Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DIENCEPHALON: (Thalamus and Hypothalamus) THALAMUS: P. 531 Many Nuclei
Uploaded by
jael920 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views7 pagesOriginal Title
DIENCEPHALON
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views7 pagesDIENCEPHALON: (Thalamus and Hypothalamus) THALAMUS: P. 531 Many Nuclei
Uploaded by
jael92Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
DIENCEPHALON; BRAINSTEM; LIMBIC &
RAS SYSTEMS; CRANIAL NERVES;
CEREBELLUM
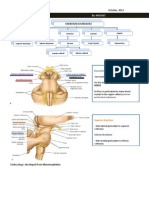
DIENCEPHALON: (Thalamus and Hypothalamus)
THALAMUS: P. 531 many nuclei
. GATEWAY TO CEREBRAL CORTEX
. Location – superior end of brainstem; beneath cerebral
hemisphere
. 5-6 cm. oval bodies
. Third ventricle –protrude medially thru here
. About 23 Nuclei (gray matter) in each lobe or
Geniculate Bodies connected by the Intermediate
Mass in 70% of the population
Medial Geniculate Body (auditory) MGN
Lateral Geniculate Body (vision) LGN
. Functions –
1. touch/pressure 7.
2. pain 8.
3. heat 9.
4.cold 10.
5 . vibrations
6.
. fMRI –tape-radio-action glucose (it glows)
. Thalamic Syndrome –burning sensation on a certain part of ur body
HYPOTHALAMUS: pp. 531-533
. Location –engulfed inside the thalamus
. Shape – highly irregular
. Structures: (12 or more nuclei)
Gray matter around the Optic Chiasmata
Tuber cinereum- stock of the pituitary
Infundibulum
Mammillary bodies
Posterior Pituitary gland ?
. Functions:
1. Highest Center of the Autonomic Nervous
System (ANS)
2. Links N.S. to Endocrine System
3. “Fight or Flight” - stress
4. Controls thirst (osmoreceptors)
5. Sleep-Wake Cycles
6. Appetite (glucoreceptors)
7. Body Temperature (shivering, sweating,VD,VC)
8.controls water and electrolytes
9.uterine contraction
10.
EPITHALAMUS: p.533
PINEAL BODY (Gland) “epiphysis”
. Location –
. Shape –
. Functions:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) –
BRAINSTEM
MESENCEPHALON: (Mid-brain) p. 528
. Location – between the diencephalon and pons
. Shape – shortest portion
. Superior Peduncle (Tract) – “little feet”;
to cerebellum
. Aqueduct of Sylvius (Cerebral aqueduct)
. Mainly white fibers (small tracts)
. Corpora Quadrigemina: (body/group of 4)
Superior colliculi- focusing; tracking an
object with the eyes; blinking;
papillary dilation and constriction
Inferior colliculi- reflex of “turning
towards a sound” or Startle Reflex;
“Righting Reflex”
. Tectum portion - contains corpora quadrigemina
. Tegumental portion – rich in dopamine
(Substantia Nigra)
. III Oculomotor and IV Trochlear Cranial Nerves
. Red nucleus –
PONS VAROLII: “bridge” pp. 525-527
. Location –
. Mainly white matter
. Middle Cerebellar Peduncle (tract) to mid-brain
. Cranial Nerves:
V Trigeminal
VI Abducens
VII Facial
VIII Vestibulocochlear
. Respiratory Center:
. Pontine Respiratory Group
Pneumotaxic Center
Apneutic Center
MEDULLA OBLONGATA: pp. 524-525
. Location-
. Nuclei (Nucleus Ambiguus, Hypoglossal Nucleus,
and Vagal Nuclei) and White Matter
. Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle -
. Cranial Nerves:
VIII Vestibulocochlear (shared with Pons)
IX Glossopharyngeal
X Vagus- means wanderer, only below neck,
parasympathetic
XI Spinal Accessory
XII Hypoglossal
. PYRAMIDAL TRACTS and decussation (80-85%)
Corticospinal and Corticobulbar tracts
Corticospinal Tracts –
Lateral –
Anterior –
Corticobulbar tracts –
EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM -
. Functional system of three layers of
Integration (cortical, basal ganglia,
mid-brain)
. Outside Pyramidal (motor tracts from
pyramidal cells)
. Postural Adjustments and Autonomic
integration
. Vital Motor Reflex Centers
1.
2.
3.
. Non-vital Reflexes (may be produced voluntarily)
1. vomiting 4.sneezing
2. hiccups 5.coughing
3.
RETICULAR ACTIVATING SYSTEM:(RAS) pp. 528-529
. Location –
. White and gray matter (several nuclei)
. "Closed Circuit" between the cerebrum and
spinal cord
. Functions:
1. Center for arousal and motivation
2. Raphe Nuclei- serotonin rich
3. Norepinephrine (NE)- excitatory
4. Gaze center- tract and fix on
an object
5. Pain modulation
6. Maintain consciousness
7. Reticulospinal tracts- tone, balance,
posture
8. Cardiovascular Control Related
Twisting of the Brain Stem –
African Sleeping Sickness -
LIMBIC SYSTEM: pp.536-537
. Location -
. "Visceral Brain" or "Reptilian Brain"
. Shape –girdles around in circles
. Structures:
1. Cingulate gyri (superior to hippocampus)-
emotions
2. Hippocampus-short term to long term memory
3. Amygdala-emotions
4. Olfactory Cranial Nerves-smell
5. Thalamus (anterior)-switch yard for sensory
info ; analyzes info
6. Mammillary bodies-
7. Fornix-transverse tract; connects old brain to
new brain
8. Septum pellucidum-btwn lateral ventricles; for
sexual pleasure
. Functions:
1. Emotions
2. Temper/Violence/Rage
3. Sorrow
4.feelings of pleasure/pleasantness
5.motivation
6.learning
CRANIAL NERVES: pp. 449-559 (Be able to IDENTIFY
the Name; Roman numeral;
Origin; Motor/Sensory/
Mixed; and FUNCTIONS)
Table 14.1
Cranial Nerves with a few functions listed
I. Olfactory Odor
II. Optic Vision
III. Oculomotor SR, MR, IR, IO (extrinsic
eye
muscles)
IV. Trochlear SO
V. Trigeminal Ophthalmic, Maxillary,
Mandibular
Divisions;
VI. Abducens LR
VII. Facial Taste, facial expression,
tears, saliva
VIII. Vestibulocochlear Auditory, Equilibrium
IX. Glossopharyngeal Posterior tongue, pharynx
X. Vagus Heart rate, visceral
sensory, etc.
XI. Spinal Accessory Trapezius, SCM
XII. Hypoglossal Tongue
. 12 Pair with Roman Numerals
. Pass through foramen magnum of skull and other
foramen/fissures
. Named anterior to posterior
. 2 pair from forebrain, 10 pair for mid-brain
and brainstem
. II and IV are contralateral
. Sensory I, II, VIII
Motor III, IV, VI, XI, XII
Mixed V, VII, IX, X
(Note: Only I, and II are “pure”,
whereas
the Motor have some afferent
fibers)
. Origin: I, II Cerebrum
III, IV Midbrain
V, VI, VII, VIII Pons (VIII
Shared
with
Medulla)
IX, X, XI, XII Medulla
CEREBELLUM: pp.529-530
. Location –posterior part of brain
. Granule and Purkinje cells -
. Two hemispheres (4 deep nuclei in each
Hemisphere)
Transverse fissure
Tenorium cerebelli (dura mater)
Falx cerebelli (dura mater)
. Arbor vitae -
. Folia –
. 10% brain mass-
. Major Structures:
1. Vermis-gross motor correlation; connects
2hemispheres
2. Lateral Hemispheres -
3. Flocculonodular Lobes-
Inferior Peduncle (tract -
FUNCTIONS:
. Smooths actions of muscle groups by
regulating and grading muscle tension
. Does not initiate any movements
. Monitors SENSORY input from muscles, tendons,
joints, and vestibular organs or
PROPRIOCEPTIVE INPUTS (the sense of
relative position of one body
part to another)
. Ataxia; Intention tremor; cerebral Palsy
You might also like
- The Wim Hof Method - Wim HofDocument13 pagesThe Wim Hof Method - Wim Hofrichard dickison100% (10)
- The Nervous System - NursingDocument59 pagesThe Nervous System - NursingDR Archana Agarwal100% (2)
- (STUART MCGILL - Core Training Evidence Translating To Better PerfoDocument15 pages(STUART MCGILL - Core Training Evidence Translating To Better PerfoSakip Hirrim100% (2)
- Rullida - EdullantesDocument36 pagesRullida - EdullantesJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Rullida - EdullantesDocument36 pagesRullida - EdullantesJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesNervous SystemHarini kumaranNo ratings yet
- Brain & Limbic SystemDocument63 pagesBrain & Limbic Systemgopscharan100% (1)
- Anatomy of The BrainDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The BrainMey RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Study MaterialDocument16 pagesAnatomy Study MaterialAyeshik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument103 pagesThe Brainrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Guided Notes For The Central Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesGuided Notes For The Central Nervous SystemJasper FajardoNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Basic FunctionalDocument50 pagesA Brief Introduction To Basic FunctionalkiflomNo ratings yet
- Brain-cerebrum-cerebellum-csf-meninges-EyeballDocument21 pagesBrain-cerebrum-cerebellum-csf-meninges-Eyeballayat ullahNo ratings yet
- Midbrain and PonsDocument8 pagesMidbrain and PonsMatet Monje100% (3)
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsVasudha RohatgiNo ratings yet
- CNS Study GuideDocument6 pagesCNS Study GuideNasibah BaruangNo ratings yet
- Stella Maris Polytechnic: The Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesStella Maris Polytechnic: The Nervous SystemKalpana jestinaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaDocument37 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaShanailNo ratings yet
- Chap-21 Neural Control and CordinationDocument48 pagesChap-21 Neural Control and CordinationMANIK CHHABRANo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Nervous System PDFDocument9 pagesNervous System PDFAfif Al BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Dissection 2Document12 pagesDissection 2hadiqaasif01No ratings yet
- CVD Case StudyDocument12 pagesCVD Case StudySean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetNo ratings yet
- Exsc 224 Chapter 12Document29 pagesExsc 224 Chapter 12api-546704939No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainLhyn BagunuNo ratings yet
- Sensory Nervous System Motor Nervous System: Sometimes Aware, I.E. Menstrual CrampsDocument8 pagesSensory Nervous System Motor Nervous System: Sometimes Aware, I.E. Menstrual CrampsGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- A 1.2 Cerebrum Dan DiencephalonDocument31 pagesA 1.2 Cerebrum Dan Diencephalonasa0411 behiraNo ratings yet
- Nervous System EditedDocument36 pagesNervous System EditedMellida Kate Winslet T.No ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument2 pagesCerebrumjnthnrsjNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDyah Ayu Pratama SariNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyremegelbristolNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum and Diencephalon AnatomyDocument39 pagesCerebrum and Diencephalon AnatomySarahNo ratings yet
- Dia GridDocument7 pagesDia GridMark Ross CanaoayNo ratings yet
- The Brain Is Composed of The,, andDocument23 pagesThe Brain Is Composed of The,, andMohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesDocument5 pagesChapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Nervous System of The FrogDocument38 pagesNervous System of The Frognone57% (7)
- The Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeDocument182 pagesThe Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeAlibasher MacalnasNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy ReviewDocument107 pagesNeuroanatomy ReviewAlan Magpantay100% (1)
- Lecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemT-Bone02135No ratings yet
- CH 12 SLOLab CardsDocument5 pagesCH 12 SLOLab Cardsmahakhadim16No ratings yet
- Diencephalon (" Interbrain ")Document29 pagesDiencephalon (" Interbrain ")marciaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Account of Brain in Vertebrates Dr. Younus Ah PDFDocument14 pagesComparative Account of Brain in Vertebrates Dr. Younus Ah PDFIsmart PraveenNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesCentral Nervous SystemCaroleNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocument61 pagesBrain Structure and FunctionBINITANo ratings yet
- The Brain - Macroscopic Organisation & Surface Features The CerebrumDocument5 pagesThe Brain - Macroscopic Organisation & Surface Features The CerebrumOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Physio. Psych Structure-Of-The-Nervous-System-Fact-SheetDocument7 pagesPhysio. Psych Structure-Of-The-Nervous-System-Fact-SheetJustynmae JusainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NOTES 4Document38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NOTES 4mike921goldNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based NursingDocument9 pagesEvidence-Based NursingKate AbadNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1laaraybmehmood1503No ratings yet
- Structure of Brain and Its FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure of Brain and Its FunctionDr.Shahana banuNo ratings yet
- AD 7 The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesAD 7 The Nervous SystemBernard SalimNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument37 pagesHuman BrainjhoenlitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Biotrans 08 ch5 - 01 PDFDocument137 pagesBiotrans 08 ch5 - 01 PDFJonNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Media and Organic Additives Interaction On in Vitro Regeneration of Dendrobium OrchidDocument6 pagesEffects of Different Media and Organic Additives Interaction On in Vitro Regeneration of Dendrobium OrchidMarco CordobaNo ratings yet
- DISEASE AGE RANGE Sex Crosstabulation: CountDocument66 pagesDISEASE AGE RANGE Sex Crosstabulation: CountchanlalNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFmariputwashercy4ca100% (15)
- Serotonin: Perception of Resource AvailabilityDocument3 pagesSerotonin: Perception of Resource AvailabilityStregattoNo ratings yet
- Edible Plants: Eduardo H. Rapoport and Barbara S. DrausalDocument8 pagesEdible Plants: Eduardo H. Rapoport and Barbara S. DrausalrafrejuNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Multiple Choice Revision QuestionsDocument8 pagesEnzymes Multiple Choice Revision QuestionsAli Sajjad50% (2)
- Lesson Plan Kkp1Document5 pagesLesson Plan Kkp1Niar SamandiNo ratings yet
- ESCMC Catalogo Da BibliotecaDocument141 pagesESCMC Catalogo Da Bibliotecaeusoqueroessapesquis0% (1)
- Biotechnology 1609322314Document100 pagesBiotechnology 1609322314Abdullah SaeedNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness Glossary of TermsDocument2 pagesMindfulness Glossary of TermsmykolayovychNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - Homology and Analogy of Plants and AnimalsDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - Homology and Analogy of Plants and AnimalsAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP q2Document6 pagesSemi Detailed LP q2mercy paduaNo ratings yet
- You Can Grow Your IntelligenceDocument6 pagesYou Can Grow Your IntelligenceSoniaNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi Sel RingkasanDocument2 pagesReproduksi Sel RingkasanMulyadi SPdNo ratings yet
- Pro Saber 8Document12 pagesPro Saber 8JAQUELINE RODRIGUEZ AGUDELONo ratings yet
- The Salt Myth Revealed Treatment of Gyro Dactyl Id Infections On Ornamental GuppiesDocument6 pagesThe Salt Myth Revealed Treatment of Gyro Dactyl Id Infections On Ornamental GuppiesNathan HillNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes On Microbodies Flagella and CiliaDocument23 pagesBiology Notes On Microbodies Flagella and CiliaLai Zhi YongNo ratings yet
- Food Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage ProteinDocument25 pagesFood Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage Proteinuminoriah80% (5)
- Activity - Camera and Human EyeDocument5 pagesActivity - Camera and Human EyeVincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins 1Document72 pagesPlasma Proteins 1reuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 James Wilson 17727701Document104 pagesAssessment 1 James Wilson 17727701api-357518223No ratings yet
- Selenoportax Vexillarius From Dhok Pathan, Chakwal District, The Punjab, PakistanDocument7 pagesSelenoportax Vexillarius From Dhok Pathan, Chakwal District, The Punjab, PakistanInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- LP OkDocument10 pagesLP OkHannah Rose ValdezNo ratings yet
- Diploma Course in Hearing, Language and Speech (DHLS)Document23 pagesDiploma Course in Hearing, Language and Speech (DHLS)sudhirpratapsinghratNo ratings yet
- Literature Please Refer To Included For Correct: Principles & Practice of Diffusion & OsmosisDocument30 pagesLiterature Please Refer To Included For Correct: Principles & Practice of Diffusion & OsmosisrezamaulanaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Semester Gasal Bing Kelas Xii Ipa Paket 3Document15 pagesUjian Semester Gasal Bing Kelas Xii Ipa Paket 3Richard sutantoNo ratings yet