Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Termodinámica Capitulo 2 Work, Heat & Energy Problems
Uploaded by
Mario GonzalezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Termodinámica Capitulo 2 Work, Heat & Energy Problems
Uploaded by
Mario GonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
Tarea #2 Termodinámica.
Capitulo 2
2.10 An object whose mass is 300 lb undergoes a change in kinetic energy owing to the
action of a resultant force. The work done by the resultant force is 100 Btu. There are no
other interactions between the object and its surroundings, and there is no change in the
object’s elevation. If the final velocity of the object is 200 ft/s, what is its initial velocity,
in ft/s?
2.21 Air is compressed in a piston-cylinder assembly from an initial state where 𝑝1 = 30
lbf/in² and 𝑉1 =25 ft³. The relationship between pressure and volume during the process
is 𝑝V1.4 = constant. For the air as the system, the work is -62 Btu. Determine the final
volume, in ft³, and the final pressure, in lbf/in².
2.25 A closed system consisting of 0.5 lbmol of air undergoes a polytrophic process
from
𝑝1= 20 lbf/in², 𝑣 1= 9.26 ft³/lb to a final state where 𝑝2= 60 lbf/in², 𝑣 2= 3.98 ft³/lb. Determine
the amount of energy transfer by work, in Btu, for the process.
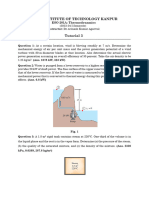
2.26 Air is trapped in a piston-cylinder assembly oriented horizontally as shown in Fig.
P2.26. Initially, 𝑝1= 100 kPa, 𝑉1= 2x10- 3 m3, and the face of the piston is at x= 0. The
spring exerts no force on the piston in the initial position. The atmospheric pressure is
100 kPa, and the area of the piston face is 0.018 m². The air expands slowly until its
volume is 𝑉2= 3x10ˉ³ m³. During the process, the spring exerts a force on the piston that
varies with x according to F= kx, where k= 16.2x10³ N/m. There is no friction between
the piston and the cylinder wall. Determine the final pressure of the air, in kPa, and the
work done by the air on the piston, in kJ.
2.28 A gas undergoes three processes in series that complete a cycle:
Process 1-2: compression from 𝑝1= 10 lbf/in², 𝑉1= 4 ft³ to 𝑝2= 50 lbf/in². During
which the pressure-volume relationship is pv=constant.
Process 2-3: constant volume to 𝑝3 = 𝑝1
Process 3-1: constant pressure
Sketch the processes on a p-V diagram and determine the net work for the cycle, in Btu.
Tarea #2 Termodinámica.
Capitulo 2
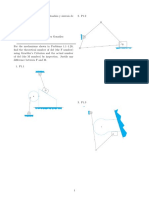
2.31 Figure P2.31 shows an object whose mass is 5 lb attached to a rope wound around
a pulley. The radius of the pulley is 3 in. If the mass falls at a constant velocity of 5 ft/s,
determine the power transmitted to the pulley, in horsepower, and the rotational speed
of the pulley, in RPM. The acceleration of gravity is g= 32.2 ft/s².
2.34 A 12-V automotive storage battery is charged with a constant current of 10 amp for
3h. Determine the amount of energy supplied to the battery, in kW·h. Convert your
answer to Btu.
2.52 A closed system of mass 2 kg undergoes a process in which there is heat transfer
of magnitude 25 kJ from the system to the surroundings. The magnitude of the work
done on the system during the process is 100 kJ. The specific internal energy of the
system decreases by 15 kJ/kg and there is no change in kinetic energy of the system.
The acceleration of gravity is constant at g= 9.6 m/s². Determine the change in elevation
of the system, in m.
2.55 A closed system of mass 2 lb undergoes two processes in series:
Process 1-2: 𝑣1= 𝑣2= 4.434 ft³/lb, 𝑝1=100 lbf/in², 𝑢1=1105.8 Btu/lb, 𝑄12= -581.36 Btu
Process 2-3: 𝑝2 = 𝑝3= 60 lbf/in², 𝑣3=7.82 ft³/lb, 𝑢3=1121.4 Btu/lb.
Kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. Determine the work and heat
transfer for Process 2-3, each in Btu.
2.60 A gas in a piston- cylinder assembly is compressed from 𝑝1= 3.4 bars, 𝑉1= 0.0283 m³
to 𝑝2= 8.2 bars in a process for which the relation between pressure and volume is
𝑝𝑉1.2=constant. The mass of the gas is 0.183 kg. During the process, the heat transfer
from the gas is 2.2 kJ. Determine the change in specific internal energy of the gas, in
kJ/kg. Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible.
You might also like
- Thermodynamics homework energy law calculationsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics homework energy law calculationsLUISRONo ratings yet
- Homework #2 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework #2 PDFNataly Yisel ArizaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 3 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tarea 5 TermodinamicaDocument4 pagesTarea 5 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Prob SetDocument4 pagesProb SetJuliet NakilaNo ratings yet
- Homework#3Document5 pagesHomework#3Ali Raza RavianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Piston cylinder problem tutorial basicsDocument1 pagePiston cylinder problem tutorial basicsRishi Raj100% (1)
- CHE 201 Engineering Thermodynamics TutorialDocument2 pagesCHE 201 Engineering Thermodynamics TutorialAdesite GodwinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Vinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 ProblemsDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 ProblemsBhavishya GuptaNo ratings yet
- ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsAnonymous dIhhKANo ratings yet
- THRM1001 Tutorial 4 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesTHRM1001 Tutorial 4 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDimitri RamloganNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MED205Document4 pagesTutorial MED205Anonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- Energy and The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesEnergy and The First Law of ThermodynamicspersonalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Khayyam JahangirNo ratings yet
- H. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)Document20 pagesH. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)HectorCabzNo ratings yet
- Applications of First LawDocument12 pagesApplications of First LawHarminder SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document46 pagesCH 2جلال بولادNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solution Manual of Thermodynamics by Hipolito STa. MariaDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Solution Manual of Thermodynamics by Hipolito STa. MariaLou Berwel Domingo85% (93)
- Thermo HW SolutionsDocument35 pagesThermo HW SolutionsekantikdevoteeNo ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- Unit2: Energy Transfer and First Law of Thermodynamics: Short QuestionsDocument5 pagesUnit2: Energy Transfer and First Law of Thermodynamics: Short QuestionsBiswa RocksNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Department Unit 1 NotesDocument5 pagesMechanical Engineering Department Unit 1 NotesNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- QB Unit 1Document6 pagesQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaNo ratings yet
- Che 217 Lecture Notes Date: 10/07/2020 Topic: Solved Examples On Conservation of Energy and First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesChe 217 Lecture Notes Date: 10/07/2020 Topic: Solved Examples On Conservation of Energy and First Law of ThermodynamicsFere GodspowerNo ratings yet
- ME3100 Solution Tut-2Document8 pagesME3100 Solution Tut-2B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- Design Problem Module 2Document2 pagesDesign Problem Module 2Ryan Philip CatapangNo ratings yet
- Homework 08Document7 pagesHomework 08BasilLeeNo ratings yet
- ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsJeevanandam ShanmugaNo ratings yet
- Reviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Document37 pagesReviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Austin BarrilleauxNo ratings yet
- MMAE 320 Homework2Document2 pagesMMAE 320 Homework2orekuronekoNo ratings yet
- PCB1043 Tutorial 2 ENERGY TRANSFER BY HEAT, WORK & MASSDocument4 pagesPCB1043 Tutorial 2 ENERGY TRANSFER BY HEAT, WORK & MASSAlex CoolNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets For Thermodynamics 02Document3 pagesTutorial Sheets For Thermodynamics 02Aditya raj sachdevNo ratings yet
- KL UNIVERSITY THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION BANKDocument20 pagesKL UNIVERSITY THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION BANKవిష్ణువర్ధన్రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Work ProblemsDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Work ProblemsSaroj BaralNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350Document1 pageSupplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350physics a2No ratings yet
- Takehome ActivityDocument5 pagesTakehome ActivityEdmond Yurag LLusalaNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermopranavNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Engineering Devices Chapter 4 NotesDocument27 pagesThermodynamic Engineering Devices Chapter 4 Notessam_kamali85No ratings yet
- Chemical engineering thermodynamics I worksheetDocument4 pagesChemical engineering thermodynamics I worksheetTesfa negaNo ratings yet
- Guía de Ejercicios ESS TermodinámicaDocument17 pagesGuía de Ejercicios ESS TermodinámicaLuis Ignacio Aguilera100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Lucas LethukuthulaNo ratings yet
- METD0213 Thermodynamics 1 Activity 2 Set C ProblemsDocument2 pagesMETD0213 Thermodynamics 1 Activity 2 Set C ProblemsRonelle Royce MarisNo ratings yet
- Aero Engineering Thermodynamics PDFDocument22 pagesAero Engineering Thermodynamics PDFSridharanNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DNo ratings yet
- Sheet No. 2Document3 pagesSheet No. 2Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document7 pagesCH 1Asad IslamNo ratings yet
- 2013Document31 pages2013Narayanan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawPratyusha SatpathyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 VannessDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 VannessMekeilah AgustinNo ratings yet
- Entropy Changes of Water and Air Processes Using Thermodynamics HomeworkDocument3 pagesEntropy Changes of Water and Air Processes Using Thermodynamics HomeworkSebastián SantarrosaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 10 TermodinamicaDocument5 pagesTarea 10 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 1 TermodinamicaMario Gonzalez100% (1)
- Tarea 4 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 4 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1Document5 pagesTarea 1Mario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 1 TermodinamicaMario Gonzalez100% (1)
- Problemas Tarea 1 TermodinamicaDocument1 pageProblemas Tarea 1 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1Document13 pagesTarea 1Mario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle Efficiency and ParametersDocument12 pagesRankine Cycle Efficiency and ParametersMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- HT HW 1Document3 pagesHT HW 1Mario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- UV - Vis Spectros PDFDocument25 pagesUV - Vis Spectros PDFNelson BarriosNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument17 pagesAtomic Theory TimelineAngelo Julius Nuque100% (3)
- Accuvac Rescue 16136 enDocument52 pagesAccuvac Rescue 16136 ensmurd112No ratings yet
- TC Unit 3 Exercise 2Document13 pagesTC Unit 3 Exercise 2priyanktutorialNo ratings yet
- Thermometer User Manual Geratherm ClinicDocument1 pageThermometer User Manual Geratherm ClinicficoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boiler Design PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Boiler Design PDFFernando Sandoval RuedaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Directional Drilling IntDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Directional Drilling IntJamel SlimaniNo ratings yet
- Chevron Sustainability Report 2020Document68 pagesChevron Sustainability Report 2020Hanif HamdaniNo ratings yet
- CV AJ Menzies Update 02142012Document8 pagesCV AJ Menzies Update 02142012Lazuardhy Vozicha FuturNo ratings yet
- Safety Testing Oh Machines - IFADocument55 pagesSafety Testing Oh Machines - IFAMarco LoiaNo ratings yet
- Green BuildingDocument6 pagesGreen BuildingAbood Buriahi100% (1)
- Cryogenic Systems Introduction - Joule-Thomson CryocoolerDocument9 pagesCryogenic Systems Introduction - Joule-Thomson CryocoolerGanesh ThoratNo ratings yet
- SD6830 Instructions SD6830 Instructions: DescriptionDocument7 pagesSD6830 Instructions SD6830 Instructions: Descriptionxerox4512No ratings yet
- Induction Hardening and Inspection PDFDocument9 pagesInduction Hardening and Inspection PDFAnonymous j0zANTHPc100% (1)
- Conveyor Auxiliaries - WPDocument47 pagesConveyor Auxiliaries - WPPaulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Heat Pump Analysis Of A Supercritical Water-cooled Nuclear Reactor And Hydrogen Production CycleDocument36 pagesChemical Heat Pump Analysis Of A Supercritical Water-cooled Nuclear Reactor And Hydrogen Production Cyclepisces1985No ratings yet
- LabVolt Industrial AC DrivesDocument121 pagesLabVolt Industrial AC Drivesumer farooqNo ratings yet
- Steam Heating Troubleshooting GuideDocument9 pagesSteam Heating Troubleshooting GuideSagar RaneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 (Chromatography)Document6 pagesExercise 4 (Chromatography)Wendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Electricity Sector in Kerala: Abey GeorgeDocument12 pagesAn Overview of Electricity Sector in Kerala: Abey GeorgeLukmanKpNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety: Photovoltaic Module PolycrystallineDocument1 pageQuality and Safety: Photovoltaic Module PolycrystallineLuis Felipe Barrera GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Force and MotionDocument18 pages4.2 Force and Motionvelavan100% (1)
- Manual Conductos HaierDocument152 pagesManual Conductos HaierdavidplanaNo ratings yet
- AUHF TS001 A6 Lineator AUHF Typical SpecificationDocument2 pagesAUHF TS001 A6 Lineator AUHF Typical SpecificationSlick72No ratings yet
- pdf74 BDocument2 pagespdf74 BPavlos TopalidisNo ratings yet
- Bomba de Alta Presion Denso Hp3Document4 pagesBomba de Alta Presion Denso Hp3Marcelo Diesel100% (5)
- vessel_update (13)Document8 pagesvessel_update (13)Lê Quyết ChungNo ratings yet
- SV420XVT1A LPL Service ManualDocument30 pagesSV420XVT1A LPL Service ManualJay HunterNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production by Steam Reforming of HC by TopsoeDocument2 pagesHydrogen Production by Steam Reforming of HC by TopsoeMainak Sarkar100% (1)
- Cyclic Simple Shear Test PrintDocument4 pagesCyclic Simple Shear Test PrintAlher HeraNo ratings yet