the inductor,
The energy stored in the inductor is transferred to the resistor
while the transistor switch is open.
which must also be the power
supplied by the source.
Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02 28
You might also like
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Example 2-1: (A) Determine The Instantaneous Power (B) Determine The Energy Absorbed byDocument7 pagesExample 2-1: (A) Determine The Instantaneous Power (B) Determine The Energy Absorbed bySyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Initially I Is Max V Is MaxDocument14 pagesInitially I Is Max V Is MaxSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 06 Ee12Document27 pagesPe 06 Ee12chinchouNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices For Power Electronics: Prelim PeriodDocument36 pagesSemiconductor Devices For Power Electronics: Prelim PeriodEd RianNo ratings yet
- Circuit For Forced Response From Ac Source : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document21 pagesCircuit For Forced Response From Ac Source : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 425 01 IntroductionDocument31 pages425 01 Introductionماجد غرابNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Document43 pagesFourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Computing Average Resistor Power: Voltage Is Defined As The Voltage That Is As Effective AsDocument26 pagesComputing Average Resistor Power: Voltage Is Defined As The Voltage That Is As Effective AsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Creating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document41 pagesCreating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Document21 pagesAssignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronic Module BDocument15 pagesIndustrial Electronic Module BYamburger LoveNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fundamentals of Cicittheo Cicittheo Circuit Theory Circuit TheoryDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Fundamentals of Cicittheo Cicittheo Circuit Theory Circuit TheoryEunmi JeongNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept and KCL - KVLDocument22 pagesBasic Concept and KCL - KVLArnab RoyNo ratings yet
- Pe 08 Ee17Document33 pagesPe 08 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document36 pagesUnit 12ahmed bashaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis 2 Laboratory Experiment 1: Power Factor CorrectionDocument13 pagesCircuit Analysis 2 Laboratory Experiment 1: Power Factor CorrectionZulqarnain KhanNo ratings yet
- Reducing Load Current Harmonics: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document5 pagesReducing Load Current Harmonics: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Resistive Load Creating A DC Component Using An Electronic SwitchDocument22 pagesResistive Load Creating A DC Component Using An Electronic SwitchSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept Operation and Control of HVDC Transmission SystemDocument74 pagesBasic Concept Operation and Control of HVDC Transmission Systempongpum100% (7)
- Pe 05 Ee12Document20 pagesPe 05 Ee12Syed Meesum HaiderNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Switching Transients Analysis FundamentalsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Switching Transients Analysis FundamentalspowdemyNo ratings yet
- Polyphase RectifierDocument72 pagesPolyphase RectifierShiela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pe Chapter 2 - 1Document16 pagesPe Chapter 2 - 1Muhammad HashirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inductance, Capacitance, and Mutual Inductance PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 6 - Inductance, Capacitance, and Mutual Inductance PDFDaniaNo ratings yet
- HVDC ControlDocument74 pagesHVDC ControlKaran SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits and RMSDocument4 pagesAC Circuits and RMSJIGNESH DESAINo ratings yet
- Cee-Ehm 468-Part 2Document26 pagesCee-Ehm 468-Part 2goshfukdNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost ConvertersDocument33 pagesBuck Boost ConvertersMuneerAhmed0% (1)
- RLCDocument65 pagesRLCabc abcNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Part OneDocument27 pagesDC-DC Part OneAbenezer ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts in Electrical TechnologyDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concepts in Electrical TechnologyDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- Ac Power Analysis 1 1: Enhancing Your CareerDocument38 pagesAc Power Analysis 1 1: Enhancing Your CareerAlaa WahoudNo ratings yet
- Half and Full Wave RectifiersDocument13 pagesHalf and Full Wave RectifiersBhishma Kant VermaNo ratings yet
- Circuit 1Document5 pagesCircuit 1richy launcherNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of MPPT Based Solar Charge ControllerDocument7 pagesComparative Analysis of MPPT Based Solar Charge ControllerMechanical Robot Designers V CreationsNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document43 pagesCH 11Cumali Türkeri100% (1)
- Power CalculationsDocument32 pagesPower Calculationsرغد كنعانNo ratings yet
- 4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersDocument12 pages4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersRodrigo PerezNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document12 pagesPower Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 01Document32 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 01Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument20 pagesChapterKyaw SoeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Concepts About BusDuctDocument6 pagesBasic Electrical Concepts About BusDuctAshish ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - AC Power AnalysisDocument20 pagesChapter 1 - AC Power AnalysisandersonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Part - 002Document9 pagesFundamentals Part - 002Ashirvad RathNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Document19 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument42 pagesPower Electronicsaswardi8756No ratings yet
- EDC MaterialDocument49 pagesEDC Materialhard.worker123hwNo ratings yet
- ECS203 - Handout 1ADocument29 pagesECS203 - Handout 1ArsrodcNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Simulation of Electric Circuits (EME 208) : Spring 2011Document28 pagesAnalysis and Simulation of Electric Circuits (EME 208) : Spring 2011Ahmed MohyNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument26 pagesElectric CircuitsObserver of mellinuimNo ratings yet
- Network Theory: Lecture 1: Introduction 2nd Yr ECE 3rd Semester ECC303Document12 pagesNetwork Theory: Lecture 1: Introduction 2nd Yr ECE 3rd Semester ECC303Sandip DasNo ratings yet
- Me 483 - 1Document69 pagesMe 483 - 1ElormeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture 05 (C) InductorsDocument17 pagesElectrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture 05 (C) InductorsnithishNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAadhil .A. KareemNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- L6 Diodes and Applications (New2024)Document44 pagesL6 Diodes and Applications (New2024)Aron DionisiusNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No 4Document3 pagesEXPERIMENT No 4English words BY Utkarsh johriNo ratings yet
- 2 PerceptionGDocument37 pages2 PerceptionGSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document19 pagesPspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductioDocument16 pages1 IntroductioSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SignalsDocument53 pagesChapter 2 SignalsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Be Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Document28 pagesBe Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document12 pages7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document4 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document20 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 36 Ee17Document21 pagesPe 36 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 38 Ee17Document22 pagesPe 38 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document18 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 27 Ee17Document11 pagesPe 27 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document19 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Document21 pagesAssignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document10 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 23 Ee17Document18 pagesPe 23 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Creating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document41 pagesCreating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document20 pagesContinuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document13 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- For Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document16 pagesFor Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document20 pagesFull-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document15 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 26 Ee17Document23 pagesPe 26 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Document20 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document12 pagesPower Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document13 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Document19 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Document43 pagesFourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Paket 6 Product InformationDocument4 pagesPaket 6 Product InformationRiskyNo ratings yet
- Liquid-to-Liquid Heat Exchanger: User ManualDocument40 pagesLiquid-to-Liquid Heat Exchanger: User ManualArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingDocument132 pages1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingOscar EspitiaNo ratings yet
- PCB MakingDocument3 pagesPCB MakingAngelica Mae BanaagNo ratings yet
- Intake System: Parts LocationDocument7 pagesIntake System: Parts LocationMenzie Peter RefolNo ratings yet
- High Quality Audiophile Operational Amplifier/Driver RT6863: RicoreDocument8 pagesHigh Quality Audiophile Operational Amplifier/Driver RT6863: Ricoreraoultrifan7560No ratings yet
- JNTUK Results KumarDocument2 pagesJNTUK Results KumarPrasad hero KonniNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Mux and DecoderDocument6 pagesLab 6 Mux and DecoderRifah Shanjida MomoNo ratings yet
- Android List FreewareDocument24 pagesAndroid List FreewareBoedisantosoNo ratings yet
- Amw MCQDocument150 pagesAmw MCQSanthosh PaNo ratings yet
- Digital Scale 340368 - A - D - IE - ENDocument47 pagesDigital Scale 340368 - A - D - IE - ENDimitar KirovNo ratings yet
- 1VAL088301-TG RevB ReliaGearSB TechGuide DigitalDocument72 pages1VAL088301-TG RevB ReliaGearSB TechGuide DigitalsimonNo ratings yet
- DMX3 Acb PDFDocument44 pagesDMX3 Acb PDFSunny K INo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Voltage Regulator Model: APR 125-5 Part Number: 9 1688 00 100Document22 pagesInstruction Manual: Voltage Regulator Model: APR 125-5 Part Number: 9 1688 00 100Guilherme ChiminelliNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Monitoring and Notification System U PDFDocument4 pagesWater Quality Monitoring and Notification System U PDFMukund KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 NetworkDocument6 pages4 Networkapi-371092170No ratings yet
- 9702 w10 QP 43Document24 pages9702 w10 QP 43Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors: Data Handbook (Ch. 6 & 7) (Ed: O. Madelung)Document221 pagesSemiconductors: Data Handbook (Ch. 6 & 7) (Ed: O. Madelung)banstalaNo ratings yet
- Substation Construction Project. Project ScheduleDocument12 pagesSubstation Construction Project. Project ScheduleBishnu Chapagai50% (2)
- SIM900 GSM Shield Users Manual PDFDocument9 pagesSIM900 GSM Shield Users Manual PDFrotvogelNo ratings yet
- ABB Transformers Protection CourseDocument56 pagesABB Transformers Protection Coursejha100% (3)
- Cat Payload Kit Electrical System For Medium Wheel Loaders: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsDocument2 pagesCat Payload Kit Electrical System For Medium Wheel Loaders: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsEddie Kelvin Isidro LauraNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Color Television Chassis: Cp-520Document85 pagesService Manual: Color Television Chassis: Cp-520Aivar SooneNo ratings yet
- TATA ReportDocument43 pagesTATA ReportNirmal Singh100% (1)
- Decimal To BC-Encoder V2Document10 pagesDecimal To BC-Encoder V2Anurag RoyNo ratings yet
- Making A Powerful 1 Watt LED Driver Using A Cell Phone ChargerDocument95 pagesMaking A Powerful 1 Watt LED Driver Using A Cell Phone ChargerHutanu Gabriel0% (1)
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPDocument42 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Types of MultiplexingDocument14 pagesTypes of MultiplexingMurli AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Bosch Mems 12 Micro Machine Symposium ErnstDocument10 pagesBosch Mems 12 Micro Machine Symposium ErnstanisatputeNo ratings yet
- Grundfos RSI: Renewable Solar Inverter For Pump Control 1.5 - 250 KWDocument20 pagesGrundfos RSI: Renewable Solar Inverter For Pump Control 1.5 - 250 KWJa AcostaNo ratings yet