Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chairman Line 25 Square Feet 0 5 Hours O 10.32 Bud...
Uploaded by
Kdmfuffad liOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chairman Line 25 Square Feet 0 5 Hours O 10.32 Bud...
Uploaded by
Kdmfuffad liCopyright:
Available Formats
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / business / accounting / accounting questions and answers / chairman line 25 square feet 0 5 hours o 10.32 budget schedules for a m…
Question: Chairman Line 25 square feet 0 5 hours O 10.32 Budget sched… Post a question
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
(1 bookmark)
Enter question
Continue to post
20 questions remaining
Snap a photo from your
phone to post a question
We'll send you a one-time download
link
888-888-8888 Text me
By providing your phone number, you agree to receive a one-time
automated text message with a link to get the app. Standard
messaging rates may apply.
My Textbook Solutions
Introduction Operations Principles of
to Materials... and Supply... Corporate...
8th Edition 14th Edition 10th Edition
View all solutions
Show transcribed image text
Expert Answer
Anonymous answered this
Was this answer helpful? 0 0
2,220 answers
Answer:
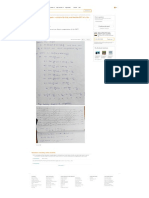
Budget schedules for a manufacturer
1a. Revenues Budget
Executive Chairman Total
Line Line
Units sold 740 390
Selling price $ 1,020 $ 1,600
Budgeted revenues $754,800 $624,000 $1,378,800
b. Production Budget in Units
Executive Chairman
Line Line
Budgeted unit sales 740 390
Add budgeted ending n. goods inventory 30 15
Total requirements 770 405
Deduct beginning n. goods. inventory 20 5
Budgeted production 750 400
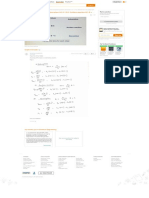
c. Direct Materials Usage Budget (units)
Oak Red Oak Red Total
Oak
Oak Legs
Legs
Executive Line:
1. Budgeted input per f.g. unit 16 – 4 –
2. Budgeted production 750 – 750 –
3. Budgeted usage (1 × 2) 12,000 – 3,000 –
Chairman Line:
4. Budgeted input per f.g. unit – 25 – 4
5. Budgeted production – 400 – 400
6. Budgeted usage (4 × 5) – 10,000 – 1,600
7. Total direct materials
usage (3 + 6) 12,000 10,000 3,000 1,600
Direct Materials Cost Budget
8. Beginning inventory 320 150 100 40
9. Unit price (FIFO) $18 $23 $11 $17
10. Cost of DM used from
beginning inventory (8 × 9) $5,760 $3,450 $1,100 $680 $10,990
11. Materials to be used from
purchases (7 – 8) 11,680 9,850 2,900 1,560
12. Cost of DM in March $20 $25 $12 $18
13. Cost of DM purchased and
used in March (11 × 12) $233,600 $246,250 $34,800 $28,080 $542,730
14. Direct materials to be used
(10 + 13) $239,360 $249,700 $35,900 $28,760 $553,720
Direct Materials Purchases
Budget
Red
Oak Oak
Oak Red Oak Legs Legs Total
Budgeted usage
(from line 7) 12,000 10,000 3,000 1,600
Add target ending inventory 192 200 80 44
Total requirements 12,192 10,200 3,080 1,644
Deduct beginning inventory 320 150 100 40
Total DM purchases 11,872 10,050 2,980 1,604
Purchase price (March) $20 $25 $12 $18 ________
Total purchases $237,440 $251,250 $35,760 $28,872 $553,322
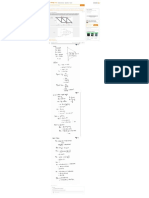
d. Direct Manufacturing Labor Budget
Output Direct
Manuf. Labor-
Units Hours per Total Hourly
Produced Output Unit Hours Rate Total
Executive Line 750 3 2,250 $30 $ 67,500
Chairman Line 400 5 2,000 $30 60,000
4,250 $127,500
e. Manufacturing Overhead Budget
Variable manufacturing overhead costs (4,250 × $35) $148,750
Fixed manufacturing overhead costs 42,500
Total manufacturing overhead costs $191,250
Total manuf. overhead cost per hour = = $45 per direct manufacturing labor-hour
Fixed manuf. overhead cost per hour = = $10 per direct manufacturing labor-hour
f. Computation of unit costs of ending inventory of nished goods
Executive Chairman
Line Line
Direct materials
Oak top ($20 × 16, 0) $320 $0
Red oak ($25 × 0, 25) 0 625
Oak legs ($12 × 4, 0) 48 0
Red oak legs ($18 × 0, 4) 0 72
Direct manufacturing labor ($30 × 3, 5) 90 150
Manufacturing overhead
Variable ($35 × 3, 5) 105 175
Fixed ($10 × 3, 5) 30 50
Total manufacturing cost $593 $1,072
Ending Inventories Budget
Cost per Unit Units Total
Direct Materials
Oak top $ 20 192 $ 3,840
Red oak top 25 200 5,000
Oak legs 12 80 960
Red oak legs 18 44 792
10,592
Finished Goods
Executive 593 30 17,790
Chairman 1,072 15 16,080
33,870
Total $44,462
g.
2. Areas where continuous improvement might be incorporated into the budgeting process:
(a) Direct materials. Either an improvement in usage or price could be budgeted. For example, the
budgeted usage amounts could be related to the maximum improvement (current usage – minimum
possible usage) of 1 square foot for either desk:
• Executive: 16 square feet – 15 square feet minimum = 1 square foot
• Chairman: 25 square feet – 24 square feet minimum = 1 square foot
Thus, a 1% reduction target per month could be:
• Executive: 15 square feet + (0.99 × 1) = 15.99
• Chairman: 24 square feet + (0.99 × 1) = 24.99
Some students suggested the 1% be applied to the 16 and 25 square-foot amounts. This can be done so
long as after several improvement cycles, the budgeted amount is not less than the minimum desk
requirements.
(b) Direct manufacturing labor. The budgeted usage of 3 hours/5 hours could be continuously revised on a
monthly basis. Similarly, the manufacturing labor cost per hour of $30 could be continuously revised down.
The former appears more feasible than the latter.
(c) Variable manufacturing overhead. By budgeting more efficient use of the allocation base, a signal is
given for continuous improvement. A second approach is to budget continuous improvement in the
budgeted variable overhead cost per unit of the allocation base.
(d) Fixed manufacturing overhead. The approach here is to budget for reductions in the year-to-year
amounts of xed overhead. If these costs are appropriately classi ed as xed, then they are more difficult
to adjust down on a monthly basis.
Comment
Questions viewed by other students
Q: Hello, currently stuck on this assignment
A: See answer 100% (2 ratings)
COMPANY LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER SERVICE
About Chegg Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Mobile Apps EasyBib Customer Service
Chegg For Good Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Give Us Feedback
College Marketing General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Thinkful Help with eTextbooks
Corporate Development Intellectual Property Rights Chegg Study Help Study 101 Help to use EasyBib Plus
Investor Relations Terms of Use College Textbooks Textbook Rental Manage Chegg Study
Jobs Global Privacy Policy eTextbooks Used Textbooks Subscription
Join Our Affiliate Program DO NOT SELL MY INFO Flashcards Digital Access Codes Return Your Books
Media Center Honor Code Learn Chegg Money Textbook Return Policy
Site Map Honor Shield Chegg Math Solver
© 2003-2021 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Question: Solve in Java Starter Code Import Java - Io. Import Java - Math.Document1 pageQuestion: Solve in Java Starter Code Import Java - Io. Import Java - Math.Jirapat ThonglekpechNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - Com97Document4 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - Com97BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Consider A Two-Stage Cascade Refrigeration System .Document5 pagesConsider A Two-Stage Cascade Refrigeration System .NaufalNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Learning Problem 12 37 Value Enginee...Document3 pagesCollaborative Learning Problem 12 37 Value Enginee...Md Rifat MotalebNo ratings yet
- Company Case Virgin America - Flight Service For Th...Document1 pageCompany Case Virgin America - Flight Service For Th...Ayu ParlindaNo ratings yet
- Question: (Practicing International Management Case BT in LocDocument1 pageQuestion: (Practicing International Management Case BT in LocMartinah Ross CoderaNo ratings yet
- The Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...Document3 pagesThe Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- C Given A Magnetic Circuit As Shown in Figure Q2c (...Document1 pageC Given A Magnetic Circuit As Shown in Figure Q2c (...Yong JinNo ratings yet
- Q2 - The Rigid Gate OAB of Figure 2 Is Hinged at O ...Document2 pagesQ2 - The Rigid Gate OAB of Figure 2 Is Hinged at O ...johan razakNo ratings yet
- Question: 1. The Following Equation Was Estimated Using The Data in CEDocument3 pagesQuestion: 1. The Following Equation Was Estimated Using The Data in CEBo NguyenNo ratings yet
- Costs in The Short Run Versus in The Long Run I...Document3 pagesCosts in The Short Run Versus in The Long Run I...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pretzel, A Pretzel Shop, Has The Followin...Document3 pagesUltimate Pretzel, A Pretzel Shop, Has The Followin...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Find The Volume of The Solid Obtained by Rotating The Region eDocument5 pagesQuestion: Find The Volume of The Solid Obtained by Rotating The Region eAdeel SyedNo ratings yet
- A Businesswoman Is Budgeting For Her Products Cam.Document4 pagesA Businesswoman Is Budgeting For Her Products Cam.Keith GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Market Structures For Each Scenario in The Foll...Document3 pagesMarket Structures For Each Scenario in The Foll...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...Document5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...Document5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- 2.calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Deman...Document5 pages2.calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Deman...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Case Study. For Your Better Understanding, Let Us Practice How TDocument1 pageQuestion: Case Study. For Your Better Understanding, Let Us Practice How Tfahad BataviaNo ratings yet
- Question: Consider The Following Performance Measurements For A ProgDocument3 pagesQuestion: Consider The Following Performance Measurements For A ProgTic tokNo ratings yet
- Short-Run Supply and Long-Run Equilibrium Consi... - Chegg - ComhDocument3 pagesShort-Run Supply and Long-Run Equilibrium Consi... - Chegg - ComhBLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximization Using Total Cost and Total ... - Chegg - Com6Document3 pagesProfit Maximization Using Total Cost and Total ... - Chegg - Com6BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- S and Discrete Probability Distributions 207 7.18 ...Document1 pageS and Discrete Probability Distributions 207 7.18 ...Yong JinNo ratings yet
- =32 MPa,人y= Given A Beam Section B × D = 450 Mm X...Document3 pages=32 MPa,人y= Given A Beam Section B × D = 450 Mm X...Civil EngineerNo ratings yet
- A Two-Start Worm Gear Rotating at 800 RPM Drives A...Document1 pageA Two-Start Worm Gear Rotating at 800 RPM Drives A...johan razakNo ratings yet
- Happy Cupcake, A Cupcake Shop, Has The Following M...Document3 pagesHappy Cupcake, A Cupcake Shop, Has The Following M...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Happy Cupcake, A Cupcake Shop, Has The Following M...Document3 pagesHappy Cupcake, A Cupcake Shop, Has The Following M...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Which Among The Following Statement/s Is/are Always TRUE AbDocument1 pageQuestion: Which Among The Following Statement/s Is/are Always TRUE Abkyle johnNo ratings yet
- Tilda Telecom Ltd. Claims That, On Average, Their ...Document3 pagesTilda Telecom Ltd. Claims That, On Average, Their ...Ushna HaiderNo ratings yet
- E. Testing Consumer Products For Some CationsDocument6 pagesE. Testing Consumer Products For Some CationsSaifullah KhawarNo ratings yet
- As An Expert in Thermodynamics, You Are Attempting...Document6 pagesAs An Expert in Thermodynamics, You Are Attempting...melisa.serpamNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - ComkijDocument5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - ComkijBLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - ComkijDocument5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - ComkijBLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - Com97Document4 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema... - Chegg - Com97BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Match Each Discrete-Time Signal With Its DFT. You Should Be AblDocument3 pagesQuestion: Match Each Discrete-Time Signal With Its DFT. You Should Be AblThePositive GuyNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...Document5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Calculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...Document5 pagesCalculating Marginal Revenue From A Linear Dema...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- A Find The Equivalent Capacitance For The Com... PDFDocument3 pagesA Find The Equivalent Capacitance For The Com... PDFRifah Shanjida MomoNo ratings yet
- The Cable AE Supports Three Vertical Loads From...Document3 pagesThe Cable AE Supports Three Vertical Loads From...BruhNo ratings yet
- A PL 3 8 X 7 Tension Member Is Connected With Thre...Document2 pagesA PL 3 8 X 7 Tension Member Is Connected With Thre...Raphael CajucomNo ratings yet
- Find Solutions For Your Homework: Enter QuestionDocument2 pagesFind Solutions For Your Homework: Enter QuestionAhmad HarithNo ratings yet
- 500,000 Revenues 200,000 Cost of Goods Sold (All V...Document3 pages500,000 Revenues 200,000 Cost of Goods Sold (All V...Hope Trinity EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Austin Electronics Manufactures Two Large Scree...Document4 pagesAustin Electronics Manufactures Two Large Scree...MahiNo ratings yet
- Question: 4.83 The Op Amp in The Precision Recti Er Circuit of Fig. P4.83 Is IDocument1 pageQuestion: 4.83 The Op Amp in The Precision Recti Er Circuit of Fig. P4.83 Is ISsebass PozzoNo ratings yet
- Substituent Effects To Use Organic Chemistry, Whet...Document8 pagesSubstituent Effects To Use Organic Chemistry, Whet...AD DNo ratings yet
- 1.16 The Power Required To Drive A Fan, P, Depends...Document3 pages1.16 The Power Required To Drive A Fan, P, Depends...نواف المالكيNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Competitive Markets The Mode...Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Competitive Markets The Mode...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Competitive Markets The Mode...Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Competitive Markets The Mode...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Sketch The Signal X Sin (2 Pi (0:7) /8) and ND The DFT of X. DoDocument2 pagesQuestion: Sketch The Signal X Sin (2 Pi (0:7) /8) and ND The DFT of X. DoThePositive GuyNo ratings yet
- Question: NO + S 1 NO.S Adsorption NO.S 1 B.S Surface Reaction B.S B +Document1 pageQuestion: NO + S 1 NO.S Adsorption NO.S 1 B.S Surface Reaction B.S B +Uh Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Q6 - Draw The - Circle Diagram - For 5.6 KW, 400 V,...Document6 pagesQ6 - Draw The - Circle Diagram - For 5.6 KW, 400 V,...krishneelNo ratings yet
- The Members Are Connected by The Details As Shown...Document2 pagesThe Members Are Connected by The Details As Shown...joizz rizzelle hilarioNo ratings yet
- Question: PROBLEM The Purpose of This Assignment Is To Review and UnDocument4 pagesQuestion: PROBLEM The Purpose of This Assignment Is To Review and UnNoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Consider The Competitive Market For Dress Shirts. ...Document4 pagesConsider The Competitive Market For Dress Shirts. ...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Consider The Competitive Market For Dress Shirts. ...Document4 pagesConsider The Competitive Market For Dress Shirts. ...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- A Uniform Rigid Bar of Length L and Mass MB Rot...Document1 pageA Uniform Rigid Bar of Length L and Mass MB Rot...Tekin EnerjiNo ratings yet
- A Unity Feedback System With Its Forward Transf...Document4 pagesA Unity Feedback System With Its Forward Transf...Cemerlang StudiNo ratings yet
- Write A C Program To Calculate The Parking Fare ...Document1 pageWrite A C Program To Calculate The Parking Fare ...Anthony PincaNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 19.2-1 Parameters of Acousto-Optic Modula.Document1 pageEXERCISE 19.2-1 Parameters of Acousto-Optic Modula.Irfan Satrio MardaniNo ratings yet
- ET Health Page-2Document1 pageET Health Page-2Kdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- ROverPlus, A Pet Product Superstore Is Considering...Document1 pageROverPlus, A Pet Product Superstore Is Considering...Kdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Beyond The Hype What Is The Strategic Business Value PDFDocument13 pagesBlockchain Beyond The Hype What Is The Strategic Business Value PDFNick DNo ratings yet
- Ten Step DecisionDocument18 pagesTen Step DecisionKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- 04 04 Creative BriefDocument1 page04 04 Creative BriefKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Beyond The Hype What Is The Strategic Business Value PDFDocument13 pagesBlockchain Beyond The Hype What Is The Strategic Business Value PDFNick DNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For ManagersDocument14 pagesBlockchain For ManagersKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- T3-FF ModelDocument137 pagesT3-FF ModelKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- T3-FF ModelDocument137 pagesT3-FF ModelKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Zalora Singapore - Creating An Omni-Channel Shopping Experience For ShoppersDocument19 pagesZalora Singapore - Creating An Omni-Channel Shopping Experience For ShoppersKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- T1 Sheet SummaryDocument216 pagesT1 Sheet SummaryKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Apple Watch - Setting The Next Concumer Lifestyle TrendDocument26 pagesApple Watch - Setting The Next Concumer Lifestyle TrendKdmfuffad liNo ratings yet
- Dharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFDocument14 pagesDharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFonlineyyk100% (1)
- Letter of IntentDocument2 pagesLetter of Intentmansoorstanikzai4No ratings yet
- Zero Voltage Switching Active Clamp Buck-BoostDocument10 pagesZero Voltage Switching Active Clamp Buck-Boostranjitheee1292No ratings yet
- Case Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodDocument5 pagesCase Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodJosielynNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Pakistani English Language LearnersDocument19 pagesFactors Affecting Pakistani English Language LearnersSaima Bint e KarimNo ratings yet
- James Bruce, One of Russian Tsar Peter The Great's Key Advisors (1669-1735)Document2 pagesJames Bruce, One of Russian Tsar Peter The Great's Key Advisors (1669-1735)Johanna Granville100% (1)
- IIRDocument2 pagesIIRJagan FaithNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CT-123 Course Title: Basic Networking Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesCourse Code: CT-123 Course Title: Basic Networking Course Descriptiondmcjr_stiNo ratings yet
- LNMIIT Course Information Form: A. B. C. D. E. FDocument2 pagesLNMIIT Course Information Form: A. B. C. D. E. FAayush JainNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Research Work at Iit Indore: ProjectsDocument2 pagesProposal For Research Work at Iit Indore: ProjectsAman GargNo ratings yet
- Aeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DataDocument4 pagesAeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DatamoussaouiNo ratings yet
- UNIABROAD PitchdeckDocument21 pagesUNIABROAD PitchdeckVikas MurulidharaNo ratings yet
- REACH ArticlesDocument12 pagesREACH ArticlesChristian SugasttiNo ratings yet
- BC Caribou Recovery Program Stakeholders Teleconference MinutesDocument5 pagesBC Caribou Recovery Program Stakeholders Teleconference MinutesRevelstoke MountaineerNo ratings yet
- ART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisDocument40 pagesART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisAarón Escorza MistránNo ratings yet
- EHS Audit - Review PaperDocument5 pagesEHS Audit - Review PaperYousef OlabiNo ratings yet
- Retail ImageDocument76 pagesRetail ImageayushiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Standard Costing - Variance AnalysisDocument50 pagesUNIT 5 Standard Costing - Variance AnalysisMohsin SheikhNo ratings yet
- But Flee Youthful Lusts - pdf2Document2 pagesBut Flee Youthful Lusts - pdf2emmaboakye2fNo ratings yet
- Inertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnDocument2 pagesInertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnSentoash NaiduNo ratings yet
- Mens and Actus ReusDocument3 pagesMens and Actus ReusBrian Okuku OwinohNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1CJ CastroNo ratings yet
- BLE Catalogue 2013Document21 pagesBLE Catalogue 2013Shahina Parvin ShaikNo ratings yet
- TP PortalDocument25 pagesTP PortalSurendranNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 5Document10 pagesAssignment No 5darshan KeskarNo ratings yet
- Screen 2014 Uricchio 119 27Document9 pagesScreen 2014 Uricchio 119 27NazishTazeemNo ratings yet
- M7Ge-Iiib-1: Renante Tillo JosolDocument3 pagesM7Ge-Iiib-1: Renante Tillo JosolRenante T. JosolNo ratings yet
- Data Science BooksDocument11 pagesData Science BooksAnalytics Insight100% (1)
- GW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetDocument6 pagesGW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetGina HuachoNo ratings yet