Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Forecasting For Strategic Growth
Uploaded by
Elizabeth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesLong-range financial planning establishes guidelines for strategic growth and change in a firm by systematically anticipating problems and formulating financial goals. Planning involves considering both short-term (12 months) and long-term (2-5 years) horizons, as well as aggregating individual investment projects. Financial planning provides benefits such as exploring different scenarios, identifying issues, ensuring consistency, and establishing alternative courses of action. Models for financial planning include assumptions about the economic environment, sales forecasts, pro forma financial statements, asset requirements, financial requirements, and calculating additional funds needed based on changes in assets, liabilities, and retained earnings.
Original Description:
Original Title
FINANCIAL FORECASTING FOR STRATEGIC GROWTH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLong-range financial planning establishes guidelines for strategic growth and change in a firm by systematically anticipating problems and formulating financial goals. Planning involves considering both short-term (12 months) and long-term (2-5 years) horizons, as well as aggregating individual investment projects. Financial planning provides benefits such as exploring different scenarios, identifying issues, ensuring consistency, and establishing alternative courses of action. Models for financial planning include assumptions about the economic environment, sales forecasts, pro forma financial statements, asset requirements, financial requirements, and calculating additional funds needed based on changes in assets, liabilities, and retained earnings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesFinancial Forecasting For Strategic Growth
Uploaded by
ElizabethLong-range financial planning establishes guidelines for strategic growth and change in a firm by systematically anticipating problems and formulating financial goals. Planning involves considering both short-term (12 months) and long-term (2-5 years) horizons, as well as aggregating individual investment projects. Financial planning provides benefits such as exploring different scenarios, identifying issues, ensuring consistency, and establishing alternative courses of action. Models for financial planning include assumptions about the economic environment, sales forecasts, pro forma financial statements, asset requirements, financial requirements, and calculating additional funds needed based on changes in assets, liabilities, and retained earnings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
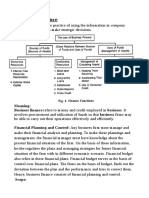
FINANCIAL FORECASTING FOR STRATEGIC GROWTH
Long-range planning is a means of systematically thinking about the future and anticipating possible
problems before they occur. Financial planning formulates the way in which financial goals are to be
achieved. It establishes guidelines for change and growth in a firm.
First dimension of the planning process: Planning Horizon
For planning purposes, it is often useful to think of the future as having a short run and a long-run. The
short-run planning, in practice, usually covers the coming 12 months while financial planning over the
long-run takes to be the coming two to five years.
Second dimension of the planning process: Level of Aggregation
Aggregation involves the determination of all of the individual projects together with the investment
required that the firm will undertake and adding up these investment proposals to determine the total
needed investment which is treated as one big project.
BENEFITS OF FINANCIAL PLANNING
1. It provides a rational way to develop, analyze and compare many different business scenarios;
various investment and financing options can be explored, and their impact on the firm's
shareholders can be evaluated.
2. It enables the proponents to show explicitly the linkages between investment proposals for the
different operating activities of the firm and its available financing choices.
3. Possible problems related to the proposal projects are identified actions to address them are
studied. Thus, one objective of financial planning is to avoid surprises and develop contingency
plans.
4. It verifies that the goals and plans made for specific areas of a firm's operations are feasible and
internally consistent. It also imposes a unified structure for reconciling goals and objectives
5. Directions that the firm would take are established, risks are calculated and educated
alternative courses of action are considered thoroughly.
FINANCIAL PLANNING MODELS
1. Economic Environment Assumption. The plan will have to state explicitly the economic
environment in which the firm expects to reside over the life of the plan, such as inflation rates,
level of interest rates and the firm's tax rate.
2. Sales Forecast. Planning will focus on projected future sales and the assets and financing
needed to support those sales, usually given as the growth rate in sales. Determinants of growth
rates are profit margin, dividend policy, financial policy, and total asset turnover.
3. Pro forma Statements. Planning makes projection of future statements: financial position,
income, cash flows, and stockholders’ equity.
4. Asset Requirement. The financial plan will describe projected capital spending.
5. Financial Requirements. The financial plan will include a section about the necessary financing
arrangements: dividend policy and debt policy.
6. Additional Funds Needed (AFN). The financial plan should determine the funds to be raised for
the expansion of its business.
AFN = Required increase in assets – spontaneous increase in liabilities – increase in retained earnings
Where: required increase in assets = change in sales x (present CA/present sales)
Spontaneous increase in liabilities = change in sales x (present CL/present sales)
Increase in retained earnings = earnings after taxes – dividend payment
You might also like
- Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument3 pagesFinancial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthVergel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Financial Forecasting for Strategic GrowthDocument17 pagesFinancial Forecasting for Strategic GrowthArmand RoblesNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument4 pagesFinancial PlanningTemesgen LealemNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument20 pagesTopic 5 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthIrene KimNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning Unit-IIDocument9 pagesFinancial Planning Unit-IIRam PriyaNo ratings yet
- Financial MGMT MODULE 2Document7 pagesFinancial MGMT MODULE 2Isabelle MariaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument17 pagesGroup 1 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthZirah Mae NiepesNo ratings yet
- FM 8 Module 1 Financial Planning and ForecastingDocument16 pagesFM 8 Module 1 Financial Planning and ForecastingJasper Mortos VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financial PlanningDocument12 pagesCorporate Financial PlanningMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Financial Management FunctionsDocument9 pagesFinancial Management FunctionsGely MhayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthMa. Jhoan DailyNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument5 pagesFinancial PlanningNamy Lyn GumameraNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Importance of Financial Planning for BusinessesDocument98 pagesUnderstanding the Importance of Financial Planning for Businessesrey mark hamacNo ratings yet
- Importance of Financial PlanningDocument18 pagesImportance of Financial PlanningSyam LaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FinmanDocument7 pagesModule 1 FinmanJane GalangueNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management: An Approach to Management that Applies Financial Techniques to Strategic Decision MakingDocument23 pagesStrategic Financial Management: An Approach to Management that Applies Financial Techniques to Strategic Decision MakingHoor ul ainNo ratings yet
- MB 0045Document32 pagesMB 0045Kawal Preet Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Financial Forecasting, Planning and ControlDocument32 pagesModule 7 - Financial Forecasting, Planning and ControlemmanvillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Meaning, Objectives and Functions Meaning of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial Management - Meaning, Objectives and Functions Meaning of Financial ManagementsupriyaswainNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I - Financial PlanningDocument5 pagesUNIT - I - Financial PlanningUnmesh SKNo ratings yet
- SFM Unit-1Document25 pagesSFM Unit-1Instagram ReelsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningDocument15 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningSoftware Lab MISKERNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning Tools and ConceptsDocument30 pagesFinancial Planning Tools and ConceptsEarl Concepcion89% (9)
- Modules in Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesModules in Financial ManagementMichael Linard Samiley100% (1)
- Financial Planning and ForcastingDocument34 pagesFinancial Planning and ForcastingFarhan JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Financial ManagementassDocument13 pagesMeaning of Financial ManagementassMayankNo ratings yet
- Financial Managment 1 - Chapter 15Document4 pagesFinancial Managment 1 - Chapter 15lerryroyceNo ratings yet
- Chapt ER: Financial Planning and StrategyDocument16 pagesChapt ER: Financial Planning and StrategySurbhi KambojNo ratings yet
- Financial Management OverviewDocument17 pagesFinancial Management OverviewCzamille Rivera GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial QTN MBADocument10 pagesStrategic Financial QTN MBAMwesigwa DaniNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning: Prepared By: Luigi Miguel B. Antonio, MBADocument20 pagesFinancial Planning: Prepared By: Luigi Miguel B. Antonio, MBAThriztan Andrei BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: 1 Quarter Lesson 3: Financial Planning ProcessDocument6 pagesBusiness Finance: 1 Quarter Lesson 3: Financial Planning ProcessReshaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning GuideDocument3 pagesFinancial Planning GuideChristine PabalanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsDocument13 pagesFinancial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsJose Conrad Nupia BagonNo ratings yet
- SFD NotesDocument125 pagesSFD NotesPampana Sainikhitha9997100% (1)
- Financial Planning and ForecastingDocument15 pagesFinancial Planning and ForecastingGeofrey RiveraNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial ManagementMik MikNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesMeaning of Financial ManagementYummyNo ratings yet
- Financial Management NotesDocument30 pagesFinancial Management NotesChaitanya DongareNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument15 pagesAssignmentagrawal.sshivaniNo ratings yet
- SFMDocument8 pagesSFMSweta BastiaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsNardsdel RiveraNo ratings yet
- FM 1Document7 pagesFM 1Rohini rs nairNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Lessons, 2,3,7,8,9, and 10Document56 pagesBusiness Finance Lessons, 2,3,7,8,9, and 10dollizonmishaeliezerNo ratings yet
- PFP NotesDocument18 pagesPFP NotesSanket CharkhaNo ratings yet
- Financialplanning 160809050639Document27 pagesFinancialplanning 160809050639Janlenn Gepaya100% (1)
- What Is Strategic Financial ManagementDocument10 pagesWhat Is Strategic Financial Managementpra leshNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial ManagementDocument72 pagesStrategic Financial Managementsheila rose lumaygayNo ratings yet
- Financial ForecastingDocument27 pagesFinancial Forecastingcali cdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementKayes Mohammad Bin HossainNo ratings yet
- Fin Management - p2Document37 pagesFin Management - p2Ma. Elene MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I - Strategic Financial Management: - SBAA7003Document125 pagesUNIT - I - Strategic Financial Management: - SBAA7003prakash kamble100% (1)
- ACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyDocument3 pagesACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyAdrienne Nicole MercadoNo ratings yet
- Management Accouning by ADDocument37 pagesManagement Accouning by ADDaniyal AwanNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and ForecastingDocument5 pagesFinancial Planning and ForecastingPRINCESS HONEYLET SIGESMUNDONo ratings yet
- Chap 1. Financial Management 1.1 Finance and Related DisciplineDocument13 pagesChap 1. Financial Management 1.1 Finance and Related DisciplineBarkkha MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning & Forecasting GuideDocument17 pagesFinancial Planning & Forecasting GuideSachin Barde50% (2)
- Role of Financial Management WorkbookDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Management WorkbookAditri MahajanNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesFinancial ManagementGogineni sai spandanaNo ratings yet
- Perform An Environmental Analysis of Current StrategiesDocument2 pagesPerform An Environmental Analysis of Current StrategiesElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 2Document2 pagesProblem 2ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Partial Productivity GrowthDocument1 pagePartial Productivity GrowthElizabethNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument1 pageEntrepreneurshipElizabethNo ratings yet
- PharmallyDocument3 pagesPharmallyElizabethNo ratings yet
- Cheer DanceDocument15 pagesCheer DanceElizabethNo ratings yet
- SCRIPTDocument2 pagesSCRIPTElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Taxation of CorporationsDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Taxation of CorporationsElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Taxation On IndividualsDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Taxation On IndividualsElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 10-5 Winter CompanyDocument2 pagesProblem 10-5 Winter CompanyElizabethNo ratings yet
- Facts About Omega-3 Fatty Acids: How They Help Your HealthDocument40 pagesFacts About Omega-3 Fatty Acids: How They Help Your HealthElizabethNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Different TaxonDocument10 pagesCharacteristics of Different TaxonElizabethNo ratings yet
- Book CritiqueDocument2 pagesBook CritiqueElizabethNo ratings yet
- 10 19Document1 page10 19ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 10-1 Amiable CompanyDocument2 pagesProblem 10-1 Amiable CompanyElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 10-7 Fall CompanyDocument2 pagesProblem 10-7 Fall CompanyElizabethNo ratings yet
- 10-11 To 10-18Document2 pages10-11 To 10-18ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 2Document1 pageProblem 2ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Problems for Sassy, Beehive, Fabulous, and Bedlam CompaniesDocument4 pagesBank Reconciliation Problems for Sassy, Beehive, Fabulous, and Bedlam CompaniesElizabethNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument2 pagesAccountingElizabethNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation and Adjusting Entries ProblemsDocument2 pagesBank Reconciliation and Adjusting Entries ProblemsElizabethNo ratings yet
- ReconciliationDocument6 pagesReconciliationElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Addressing Working Capital Policies and Management of ShortDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Addressing Working Capital Policies and Management of ShortElizabethNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Cash and Cash Equivalents p1Document2 pagesQuiz 1 Cash and Cash Equivalents p1ElizabethNo ratings yet
- How Can Operating Cycle Be ReducedDocument2 pagesHow Can Operating Cycle Be ReducedElizabethNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document1 pageProblem 1ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Relationship of Financial Objectives To Organizational Strategy and Other Organization ObjectivesDocument1 pageChapter 2 - Relationship of Financial Objectives To Organizational Strategy and Other Organization ObjectivesElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ForecastingDocument2 pagesChapter 10 ForecastingElizabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument2 pagesChapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthElizabethNo ratings yet
- Futsal QuizDocument1 pageFutsal QuizElizabethNo ratings yet
- HTML MCQDocument22 pagesHTML MCQBuxar Students LifeNo ratings yet
- Linkstar RCST Installation Guide: Version DDocument56 pagesLinkstar RCST Installation Guide: Version Djorge_chavez01No ratings yet
- AP Poetry TermsDocument8 pagesAP Poetry TermsTEACHER BARAY LLCE ANGLAISNo ratings yet
- January 2011Document64 pagesJanuary 2011sake1978No ratings yet
- (World of Art) John Boardman - Athenian Black Figure Vases-Thames and Hudson (1974)Document128 pages(World of Art) John Boardman - Athenian Black Figure Vases-Thames and Hudson (1974)Karen SantosNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingDocument2 pagesCognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingNik ZazlealizaNo ratings yet
- Max-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsDocument21 pagesMax-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsPhong QuachNo ratings yet
- Duane Grant, A099 743 627 (BIA Sept. 9, 2016)Document12 pagesDuane Grant, A099 743 627 (BIA Sept. 9, 2016)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCNo ratings yet
- Mri BrainDocument74 pagesMri Brainagithia100% (1)
- SKM 4 - COCU - CU2 - Child - Care - Centre - HealthDocument14 pagesSKM 4 - COCU - CU2 - Child - Care - Centre - HealthShireen TahirNo ratings yet
- E-Way BillDocument1 pageE-Way BillShriyans DaftariNo ratings yet
- PV380 Operations ManualDocument20 pagesPV380 Operations ManualCarlosNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs Multiple Choicecloudcatching0% (1)
- Airport Design GuidelinesDocument408 pagesAirport Design Guidelinesnickolololo67% (9)
- Gauss Jordan MethodDocument6 pagesGauss Jordan MethodnNo ratings yet
- Diosdado MacapagalDocument13 pagesDiosdado MacapagalMermie ArmentaNo ratings yet
- African in The Modern WorldDocument18 pagesAfrican in The Modern WorldSally AnkomaahNo ratings yet
- Rate of ChangeDocument22 pagesRate of ChangeTrisha MariehNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Weaving A Mannahatta Muir WebDocument2 pagesLesson 2: Weaving A Mannahatta Muir WebTamas SzamosfalvyNo ratings yet
- Serv Manual SM 100 FREEDocument75 pagesServ Manual SM 100 FREEGustavo Vargas Ruiz100% (1)
- The Brain from Inside Out Chapter 4 SummaryDocument20 pagesThe Brain from Inside Out Chapter 4 SummaryjuannnnNo ratings yet
- 22m Fast Patrol Craft Features & SpecsDocument1 page22m Fast Patrol Craft Features & SpecsNico BossiNo ratings yet
- Meta Hids by eBPFDocument27 pagesMeta Hids by eBPFninggou.yangNo ratings yet
- INTELLISPEC SERIE V-Páginas-31-46Document16 pagesINTELLISPEC SERIE V-Páginas-31-46Antonio Valencia VillejoNo ratings yet
- Lyrics: Original Songs: - JW BroadcastingDocument56 pagesLyrics: Original Songs: - JW BroadcastingLucky MorenoNo ratings yet
- SHP 21 DS en 20Document4 pagesSHP 21 DS en 20Marko Maky ZivkovicNo ratings yet
- Lifeboat Equipment ListDocument1 pageLifeboat Equipment Listjosua albertNo ratings yet
- Contoh Skripsi Bahasa Inggris Case StudyDocument18 pagesContoh Skripsi Bahasa Inggris Case StudyRizki Fajrita100% (14)
- Frogkisser! by Garth Nix (Excerpt)Document17 pagesFrogkisser! by Garth Nix (Excerpt)I Read YA0% (1)
- XFARDocument14 pagesXFARRIZA SAMPAGANo ratings yet
- Product-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfFrom EverandProduct-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerFrom EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)From EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successFrom EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessFrom EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityFrom EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialFrom EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialNo ratings yet
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Angel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000From EverandAngel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (86)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursFrom EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Mastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsFrom EverandMastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsNo ratings yet
- Note Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualFrom EverandNote Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualNo ratings yet
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelFrom Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNo ratings yet
- Add Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthFrom EverandAdd Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthNo ratings yet
- 2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNFrom Everand2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)