Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Titrations 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106
Uploaded by
JoeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Titrations 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106
Uploaded by
JoeCopyright:
Available Formats
TITRATIONS 2
3 3 3
1 25.0 cm of a solution of sodium hydroxide solution required 21.5 cm of 0.100 mol/dm sulfuric acid for neutralisation.
H2SO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
3
a Find the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution in mol/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3
b Find the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution in g/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3 3 3
2 Find the volume of 1.20 mol/dm hydrochloric acid that reacts with 25.0 cm of 1.50 mol/dm sodium hydroxide. Give
your answer to 3 significant figures.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3 3 3
3 25.0 cm of arsenic acid, H3AsO4, required 37.5 cm of 0.100 mol/dm sodium hydroxide for neutralisation.
3 NaOH(aq) + H3AsO4(aq) → Na3AsO4(aq) + 3 H2O(l)
3
a Find the concentration of the arsenic acid in mol/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3
b Find the concentration of the arsenic acid in g/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3 3 3
4 What volume of 0.0400 mol/dm calcium hydroxide just neutralises 25.0 cm of 0.100 mol/dm nitric acid? Give your
answer to 3 significant figures
Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2 HNO3(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106
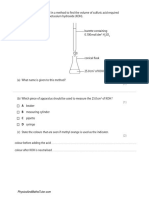
5 A series of titrations was carried out to find the concentration of the ethanoic acid in white vinegar.
CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa (aq) + H2O(l)
3
In each titration, a student placed 25.0 cm samples of the vinegar in a conical flask. She then added a few drops of the
3
indicator phenol red. She titrated the vinegar against a solution of sodium hydroxide with concentration 0.100 mol/dm .
She recorded the results in the table below.
titration 1 titration 2 titration 3 titration 4
3
start reading / cm 0.0 23.5 0.1 22.8
3
final reading / cm 23.5 46.9 22.8 46.1
3
volume used / cm
3
a Name the piece of apparatus that should be used to measure the 25.0 cm samples of the vinegar into the conical
flask.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
b Name the piece of apparatus that is used for the sodium hydroxide solution.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
c Complete the table to show the volume used in each titration.
d Calculate the mean volume of sodium hydroxide, leaving out any anomalous results.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3
e Find the concentration of the ethanoic acid in mol/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
3
f Find the concentration of the ethanoic acid in g/dm . Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
g Explain why this titration may have been difficult to do with brown vinegar.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………….
Area Strength To develop Area Strength To develop Area Strength To develop
Done with care and thoroughness Can convert mol/dm3 to g/dm3 Can find mean (excluding anomalous)
Shows suitable working Does not round too much Understands issue of coloured solution
Can work out moles from conc & vol Can use sig figs Gives units
Uses equation for other reactant moles Can use readings to find titres
Can find conc or vol of other reagent Can name suitable apparatus
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106
You might also like
- Chemsheets GCSE 1106 (Titrations 2)Document2 pagesChemsheets GCSE 1106 (Titrations 2)J 6342No ratings yet
- C4.8 CalculationsChemsheets GCSE 1105 (Titrations 1)Document2 pagesC4.8 CalculationsChemsheets GCSE 1105 (Titrations 1)Bee AbeilleNo ratings yet
- Titrations 1Document2 pagesTitrations 1kayo lumasyNo ratings yet
- 1279 Calculations Mixture 3Document2 pages1279 Calculations Mixture 3Mo2279No ratings yet
- Paper 3 Practice Paper 4Document22 pagesPaper 3 Practice Paper 4EmoryNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 3 QPDocument9 pagesRate of Reaction 3 QPPirate HunterNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Assessed HomeworkDocument8 pages1.2 Assessed HomeworkNavine NavNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases Al Q& ADocument99 pagesAcids Bases Al Q& ABaanu ThushyanthanNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance Assessed HomeworkDocument15 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance Assessed Homeworkkarima akterNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Value of The Acid Dissociation Constant, K: Year 2 - Acids and BasesDocument99 pagesQ1. The Value of The Acid Dissociation Constant, K: Year 2 - Acids and BasesshradhaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Action 1 QPDocument8 pagesBuffer Action 1 QPvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Calculations QuestionsDocument14 pagesCalculations Questionsan7li721No ratings yet
- Buffer Action 5 QPDocument7 pagesBuffer Action 5 QPvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet C6.04Document3 pagesWorksheet C6.04anduushNo ratings yet
- Standardisation of HCLDocument6 pagesStandardisation of HCLRicardo AndersonNo ratings yet
- Module 20A Paper 3Document11 pagesModule 20A Paper 3Mohd HafiezNo ratings yet
- Titration Calculations 1Document55 pagesTitration Calculations 1Segun HursheeNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance TestDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance Testkarima akterNo ratings yet
- 9701 w16 QP 53Document12 pages9701 w16 QP 53Ahmed AttaNo ratings yet
- Using Conc. of Solutions in Mol (DM) - 3 QPDocument15 pagesUsing Conc. of Solutions in Mol (DM) - 3 QPw276No ratings yet
- Mohamed Bulbul - Acids, Alkalis and Titrations QPDocument15 pagesMohamed Bulbul - Acids, Alkalis and Titrations QPMohamed BulbulNo ratings yet
- Atp Titartion and Salt Anaylasis Code-0030Document4 pagesAtp Titartion and Salt Anaylasis Code-0030zafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance 2 QPDocument13 pagesAmount of Substance 2 QPSheikhNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document23 pagesQuiz 1FIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 19Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 19Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Document20 pagesA-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Jesus ChristNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerine, C3H5N3O9, Is An Explosive Which, On Detonation, Decomposes RapidlyDocument14 pagesNitroglycerine, C3H5N3O9, Is An Explosive Which, On Detonation, Decomposes Rapidlyapi-25909541No ratings yet
- 2019 Chem Skills PaperDocument10 pages2019 Chem Skills PaperVictor GuanNo ratings yet
- Module 8A Acid and BasesDocument6 pagesModule 8A Acid and BasesMohd HafiezNo ratings yet
- As-Level Paper 1 pp9Document15 pagesAs-Level Paper 1 pp9ConorNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 ChemDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 ChemFIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- 525 1 Eot 3 2022Document17 pages525 1 Eot 3 2022OTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 18Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 18Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry AFL QPDocument4 pagesStoichiometry AFL QPdrake lordNo ratings yet
- Acid and Bases QuestDocument4 pagesAcid and Bases QuestSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Chem SS2 Practical 2022 First TermDocument4 pagesChem SS2 Practical 2022 First TermUgbede Huxley HarunaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Exam Questions 3Document18 pagesAcid-Base Exam Questions 3Jake RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Equilibria A2Document48 pagesEquilibria A2javedkaleemNo ratings yet
- MHCO3Document5 pagesMHCO3patrice green - SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Buffer Action 3 QPDocument8 pagesBuffer Action 3 QPvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Aceiteka Chem3.o 2023Document6 pagesAceiteka Chem3.o 2023EMMANUEL BIRUNGINo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument84 pagesAcid BaseRyantyler13No ratings yet
- S6 139 1587157907Document8 pagesS6 139 1587157907AYEBAZIBWE EDWINNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 U2 Chem RedoxDocument34 pagesAssignment 4 U2 Chem RedoxMoshiurNo ratings yet
- S.4 Chem P3 KololoDocument6 pagesS.4 Chem P3 KololoW. Joseph the chemistNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Titration Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesIGCSE Titration Practice Questionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certifi Cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certifi Cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 9701 m16 QP 52Document8 pages9701 m16 QP 52SanthiKalyanaGrantNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDocument9 pagesBritish International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment ChemistryDocument9 pagesBritish International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment ChemistryHarry SonNo ratings yet
- ALHAIL PRIVATE SCHOOL 9 2nd WorksheetDocument15 pagesALHAIL PRIVATE SCHOOL 9 2nd WorksheetdodoNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 2CR Que 20160615Document20 pages4CH0 2CR Que 20160615abhayNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Amount of Substance TestDocument8 pages1.2 Amount of Substance Testviyas07No ratings yet
- 1.2 Assessed HomeworkDocument8 pages1.2 Assessed HomeworkJeew HemrajNo ratings yet
- WS2 Molesgr9Document6 pagesWS2 Molesgr9irabedi9No ratings yet
- S.4 Mock Chem Paper 4Document7 pagesS.4 Mock Chem Paper 4W. Joseph the chemistNo ratings yet
- Accounting QuestionDocument25 pagesAccounting Questionmay thansinNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles of Medical UltrasonicsFrom EverandPhysical Principles of Medical UltrasonicsC. R. HillNo ratings yet
- C10.3 Student Practical: Comparing The Reactions of AlcoholsDocument5 pagesC10.3 Student Practical: Comparing The Reactions of AlcoholsJoeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsDocument2 pagesChemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- C4 Chemical Calculations Exam-Style Questions: (1 Mark)Document4 pagesC4 Chemical Calculations Exam-Style Questions: (1 Mark)JoeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsDocument2 pagesChemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsJoeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupDocument2 pagesAlcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- $RKT717YDocument10 pages$RKT717YJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- Questions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsDocument36 pagesQuestions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsJoeNo ratings yet
- $RI751EEDocument13 pages$RI751EEJoeNo ratings yet
- $RPDLGVLDocument42 pages$RPDLGVLJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Infection and ResponseDocument16 pagesAQA GCSE Infection and ResponseJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- $RUUARVPDocument27 pages$RUUARVPJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Infection and ResponseDocument16 pagesAQA GCSE Infection and ResponseJoeNo ratings yet
- $RPDLGVLDocument42 pages$RPDLGVLJoeNo ratings yet
- $ROYVKDKDocument34 pages$ROYVKDKJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Cell Biology: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument10 pagesAQA GCSE Cell Biology: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- $RUUARVPDocument27 pages$RUUARVPJoeNo ratings yet
- $ROYVKDKDocument34 pages$ROYVKDKJoeNo ratings yet
- $RI751EEDocument13 pages$RI751EEJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- Questions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsDocument36 pagesQuestions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsJoeNo ratings yet
- TYPE A - Real Time Quiz End Semester Examination - ME331Document7 pagesTYPE A - Real Time Quiz End Semester Examination - ME331Selvi RNo ratings yet
- Colori Siser-HiresDocument6 pagesColori Siser-HiresjohnNo ratings yet
- Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Document17 pagesAakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Indian VanguardsNo ratings yet
- 4311Document2 pages4311mboraeskiNo ratings yet
- Osha PelsDocument30 pagesOsha PelshydroNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of High Purity Hydroxyapatite Nanopowder Via Sol-Gel Combustion Process PDFDocument5 pagesSynthesis of High Purity Hydroxyapatite Nanopowder Via Sol-Gel Combustion Process PDFfishvalNo ratings yet
- Fischer Tropsch - Process 2Document14 pagesFischer Tropsch - Process 2bryan lillibridgeNo ratings yet
- 00 - WWT EngineeringDocument188 pages00 - WWT EngineeringFaisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Memo 097.7 - 032822 - Hazard Pay Guidelines DPWH Personnel Exposed To Hazardous Substances Pollution Control OfficersDocument4 pagesMemo 097.7 - 032822 - Hazard Pay Guidelines DPWH Personnel Exposed To Hazardous Substances Pollution Control Officersbrian paulNo ratings yet
- HPS Product CatalogDocument76 pagesHPS Product CatalogLuis Avit Medina QuispeNo ratings yet
- Protein ArrayDocument21 pagesProtein Arrayryu rayNo ratings yet
- Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument14 pagesMelting Point and Boiling PointMALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical Sludge Handling Study GuideDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Sludge Handling Study GuideBuenaventura Jose Huamani TalaveranoNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures Practice Worksheet: Draw The Lewis Structures For The Following Compounds: 1) PBRDocument2 pagesLewis Structures Practice Worksheet: Draw The Lewis Structures For The Following Compounds: 1) PBRabvajaNo ratings yet
- MSDS CC 6097-100-A96Document18 pagesMSDS CC 6097-100-A96NDRUPADRI PRATIWINo ratings yet
- '-Daftar Harga Reagen LabtestDocument1 page'-Daftar Harga Reagen LabtestUPT Labkes R/LNo ratings yet
- The Nature Reduced and Excited States of r-Electron-Deficient Complexes Between Re (CO) 3halDocument6 pagesThe Nature Reduced and Excited States of r-Electron-Deficient Complexes Between Re (CO) 3halPablo MellaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Rganic Chemistry Note For Year I PharmacyDocument151 pagesFundamentals of Rganic Chemistry Note For Year I PharmacySelam 1No ratings yet
- VADOSE ZONE Microbial EcologyDocument9 pagesVADOSE ZONE Microbial EcologySh MbaNo ratings yet
- Xpert MTB-XDR ENGLISH Package Insert 302-3514 Rev BDocument40 pagesXpert MTB-XDR ENGLISH Package Insert 302-3514 Rev BEric MaumejeanNo ratings yet
- Mariane Rabelo - Artigo QuakerDocument10 pagesMariane Rabelo - Artigo QuakerTibis GNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties 1Document80 pagesElectrical Properties 1SarumathiNo ratings yet
- Microplastic in CosmeticsDocument40 pagesMicroplastic in CosmeticsTavishi DarbariNo ratings yet
- 4 Principles and Concepts of Laboratory Design and Ventilation - 4Document93 pages4 Principles and Concepts of Laboratory Design and Ventilation - 4rizky anandaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityDocument13 pagesCell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityRohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- TFYA30 Supramolecular Chemistry: OrganizationDocument16 pagesTFYA30 Supramolecular Chemistry: OrganizationSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- Dunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - HTMLDocument38 pagesDunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - HTMLForbes Kamba100% (1)
- Charcoal Kettle Barbecue With Interchangeable GrateDocument36 pagesCharcoal Kettle Barbecue With Interchangeable Gratem mNo ratings yet
- MSDS MB-215 (SDS EN 20160322) EnglishDocument6 pagesMSDS MB-215 (SDS EN 20160322) EnglishJust Rysdan100% (1)