Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell Wall
Uploaded by
NazimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell Wall
Uploaded by
NazimCopyright:
Available Formats
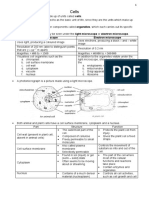
What is the function of the nucleus?
Describe the functions of the Describe the functions of Put these cells in size order from smallest to biggest
3 features found in plant cells mitochondria and ribosomes
It contains genetic material such as DNA Plant animal bacterial
(not animal cells)
therefore controlling the cells activities The function of ribosomes is to
Cell wall has the function of synthesise proteins. Bacteria Animal Plant
What is the function of the cytoplasm? providing structural support
and protection. The central Mitochondria is the
This is where many chemical reactions occur. powerhouse of the cell. This is Put these units into size order and write the shortened
vacuole maintains turgor
pressure against the cell wall. where respiration occurs. term for each (e.g. kilogram = kg)
Chloroplast have a pigment
millimetre nanometre micrometre centimetre
What is the function of the cell membrane? called chlorophyll which
absorbs sunlight and is where NM μM MM CM
It holds the cell together and controls the
photosynthesis occurs.
substances entering and leaving the cell
What is a eukaryotic cell? Describe the structure of a B4.1 – Cell Structure What are plant and algal cell Give 3 examples of eukaryotic
bacterial (prokaryotic) cell. (combined science) walls made from? glycoproteins organisms.
Eukaryotes are organisms with a Bacteria cells have no and polysaccharides for algal and
nucleus in their cells. Describe & explain the Plants, animals and fungus
nucleus. They have small cellulose for plant
closed circles that have adaptations of sperm cells. The
DNA inside them they are head of the sperm cell
Define magnification and resolution What are the advantages of
called Plasmids. They have a (acrosome) contains enzymes
Describe & explain the adaptations Magnification is enlarging the electron microscopes?
cell wall, and some have so that the sperm can
of a root hair cell. Root hair cells physical appearance or image of
flagella. They also have DNA penetrate the egg. The middle Electron microscopes can
function is to absorb nutrients and something. Resolution is the degree
inside the cytoplasm, and is packed with mitochondria so enlarge something much
water from the soil. Root hair cells of accuracy and detail.
this is called Chromosomal there is energy for it to swim. more than a light
have a large surface area and a large
DNA. The tails enable it to swim microscope.
permanent vacuole
Describe & explain the Describe & explain the Describe & explain the Describe and explain the What are the
adaptations of xylem cells adaptations of phloem cells? adaptations of muscle cells. adaptations of nerve cells advantagesdisadvantages of
electron microscopes?
The function pf xylem cells are to Phloem transports sucrose Muscle cells have a lot of They have a long fibre (axon)
transport water up the plant. It is and amino acids up and down developed mitochondria to which is insulated by a fatty The disadvantages of
adapted tot their function by the plant. The tubes in phloem provide energy for muscle sheath. They have tiny branches electron microscope
being composed of dead cells have no nucleus. contraction. (dendrons) which branch further is that its expensive,
therefore no reaction would take as dendrites at each end. its large and its
place. maintenance.
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (1)
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (2)
- GCSE Comb Biology 2023Document70 pagesGCSE Comb Biology 2023Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- GCSE Triple Biology 2023Document91 pagesGCSE Triple Biology 2023Ramy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- GcsebioDocument94 pagesGcsebioemen ulhaqNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Topic 1 - Cells Revision SheetDocument1 pageIB Biology Topic 1 - Cells Revision SheetMarwan PharaonNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Define The Term Resolution. Distinguish The Resolution of Light and Electron MicroscopesDocument44 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Define The Term Resolution. Distinguish The Resolution of Light and Electron MicroscopesBader Al-SaloumNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1umaimahhabib78No ratings yet
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Your Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesYour Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsVisca El BarcaNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryDocument16 pagesYear 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryOlivia YinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument15 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEMaic Audolin SihombingNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesDocument17 pagesModule 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesNicholas MichailouNo ratings yet
- Cells Questions and VocabDocument12 pagesCells Questions and VocabFanna Sharma100% (1)
- Essential Biology 02.2: Prokaryotes: Ribosomes and A Scale BarDocument4 pagesEssential Biology 02.2: Prokaryotes: Ribosomes and A Scale BarjoeyacomineNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 02.2: Prokaryotes: Ribosomes and A Scale BarDocument4 pagesEssential Biology 02.2: Prokaryotes: Ribosomes and A Scale Barjoeyacomine100% (1)
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Learner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsDocument31 pagesLearner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsLyaz Antony91% (91)
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- 1st Ch. CellsDocument27 pages1st Ch. CellsAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Science Guidebook For SSC CGL, CHSL, Railways & PSC Exams - Exampundit - in PDFDocument55 pagesScience Guidebook For SSC CGL, CHSL, Railways & PSC Exams - Exampundit - in PDFvilas bollabathiniNo ratings yet
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetsDocument28 pagesPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetsMarisol Leal PradoNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Science Learner 7-AnswersDocument4 pagesLower Secondary Science Learner 7-Answershiori San83% (12)
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- 01 Cells A3 Revision-Sheet A3format Modela-Swers - Pdfviewer.action DownloadDocument1 page01 Cells A3 Revision-Sheet A3format Modela-Swers - Pdfviewer.action DownloadNoam ZivNo ratings yet
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- BIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesBIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyJake EverettNo ratings yet
- Mindmap - Cell Structure - AS LevelDocument1 pageMindmap - Cell Structure - AS LevelDr Selvakumari100% (2)
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument64 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanAdham EtmanNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology TermsDocument3 pagesCell Biology TermsHelen VicenteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Bmat Biology KnowledgeDocument22 pagesBmat Biology KnowledgeAngel SyNo ratings yet
- Células y Tejidos VegetalesDocument5 pagesCélulas y Tejidos VegetalesNathalyVargasFreireNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124No ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument8 pagesThe CellJessa Nicole ReteracionNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument65 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #2Document6 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #2Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Document3 pagesKami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Achionta NandyNo ratings yet
- Topic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellDocument2 pagesTopic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellJonalyn OcampoNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologyDocument4 pagesPractice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologySamantha DAIRONo ratings yet
- The Cell: Exercise 2Document5 pagesThe Cell: Exercise 2Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Everett Gabel - Activity - Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells (PG) .PDF - KamiDocument6 pagesEverett Gabel - Activity - Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells (PG) .PDF - KamiEverett GabelNo ratings yet
- Samillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Document11 pagesSamillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Gem Kyla Mae SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function WorksheetKiersten RobertsNo ratings yet
- River Assignment 8 MarkDocument1 pageRiver Assignment 8 MarkNazimNo ratings yet
- Geog 8 MarkDocument1 pageGeog 8 MarkNazimNo ratings yet
- Geodraphy PrepDocument1 pageGeodraphy PrepNazimNo ratings yet
- A Level Business Numeracy Assessment Ed1 - QuestionsDocument7 pagesA Level Business Numeracy Assessment Ed1 - QuestionsNazimNo ratings yet
- 20 Mark BusinessDocument1 page20 Mark BusinessNazimNo ratings yet
- F Plasmids PDFDocument2 pagesF Plasmids PDFNickNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellsMark Lorenz LorillaNo ratings yet
- BirknerDocument40 pagesBirknerSylvain ContiéNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Free Response On Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesAP Biology Free Response On Protein Synthesisafktgvllsgajfw100% (2)
- Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesDocument25 pagesImmunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer - Insights Into Tumor Immune Landscape and Therapeutic OpportunitiesLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- BestPractices Diastaticus DigitalDocument1 pageBestPractices Diastaticus DigitalMario JammaersNo ratings yet
- Fatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8Document6 pagesFatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8api-542684299No ratings yet
- ML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LuceDocument1 pageML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LucenurjNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skeletal Muscle by Dr. RoomiDocument33 pagesPhysiology of Skeletal Muscle by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Molecules 27 02977Document18 pagesMolecules 27 02977Didi Nurhadi IllianNo ratings yet
- Biol BDs SingaporeDocument24 pagesBiol BDs Singaporestevekct10No ratings yet
- DNA DamageDocument49 pagesDNA DamagekurniaadhiNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTest 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsChrisNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section: ConfidentialDocument6 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section: ConfidentialMi MiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in PregnancyDocument24 pagesDiabetes in PregnancyMazlina MaidinNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument17 pagesBiomolecules NotesManit GroverNo ratings yet
- Ernesto Picardi - RNA Bioinformatics-Humana (2021)Document576 pagesErnesto Picardi - RNA Bioinformatics-Humana (2021)Guilherme Jung100% (1)
- Exhibitor Name Alloted Booth: Anzen ExportsDocument5 pagesExhibitor Name Alloted Booth: Anzen ExportsRichard OrtizNo ratings yet
- ENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Document9 pagesENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Ben Jenkins100% (4)
- Properties: GeneticDocument24 pagesProperties: Geneticpalak singhNo ratings yet
- 2024-02-28-T-B.SC. (H) 23-Sem - IiDocument6 pages2024-02-28-T-B.SC. (H) 23-Sem - IiHarshit RawatNo ratings yet
- Please Note! According To University Regulations, Only The Students Who Have Completed Their Laboratories, and ExamsDocument3 pagesPlease Note! According To University Regulations, Only The Students Who Have Completed Their Laboratories, and ExamsMetehan KaraNo ratings yet
- Muscle Fiber Type Transitions With Exercise Training: Shifting PerspectivesDocument11 pagesMuscle Fiber Type Transitions With Exercise Training: Shifting PerspectivesEnzoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Article 1407Document12 pages2019 Article 1407Paviliuc RalucaNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodyDocument8 pagesMonoclonal AntibodySadaf Sumdani NirvikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Active Reading Guide The Cell Cycle: Key Role ExampleDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Active Reading Guide The Cell Cycle: Key Role ExampleAulia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- MTT AssayDocument12 pagesMTT AssaySurampalliGuruNo ratings yet
- TB Final2023 643ef57734b858.643ef57a5a0fb6.40844090Document71 pagesTB Final2023 643ef57734b858.643ef57a5a0fb6.40844090Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Final Exam Preview Guide - 2019Document3 pagesBiochemistry Final Exam Preview Guide - 2019jake0% (1)