Professional Documents
Culture Documents
bIOLOGICAL CHO, CHON
Uploaded by
galauraaprilrose960 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views82 pagesbiological
Original Title
bIOLOGICAL CHO,CHON
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbiological
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views82 pagesbIOLOGICAL CHO, CHON
Uploaded by
galauraaprilrose96biological
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 82
IODINE TEST FOR STARCH
NOTE THAT LUGOL'S IODINE SOLUTION OR
TINCTURE OF IODINE CHANGES FROM
YELLOW TO BLUE OR BLACK IN THE
PRESENCE OF STARCH.
Positive Test: Benedict's solution changes from
blue to green (very small amount of reducing
sugar), to yellow (higher amount of reducing
sugar) to orange or brick red (highest amount of
reducing sugar). The color change is due to the
formation of the red brick precipitate, Cu2O.
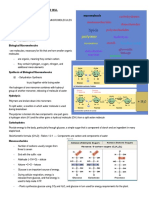
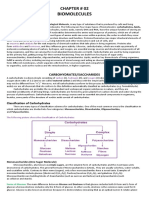
CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy
for the body.
These are simple sugar, starch, and cellulose.
All carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and
oxygen.
CHO classified into the following:
1. Monosaccharides
From the prefix "mono," which means one
is the simplest sugar and the essential subunit
of a carbohydrate.
These compounds are white solids at room
temperature.
Because they have polar, hydroxyl (-OH) groups
in their molecular structures, they are very
soluble in water.
The most common monosaccharides are glucose
monosaccharides have the formula C6H12O6,
their structural formulas differ.
Glucose in water solution forms a ring made up of
five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, and
fructose in a water solution includes a ring made
up of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
Compounds with the same molecular formulas are
called isomers. So, glucose and fructose are
isomers. Though they have the same molecular
formula, these sugars cannot be used in the same
way by cells in the body. The C, H, and O atoms'
arrangement determine the shape and properties of
each sugar.
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken
down into monosaccharide which is absorbed
into the blood and transported to the cells
providing "instant" energy to perform our
activities.
Sometimes we overeat, especially when we are
tired, the excess glucose is stored in the liver as
glycogen for later use. It is essential to have a
steady supply of glucose in the blood to maintain
body functions. As they say, too much or too
little of anything may lead to some diseases.
Too much glucose is in the blood, the Pancreas
secretes a hormone called insulin, which
stimulates cells in the liver, muscles, and fat to
absorb glucose and transform it into glycogen or
fats, stored for some time.
Blood glucose drops, the Pancreas secretes
glucagon, which causes the liver, muscles, and fat
to convert glycogen back to glucose.
Fruits contain a monosaccharide called fructose.
It is considered the sweetest naturally occurring
sugar. Due to its sweetness, fructose is
sometimes used as a low-calorie sweetener
because less fructose is needed to produce the
same sweetness that table sugar does.
Starchy food that we eat is widely distributed in
the plant world. Thus, its principal constituent
glucose is found in all plants and the sap of
trees. However, glucose is also found in
glycogen that is produced in animal cells.
Disaccharides
It is also called sucrose with the molecular
formula C12H22O11.
How sucrose, which is a disaccharide, is formed?
The formation and breakdown of sucrose to
glucose involves two reactions
A condensation reaction is a reaction in which
two molecules or parts of the same molecule
combine. During the condensation of
monosaccharides to form disaccharides, one
molecule of water is lost..
When two glucose molecules are combined,
maltose is created, and water is lost during
the process
A hydrolysis reaction occurs when the bond
between monosaccharides is broken with the
addition of a water molecule.
Lactose is made up of a sugar called galactose
and glucose. In our body, a specific enzyme,
lactase, is necessary to help break the bond
between the two monosaccharides when lactose is
digested.
People who cannot digest milk products are called
"lactose intolerant" because they do not produce
the enzyme (lactase) necessary to break the bond
between glucose and galactose.
Since lactose molecules are too large to be
absorbed into the circulatory system, they
continue through the digestive system, where
bacteria eventually break them down in the large
intestine. These bacteria digest monosaccharides,
producing carbon dioxide gas in the process.
As a result, a common symptom of lactose
intolerance is a buildup of intestinal gas along
with a bloated feeling, and more often, the
passing out of undigested lactose as diarrhea.
Shows that when a combination reaction joins
two monosaccharides, a glycosidic bond will be
formed between the two monosaccharide
molecules. The reaction produces water as a
side product
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (the prefix poly means many) or
complex carbohydrates. They are large molecules
that are made up of many smaller units that are
joined. The reason why these foods turn blue-
black is that they contain starchy components.
Three common polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
The starch breakdown requires a water molecule
to provide a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group
to the site where the bond is broken. With the help
of enzymes in the digestive system, the glucose
units can be separated.
When a glucose molecule is separated from the
rest of the starch polymer, it can be absorbed and
used as fuel by your cells.
Since it takes time for glucose to be separated
from the polysaccharide, it is gradually released
to the cells. Thus, the glucose from starch reaches
muscle cells over a period providing energy as it
is needed. For this reason, athletes often eat meals
rich in complex carbohydrates before an athletic
event.
Starch is the chief storage form of carbohydrates
in plants and the most important carbohydrates
source in human nutrition.
A starch molecule is a polysaccharide assembled
from the simple sugar glucose;
Starch is made up of two types of Structure of
Starch polysaccharides:
amylose, which is a coiled or helical structure,
and amylopectin, which is branched.
Plants make starch. All individuals whose
glucose intake is excessive will store the excess
glucose as fat for long-term storage, and some
are converted to another polysaccharide
glycogen.
Glycogen is a polysaccharide that is similar to
starch because it is also composed of alpha
glucose units. It differs from starch since
glycogen shows a higher degree of branching
and is a polysaccharide made by an animal.
On the other hand, starch contains both straight-
chain and branched polysaccharides with much
less branching than that of glycogen and is
produced only by the plant.
Figure shows the glycogen structure, which
consists of long polymer chains of glucose units
connected by an alpha glycosidic linkage. It is a
multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that
serves as a form of energy storage in animals.
The polysaccharide structure represents the main
storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen is the readily available energy stored in
the liver and muscles and is quickly metabolized.
Fats are stored in adipose tissues but,
Lipids
Another class of biomolecules called lipids have
the "job" of storing energy for later use. Lipids are
also found in hormones and cell membrane
components.
Lipids have different structural types such as
carboxylic acids or fatty acids, triglycerides
or neutral fats, steroids, and waxes
Naturally occurring esters are lipids that contain
one or more long-chain carboxylic acids called
fatty acids. These are insoluble in water but
soluble in nonpolar solvents.
oil and water do not mix because they do not
have the same polarity.
oil composed primarily of long hydrocarbon
chains. They are formed reaction between an
alcohol and one or more long-chain carboxylic
acids. The most abundant of the lipids are fats
and oils, also called triglycerides.
The presence of double bonds in the fatty acids
lowers its melting point.
Fats are solids at room temperature and contain
saturated fatty acids.
all saturated hydrocarbons contain single bonds
and are produced only by animals. Examples of
animal fats are lard and butter.
Oils are liquids at room temperature and contain
unsaturated fatty acids. Again, he recalled that
unsaturated hydrocarbons have one or more
double bonds. Most oils, such as vegetable oil,
corn oil, and olive oil, are produced by plants.
If you eat in moderation, fats are good sources of
body fuel. They are regarded as good emergency
food and are an efficient energy storage system.
However, an excess quantity of fats is not good
for the heart. Fats are not good for the heart
because they tend to clog arteries and overwork
the heart.
While carbohydrates are the primary energy
source in your body, your system turns it to fat as
a backup energy source when carbohydrates are
not available. Vitamins A, D, E, and K cannot
function without adequate daily fat intake since
they are fat-soluble vitamins.
If you don't meet your daily fat intake or follow a
low-fat diet, absorption of these vitamins may be
limited, resulting in impaired functioning.
Steroids are another class of lipids whose
molecules are composed of fused rings of atoms.
The most important steroid is cholesterol. It is a
sterol because of the presence of alcohol or the
hydroxyl functional group.
It is found mainly in animal cells, although cell
membranes of plants may contain small
quantities of cholesterol and its major
derivatives, sitosterol.
Cholesterol plays an essential role in eukaryotes
and especially abundant in the cell membranes of
animal cells. A small amount of cholesterol can
also be found in the membrane of some
organelles inside the cells, such as the
mitochondrion and the endoplasmic reticulum.
It is not only abundant in the cell membrane but
also in brain tissues of the nervous system. An
important nerve cell, myelin, covers nerve axons
to help conduct the electrical impulses that make
movement, sensation, thinking, learning, and
remembering possible.
Studies have shown that cholesterol was the most
important factor in forming synapses, affecting
our memory and learning ability.
Animals can use cholesterol to synthesize other
steroids like cortisone, testosterone, and estrogen.
Although cholesterol is an essential lipid for
humans, excessive cholesterol levels in the blood
can lead to deposits in the arteries of the heart.
These arterial deposits are a leading cause of
heart disease.
Which form of glucose is stored in the human
liver and muscle?
A. Cellulose B. Glycogen C. Lipids D. Starch
Which form of glucose is stored in the human
liver Disaccharide is formed by combining two
monosaccharides. What do you call the process
of combining two or more simple sugars?
A. Hydrolysis C. Peptide bonding
B. B. Condensation D. Saccharide bonding
Which of the following term refers to the
combination of two types of monosaccharides?
A. Monosaccharide C. Polysaccharide
B. . Disaccharide .D Lygase
Which of the following is a term that refers to an
energy source obtained from plants?
A. Cellulose B. Glycogen C. Lipids D. Starch
Which of the following is a correct pair?
A. glucose: disaccharide C. starch:
polysaccharide B. sucrose: monosaccharide D.
triglyceride: polysaccharide
Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE
of carbohydrates?
A. Carbohydrates contain one or more OH
groups B. Carbohydrates are all solids
B. C. Carbohydrates can be aldoses
C. D. Carbohydrates are esters
Starch is characterized by all the following
EXCEPT:
A. It is composed of non-glucose units
B. B. It contains a linear polymer
C. C. It is composed of glucose units
D. D. It contains a branched polymer
Which of the following groups are all classified
as polysaccharides?
A. sucrose, glucose and fructose C. glycogen,
sucrose and maltose
B. B. maltose, lactose, and fructose D.
glycogen, cellulose and starch
Which of the following is the major function of
carbohydrates?
I. structural framework
II. II. Storage
III. III. energy production
IV. A. I only B. II only C. III only D. I & III only
Nutritional chemists have found that burning 1
gram of fat releases twice the amount of heat
energy as burning 1 gram of starch. Based on this
information, which type of biomolecule would
cause a person to gain more weight?
A. carbohydrate B. fat C. proteins D. nucleic acid
In which organs are glycogen stored in the body?
A. Liver and spleen C. liver and bile
B. Liver and muscle D. liver and adipose tissue
When digesting a complex carbohydrate, water is
added and simple sugar is obtained through
which process?
A. Photosynthesis B. Condensation C. Hydrolysis
D. Dehydration
What kind of molecule is represented by the
structure below?
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH=CHCH2CH2CH2CH2C
H2CH2CH2CH2COOH
A. monosaccharide C. saturated fatty acid
B. unsaturated fatty acid D. phospholipid
Disaccharide is formed by combining two
monosaccharides. What do you call the process
of combining two or more simple sugars?
A. Hydrolysis C. Condensation
B. Peptide Bonding D. Saccharide bonding
Which of the following elements is NOT present
in carbohydrates?
A. carbon B. oxygen C. nitrogen D. hydrogen
Which of the following sugars are the
components of lactose?
A. glucose & galactose C. glucose & fructose
B. fructose and galactose D. glucose and
glucose
You might also like
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocument15 pagesBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet COT4Document5 pagesActivity Sheet COT4Abbie Gail CabatañaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY: Carbohydrates, Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument41 pagesBIOMOLECULESbam yeontanieNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - MetabolismDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates - MetabolismSathish PillaiNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TDocument28 pagesNutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TAnab ArifNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Power Point-CompleteDocument80 pagesCarbohydrates Power Point-CompleteJocel Rose TorresNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesidkmyname100% (5)
- What Are Carbohydrates?Document1 pageWhat Are Carbohydrates?Inês CarmoNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document12 pagesWeek 1Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesDocument14 pagesAsia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesJake LaylaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument64 pagesBiology ReportChelo IlagNo ratings yet
- Registration For Wiki Conference India 2011Document3 pagesRegistration For Wiki Conference India 2011ajaylove3733No ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument20 pagesBIOLOGYBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Disaccharide QuestionsDocument2 pagesDisaccharide QuestionsMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- q4 Module 2 CompressedDocument4 pagesq4 Module 2 CompressedFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- Introduction To MacronutrientsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To MacronutrientsBenard NyaumaNo ratings yet
- Ahn-Unit 2Document21 pagesAhn-Unit 2Dilshad TasnimNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 5 & 6. Function of CarbohydratesDocument25 pagesLecture No 5 & 6. Function of Carbohydratesmaryam khanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 4th Quarter Week 3Document12 pagesGrade 10 4th Quarter Week 3KarenNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document55 pagesUnit 8Rediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PresentationDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates PresentationRahmayuni FItrianti100% (2)
- VojoyDocument7 pagesVojoyFerds SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesCarbohydratesSHIFA ALTAFNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersDocument5 pagesLecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersNikhil TutejaNo ratings yet
- Carb Digestion & MetabolismDocument112 pagesCarb Digestion & MetabolismOltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALDocument19 pagesAsynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Carb Energy: Guide to Carbohydrates (CHODocument6 pagesCarb Energy: Guide to Carbohydrates (CHOIra Lilian DumadaugNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates Notesaliasger786inNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesCarbohydratesstudents athloneNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesCris PorlasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateDocument24 pagesLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashir100% (1)
- SCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 3)Document4 pagesSCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 3)Sitti Rohima MarajanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 3)Document4 pagesSCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 3)Sitti Rohima MarajanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument35 pagesCarbohydratesJaezean Jules B. GomezNo ratings yet
- I. CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesI. CarbohydratescelynjasminegNo ratings yet
- Human Biology and HealthDocument14 pagesHuman Biology and HealthYegna LemaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Topic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20Document20 pagesTopic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20lisaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About CarbohydratesDocument46 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Carbohydratesaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: How the Body Breaks Down and Uses Carbs for EnergyDocument16 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: How the Body Breaks Down and Uses Carbs for Energyalexa manatadNo ratings yet
- Lesson On CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesLesson On CarbohydratesTweenieSumayanMapandiNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- I Dun Like Study (Print Ver) - Levi FINALDocument12 pagesI Dun Like Study (Print Ver) - Levi FINALlevisha suppiahNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Have The General Molecular Formula CH2ODocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Have The General Molecular Formula CH2OIaa Eewi'No ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesModule 1 CarbohydratesBig BrotherNo ratings yet
- What Role Do Carbohydrates Play in Metabolism?Document3 pagesWhat Role Do Carbohydrates Play in Metabolism?alexa manatadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Biomolecules ReviewerDocument15 pagesLesson 3 Biomolecules Reviewerjohnromar VilasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument6 pagesTopic 1 Carbohydrates and LipidsAddan AddanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Sources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Document10 pagesSources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Narges Malik100% (1)
- Carbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCarbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesMonica CreangaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesChemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Types of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesTypes of CarbohydratesGarcia LovelyzilNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesCarbohydratesSurbhi JainNo ratings yet
- CatalystDocument28 pagesCatalystgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Calculate The Production Input and OutputDocument5 pagesCalculate The Production Input and Outputgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Demo 2nd QDocument36 pagesDemo 2nd Qgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Non - Parametric TestsDocument8 pagesNon - Parametric Testsgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument70 pagesCarbohydrates NotesRavindra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Carbohydrates IntroductionDocument17 pagesLecture 1-Carbohydrates IntroductionOwor OrikoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates TestsDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates TestsTk MakotoseNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument29 pagesIlovepdf MergedJhanin steph BelloNo ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers - Module 2-Biomolecules-09.10.2020Document25 pagesBiology For Engineers - Module 2-Biomolecules-09.10.2020PRAMODH R PRAMODH RNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Biochemistry IDocument59 pagesCarbohydrates: Biochemistry IanaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology Q3Document3 pagesAdvanced Biology Q3MARITHE ROJIANNE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Proteins, amino acids and enzymesDocument6 pagesProteins, amino acids and enzymesChandrapal RathoreNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesLesson 2 - CarbohydratesWycliffe AsmanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NcertDocument28 pagesBiomolecules NcertB. Rajeev Kungur80% (5)
- Chapter 11: Sugars and Polysaccharides MatchingDocument14 pagesChapter 11: Sugars and Polysaccharides MatchingEnjie ElrassiNo ratings yet
- Carbs: Energy Storage, Structural Roles and MoreDocument75 pagesCarbs: Energy Storage, Structural Roles and MoreRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Tests Identify XyloseDocument7 pagesGeneral and Specific Tests Identify XyloseAudrey DiolataNo ratings yet
- Functions of CarbohydrateDocument9 pagesFunctions of CarbohydratekwinixxNo ratings yet
- 01 CarbohydratesDocument119 pages01 CarbohydratesDesiree LadabanNo ratings yet
- AUCET - 2011 SyllabusDocument39 pagesAUCET - 2011 SyllabussnagabiruNo ratings yet
- CHO Classification, Example, Chemical Structure, FuctiDocument108 pagesCHO Classification, Example, Chemical Structure, FuctiYo'el Onaznam50% (2)
- Syllabus 2020Document66 pagesSyllabus 2020NarasimharaoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Empirical Formula and Identification of a Substance from Combustion AnalysisDocument2 pagesDetermination of Empirical Formula and Identification of a Substance from Combustion AnalysisELSA OKTAVIANI SOPYANNo ratings yet
- Pattern Matching: Classifying Organic MoleculesDocument8 pagesPattern Matching: Classifying Organic MoleculesBhaavana AnnaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NEET 2022 Biomolecules VMC Module: 20 August 1779 Väversunda,, 7 August 1848 (Aged 68), SwedenDocument52 pagesChemistry NEET 2022 Biomolecules VMC Module: 20 August 1779 Väversunda,, 7 August 1848 (Aged 68), SwedenMISHANo ratings yet
- New A Level Teacher Notes Part 1Document165 pagesNew A Level Teacher Notes Part 1James ChongNo ratings yet
- Structure of GlucoseDocument3 pagesStructure of Glucoseuserdev987No ratings yet
- Biology Unit # 1 Module 1 - Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument15 pagesBiology Unit # 1 Module 1 - Cell and Molecular BiologyLton LuisNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Properties of CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesStructural and Functional Properties of Carbohydratesroncv100% (1)
- Biochemistry - WikipediaDocument14 pagesBiochemistry - WikipediaAchilles ManthosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xam IdeaDocument9 pagesChemistry Xam Ideagowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- Polysaccharides Structural Diversity and Functional VersalityDocument1,223 pagesPolysaccharides Structural Diversity and Functional VersalityTueNo ratings yet