Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Bio 110
Uploaded by
Sir Majid the 21stCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4 Bio 110
Uploaded by
Sir Majid the 21stCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic units of —> structure and
function in organisms.
Cell theory
Cells come only from pre-existing
cells because cells are —> self
reproducing
1- Cell structure Quite small than 1mm ; some are
and function even as small as 1um .
Light microscope
Outlines visual rang of the eye :
Electron microscope.
Cell shape
Likely to have an adequate
surface area for —> exchanging
wastes for nutrients.
Why are cells so small?
Ex .. cutting a large cube into
smaller cubes provides a
lot more surface area per volume.
they lack a membrane-
bound nucleus.
They present in great numbers in
the air and soil.
are so named because :
live in and on other organisms.
Eukaryotic cell: cell with a
nucleus.
they cause some serious diseases.
tuberculosis and decompose the
Based on DNA and RNA remains
base sequences, divided into two separate types or Bacteria and Archaea. of dead organisms and, —> hence,
Bacteria are well known because: contribute to ecological cycles
prokaryotic cells domains called:
2- Prokaryotic are manufacturing all sorts of
Cells. products, from
Bacteria also assist humans in industrial chemicals to foodstuffs
: and
drugs (ex., human insulin).
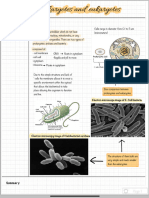
A rod-shaped bacterium
called a bacillus, occur as
pairs or chains.
Spherical-shaped bacterium
The Structure of is a coccus, occur as pairs.
The three common shapes are:
Prokaryotes Some long rods are twisted
into spirals.
Spirillum (long rod) if it is
rigid or spirochete if it is
flexible.
A phospholipid belayer with regulating the entrance/exit of
Plasma membrane: embedded ( proteins with substances into/out of
important function) of The Cytoplasm
Plant cell has —> cellulose.
. Cell wall To maintain cell’s shape .
Peptidoglycan ( amino
1. Cell Envelope :
disaccharide and peptid
fragments ) —> in bacteria .
A layer of polysaccharide lying
outside the cell wall —> ( a
capsule ).
. Glycocalyx
It AIDS against drying out and
3- Organization helps bacteria resist a host’s —>
immune system.
of Bacteria: Semi-fluid solution.
Cytoplasm
Composed : water and inorganic ,
organic molecules ( encased by a
—> plasma membrane).
In chromosome , region called—>
nucleoid
DNA
2. Cytoplasm: Extra chromosome piece of
circular super coiled DNA —> (
plasmid )
Used in biotechnology To transport DNA into a
Plasmids
laboratories in —> Vectors. bacterium.
thousands of With ( RNA -Protein ) in 2
protein-synthesizing—> ribosomes subunits
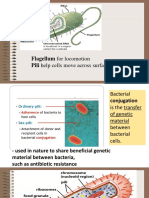
A bacterial cell
Motile bacteria can move in flagella
water by can be used to help distinguish
the means of flagell ( a protein). different types of bacteria.
regulates the passage of
molecules into\ out the —>
Cytoplasm.
Has —> Plasma membrane.
To separate the content of cell
from the environment.
Nucleus is evolved as a result
of ( Plasma membrane
invagination)
Endosymbiotic theory :
mitochondria and chloroplasts —>
the two energy related
organelles .
Origin
Arose : large eukaryotic cell —>
engulfed independent
prokaryotes .
they are bound by a double
membrane, and contain their own
genetic material separate.
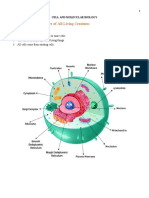
4- Eukaryotic
Cell wall Plant Contains —> cellulose fibrils
Cells Eukaryotic and plant cells have a
Plasma membrane
compartments of a eukaryotic
cell called: organelles, are membranous
.
Is an organelle , the houses the
genetic material——> within
eukaryotic chromosomes.
The nucleus with ribosomes in
the cytoplasm .
Organelles of the endomembran
and the endoplasmic reticulum
The communicates : and the Golgi apparatus ———>
The nucleus:
transport vesicles.
the energy-related organelles(
Structure mitochondria
and chloroplasts) —>is less obviou
An animal cell has only
mitochondria
A plant cell has
mitochondria and chloroplasts.
That maintains the shape of the
cell.
Assist in the movement of
The cytoskeleton Composed of protein fibres . organelles.
Protein fibres —> Serve tracks
for the transport vesicles that
take molecules from one
organelle to another.
Cells can become specialized by
the presence or absence of
particular organelles.
The nucleus is essential
to the life of a cell. It passed from cell to cell and from The ribosomes use this
to carry out protein synthesis.
contains the genetic generation to generation. information
information
appears as
an oval structure located
near the center of most
eukaryotic cells .
a network of
strands that undergoes
Contains : Chromatin Called : chromosomes
coiling into rod-like
structures;
5- The nucleus All the cell on an individual
The same number of chromosomes.
and Ribosomes contain :
cell division ensures that
except for the
daughter cells
egg and sperm, which usually
receive the same number of
have half this number (n)
chromosomes (2n).
The chromosomes are
Genes, composed of
the carriers of genetic
DNA, are units of
information containing
heredity located on the
DNA, protein and
chromosomes..
some RNA
The nucleus is separated from Out of the nucleus—( to )—> the
The nucleus the cytoplasm by a double with nuclear pores to permit the cytoplasm—( passage of )—>
membrane known as the nuclear passage of mRNA proteins , from the cytoplasm—(
envelope to )—> the nucleus.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA), joins with to form subunits of
proteins ribosomes.
specifies the sequence of amino
RNA are produced: messenger RNA (mRNA), acids in
a protein.
participates in the assembly of
transfer RNA (tRNA) amino acids
during protein synthesis.
are particles where protein
synthesis occurs.
composed of two subunits, one
large and one
small; represent a mix of
proteins and rRNA.
Ribosomes either singly or in groups called :
some ribosomes occur freely polyribosomes
In eukaryotic cells: within the
The cell cytoplasm. others are attached to the
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
the genetic code indicating the
needed sequence
of amino acids in a particular
protein
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is
that transport molecules to
membranous flattened ER consists of rough ER and
other parts of the cell, ex., the
small sacs physically continuous smooth ER forming vesicles:
Golgi apparatus.
with the nuclear envelope
Rough ER contains enzymes that
Endoplasmic Reticulum can add carbohydrate (sugar) eg., glycoproteins.
chains to proteins,
is associated with the production
of lipids and
Smooth ER:
testosterone and with the
detoxification of drugs.
consists of
a stack of three to twenty
curved.
ER to a signal
6- The The Golgi Apparatus molecule that determines the
It can modify the carbohydrate
protein’s final destination in the
Endomembrane It contains enzymes that change
cell.
System one sugar for the other. ,sorts the modified
molecules and packages them
into vesicles that depart from the
outer face; secretion or
exocytosis
are membrane-bounded vesicles
produced by the
Golgi apparatus.
to assist in digesting
material taken into the cell and
They store powerful digestive destroy
Lysosomes enzymes nonfunctional
organelles and portions of
cytoplasm
that are enclosed within
Some white blood cells defend vacuoles. When lysosomes fuse
the body by engulfing bacteria with these vacuoles, the
bacteria are digested.
Chloroplasts and
mitochondria are the two that specialize in converting
eukaryotic (plant energy to a form that can be
used by the cell.
and algae) membranous
organelles
chloroplasts, use solar energy
through photosynthesis to solar energy + carbon dioxide +
photosynthesis synthesize carbohydrates; an water → carbohydrate +
organic nutrient molecule for oxygen
plants and all living things.
carbohydrate + oxygen → carbon
is the process by which dioxide + water + energy
carbohydrates
Cellular respiration: are broken down in mitochondria The energy is used for active
to produce ATP transport and energy-requiring
processes in cells.
Some algal cells have only one
chloroplast.
Some plant cells have as many
as a hundred.
They are bounded by a double
have a three-membrane system. membrane enclosing the semi-
fluid.
Chloroplasts stroma enzymes and thylakoids.
disk-like sacs formed from a
third chloroplast membrane.
consists of two separate sets of
reaction .
solar energy is absorbed.
the light reactions and the Calvin water is split so that oxygen is
cycle reactions and Steps of released.
Photosynthesis
light reactions are:
ATP and NADPH are produced.
CO2 is absorbed
Steps of the Calvin cycle
reactions are: so
(CH2O) by utilizing AT P
CO2 is reduced to a then, ADP and NADP+ go back to that carbohydrate
and NADPH from the light become AT P and NADPH
carbohydrate (CH2O) light reactions, production can
reaction. once more
continue.
The number of mitochondria
varies in cells depending on their
activities.
Nearly all eukaryotic cells
contain mitochondria liver cells have as many as 1000
mitochondria, while
fat cells contain few
mitochondria.
mitochondrial.
DNA
the inner is highly
ribosomes.
7- The Energy- It has two membranes;
twisted to increase the
surface area into cristae
The matrix contains:
highly
Related that flew into a semi-
fluid matrix.
concentrated mixture of enzymes
that break down carbohydrates.
Organelles
other nutrient molecules.
to supply
produce most of the AT P utilized the chemical energy through a
by the cell process called (cellular
respiration).
oxygen (O2) .
by breaking
is the process by which cells down nutrient molecules
the breakdown of glucose to
acquire energy produced by photosynthesis
release carbon
through the use :
dioxide, water (H2O) and energy (
enough to produce 36-38 AT P
molecules).
Respiration
1. Glycolysis
2. Preparatory reaction,
Cellular respiration involves
Mitochondria four phases: 3. The citric acid cycle.
4. The electron transport
chain.
takes place outside the
mitochondria and does not require
Phases of glucose breakdown.
the presence of oxygen;
anaerobic, while other phases
Glycolysis. take place inside the
mitochondria, where oxygen is
required, aerobic.
Oxidation results in
Glycolysis; breakdown of
NADH and provides energy
glucose to two molecules of
for the net gain of two AT P
pyruvate.
molecules.
where pyruvate is broken down
The preparatory (prep) reaction: to two acetyl groups and CO2 is
released..
where oxidation occurs—( results )
—>NADH
The citric acid cycle and more CO2 is released.
Because two acetyl groups enter
is able to produce one ATP
the cycle per glucose molecule,
per turn.
the cycle turns twice
The electron transport chain (
ETC); where NADH and energy are
used to produce AT P.
The equation for photosynthesis
in a chloroplast is opposite to
that of cellular respiration in a
mitochondrion .
The ultimate source of energy
Flow of energy the sun: for producing a carbohydrate in
chloroplasts .
Therefore, there is a flow of
The ultimate goal of cellular conversion of carbohydrate
energy through chloroplasts to
respiration in a mitochondrion is energy into that of AT P
carbohydrates and then through
the: molecules.
mitochondria to AT P molecules.
carbohydrate and
oxygen produced by chloroplasts
during photosynthesis.
the
carbon dioxide produced by
During cellular
8- Cycling of mitochondria return back to
respiration, living things chloroplasts.
Chemicals: utilize:
Therefore, chloroplasts and
through living things and permit
mitochondria allow a flow of
a cycling of chemicals.
energy
are membrane-bounded vesicles enzymes whose actions result in
RH2 + O2 → R + H2O2
that enclose hydrogen peroxide (H2O2):
a toxic molecule.
Hydrogen peroxide, is immediately broken down to
Peroxisomes water and oxygen by another
peroxisomal enzyme called (
catalase)
peroxisomes oxidize fatty acids that can be converted to sugars
In germinating seeds :
into molecules needed by the growing plant.
are membranous sacs specialized
for storing excess for breaking down
Other Vesicles water, substances and digestive nutrients in the cell .
enzymes
and Vacuoles-9
Few animal cells contain vacuoles.
Typically, plant cells have a
large central vacuole that may
take up
to 90% of the volume of the cell.
Plant vacuoles contain cell sap of
Vacuoles water, sugars, salts, water-
soluble pigments and toxic
molecules.
are responsible for many of the
The pigments : red, blue, or purple
colors of flowers and some leaves.
help protect a plant from
Toxic substances:
herbivorous animals.
plant cell can rapidly increase in
by enlarging its vacuole.
size —>
You might also like
- Topic1 Revision Sheet Cell Special.Document2 pagesTopic1 Revision Sheet Cell Special.dionegarrentNo ratings yet
- L1 Cells and OrganisationDocument27 pagesL1 Cells and OrganisationGaurav RathiNo ratings yet
- GeneralBiology1 Module1Document4 pagesGeneralBiology1 Module1Kirsteen KimNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- Your Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesYour Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsVisca El BarcaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyESTHER NDUNGENo ratings yet
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Document11 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Jayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Bio RevisionDocument58 pagesBio RevisionKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology TermsDocument3 pagesCell Biology TermsHelen VicenteNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- B4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallDocument1 pageB4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallNazimNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 LDocument7 pagesWeek 2 Lrachel2854No ratings yet
- IB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesDocument26 pagesIB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesannaninaibNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument13 pagesProtozoansGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- Chem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Document21 pagesChem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Elif Deniz YeşilyaprakNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryDocument16 pagesYear 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryOlivia YinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Plant CellsDocument6 pagesLesson 2: Plant CellslalaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Tumbuhan 02-DikonversiDocument49 pagesFisiologi Tumbuhan 02-DikonversiRatih AyuNo ratings yet
- 1794853-P2. - Cell Structure and DivisionDocument8 pages1794853-P2. - Cell Structure and DivisionCrisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesDocument17 pagesModule 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesNicholas MichailouNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Pages 51-62Document19 pagesModule 5 Pages 51-62Yuritzi Carrillo-JavanaNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument19 pagesCell Ultrastructurezaydharoon419No ratings yet
- Activity 1Document3 pagesActivity 1MANALANG JULIA ALEXISNo ratings yet
- GCSE Comb Biology 2023Document70 pagesGCSE Comb Biology 2023Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Life Science Activity 2Document13 pagesLife Science Activity 2Camila PrzNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membran E: Function Cont. Function Structure Importance World DependenceDocument1 pageCell Membran E: Function Cont. Function Structure Importance World DependenceendlessNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cell TypesDocument4 pagesGen Bio Cell TypesRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Organiser: Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells MicroscopesDocument2 pagesKnowledge Organiser: Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells Microscopesisaaceden24No ratings yet
- 1.2 NotesDocument16 pages1.2 Notesyara hazemNo ratings yet
- 1 Chem113 LecDocument10 pages1 Chem113 LecJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Assignment Cell - ANSDocument3 pagesAssignment Cell - ANSAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: General OutcomesDocument48 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: General OutcomesNo NameNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organelles CompleteDocument33 pagesCells & Organelles CompleteShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument1 pageCell Structurekivepe9583No ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (2)
- Parts of The Microscope and Fundamentals of Microorganisms WorksheetDocument4 pagesParts of The Microscope and Fundamentals of Microorganisms WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BS TM EM New Text Book 2022Document21 pagesBS TM EM New Text Book 2022BALA VIKAS ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL RENTACHINTALANo ratings yet
- Topic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellDocument2 pagesTopic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellJonalyn OcampoNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- O Bio Summarize Notes For RevisionDocument31 pagesO Bio Summarize Notes For RevisionAfifa AmerNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- 1st Ch. CellsDocument27 pages1st Ch. CellsAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Work Activity 2 Microbiology & ParasitologyDocument3 pagesWork Activity 2 Microbiology & ParasitologyAmy Angelica DataNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsDocument9 pagesUnit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsIrenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- Everett Gabel - Activity - Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells (PG) .PDF - KamiDocument6 pagesEverett Gabel - Activity - Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells (PG) .PDF - KamiEverett GabelNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 1Document14 pagesBiology Module 1Excalibur valNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE WorksheetsDocument53 pagesSCIENCE WorksheetsHsje GhaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsChristine Suizo SebucaoNo ratings yet
- AQA Cell Biology Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Cell Biology Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and Higher: e e e e e e e e e e e e eDocument4 pagesCell Biology Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and Higher: e e e e e e e e e e e e eQUAH XIN YUE -No ratings yet
- EE Biolo Examplee enDocument22 pagesEE Biolo Examplee engiselle veneziaNo ratings yet
- ALP IsoenzymesDocument32 pagesALP IsoenzymesGawri AbeyNo ratings yet
- Cap. 6 - J. Lapponi Estatística Usando Excel (2005) (173-195)Document8 pagesCap. 6 - J. Lapponi Estatística Usando Excel (2005) (173-195)Joabson EstevesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - The Continuity of Life Cellular ReproductionDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - The Continuity of Life Cellular Reproductionapi-255024595No ratings yet
- Mutation NomenclaturDocument43 pagesMutation NomenclaturHakimRifqiNo ratings yet
- Genome Analysis of ESBL-Producing Escherichia ColiDocument18 pagesGenome Analysis of ESBL-Producing Escherichia ColiAYODELE ADESOJINo ratings yet
- Mayur - 01Document2 pagesMayur - 01mukesh jambukiyaNo ratings yet
- In Spermatogenesis, 4 Genetically Unique Sperm Cells Are Created. in Oogenesis, 1 Ovum Forms and 3 Polar BodiesDocument1 pageIn Spermatogenesis, 4 Genetically Unique Sperm Cells Are Created. in Oogenesis, 1 Ovum Forms and 3 Polar Bodiesscooter brewerNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous Bases PDFDocument1 pageNitrogenous Bases PDFSeekerNo ratings yet
- Gene It's Nature Expression and Regulation - Final PDF-4Document3 pagesGene It's Nature Expression and Regulation - Final PDF-4Aishwarya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Protein SynthesisDocument70 pagesClass 12 Protein SynthesisAqua Regia100% (1)
- Drug Delivery in Biotechnology - Present and FutureDocument6 pagesDrug Delivery in Biotechnology - Present and FutureGeorge CuniaNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins: © 2017 W. H. Freeman and CompanyDocument43 pages4 - The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins: © 2017 W. H. Freeman and CompanyRegis BetaNo ratings yet
- KBSM T4 Biologi K1Document24 pagesKBSM T4 Biologi K1Eliza FatimahNo ratings yet
- Integrative Functional Genomic Analysis of Brain DevelopmentDocument15 pagesIntegrative Functional Genomic Analysis of Brain Developmentiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- Methods To Produce Marker-Free Transgenic Plants: ReviewDocument8 pagesMethods To Produce Marker-Free Transgenic Plants: ReviewVishwanath HebbiNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer PrelimsDocument10 pagesBiology Reviewer PrelimsShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Ch. 1 PowerPointDocument25 pagesNeuroscience Ch. 1 PowerPointKagiroNo ratings yet
- PCR Gelatin PermenDocument8 pagesPCR Gelatin PermenyuniarianaNo ratings yet
- Nonsense MutationsDocument9 pagesNonsense MutationseminaNo ratings yet
- Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 Functions As An Efferocytosis Receptor in in Ammatory MacrophagesDocument21 pagesIntercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 Functions As An Efferocytosis Receptor in in Ammatory MacrophagesOlfisusan TumbolNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument11 pagesCilia and FlagellaDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Objective QuestionsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Objective Questionsg c lallNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering (Module 4) : Task A. Modified True or False Task C. Discussion/InsightsDocument2 pagesGenetic Engineering (Module 4) : Task A. Modified True or False Task C. Discussion/InsightsJerald De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Protoonkogen OnkogenDocument22 pagesProtoonkogen OnkogenkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Divergence and Functions of The Human Interleukin (IL) Gene Family". Human Genomics. 5 (1) : 30Document19 pagesDivergence and Functions of The Human Interleukin (IL) Gene Family". Human Genomics. 5 (1) : 30nastella7No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 101 PTC8 PDFDocument12 pagesBiochemistry 101 PTC8 PDFvNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Lecture SlidesDocument34 pagesCh4 Lecture SlidesJad AwadNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Quick Facts Step1Document31 pagesBasic Science Quick Facts Step1Hannah Jackson100% (20)
- A Generalised Enzyme Kinetic Model For Predicting The Behaviour of Complex Biochemical Systems PDFDocument14 pagesA Generalised Enzyme Kinetic Model For Predicting The Behaviour of Complex Biochemical Systems PDFEmanuel PataquivaNo ratings yet