Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Starch
Bio Starch
Uploaded by
Kishan MorjariaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Starch
Bio Starch
Uploaded by
Kishan MorjariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Describe the journey of a glucose molecule from its formation in a plant, to you eating it from a
piece of meat, to your brain.
Glucose is formed though photosynthesis which is the how plants make their food. This takes place
in the chloroplasts of plants which contain chlorophyll and during photosynthesis light energy is
absorbed by the chlorophyll in the chloroplasts and energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide
from air the plus water from the soil into glucose.
This is then converted into starch for storage although some glucose is used immediately used by
the cells of the plant. Starch is insoluble so it stores it in the cells of the plant to provide an energy
store for when it is dark or when light levels or low and because starch is insoluble it doesn’t have to
worry about it having an effect on the water balance of the plant.
This is then eaten by cows which digest the starch and convert this back into glucose which they use
for respiration for energy although some starch is still left within the animal for an energy store
Then these cows are killed and turned into beef and when you eat this beef it passes into the
salivary glands. Amylase is produced in the salivary glands which is a carbohydrase. Because of this
the digestion of starch starts in the mouth. Amylase is also produced in the pancreas and the small
intestine although no digestion happens in the pancreas. All the enzymes made in the pancreas then
flow into the small intestine. The beef first goes to the stomach from the salivary glands where the
stomach lining secrets hydrochloric acid which creates the ideal conditions for protein digesting
enzymes to work. This food then passes into the small intestine where bile is squirted onto it which
makes the semi-digested food alkaline so it creates the ideal conditions for enzymes in the small
intestine such as amylase. The Bile also emulsifies the fats in your food.
The amylase then digests the starch in the beef into glucose and this glucose is diffused into the
bloodstream. This glucose then reaches the brain where it is used for respiration by cells in the
brain. But glucose is used by all cells in your body by respiration.
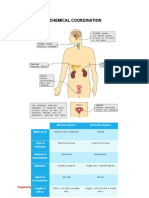
But when you digest a meal large of amounts of glucose pass into your blood and so the pancreas
controls the amount of glucose in your blood. It constantly monitors blood glucose concentration
and controls it using two hormones known as insulin and glucagon.
When your blood glucose concentration rises above the ideal range after you have eaten a meal,
insulin is released which travels in your bloodstream to the target organs which are the muscles and
the liver and excess glucose is converted into glycogen which is stored in the liver .
But when you exercise your blood glucose concentration falls and if this falls below ideal range the
pancreas released glucagon and this makes your liver break down glycogen converting it back into
glucose and in this way stored sugar is released back into the blood.
You might also like
- Proposed Budget For The Introduction Ceremony of Mr. Mbabazi Isaac Katuramu & Ms. Judith Katushabe Scheduled On 15Th/01/2022Document3 pagesProposed Budget For The Introduction Ceremony of Mr. Mbabazi Isaac Katuramu & Ms. Judith Katushabe Scheduled On 15Th/01/2022Derrick Prince Muyambi94% (16)
- Full Spectrum StrengthDocument16 pagesFull Spectrum Strengthraja varman100% (2)
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesDigestion of CarbohydratesVarsha SadhwaniNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet COT4Document5 pagesActivity Sheet COT4Abbie Gail CabatañaNo ratings yet
- How Food WorksDocument10 pagesHow Food Worksapi-3709951No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJohn Rey Abad67% (3)
- How To Change Foods To EnergyDocument1 pageHow To Change Foods To EnergyBoaz LiyonNo ratings yet
- 4M TheoryDocument10 pages4M TheoryGwenn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Script For BiochemDocument12 pagesScript For Biochemotep freecsNo ratings yet
- Avian Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesAvian Digestive Systemnadz karimNo ratings yet
- Functions of CarbohydrateDocument11 pagesFunctions of CarbohydrateAbdulbaasit AyoolaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument41 pagesBIOMOLECULESbam yeontanieNo ratings yet
- The Human Pancreas Has 1 To 2 Million Islets of LangerhansDocument5 pagesThe Human Pancreas Has 1 To 2 Million Islets of LangerhansCHAYNEX 1No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyernestoNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients SummaryDocument2 pagesMacronutrients Summaryapi-259949424100% (1)
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument16 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismalexa manatadNo ratings yet
- What Role Do Carbohydrates Play in Metabolism?Document3 pagesWhat Role Do Carbohydrates Play in Metabolism?alexa manatadNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document12 pagesWeek 1Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02.5 Insulin HKBDocument14 pagesChapter 02.5 Insulin HKBRohan GohilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyDocument26 pages1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyRamsses ValenciaNo ratings yet
- bIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONDocument82 pagesbIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in HomeostasisDocument1 pageBlood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in HomeostasisShemeka LaroseNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument32 pagesNutrition in AnimalsIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- GlycogenDocument3 pagesGlycogenelianagerzon08No ratings yet
- Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument4 pagesCells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsSophia OcayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersDocument5 pagesLecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersNikhil TutejaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2 Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy (With Obj)Document18 pagesWeek 1 2 Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy (With Obj)Cherry Louise O. SanvictoresNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESjaizamaeenriquez59No ratings yet
- Anaphy PancreasDocument6 pagesAnaphy PancreasAELYN SEVILLANo ratings yet
- Ahn-Unit 2Document21 pagesAhn-Unit 2Dilshad TasnimNo ratings yet
- Macronutrient Project FinalDocument6 pagesMacronutrient Project Finalapi-259363834No ratings yet
- Interrelated Function Bio MolecularDocument2 pagesInterrelated Function Bio MolecularAlifah SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- Glucose Homestasis and Diabetes PresentationDocument23 pagesGlucose Homestasis and Diabetes Presentationapi-320112884No ratings yet
- 3 CarbohydratesDocument12 pages3 CarbohydratesconcepcionsofiakarylleNo ratings yet
- LetDocument2 pagesLetNapalang EdrianNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption - 101328Document10 pagesDigestion and Absorption - 101328Emmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomy of The PancreasDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Anatomy of The PancreasIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rahman AlwiDocument46 pagesAbdul Rahman Alwiaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document8 pagesNutrition 1Princess Mae SabadoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Other Foreign Substances These Substances Have Entered The Blood Supply EitherDocument15 pagesOther Foreign Substances These Substances Have Entered The Blood Supply EitherAnis Assila Mohd RohaimiNo ratings yet
- How Food WorksDocument19 pagesHow Food WorksnafeesNo ratings yet
- MacronutrientsDocument2 pagesMacronutrientsapi-253348067No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - MetabolismDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates - MetabolismSathish PillaiNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesCarbohydratesstudents athloneNo ratings yet
- Final Report Ni KishDocument3 pagesFinal Report Ni KishNapalang EdrianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and PharynxDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and Pharynxitachi278No ratings yet
- Why Our Blood Glucose Level Increases ?Document1 pageWhy Our Blood Glucose Level Increases ?api-65434455No ratings yet
- CSEC Biology - AssimilationDocument1 pageCSEC Biology - AssimilationRaveena SinghNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesCris PorlasNo ratings yet
- PolysaccharidesDocument30 pagesPolysaccharidesbam yeontanieNo ratings yet
- Z P CRISTOBAL Homeostasis of The BodyDocument48 pagesZ P CRISTOBAL Homeostasis of The BodyAienna Lacaya Matabalan100% (1)
- BIOCHEM DigestionDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PPT 1Document17 pagesCarbohydrates PPT 1Cristine Mae Pisquel TabunotNo ratings yet
- Absorption and AssimilationDocument19 pagesAbsorption and AssimilationChe SalNo ratings yet
- Bio 270 Lecture 10 University of TorontoDocument24 pagesBio 270 Lecture 10 University of TorontoJD BaruaNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment AFDocument6 pagesDiet Assessment AFAdamFerris94No ratings yet
- Introduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Thorough Discussion of New Zealand Dairy BangladeshDocument26 pagesThorough Discussion of New Zealand Dairy BangladeshNafis Rahman100% (1)
- Ngampeerapong C 2019Document12 pagesNgampeerapong C 2019Fauzi SatriaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Buying Behavoiur in Respect of Godrej ProductsDocument56 pagesConsumer Buying Behavoiur in Respect of Godrej ProductssaurabhNo ratings yet
- Rice Mill-2 PDFDocument7 pagesRice Mill-2 PDFPriyal Savla100% (1)
- Xii CH14 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesXii CH14 BiomoleculesKrish KambojNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbkcdrd6 Qkcq9vuhqu2qirx7 Hi70pdo4wpc8ickgarstn g1wleeu4w9ig8igr6mckulf2zvtwvaeeawkaa9gdwmdr3dewmj-Kz0avgq-Eqpyxbv8msbsubiDocument2 pagesAcfrogbkcdrd6 Qkcq9vuhqu2qirx7 Hi70pdo4wpc8ickgarstn g1wleeu4w9ig8igr6mckulf2zvtwvaeeawkaa9gdwmdr3dewmj-Kz0avgq-Eqpyxbv8msbsubiKatarzyna Agata KrzyczmonikNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science - Nutrition in AnimalsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Animalssifat mongaNo ratings yet
- Dunkin Donuts Strategic AnalysisDocument24 pagesDunkin Donuts Strategic AnalysisSALONI SHAHNo ratings yet
- Bone Crusher Machine Bone Powder Machine PriceDocument3 pagesBone Crusher Machine Bone Powder Machine PriceNenad RadovicNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living 2017 Food TriangleDocument5 pagesHealthy Living 2017 Food TriangleAndrea CamachoNo ratings yet
- Oh BessDocument19 pagesOh Besslola&losa farhanNo ratings yet
- 15 PDFDocument4 pages15 PDFPh0nG TrAnNo ratings yet
- Sin-a-Min Health Foods: PowerbarsDocument1 pageSin-a-Min Health Foods: Powerbarsguess whoNo ratings yet
- English Class V Worksheet For Aditi Fa1 RevisionDocument10 pagesEnglish Class V Worksheet For Aditi Fa1 RevisionVolety Sai SudheerNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab Report Title of Report: Cardiorespiratory Effects of ExerciseDocument9 pagesPhysiology Lab Report Title of Report: Cardiorespiratory Effects of ExerciseKogo VickNo ratings yet
- Masteb 2021 10 3 251 257 922865 Published1Document8 pagesMasteb 2021 10 3 251 257 922865 Published1zainNo ratings yet
- Upgrading The Traditional Bamboo Fish Cage of Rodelio Fish Cage To Norwegian-Style Fish Cage TechnologyDocument30 pagesUpgrading The Traditional Bamboo Fish Cage of Rodelio Fish Cage To Norwegian-Style Fish Cage TechnologyMark Vincent Jayson BaliñaNo ratings yet
- Reading CamelDocument3 pagesReading CamelEmilce CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Food EngineeringDocument26 pagesFood EngineeringKidus Seleshi100% (2)
- A General Walk, - Prefers Ina: Mr. Ramamurty, Who Was Admitted Due To PneumoniaDocument2 pagesA General Walk, - Prefers Ina: Mr. Ramamurty, Who Was Admitted Due To PneumoniaCristina FriasNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Nutritional Value of Yam Jand and Rice JandDocument34 pagesA Comparative Study On Nutritional Value of Yam Jand and Rice JandUmesh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Eating: Easy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet and Sticking To ItDocument13 pagesHealthy Eating: Easy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet and Sticking To Itfarah hanimNo ratings yet
- Copycat Red Lobster Cheddar Bay Biscuits - Spend With PenniesDocument1 pageCopycat Red Lobster Cheddar Bay Biscuits - Spend With Penniesponyrider4No ratings yet
- Effect of Xylitol With Various Concentration and Duration On The Growth of Candida Albicans (In Vitro Study)Document5 pagesEffect of Xylitol With Various Concentration and Duration On The Growth of Candida Albicans (In Vitro Study)gien fortunasiaNo ratings yet
- Bio 10th - Life Processes - Revision WorksheetDocument13 pagesBio 10th - Life Processes - Revision WorksheetDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical, Textural and Sensory Evaluation of Sponge Cake Supplemented With Pumpkin FlourDocument7 pagesPhysico-Chemical, Textural and Sensory Evaluation of Sponge Cake Supplemented With Pumpkin FlourVirda Ayu Nia SaputriNo ratings yet
- Aejm 106Document8 pagesAejm 106Jaydeep BhawalNo ratings yet
- Las. SG VitaminsDocument18 pagesLas. SG VitaminsZeian Jacob BaylaNo ratings yet