Professional Documents
Culture Documents
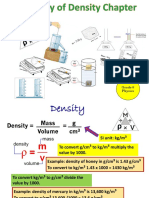
Density: Density= Mass ρ= m V
Uploaded by
Raheem Abdul ManyambaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Density: Density= Mass ρ= m V
Uploaded by
Raheem Abdul ManyambaCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1 of 4
DENSITY
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume.
Mass
Density=
Volume
m
In symbols, ρ=
V
The SU unit of density is the kilogram per cubic metre (kg/m3). Sometimes the g/cm3 is also
used.
To convert g/cm3 to kg/m3, multiply by 1000. To convert kg/m3 to g/cm3, divide by 1000.
For example, the density of water is 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3.
Examples
1. What is the density of:
(a) an object of mass 500kg whose volume is 0.4m3,
(b) a 15cm3 piece of wood of mass 12g.
2. Taking the density of copper as 9g/cm3, find:
(a) the mass of 5cm3,
(b) the volume of 63g.
3. A piece of steel has a mass of 32g and volume of 4cm3. What is it’s density in:
(a) g/cm3
(b) kg/m3.
Relative density
This is the ratio of the mass of any volume of substance to the mass of an equal volume of
water.
Mass of substance
Relative density =
Mass of equal volume of water
Relative density can also be found using:
Density of substance
Relative density =
Density of water
Relative density has no units; it’s just a ratio.
Examples
1. If the density of water is 1g/cm3, find the relative density of each of the following
substances:
(a) sea water of density 1.02g/cm3;
(b) mercury of density 13.6g/cm3;
(c) alcohol of density 0.85g/cm3.
Physics Density Chola M
Page 2 of 4
2. A pupil carried out an experiment to determine the relative density of petrol using a
density bottle. She obtained the following results:
Mass of empty bottle = 10.3g
Mass of bottle filled with water = 40.3g
Mass of bottle filled with petrol = 34.3g
Using these results calculate the relative density of petrol.
3. .
Uses of density
Assignment: Write about the uses of density.
Examples
DETERMINATION OF DENSITY
1. Density of a regular solid
Measure the mass using a beam balance.
To find the volume, measure its dimensions and apply an appropriate formula.
Calculate the density using the formula:
mass m
Density= or ρ=
volume V
2. Density of an irregular solid(stone)
Measure the mass (m) by placing the solid on a beam balance.
Measure the volume (V) of the solid as follows:
Place water in a measuring cylinder and record its initial volume (V1).
Gently lower the solid into the water and record the final volume (V2)
The volume of the solid will be:
V =¿V1 +¿ V2
Calculate the density using the formula:
mass
Density=
volume
3. Density of a solid that floats in a liquid
Measure the mass (m) of the solid using a beam balance.
Measure the volume (V) of the solid as follows:
Physics Density Chola M
Page 3 of 4
Place water with a sinker in it into a measuring cylinder and record the initial volume
(V1)
Attach the solid to the sinker and gently lower them into the measuring cylinder until
they are fully submerged. Record the final volume (V2)
The volume of the solid is:
V =¿V2 −¿ V1
Calculate the density using the formula:
mass
Density=
volume
4. Density of a liquid
Measure the volume (V) by placing the liquid in a measuring cylinder.
Place an empty beaker on a beam balance and measure the mass (m1)
Pour the liquid in the beaker and measure the final mass (m2)
The mass(m) of the liquid only will be
m=m2 −¿ m1
Calculate the density using the formula:
mass
Density=
volume
5. Density of a gas (air)
Take a container of known volume and evacuate (remove air from) it using a vacuum
pump.
Measure its mass (m1) using a balance.
Fill the container with air and measure the final mass (m2)
The mass(m) of the air only will be
m=m2 −¿ m1
Calculate the density using the formula:
mass
Density=
volume
6. Relative density of a liquid
Physics Density Chola M
Page 4 of 4
Physics Density Chola M
You might also like
- Equilibrium of Bodies in Liquids Density and Relative DensityDocument16 pagesEquilibrium of Bodies in Liquids Density and Relative DensityAdegoke TofunmiNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle and Buoyancy Force ExperimentDocument9 pagesArchimedes' Principle and Buoyancy Force Experimentmohammad. 21No ratings yet
- Practicals AwDocument15 pagesPracticals Awrnimlik668No ratings yet
- ρ, of an object is defined as the ratio of its: Goals or objectivesDocument5 pagesρ, of an object is defined as the ratio of its: Goals or objectivesMaran Kachocha AlkldaneNo ratings yet
- Density: Density Is The Mass Per Unit Volume of A SubstanceDocument4 pagesDensity: Density Is The Mass Per Unit Volume of A SubstancemelissaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Bodies in FliudDocument12 pagesEquilibrium of Bodies in FliudOLAIYANo ratings yet
- Modified Notes of VolumeDocument14 pagesModified Notes of VolumeVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- Mass Weight and DensityDocument3 pagesMass Weight and DensityChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument7 pagesDensityChanda Munkonge Jr.No ratings yet
- IX Lab Manual Physics 2021-2022 Term 2Document12 pagesIX Lab Manual Physics 2021-2022 Term 2C20085708 KAVIN PRANAV SNo ratings yet
- Exp. 1 FluidDocument8 pagesExp. 1 FluidX2urNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3, Mesurement of Density NewDocument2 pagesExperiment 3, Mesurement of Density NewlpborrajoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 3.0 With PracticeDocument92 pagesFluid Mechanics 3.0 With PracticeCosmic BrilliantNo ratings yet
- Mass, Weight and DensityDocument19 pagesMass, Weight and DensityKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Density A SummaryDocument11 pagesDensity A SummaryshamsNo ratings yet
- 1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityDocument13 pages1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityShaniCoolestNo ratings yet
- Engineering Technical College/ Basrah Departments of Fuel and Energy Practical Physical Chemistry Second YearDocument26 pagesEngineering Technical College/ Basrah Departments of Fuel and Energy Practical Physical Chemistry Second Yearاحلام علي فايز ANo ratings yet
- Understanding DensityDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Density4685752No ratings yet
- 1 Density-PycnometerDocument4 pages1 Density-PycnometerYasirNo ratings yet
- Density Upthrust Archimedes Principle and FloatationDocument21 pagesDensity Upthrust Archimedes Principle and Floatationkasumbaashraf3No ratings yet
- 1.density PycnometerDocument4 pages1.density PycnometerShivpreet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Density Determination by PycnometerDocument5 pagesDensity Determination by PycnometerAlexandre Argondizo100% (1)
- Volume and DensityDocument8 pagesVolume and DensityblueegofxNo ratings yet
- Density: Q) Which Weighs More:-A Kilogram of Feathers or A Kilogram of Iron?Document24 pagesDensity: Q) Which Weighs More:-A Kilogram of Feathers or A Kilogram of Iron?robin biswasNo ratings yet
- density determinationDocument16 pagesdensity determinationnorewa9632No ratings yet
- Formulas On Properties of FluidsDocument5 pagesFormulas On Properties of FluidsJay Escalera BahulayNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Chem NF 1st Term (1) - 1-6Document6 pagesGrade 7 Chem NF 1st Term (1) - 1-6zizo gamingNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidsDocument21 pagesProperties of FluidsJhay-Pee QueliopeNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 Density and Buoyancy Force PresentationDocument32 pagesGRADE 7 Density and Buoyancy Force PresentationThirdy CatalanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LabDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics LabMarco PlaysNo ratings yet
- PHS 001 HydrostasticsDocument77 pagesPHS 001 HydrostasticsRaphaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Fluid Properties by Ahmed YASHARDocument37 pagesChapter One: Fluid Properties by Ahmed YASHARSogolNo ratings yet
- Student: Basim Gohdar Lecturer: MR - Kawar AbidDocument11 pagesStudent: Basim Gohdar Lecturer: MR - Kawar Abidbasim gohdarNo ratings yet
- 54 FluidsDocument2 pages54 FluidsnikobelookNo ratings yet
- Measurement of The Density of Solid and LiquidDocument3 pagesMeasurement of The Density of Solid and LiquidPatrick OmoyonNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document3 pagesExp 5Kabir MdNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (1-3)Document8 pagesLab 1 (1-3)Eijay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 1Document2 pagesPhysics Test 1jonahorjiNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument3 pagesDensityapi-239131622No ratings yet
- Ch5 Static FluidDocument30 pagesCh5 Static FluidALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- Measuring Mass Volume and DensityDocument40 pagesMeasuring Mass Volume and DensityCASUL, ARAVELANo ratings yet
- Matter Booklet: Lesson 1 Particles and DensityDocument17 pagesMatter Booklet: Lesson 1 Particles and Densityapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Physics - Expt 3Document6 pagesPhysics - Expt 3Bianca ThereseNo ratings yet
- Process Variables: Amounts, Compositions, and Condition of MaterialsDocument13 pagesProcess Variables: Amounts, Compositions, and Condition of MaterialsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- SLG 8.1.2 Properties of Fluids IIDocument7 pagesSLG 8.1.2 Properties of Fluids IIHaruto “kai” WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Experiment A PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment A PDFAWM KassimNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C04Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C04Vishwajeet Ujhoodha75% (4)
- EXPT. 1A - DENSITY DETERMINATION USING A PYCNOMETERDocument3 pagesEXPT. 1A - DENSITY DETERMINATION USING A PYCNOMETEREunice AnneNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (Archimedes Principle)Document3 pagesExperiment 3 (Archimedes Principle)shark eyeNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 DensityDocument3 pagesTopic 3 DensitygoldphishNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics SanfoundaryDocument277 pagesFluid Mechanics Sanfoundaryengineersalam786No ratings yet
- 5 .DensityDocument26 pages5 .Densityrtesdfr100% (1)
- Densityand PressureDocument68 pagesDensityand PressureStarFireFoxNo ratings yet
- Physics Work Sheet 2Document6 pagesPhysics Work Sheet 2Debela mendaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementHarshita MunotNo ratings yet
- DENSITY and BUOYANCY PresentationDocument32 pagesDENSITY and BUOYANCY PresentationKyla Athena Perlas PulidoNo ratings yet
- SOILMECH1Document5 pagesSOILMECH1joseph marimlaNo ratings yet
- Chem 11Document7 pagesChem 11Raheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- 1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomDocument18 pages1 18 Atomic Physics The Nuclear AtomRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- David Livingstone College of Education: TopicDocument7 pagesDavid Livingstone College of Education: TopicRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- Final Research - JosephDocument31 pagesFinal Research - JosephRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- Joshua MwilaDocument30 pagesJoshua MwilaRaheem Abdul ManyambaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDDocument6 pagesLab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDLee-Ann LimNo ratings yet
- Second Assessment in Math 4 WK 5 8 3rdDocument2 pagesSecond Assessment in Math 4 WK 5 8 3rdjenilynNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document56 pagesCH 13bp9243798No ratings yet
- 4th QUARTER - MATH 5 - SUMMATIVE TEST NO.1Document3 pages4th QUARTER - MATH 5 - SUMMATIVE TEST NO.1Mary Ann PontillasNo ratings yet
- 6th Science & Social T1 EMDocument216 pages6th Science & Social T1 EMJulius Mera Smith JNo ratings yet
- Dropper - Motion in 1 D - DPP 2Document7 pagesDropper - Motion in 1 D - DPP 2Shashwat KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Wired Math Sa V AnswersDocument5 pagesWired Math Sa V Answersapi-302068715100% (2)
- College Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test BankDocument34 pagesCollege Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test Bankwilma100% (18)
- FORCE and MOTIONDocument3 pagesFORCE and MOTIONKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mensuration Class NotesDocument21 pagesGrade 8 Mensuration Class Notessafa sahebNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Guide to SI Units, Vectors, Motion, Forces & EnergyDocument76 pagesMechanics Guide to SI Units, Vectors, Motion, Forces & EnergyTak ProNo ratings yet
- Notes Form4Document132 pagesNotes Form4Maliki MohammadNo ratings yet
- Seametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsDocument81 pagesSeametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsPromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 4 (Sir Bien Cruz) - For MergeDocument43 pagesGrade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 4 (Sir Bien Cruz) - For MergeMary Rose del RosarioNo ratings yet
- FSMA Perimeter and Area StudentDocument4 pagesFSMA Perimeter and Area StudentHassan HassimovNo ratings yet
- CSHDocument4 pagesCSHn02021908gNo ratings yet
- Z7 Bpe CPV BP Q3 AZTdDocument5 pagesZ7 Bpe CPV BP Q3 AZTdsaurav kuriNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics MCQs Perimeter and AreaDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 7 Mathematics MCQs Perimeter and Areasiba padhy100% (3)
- Density Volume MassDocument3 pagesDensity Volume MassAariz KhanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFRa RsNo ratings yet
- Centre of MassDocument5 pagesCentre of MassSiddhesh ThoratNo ratings yet
- Punjab Patwari MensurationDocument7 pagesPunjab Patwari Mensurationmrafridi44No ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume - 2023-24Document6 pagesSurface Area and Volume - 2023-24Aaratrika DasNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Science ch-10 Gravitation NotesDocument4 pagesClass 9th Science ch-10 Gravitation NotesPlay like pro.No ratings yet
- 6 - Mass, Weight and C.GDocument17 pages6 - Mass, Weight and C.GRafayNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 02 Unit ConversionsDocument42 pagesNotes Unit 02 Unit Conversionsapi-244107705100% (1)
- Femh 110Document16 pagesFemh 110ramesh_balakNo ratings yet
- Physics Dimensional Analysis ActivityDocument2 pagesPhysics Dimensional Analysis Activityshamnadhm371100% (1)
- Newton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Document2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Llama jennerNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Part - IDocument9 pagesMensuration Part - IDebjani MondalNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)