Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: Acids
Uploaded by
Joe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesChemisty
Original Title
$R6C95FD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChemisty
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesChemical Changes Mastery Part 4: Acids
Uploaded by
JoeChemisty
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: Acids
Acids and metals
Acids are substances that have a pH of less than 7. Alkalis have a pH of more than 7. A pH of 7 exactly is called a neutral
solution.
The three main acids are:
• Hydrochloric acid: HCl(aq)
• Nitric acid: HNO3(aq)
• Sulfuric acid: H2SO4(aq)
Each of these splits up into ions when dissolved in water:
• HCl splits into H+ and Cl-
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
• HNO3 splits into H+ and NO3-
HNO3 (aq) → H+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
• H2SO4 splits into 2H+ and SO42-
H2SO4 (aq) → 2H+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
It is the H+ which makes them acidic, and the pH scale is based on how much H+ there is present. The more H+, the lower the
pH.
1. Reactions of acids with metals
When a metal is added to acid, it will react to form a salt and hydrogen gas. A salt is a compound where the hydrogen from an
acid has been replaced with a metal. For example:
Calcium + sulfuric acid calcium sulfate + hydrogen
Ca(s) + H2SO4(aq) CaSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Here, the hydrogens from the sulfuric acid have been replaced by calcium.
• Hydrochloric acid makes metal chlorides
• Nitric acid makes metal nitrates
• Sulfuric acid makes metal sulfates
1. Complete the table below. The first one has been done for you
Formula of salt Name of salt Original metal Original acid
NaCl Sodium chloride Sodium Hydrochloric acid
LiCl Lithium chloride Lithium Hydrochloric acid
CaSO4 Calcium sulfate Calcium Sulfuric acid
MgSO4 Magnesium sulfate Magnesium Sulfuric acid
KNO3 Potassium nitrate Potassium Nitric acid
2. Write a word equation for the reactions between:
a. Aluminium and hydrochloric acid
Aluminium + hydrochloric acid → aluminium chloride + hydrogen
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
b. Magnesium and hydrochloric acid
magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
c. Calcium and nitric acid
calcium + nitric acid → calcium nitrate + hydrogen
Ca + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2
d. Beryllium and sulfuric acid
beryllium + sulfuric acid → beryllium sulfate + hydrogen
Be + H2SO4 → Be SO4 + H2
e. Iron and sulfuric acid
iron + sulfuric acid → iron(II) sulfate + hydrogen
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
OR
iron + sulfuric acid → iron(III) sulfate + hydrogen
2Fe + 3H2SO4 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 3H2
3. Write a word equation for a reaction which forms:
f. Aluminium sulfate
aluminium + sulfuric acid → aluminium sulfate + hydrogen
2Al + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
g. Calcium chloride
calcium + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + hydrogen
Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2
h. Barium nitrate
barium + nitric acid → barium nitrate + hydrogen
Ba + 2HNO3 → Ba(NO3)2 + H2
i. Rubidium chloride
rubidium + hydrochloric acid → rubidium chloride + hydrogen
2Rb + 2HCl → RbCl + H2
Challenge: write symbol equations for every reaction in Q2 and Q3
You might also like
- Acids and BasesDocument73 pagesAcids and Basesapi-305909325100% (4)
- RNA and Protein Synthesis QuizDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis QuizJeremy Guggenheim100% (2)
- Nickle Based SuperalloyDocument25 pagesNickle Based SuperalloyLavesh Kumar100% (1)
- Preparing Common Salts G8Document21 pagesPreparing Common Salts G8shanaayaa kunder100% (1)
- B.K Dutta - TextDocument957 pagesB.K Dutta - TextRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Arlan Neutralization WorksheetDocument3 pagesArlan Neutralization WorksheetHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Quiz ChemDocument4 pagesQuiz ChemCherryNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science Worksheet ReactionsDocument7 pagesYear 10 Science Worksheet ReactionsLachlanNo ratings yet
- Solution 805196Document4 pagesSolution 805196scNo ratings yet
- Preparing Common Salts G8Document20 pagesPreparing Common Salts G8diamehta1512No ratings yet
- Reactions of AcidsDocument27 pagesReactions of AcidsLawrenceNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlkalisDocument3 pagesPhysical Properties of AlkalisTravel Unlimited0% (1)
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Salts FormationDocument19 pagesSalts FormationUrwa Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
- Writing and Balancing EquationsDocument22 pagesWriting and Balancing EquationsMannat KHICHA [07R17M]No ratings yet
- Reactions You Need To Know - Inorganic ChemDocument7 pagesReactions You Need To Know - Inorganic ChemSaad AatirNo ratings yet
- Viva 1Document4 pagesViva 1Nao tomoriNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument6 pagesAcid Base and SaltRajnish kumarNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter-4: Answer To The Short QuestionsDocument17 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Chapter-4: Answer To The Short Questionskawsar22No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts ADocument7 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts AYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acids + CarbonatesDocument13 pagesAcids + CarbonatesVithuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equation ExerciseDocument2 pagesChemical Equation ExerciseMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab 21Document3 pagesLab 21KeenanNo ratings yet
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquationDocument2 pagesChemical EquationChris McLeanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document (1)Document4 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document (1)dalvishreyhansNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideDocument5 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Document3 pages8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Stephan MinhNo ratings yet
- Chem 115: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesChem 115: Types of Chemical ReactionsJhin KhadaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document12 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4api-292313678No ratings yet
- REACTION OF METALS WITH ACIDS AND SALTSDocument3 pagesREACTION OF METALS WITH ACIDS AND SALTSDarshanaK 728714No ratings yet
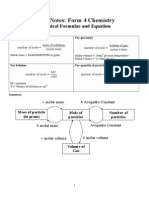
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationJasmeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- NeutralizationDocument13 pagesNeutralizationbarakahmuluziNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Chemical Word: EquationsDocument20 pagesChemistry: Chemical Word: EquationsPrimoNo ratings yet
- Word Equation PracticeDocument20 pagesWord Equation PracticePrimoNo ratings yet
- Equations Involving AcidsDocument1 pageEquations Involving AcidsYoussef AmrNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsbubutrain2003No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument18 pagesAcid BasechaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sulphuric Acid SolutionsDocument7 pagesChemistry Sulphuric Acid SolutionsGurjapsingh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Class XDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions Class Xaprajita royNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Document5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Gopal PenjarlaNo ratings yet
- General EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral EquationsPyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- Topic7-Oxides and Salts-L2Document43 pagesTopic7-Oxides and Salts-L2haotongxu14No ratings yet
- Assignment Neutralisation Reaction Answer KeyDocument1 pageAssignment Neutralisation Reaction Answer KeyMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- 10 TH Acids, Bases, and Salts ChemistryDocument12 pages10 TH Acids, Bases, and Salts ChemistryShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- (AGRIPA, DARYLL A. DDM1) Balancing - and - Prediction - Products - For - Chemical - ReactionsDocument7 pages(AGRIPA, DARYLL A. DDM1) Balancing - and - Prediction - Products - For - Chemical - ReactionsDaryll AgripaNo ratings yet
- Acids: Common Acids in Daily LifeDocument47 pagesAcids: Common Acids in Daily LifeElanIe InspiritNo ratings yet
- Booklet On Acid and Base and Redox MSDocument43 pagesBooklet On Acid and Base and Redox MShalahossam8899No ratings yet
- Acids and Carbon Dioxide Reactions Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesAcids and Carbon Dioxide Reactions Worksheet Answersmintesinot esayasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Element Making Salts: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDocument17 pagesLesson Element Making Salts: Instructions and Answers For TeachersGracey- Ann JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CA DEM Y: Chapter - 2 - NOTESDocument2 pagesCA DEM Y: Chapter - 2 - NOTESvarun puriNo ratings yet
- Acids RecallDocument4 pagesAcids RecallAssumpta McguckinNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989564Document6 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989564abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Study Sulphuric Acid Properties UsesDocument4 pagesStudy Sulphuric Acid Properties UsesKavya YadavNo ratings yet
- Complete Inorganic in One Shot PDFDocument21 pagesComplete Inorganic in One Shot PDFADITYA PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsDocument7 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsView TubeNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)Document14 pagesCBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)aanwidivNo ratings yet
- 8A Salts - AnswerDocument14 pages8A Salts - AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument14 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationanisnazihahNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- Titrations 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106Document2 pagesTitrations 2: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 22-May-2018 Chemsheets GCSE 1106JoeNo ratings yet
- C10.3 Student Practical: Comparing The Reactions of AlcoholsDocument5 pagesC10.3 Student Practical: Comparing The Reactions of AlcoholsJoeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupDocument2 pagesAlcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupJoeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsDocument2 pagesChemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsJoeNo ratings yet
- $RI751EEDocument13 pages$RI751EEJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- C4 Chemical Calculations Exam-Style Questions: (1 Mark)Document4 pagesC4 Chemical Calculations Exam-Style Questions: (1 Mark)JoeNo ratings yet
- $RKT717YDocument10 pages$RKT717YJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Infection and ResponseDocument16 pagesAQA GCSE Infection and ResponseJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- $RPDLGVLDocument42 pages$RPDLGVLJoeNo ratings yet
- Questions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsDocument36 pagesQuestions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- Ancestral Species TimesDocument27 pagesAncestral Species TimesJoeNo ratings yet
- $ROYVKDKDocument34 pages$ROYVKDKJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Infection and ResponseDocument16 pagesAQA GCSE Infection and ResponseJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Cell Biology: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument10 pagesAQA GCSE Cell Biology: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- $RPDLGVLDocument42 pages$RPDLGVLJoeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- $RI751EEDocument13 pages$RI751EEJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- Ancestral Species TimesDocument27 pagesAncestral Species TimesJoeNo ratings yet
- $ROYVKDKDocument34 pages$ROYVKDKJoeNo ratings yet
- Questions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsDocument36 pagesQuestions: Q1. Transport and Exchange of MaterialsJoeNo ratings yet
- Biocementation Effects on Cement MaterialsDocument17 pagesBiocementation Effects on Cement Materialsmr robartNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4: Materials: Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesChapter - 4: Materials: Metals and Non MetalsDyah IndraNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument15 pagesPhysical ScienceemNo ratings yet
- Formative Quiz 4 PS 3rd QuarterbqbqbqDocument2 pagesFormative Quiz 4 PS 3rd QuarterbqbqbqjajajajNo ratings yet
- Chem Form One Midterm (1) Page 1Document5 pagesChem Form One Midterm (1) Page 1nerrick thiakaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemical BondingDocument10 pagesGrade 9 Chemical BondingAmonique DaveyNo ratings yet
- 3.17 Enthalpies of Solution: Using Hess's Law To Determine Enthalpy Changes of Solution Enthalpy of SolutionDocument4 pages3.17 Enthalpies of Solution: Using Hess's Law To Determine Enthalpy Changes of Solution Enthalpy of SolutionshowhardoNo ratings yet
- US5198281 Towpreg FabricDocument20 pagesUS5198281 Towpreg FabricyigitilgazNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Chapter 13Document46 pagesGeneral Chemistry Chapter 13SEMİH PALAZNo ratings yet
- Celazole PBI U 60 Typical PropertiesDocument4 pagesCelazole PBI U 60 Typical PropertiesnomeNo ratings yet
- Forging Processes MEE 3024 2014Document25 pagesForging Processes MEE 3024 2014Ali M. ElghawailNo ratings yet
- Problem 26 Chemical Structure and Absolute Stereochemistry of ConiineDocument6 pagesProblem 26 Chemical Structure and Absolute Stereochemistry of ConiineLê Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering JournalDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering JournalAgrimart IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Study of Organic-HF Blends Leads To Improved FluidsDocument4 pagesChemical Study of Organic-HF Blends Leads To Improved FluidsAymen KASMINo ratings yet
- Safe MaticDocument4 pagesSafe Maticsulai2000No ratings yet
- Properties Materials 5Document8 pagesProperties Materials 5ayariseifallahNo ratings yet
- ChromophoresDocument2 pagesChromophoresArshdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- MSDS All DNA RNA Purification KitsDocument6 pagesMSDS All DNA RNA Purification Kitsjusman sadorraNo ratings yet
- Railway Internship FINAL REPORTDocument62 pagesRailway Internship FINAL REPORTsubhendu sardarNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pharmacy PDFDocument692 pagesIntegrated Pharmacy PDFBrhanu belay100% (1)
- Exp 5 Lit ReviewDocument3 pagesExp 5 Lit ReviewDhanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Holt Chapter 3 PPT 07Document44 pagesBiology Holt Chapter 3 PPT 07Dini HanifaNo ratings yet
- MFL Tank Cleaning Requirements for InspectionDocument2 pagesMFL Tank Cleaning Requirements for Inspectioncal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Faradays 1 Law of Electrolysis States That The Mass of A Substance Produce, Liberated At/ or DissolvedDocument3 pagesFaradays 1 Law of Electrolysis States That The Mass of A Substance Produce, Liberated At/ or DissolvedAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- J.C. Bose University of Science and Technology, Ymca, FaridabadDocument18 pagesJ.C. Bose University of Science and Technology, Ymca, FaridabadSumit MeghNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument2 pagesIonic Equilibriumpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Attempted Organic Synthesis of Two Nitrated Benzene Com-PoundsDocument4 pagesAttempted Organic Synthesis of Two Nitrated Benzene Com-PoundskhekhyNo ratings yet