Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abuse and Violence
Uploaded by
Ray Anne Labra-PepitoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abuse and Violence
Uploaded by
Ray Anne Labra-PepitoCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12:
Abuse and Violence
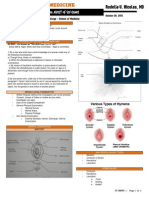
Clinical Picture of Abuse and Violence
v Abuse: wrongful use and maltreatment of another
o Perpetrator typically someone the person knows
v Victims across life span: spouses, partners, children,
elderly parents
v Types of injuries
o Physical
o Psychological
v Effect on survivors
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Characteristics of Violent Families
v Family violence: spouse battering; neglect and physical,
emotional, or sexual abuse of children; elder abuse;
marital rape
v Common characteristics
o Social isolation
o Abuse of power and control
o Alcohol and other drug abuse
o Intergenerational transmission process
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Cultural Considerations
v Domestic violence spanning families of all ages and from
all ethnic, racial, religious, socioeconomic, and sexual
orientation backgrounds
v Battered immigrant women at particular risk
o Face legal, social, and economic problems different
from the U.S. citizens
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Intimate Partner Violence #1
v Mistreatment or misuse of one person by another in
context of emotionally intimate relationship
v Psychological abuse (emotional abuse) can be overt or
subtle.
v Physical abuse: shoving, pushing, battering, choking
v Sexual: assaults during sexual relations, rape
v Rates higher among women
v Increased rates during pregnancy
v Domestic violence occurs in same-sex relationships with
same statistical frequency.
o Victims have fewer protections.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Intimate Partner Violence #2
v Clinical picture
o Abuse often perpetrated by husband against wife
o Abuser’s view of wife as belonging to him; strong
feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem; poor
problem-solving and social skills
o Increasing violence, abuse with any signs of
independence
o Dependency trait most commonly found in abused
women who stay with their husbands
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Intimate Partner Violence #3
v Cycle of abuse and violence
o Violent episode → honeymoon period → tension-
building phase → violent episode
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Intimate Partner Violence #4
v Assessment
o Victims do not commonly seek direct help for abuse.
§ Some may be seeking treatment for other
conditions.
v Ask all clients if they feel safe
v Ask questions about safety (see Box 12.2)
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
1. Question #1
Is the following statement true or false?
v The honeymoon period of violence often occurs before
the first episode of violence.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
1. Answer to Question #1
False
v Rationale: The honeymoon period occurs after an episode
of violence; this is the period in which the abuser
expresses regret and then apologizes and promises it will
never happen again.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Intimate Partner Violence #5
v Treatment and interventions
o Laws related to domestic violence; arrest
o Restraining order/protection order
o Recognition of stalking
o Shelters
o Individual psychotherapy/counseling, group therapy,
support and self-help groups
o Treatment for PTSD
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Child Abuse #1
v Intentional injury of a child
o Physical abuse or injuries
o Neglect or failure to prevent harm
o Failure to provide adequate physical or emotional
care or supervision
o Abandonment
o Sexual assault or intrusion
o Overt torture or maiming
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Child Abuse #2
v Clinical picture of parents
o Minimal parenting knowledge and skills
o Emotionally immature, needy, incapable of meeting
own needs
o Frequently view children as property
o Cycle of family violence: adults raising children in
same way they were raised
§ Adults who were victims of abuse frequently abuse
their own children.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Child Abuse #3
v Detection and accurate identification are the first steps
(see Box 12.3).
v Report suspected child abuse
o Nurse does not have to decide for certainty if abuse
occurred.
v Treatment and intervention
o Child’s safety and well-being is a priority.
o Psychiatric evaluation
o Therapy may be indicated over significant period.
o Approach depends on the age of a child.
o Social services involvement
o Family therapy/requirements for parents
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Elder Abuse #1
v Maltreatment of older adults
o Physical, sexual, psychological abuse
o Neglect of self-neglect
o Financial exploitation
o Denial of adequate medical treatment
v Estimated 10% of population over age 65 abused by
caregivers.
v 60% to 65% of victims are women.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Elder Abuse #2
v People who abuse elders almost always in caretaker role
or elders depend on them in some way.
v Most cases when one older spouse is taking care of
another
v Bullying between residents in senior living facilities
v Elders often reluctant to report abuse
o Want to protect family members
o Fear losing support
v Clinical picture: variable depending on the type of abuse
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Elder Abuse #3
v Assessment (possible indicators, see Box 12.4)
v Treatment and intervention
o Caregiver stress relief
o Additional resources
o Possible removal of elder or caregiver
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
2. Question #2
Is the following statement true or false?
v Adults who were abused as children are more likely to
abuse their own children.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
2. Answer to Question #2
True
v Rationale: The tendency for adults to raise children in the
same way they were raised perpetrates the cycle of
family violence. Adults who were victims of abuse as
children frequently abuse their own children.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Rape and Sexual Assault #1
v Perpetration of act of sexual intercourse with person
against his or her will and without consent
o Will overcome by force, fear of force, drugs,
intoxicants
v Crime of violence and humiliation of victim expressed
through sexual means
v Also rape if victim cannot exercise rational judgment
v Only slight penetration necessary
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Rape and Sexual Assault #2
v Committed by strangers (~28% of rapes),
acquaintances, married people, people of same sex
v Date rape (acquaintance rape)
v Highly underreported crime
v Most commonly occurs in victim’s neighborhood, often
inside or near home
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Rape and Sexual Assault #3
v Most rapes are premeditated.
v Male rape is significantly underacknowledged and
underreported.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Rape and Sexual Assault #4
v Dynamics of rape
o Generally accepted that rape is not sexual crime
§ Exertion of power, control, infliction of pain or
punishment.
o Feminist theory: women historically objects for
aggression.
o Primary motivation of victim is to stay alive.
o Severe physical and psychological trauma
o Treatment has improved, but many still believe a
woman provokes rape with behavior.
o Common myths (see Box 12.5)
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Rape and Sexual Assault #5
v Assessment
o Physical examination to preserve evidence
o Description of what happened
o Rape kits, rape protocols
v Treatment and intervention
o Immediate support
o Education (see Box 12.6)
o Give control back to victim
o Prophylactic treatment for STIs, pregnancy
o Counseling
o Supportive therapy
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Community Violence
v School violence (homicides, suicides, theft, violent
crimes)
v Bullying
o Ostracism
v Hazing
v Effects on children, young adults
v Violence on a larger scale (e.g., terrorism)
o PTSD and depression
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
3. Question #3
v Which of the following statements about rape is most
accurate?
A. It is a highly reported crime.
B. Most rapes are premeditated.
C. Rape requires ejaculation.
D. Provocative dress invites rape.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
3. Answer to Question #3
B. Most rapes are premeditated.
v Rationale: Most rapes are premeditated.
o Rape, an underreported crime, requires only slight
penetration of the vulva. Full erection or ejaculation
is not necessary. Provocative dress leading to rape is
a myth.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Self-Awareness Issues
v Be aware of own beliefs.
v Contain feelings of horror or revulsion, focus on client’s
needs.
o Validate the client’s feelings.
v Ask all women about abuse.
v Help client focus on the present.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Criminal Justice System Response To Crime VictimsDocument21 pagesCriminal Justice System Response To Crime VictimsDave FutalanNo ratings yet
- Forensic SerologyDocument13 pagesForensic Serologyempress venus bonillaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Rape Victim 2Document27 pagesExamination of Rape Victim 2preetNo ratings yet
- Philosophical PowerpointDocument12 pagesPhilosophical PowerpointChesli NapalitNo ratings yet
- Sexual DisorderDocument15 pagesSexual DisorderNurul Istiqomah0% (1)
- RPC Book IIDocument39 pagesRPC Book IILois D100% (1)
- Kinship Care: A Lived Experience of Young AdultsDocument12 pagesKinship Care: A Lived Experience of Young AdultsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Bipolar and Related Disorder - OdpDocument31 pagesBipolar and Related Disorder - OdpShielamae PalalayNo ratings yet
- Vaw FinalDocument8 pagesVaw FinalBreth1979No ratings yet
- Advocacy Campaign SpeechDocument2 pagesAdvocacy Campaign SpeechJOSHUA BECARESNo ratings yet
- Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act OF 2004Document15 pagesAnti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act OF 2004Noreen BughaoNo ratings yet
- Article I: Republic Act No. 2644 - An Act Regulating Midwifery Training and PracticeDocument5 pagesArticle I: Republic Act No. 2644 - An Act Regulating Midwifery Training and PracticeSheena Salva QuilangNo ratings yet
- Handout About Violence Against Women and Their ChildrenDocument6 pagesHandout About Violence Against Women and Their ChildrenAnonymous hWhsDI1zvhNo ratings yet
- Changes in Physical and Sexual SelfDocument1 pageChanges in Physical and Sexual SelfShiela Faye ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Assualt Harassment SlidesDocument29 pagesSexual Assualt Harassment Slidesapi-554136472No ratings yet
- Crises. It Includes The Art of Negotiation and The Application of Appropriate ForceDocument13 pagesCrises. It Includes The Art of Negotiation and The Application of Appropriate ForceElecer Gregorio GenovaNo ratings yet
- Juvenile DelinquencyDocument11 pagesJuvenile DelinquencyRocky Anthony100% (1)
- Deontological vs. Teleological Approaches To Ethical Evaluation of The Human ConductDocument22 pagesDeontological vs. Teleological Approaches To Ethical Evaluation of The Human ConductFrancine Nicole Arceo ElementoNo ratings yet
- Polygraph Examination: 02A-Forensic5-Wk1 Development of The LessonDocument3 pagesPolygraph Examination: 02A-Forensic5-Wk1 Development of The LessonAiven BarroaNo ratings yet
- Juvenile DelinquencyDocument34 pagesJuvenile Delinquencyjihan latifahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process DiagnosingDocument49 pagesNursing Process DiagnosingAnuchithra100% (2)
- Juvenile DelinquencyDocument8 pagesJuvenile Delinquencyapi-3850829No ratings yet
- Cyber CrimeDocument4 pagesCyber CrimeVarshini PrabaharanNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Funda NotesDocument50 pagesCompilation of Funda Notestempter_10No ratings yet
- Guidelines On Disaster ReportingDocument11 pagesGuidelines On Disaster ReportingAnonymous rxFEHHm8bNo ratings yet
- REED 102 M2 Lesson 3 For SFDocument9 pagesREED 102 M2 Lesson 3 For SFHaries Vi Traboc MicolobNo ratings yet
- Bill of RigthsDocument5 pagesBill of RigthsMarjo Catabay OconNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cdi, DrugsDocument25 pagesNotes On Cdi, DrugsReyvie Ylyx AgasNo ratings yet
- NSTP CWTS Specific Module 3 Peace EducationDocument41 pagesNSTP CWTS Specific Module 3 Peace EducationShai MacapillarNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior and VictiminologyDocument20 pagesHuman Behavior and VictiminologyKhristel Alcayde100% (1)
- Anti - Discrimination and Non - HarassmentDocument6 pagesAnti - Discrimination and Non - HarassmentKishore AustinNo ratings yet
- R.A 10821Document11 pagesR.A 10821Riza Gaquit100% (1)
- Cohort DesignDocument41 pagesCohort DesignHope EkwensiNo ratings yet
- Info-What Is Anger PDFDocument1 pageInfo-What Is Anger PDFClarisse MachadoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Victims of Violence: Sherwyn U. Hatab RNDocument49 pagesAssessing Victims of Violence: Sherwyn U. Hatab RNSherwyn Uy HatabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Personnel SecurityDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Personnel SecurityGOMEZ, LANI B.No ratings yet
- 1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesDocument2 pages1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesJaybee SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Drug Symp For StudentsDocument54 pagesDrug Symp For StudentsJoseph AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Modalities Midterm To FinalsDocument33 pagesTherapeutic Modalities Midterm To FinalsCriminegrology TvNo ratings yet
- Criminological Research & Basic Statistics Introduction PDFDocument14 pagesCriminological Research & Basic Statistics Introduction PDFMaria Claret Amor100% (1)
- Effectiveness, Scientific Validity and Limitations of The Polygraph TestDocument18 pagesEffectiveness, Scientific Validity and Limitations of The Polygraph TestLarry SiscarNo ratings yet
- Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDocument2 pagesNeurobiologic Theories and Psychopharmacologymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- CRIMINOLOGY 4 - Juvenile Delinquency & Crime Prevention Notes Md. 2Document54 pagesCRIMINOLOGY 4 - Juvenile Delinquency & Crime Prevention Notes Md. 2Ne JaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Good CharacterDocument5 pagesBenefits of Good CharacterMaviesdz DsouzaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Pres of Laws On WomenDocument21 pagesPowerPoint Pres of Laws On WomenEloisa CarilloNo ratings yet
- RA 9208 and RA 10364Document22 pagesRA 9208 and RA 10364edrea_abonNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BEHAVIOR AND VICTIMOLOGYDocument17 pagesHUMAN BEHAVIOR AND VICTIMOLOGYAirah Dela Rita TilapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ethics: Presented By: Mica Ella S. Gemino A2-3BSMA-02Document13 pagesIntroduction To Ethics: Presented By: Mica Ella S. Gemino A2-3BSMA-02Mica Ella GeminoNo ratings yet
- Women and Children With Law ScaleDocument30 pagesWomen and Children With Law ScaleDeanette MichaelaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Drug TalkDocument57 pagesAnti-Drug TalkMichael Paca-anasNo ratings yet
- 2005, The Effects of Imprisonment On Families and Children of PrisonersDocument22 pages2005, The Effects of Imprisonment On Families and Children of PrisonersEduardo RamirezNo ratings yet
- CHN - JoyDocument3 pagesCHN - JoyJoy VelascoNo ratings yet
- Concepts On Mental Health IllnessDocument13 pagesConcepts On Mental Health IllnessKoleen Lhyte UyNo ratings yet
- Moral Decision-MakingDocument2 pagesMoral Decision-MakingYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Classification of DrugsDocument58 pagesClassification of DrugsLerma Manalac100% (1)
- Human Rights Issues in The Context of Investigation Procedures With Case AnalysisDocument117 pagesHuman Rights Issues in The Context of Investigation Procedures With Case AnalysisLenin Mark Obera LesiguesNo ratings yet
- Domestic ViolenceDocument29 pagesDomestic ViolenceChester Alan Julian RicardoNo ratings yet
- Ch55Document36 pagesCh55Joanna Mie EstrososNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health NursingDocument32 pagesFoundations of Psychiatric Mental Health NursingRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Abuseand ViolenceDocument36 pagesAbuseand ViolenceKathreen TamayoNo ratings yet
- Anger, Hostility and AggressionDocument29 pagesAnger, Hostility and AggressionRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health NursingDocument32 pagesFoundations of Psychiatric Mental Health NursingRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDocument54 pagesNeurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Trauma and Stressor-Related DisordersDocument32 pagesTrauma and Stressor-Related DisordersRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy For Young ProfessionalsDocument44 pagesFinancial Literacy For Young ProfessionalsRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment (Compressed)Document68 pagesHandbook of COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment (Compressed)Vanessa SánchezNo ratings yet
- Module 4 WorksheetDocument1 pageModule 4 WorksheetRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Man, Microorganism and The Environment - ENVIROMENTAL HEALTHDocument94 pagesMan, Microorganism and The Environment - ENVIROMENTAL HEALTHRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Group DynamicsDocument2 pagesModule 4 - Group DynamicsRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene in The Healthcare Setting: Ray Anne Labra-Pepito, MSN, RNDocument11 pagesHand Hygiene in The Healthcare Setting: Ray Anne Labra-Pepito, MSN, RNRay Anne Labra-PepitoNo ratings yet
- Social Studies (SBA) (YEAR 2021) Single ParentDocument18 pagesSocial Studies (SBA) (YEAR 2021) Single Parentshantoy cunninghamNo ratings yet
- 9242-Article Text-18213-1-10-20160204Document6 pages9242-Article Text-18213-1-10-20160204timaNo ratings yet
- Discussion EssayDocument2 pagesDiscussion EssayEmilyNo ratings yet
- How To Build Emotional Intimacy With Your PartnerDocument17 pagesHow To Build Emotional Intimacy With Your Partnerdaniel DanladiNo ratings yet
- LGBT ReportDocument4 pagesLGBT ReportRodalyn Joy DizonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Relevant LiteratureDocument7 pagesSummary of Relevant LiteratureFenny Mei LinaNo ratings yet
- Personal Relationship - 10Document17 pagesPersonal Relationship - 10Mandy Xi100% (2)
- Child Care Facilities List March 23Document20 pagesChild Care Facilities List March 23Jennifer MontielNo ratings yet
- Final Practicial ResearchDocument9 pagesFinal Practicial ResearchMark VirgilNo ratings yet
- History of Ece in PakistanDocument5 pagesHistory of Ece in PakistanmhumayounNo ratings yet
- Why I Fight With My PeersDocument3 pagesWhy I Fight With My PeersDaniel SutterNo ratings yet
- AdulteryDocument49 pagesAdulterysonal_law88% (8)
- Survey FinalDocument3 pagesSurvey FinalbmharveyNo ratings yet
- KidsMatter Parent SurveyDocument2 pagesKidsMatter Parent SurveyAlice Del Rosario CabanaNo ratings yet
- Development TaskDocument7 pagesDevelopment TaskNorienne Teodoro0% (1)
- Lecture On Sexual AbnormalitiesDocument33 pagesLecture On Sexual AbnormalitiesRenz L. Salumbre80% (5)
- Bullies 3Document5 pagesBullies 3api-291823000No ratings yet
- Developmental Tasks According To Developmental Stages Lesson 3 Group 2Document22 pagesDevelopmental Tasks According To Developmental Stages Lesson 3 Group 2Shelina Obnimaga100% (1)
- Marriage EssayDocument9 pagesMarriage Essayapi-488081108No ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesLau AngelNo ratings yet
- Family Law I Introductory Lecture W1Document2 pagesFamily Law I Introductory Lecture W1JelisaNo ratings yet
- AHS Stress ScaleDocument3 pagesAHS Stress Scaleshamoon8100% (1)
- Abnormal Sex BehaviorsDocument4 pagesAbnormal Sex BehaviorsannthemsNo ratings yet
- Philippine Star, Aug. 15, 2019, Transgender's Arrest in QC Mall Cause Stir PDFDocument1 pagePhilippine Star, Aug. 15, 2019, Transgender's Arrest in QC Mall Cause Stir PDFpribhor2No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam in Personal DevelopmentDocument3 pages2nd Quarter Exam in Personal DevelopmentMarie Villanueva100% (1)
- An Ex Post Facto Study On The Relationship Between Parenting Style and Teenage Pregnancy of The Selected AdolescenceDocument14 pagesAn Ex Post Facto Study On The Relationship Between Parenting Style and Teenage Pregnancy of The Selected AdolescenceJanelle DionisioNo ratings yet
- Transgender - Who Are TheyDocument49 pagesTransgender - Who Are Theyurmimala21100% (1)
- Reasons Why A Child Becomes A Bully: BullyingDocument2 pagesReasons Why A Child Becomes A Bully: BullyingKeran VarmaNo ratings yet
- The Mauritian FamilyDocument1 pageThe Mauritian FamilyAshnaBeeslall0% (1)
- Gender Gap EssayDocument5 pagesGender Gap Essayapi-269633318No ratings yet