Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topics - 6: Co-Ordinate Geometry: Formula
Uploaded by
Mohammad Ali ZawadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topics - 6: Co-Ordinate Geometry: Formula
Uploaded by
Mohammad Ali ZawadCopyright:
Available Formats
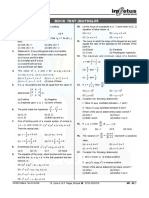
Topics – 6 : Co–ordinate Geometry
Formula:
B ( x2 , y 2 )
x x y y
1. Midpoint of A and B is 1 2 , 1 2 .
2 2
A( x1 , y1 )
2. Distance between A and B i. e. length AB = x1 x2 2 y1 y2 2 .
C ( x3 , y3 )
1 x1 x2 x3 x1
3. Area of ABC =
2 y1 y2 y3 y1
1
= x1 y2 x2 y3 x3 y1 x1 y3 x3 y2 x2 y1 A( x1 , y1 ) B( x2 , y 2 )
2
1 x1 x2 x3 x1
4. When A, B and C lie on a straight line. Then Area of ABC = 0 i, e, =0
2 y1 y2 y3 y1
B ( x2 , y 2 )
y2 y1
5. Gradient of line AB is m .
x2 x1
A( x1 , y1 )
6. Let, m1 be the gradient of line l1 and m2 be the gradient of line l2 .
(a) When the line l1 is parallel to the line l2 , then m1 = m2 .
(b) When the line l1 is perpendicular to the line l2 , then m1 m2 = - 1.
7. Equation of the straight line y y1 m( x x1 ) .
mx nx1 my2 ny1
8. when AC : BC = m : n, then C 2 , .
mn m n
AC BC AC
9. (i) Sin , (ii) Cos , (iii) tan .
AB AB BC
10. (i) Sin(1800 ) Sin , (ii) Cos(1800 ) Cos , (iii) tan(1800 ) tan .
1
11. (a) Gradient of x–axis is zero. (b) Gradient of y–axis is infinity .
0
12. (a) Equation of x-axis is y = 0. (b) Equation of y-axis is x = 0.
You might also like
- Coordinate GeometryDocument27 pagesCoordinate GeometryVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry PDFDocument11 pagesCoordinate Geometry PDFManoj SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Straight LineDocument3 pages11 - Straight LineHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesShanaz ParsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry NotesDocument11 pagesCoordinate Geometry NotesThe Unwanted RogueNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Theory (1-27) - F24Document27 pagesStraight Line Theory (1-27) - F24neerajNo ratings yet
- Math NotesDocument107 pagesMath Notesahmed5030 ahmed5030100% (1)
- James Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument9 pagesJames Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts:) y y X X (Document5 pagesKey Concepts:) y y X X (virat gandhiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Coordinate Geometry HyperbolaDocument11 pagesMathematics: Coordinate Geometry HyperbolaHairy Balls2No ratings yet
- Maths IBDocument376 pagesMaths IBAddalla veerrajuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formula: Topic Phase-1Document7 pagesMathematics Formula: Topic Phase-1testerNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryDocument10 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryAmaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Test 1 (Q20)Document2 pagesTest 1 (Q20)Mitadru DattaNo ratings yet
- Caps 22Document4 pagesCaps 22Sai Venkata Krishna GNo ratings yet
- Key Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Document21 pagesKey Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Ayah100% (1)
- 2D Part 01 C of PointsDocument11 pages2D Part 01 C of PointsVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet of Coordinate GeometryDocument14 pagesFormula Sheet of Coordinate GeometryBhavesh Kumar100% (1)
- Straight LinesDocument15 pagesStraight Linescatchshawty1614No ratings yet
- Straight Lines - IIT-JEE Advanced Level QuestionsDocument7 pagesStraight Lines - IIT-JEE Advanced Level QuestionsEr. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)100% (1)
- Exam in Analytic Geometry With AnswersDocument3 pagesExam in Analytic Geometry With AnswersGERRY MAKILAN100% (1)
- StraightLines FinalSendDocument14 pagesStraightLines FinalSendAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- IB 01 Coordinate System (1 5)Document5 pagesIB 01 Coordinate System (1 5)eamcetmaterials86% (7)
- KCET MathDocument9 pagesKCET MathHarshNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions SolutionsDocument12 pagesSec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions Solutionsjiajing shenNo ratings yet
- 024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Document8 pages024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- F3 Ch11 SuppWSDocument16 pagesF3 Ch11 SuppWSJustin ChanNo ratings yet
- Straght Lines TheoryDocument24 pagesStraght Lines TheorySk 3jNo ratings yet
- 2022 Prelim P2 Qns (Non Booklet) - RemovedDocument1 page2022 Prelim P2 Qns (Non Booklet) - Removedjishna.rao21No ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument12 pagesCo-Ordinate GeometrymohithheadspaceNo ratings yet
- Ellipse-02 - Solved ExampleDocument11 pagesEllipse-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Handbook: General Mathematics III: Geometry, Vectors and DynamicsDocument124 pagesHandbook: General Mathematics III: Geometry, Vectors and DynamicsNabil-babayo WANKANo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Straight LinesDocument15 pagesSheet - 01 - Straight LinesNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- JEE Advance (2011-2020)Document95 pagesJEE Advance (2011-2020)SachinNo ratings yet
- GraphingDocument2 pagesGraphingChiam Jia HaoNo ratings yet
- Three Dimension - Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesThree Dimension - Chapter NotesDivyanshi VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- True Light Girls' College S.4 Mathematics (Compulsory Part) CNY Homework (21-22)Document6 pagesTrue Light Girls' College S.4 Mathematics (Compulsory Part) CNY Homework (21-22)Christina GurungNo ratings yet
- Problem Practice For Class XIIDocument42 pagesProblem Practice For Class XIISunil SinghNo ratings yet
- 07 Straight Line BrahmastraDocument16 pages07 Straight Line BrahmastraAnkit Ranjan100% (1)
- Calculus BookDocument4 pagesCalculus BookMuhammad Noman Khalid0% (1)
- Maths Module 3B Solutions PDFDocument41 pagesMaths Module 3B Solutions PDFShashankAnilNo ratings yet
- F5 Am (CLB 2020-08)Document3 pagesF5 Am (CLB 2020-08)wickeromg12No ratings yet
- Vector 3d MathongoDocument13 pagesVector 3d MathongoArya NairNo ratings yet
- Areas Test 15-09-2020Document4 pagesAreas Test 15-09-2020lash73752No ratings yet
- For Jac & Cbse Board: Mathematics ClassesDocument11 pagesFor Jac & Cbse Board: Mathematics ClassesAnonymous kIvKBSfnxNo ratings yet
- Pastpaper DoubtsDocument34 pagesPastpaper DoubtsArishaNo ratings yet
- IIT - Derivadas Na Geometria AnalíticaDocument11 pagesIIT - Derivadas Na Geometria AnalíticalucasNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 01 Circle: Check Your GraspDocument13 pagesExercise - 01 Circle: Check Your GraspsuryaNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines-02 - Solved ExampleDocument14 pagesStraight Lines-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirDocument44 pages07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirPiyush Agarwal100% (1)
- Revision (A8) : 1, 2,, 2 2 Ak K BKK 1 2,7, 11,6 1, 2Document8 pagesRevision (A8) : 1, 2,, 2 2 Ak K BKK 1 2,7, 11,6 1, 2bjyxyydsNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument14 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformDev PuriNo ratings yet
- Solomon G QP - C1 Edexcel PDFDocument4 pagesSolomon G QP - C1 Edexcel PDFkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Solomon G QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon G QP - C1 EdexcelMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document7 pagesPaper 1krishjhunjhunwala1254No ratings yet
- Advanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedDocument299 pagesAdvanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedShikhar Gupta90% (31)
- Introduction To Three Dimensional Geometry Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 12 (PDF)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Three Dimensional Geometry Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 12 (PDF)Govind Mani BhattNo ratings yet
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Healthy Clean Eating Guide + Sample RecipesDocument11 pagesHealthy Clean Eating Guide + Sample RecipesNguyễn Thế SơnNo ratings yet
- Topical Eco Bus ScheduleDocument2 pagesTopical Eco Bus ScheduleMohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Mock Calender 2022 May-June: 1 2 Economics P1 & P2Document3 pagesMock Calender 2022 May-June: 1 2 Economics P1 & P2Mohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Average Reports of Class Test (May/June 2020) Subject: Mathematics - D Batch ST-4 Time Duration: 1 June, 2020 To ContinuousDocument2 pagesAverage Reports of Class Test (May/June 2020) Subject: Mathematics - D Batch ST-4 Time Duration: 1 June, 2020 To ContinuousMohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Logarithm Formula:: DifferentiationDocument3 pagesLogarithm Formula:: DifferentiationMohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Topics - 6: Co-Ordinate Geometry: FormulaDocument2 pagesTopics - 6: Co-Ordinate Geometry: FormulaMohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Mock Routine 2021 2022Document1 pageMock Routine 2021 2022Mohammad Ali ZawadNo ratings yet
- Multiaxial FatigueDocument32 pagesMultiaxial FatigueKittikun JitpairodNo ratings yet
- Rocket Equation Derivation NotesDocument7 pagesRocket Equation Derivation NotesSrikar GhooliNo ratings yet
- Propensity Toward Indebtednes - Evidence From MalaysiaDocument13 pagesPropensity Toward Indebtednes - Evidence From MalaysiaWihelmina DeaNo ratings yet
- Process Synchronization and DeadlockDocument41 pagesProcess Synchronization and DeadlockRemy Kuswara Putra KelanaNo ratings yet
- Python IteratorsDocument8 pagesPython Iteratorssaad_plivo0% (1)
- Gas Absorption - Lecture 3Document37 pagesGas Absorption - Lecture 3aminsubriNo ratings yet
- Mine System Analysis - Transportation, Transshipment and Assignment ProblemsDocument87 pagesMine System Analysis - Transportation, Transshipment and Assignment ProblemsAli ÇakırNo ratings yet
- Physics ElasticityDocument23 pagesPhysics ElasticityDaniel Danille KristianNo ratings yet
- SimA Fracture MechanicsDocument22 pagesSimA Fracture MechanicsВладимир СмирновNo ratings yet
- LAb Manual For Deflection of Beam Experiment Three Handout PDFDocument6 pagesLAb Manual For Deflection of Beam Experiment Three Handout PDFmehwish arshadNo ratings yet
- Statistics Hand-Outs (NEW)Document21 pagesStatistics Hand-Outs (NEW)Marc Voltaire DaquiganNo ratings yet
- MATH2239-Complex Number E1Document21 pagesMATH2239-Complex Number E1Lê Gia HânNo ratings yet
- Atkinson 2003Document64 pagesAtkinson 2003Akshay29No ratings yet
- Imso 2013 Math - Short AnswerDocument6 pagesImso 2013 Math - Short AnswerNova RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document7 pagesLesson 9Mitzi. SumaderoNo ratings yet
- 01 Mathematical Physics QBDocument14 pages01 Mathematical Physics QBMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Cell Name Original Value Final Value IntegerDocument5 pagesCell Name Original Value Final Value IntegerBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity and Minkowski SpacesDocument13 pagesSpecial Relativity and Minkowski Spacesgraviton6No ratings yet
- Visualize RF Impairments - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument15 pagesVisualize RF Impairments - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks Indiatiblue.black.36No ratings yet
- Introduccion: Encuentre La Segunda Derivada de Las Funciones Dadas: 1Document3 pagesIntroduccion: Encuentre La Segunda Derivada de Las Funciones Dadas: 1Miguel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Quarter Price Per Chip $ Forecast with α=.20 Forcast with α=.50Document3 pagesQuarter Price Per Chip $ Forecast with α=.20 Forcast with α=.50Robin LusabioNo ratings yet
- A Miniature Cross-Coupled Wide Band Microstrip Bandpass FilterDocument3 pagesA Miniature Cross-Coupled Wide Band Microstrip Bandpass FilterAnil Pandey100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Plant Economics MCQ Questions & Answers - Chemical EngineeringDocument6 pagesChemical Engineering Plant Economics MCQ Questions & Answers - Chemical Engineeringsrinu02062No ratings yet
- SmalloscillationsDocument12 pagesSmalloscillationsrajbaxeNo ratings yet
- Ckfëtf Epsf Jolqmx? SF) CLWSF/ DJGWL DXF +WL PJ+:J) Lr5S K - F) 6F) SN @) )Document14 pagesCkfëtf Epsf Jolqmx? SF) CLWSF/ DJGWL DXF +WL PJ+:J) Lr5S K - F) 6F) SN @) )Krishna ThapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02b Available Solar RadiationDocument37 pagesChapter 02b Available Solar RadiationOmar AljohaniNo ratings yet
- Fema BoschDocument52 pagesFema Boschxxsh100% (1)
- STD 8-Portion - TT - Annual EvaluationDocument3 pagesSTD 8-Portion - TT - Annual EvaluationShreya KamathNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic TheoryDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic TheoryAlakaaa PromodNo ratings yet
- 55 The Vector Equation of A PlaneDocument37 pages55 The Vector Equation of A PlaneShammus SultanNo ratings yet