Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Name: ENV2002 - Chemodynamics
Uploaded by
Aslıhan KayaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Name: ENV2002 - Chemodynamics
Uploaded by
Aslıhan KayaCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING FACULTY
DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
Year: 2019-2020 Semester: Spring
Course Name: ENV2002 – Chemodynamics
MAKEUP EXAM QUESTION-ANSWER SHEET
SIGNATURE: DATE ISSUED:
INSTRUCTOR’S NAME & TITLE: Pr of. Dr . Ön d er AY Y IL DI Z 25/06/2020
13:00
SIGNATURE: DUE DATE:
STUDENT’S NAME/SURNAME: 25.06.2020
STUDENT ID #: 16:00
Question 1 (15p.) 2 (15p.) 3 (15p.) 4 (15p) 5 (20p) 6 (20p) TOTAL POINT:
100
Point
Prog.Outcomes P1, P2 P1, P2 P1, P2 P1, P2 P1, P2 P1, P2
I certify that I worked independently on this makeup exam and that these
solutions are an honest measure of my understanding of the materials in this course.
Signed_____________________________________________
PROBLEMS
1. Solubility of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in water is 3.4 g/L at 25 oC. The Henry’s
constant for H2S at 25 oC is 500 atm. Calculate the saturated concentration of H2S
in air as mg/L. (15p)
Molecular weights (g/mole): S = 32; H = 1
2. A domestic wastewater with a flow rate (Q) of 10 m3/min will be treated in an
aerobic CSTR reactor. The input BOD concentration to CSTR reactor is 300 mg/L.
The degradation of organic compounds (BOD) obeys to first order rate kinetic with
a degradation rate constant (k) of 0,04 min-1. To achieve 90% BOD removal, what
should be the minimum volume of CSTR reactor for steady state conditions? (15p)
3. The surface water receives oxygen from atmosphere up to a saturation value let
say 8.6 mg/L at 25 oC. Elaborate how increasing the value of each parameter listed
below will affect the oxygen flux from air to water (kg/m2.min). Your answer
should be “increase”, “decrease”, or “no change”). Explain your answer briefly
with a single sentence. (15p)
Water-air surface area (A)
Temperature (T)
Elevation (altitude) from sea level assuming temperature is constant
Dissolved oxygen concentration (A2) in water
Water height (h)
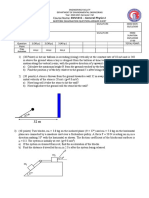
4. A rectangular swimming pool has a volume of (V) of 400 m3 and water depth (h) of
2 m. The water in the swimming pool is evaporated to atmosphere at 30 oC.
Assuming dry air conditions (no humidity), the constant evaporation flux from the
pool is given as 0.25 kg/m2.min, calculate
a) Two-film mass transfer coefficient (KA2) as cm/h. (5p)
b) The volume of water (m3) which will be evaporated from pool within 1 day. (5p)
c) How long it will take to evaporate all water in the swimming pool. (5p)
Not: The density of water is 1000 kg/m3.
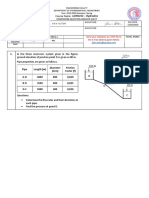
5. A lake has an area of 104 m2 and a depth of 5 m and receives an input of 200 moles of
chemical per day from an industrial effluent discharge. The same chemical is also
present in the influent water (103 m3/d) at a concentration of 0.02 mole/m3. The chemical
reacts with a first order rate constant k = 0.0015 h-1 and it volatilizes at a rate of 10-4
cA2 mole/(m2.s), where m2 refers to the air-water interfacial area. The outflow is 5000
m3/d; there is some additional loss of water by evaporation. Assuming that the lake water
is well mixed and in a steady state with respect to the concentration of the chemical,
calculate the concentration of the chemical in the lake and the loadings in all the inputs
and outputs in units of mole/d. (20p)
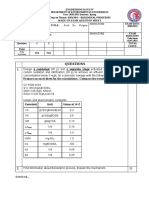
6. The organic content of the soil strongly affects the partitioning of organic pesticides
between the soil and water phases. The table below contains experimental results of an
equilibrium study with soils of organic matter 1%. For each test 4 mL of a 1.0 ppm
solution was added to each 1.0 g soil. The pH was adjusted to 2 with HNO 3 and the
slurry incubated for 1 hr.
a. Determine the soil-water partition coefficient, *A 3 2 (L/kg soil) for each. (10p)
b. Determine the organic matter-water partition coefficient, *A C 2 (L/kg OM), for each.
(10p)
Sorption of 4-Amino-3,5,6-Trichloropicolinic Acid by Soils at pH 2 (wt%).
Soil Organic Matter Acid in Solution Acid Sorbed on Soil
Content of Soil at Equilibrium at Equilibrium
A 1.0 51 49
B 2.7 23 77
C 10.7 5.8 94
You might also like
- Chemistry: Trial ExaminationDocument46 pagesChemistry: Trial ExaminationYuanfeng WeiNo ratings yet
- Calixto - Environmental Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument17 pagesCalixto - Environmental Engineering Questions and AnswersLina MaeNo ratings yet
- LWUADocument4 pagesLWUARALSTON TUYOKNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Day 1 Pre-BoardDocument4 pagesChemical Engineering Day 1 Pre-BoardAron BalinesNo ratings yet
- A Study On Methods To Improve Water Quality With BokashiDocument11 pagesA Study On Methods To Improve Water Quality With BokashiRamilyn bulataoNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument23 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringshubhamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Oxygen Demand COD PDFDocument7 pagesChemical Oxygen Demand COD PDFjiwa remajaNo ratings yet
- ASOE Chemistry 2020 SsDocument33 pagesASOE Chemistry 2020 Ssnavraj singhNo ratings yet
- Ce 1304 Environmental EngineeringDocument44 pagesCe 1304 Environmental EngineeringprashmceNo ratings yet
- 3510 Prob - Set 4 (2017)Document3 pages3510 Prob - Set 4 (2017)ShorOuq Mohammed MalkawiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Liquor Suspended SolidsDocument4 pagesMixed Liquor Suspended SolidsRahmi Arslan100% (2)
- COD Test Report Latest 2012Document10 pagesCOD Test Report Latest 2012emmafatimah0% (1)
- The Chemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)Document7 pagesThe Chemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)arif hilimiNo ratings yet
- COD Lab ReportDocument13 pagesCOD Lab ReportAmirulizwan Azamri83% (12)
- COD Lab Report FullDocument9 pagesCOD Lab Report FullLutfi Amin67% (3)
- Ünit Final 2Document4 pagesÜnit Final 2Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Cod Lab SheetDocument13 pagesCod Lab SheetPink MerahJambuNo ratings yet
- Atm Büt 2019-2020Document3 pagesAtm Büt 2019-2020Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- CHM3103 Lab Experiment 2Document15 pagesCHM3103 Lab Experiment 2husnaNo ratings yet
- Water ChemistryDocument14 pagesWater ChemistryDr Olayinka OkeolaNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet CODDocument6 pagesLab Sheet CODfahmyNo ratings yet
- Final Sku 3023 A201Document15 pagesFinal Sku 3023 A201Hafiz HafizanNo ratings yet
- 3-COD LABSHEET WORD Tim & PikaDocument22 pages3-COD LABSHEET WORD Tim & PikadanielseleyNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 5 PresentationDocument14 pagesExperiment - 5 PresentationMohammad ShariqNo ratings yet
- 2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial ExamDocument24 pages2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial ExamJane YooNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIDocument4 pagesCourse Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIDocument4 pagesCourse Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- 2017 ASOE Paper-ChemistryDocument28 pages2017 ASOE Paper-ChemistryFaisal AldiasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Written Examination 1Document25 pagesChemistry: Written Examination 1luctonNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 2Document10 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2Clara MazangoNo ratings yet
- (ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsDocument12 pages(ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- SMTI Yogyakarta International Exam Chemical Analyst REMEDIAL 2015 PDFDocument12 pagesSMTI Yogyakarta International Exam Chemical Analyst REMEDIAL 2015 PDFFaurinnisa MahendaruNo ratings yet
- 2020 ASOC PaperDocument29 pages2020 ASOC PapernuofanxiaNo ratings yet
- STFALKKC F2IS AnsDocument3 pagesSTFALKKC F2IS AnsVic KyNo ratings yet
- Che505 PDFDocument8 pagesChe505 PDFIzzati AhmadNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Environmental Science and EngineeringYami SukehiroNo ratings yet
- Open Vs Closed RefluxDocument3 pagesOpen Vs Closed RefluxDelin NANo ratings yet
- Exam CEMI313 June 5 2013 With AnswersDocument5 pagesExam CEMI313 June 5 2013 With AnswersReaper0007No ratings yet
- 2020 ASOC AnswersDocument35 pages2020 ASOC AnswersnuofanxiaNo ratings yet
- Example of Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesExample of Laboratory Reportpowasloopas258No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Written Examination 1Document21 pagesChemistry: Written Examination 1ninja980117No ratings yet
- CHBE 373 - Water Pollution Control Mid-Term ExamDocument4 pagesCHBE 373 - Water Pollution Control Mid-Term ExamLim Chong SiangNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV302 - Unit Operations IIDocument1 pageCourse Name: ENV302 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Lab Mauanl For Chemistry Btech 1 YearDocument35 pagesLab Mauanl For Chemistry Btech 1 YearTilak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonaceous Constituents: Biochemical Oxygen DemandDocument26 pagesCarbonaceous Constituents: Biochemical Oxygen DemandSanthoshMBSanthuNo ratings yet
- 2 Feb 2022Document35 pages2 Feb 2022Hannah NNo ratings yet
- 2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial SolutionsDocument27 pages2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial SolutionsJane YooNo ratings yet
- CET304 - Ktu QbankDocument9 pagesCET304 - Ktu QbankdipinnediyaparambathNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Trial HSC 2023 (WITH LINES)Document28 pagesChemistry Trial HSC 2023 (WITH LINES)bianhua006No ratings yet
- Paper On KDocument7 pagesPaper On KShabanaNo ratings yet
- Nor Iftiha Binti Abdul Aziz (2022991399) - Lab Report CodDocument6 pagesNor Iftiha Binti Abdul Aziz (2022991399) - Lab Report CodNor Iftiha AzizNo ratings yet
- B11 - B12 - B13 - 0301 - CHY1001 - Engineering ChemistryDocument1 pageB11 - B12 - B13 - 0301 - CHY1001 - Engineering ChemistryUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Year 12 Assessment Block Semester 1Document23 pagesChemistry: Year 12 Assessment Block Semester 1nichollsl24No ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator TitrationDocument4 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator TitrationYamiyoNo ratings yet
- 5 0114936Document7 pages5 0114936yusuf rosadiNo ratings yet
- Wastewater - Types, Characteristics & RegulationDocument50 pagesWastewater - Types, Characteristics & Regulationsam samNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment (CCB31403)Document4 pagesFinal Assessment (CCB31403)Naz HelmiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Temperature Initial PH and Glucose Concentration On Biohydrogen Production From Clostridium AcetobutylicumDocument7 pagesThe Effects of Temperature Initial PH and Glucose Concentration On Biohydrogen Production From Clostridium Acetobutylicumankita pandeyNo ratings yet
- Env. EM - Environmental Engineering and Management - 221TCH002Document7 pagesEnv. EM - Environmental Engineering and Management - 221TCH002Vis 22777No ratings yet
- Determination of Bod of Waste Water: Submitted by Shuva Chandra Bose ID: 161116Document8 pagesDetermination of Bod of Waste Water: Submitted by Shuva Chandra Bose ID: 161116shuvobosu262No ratings yet
- Reactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsFrom EverandReactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsYitian XiaoNo ratings yet
- Atm-Quiz 2-CIFT (Even)Document2 pagesAtm-Quiz 2-CIFT (Even)Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Prof - Dr.Hasan or Hu N KÖK SALDocument3 pagesProf - Dr.Hasan or Hu N KÖK SALAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Atm-Quiz 2-TEK (Odd)Document2 pagesAtm-Quiz 2-TEK (Odd)Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Quiz 1Document2 pagesStatistics Quiz 1Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIDocument4 pagesCourse Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Answers 2-3-4Document7 pagesMidterm Exam Answers 2-3-4Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- 14ENV212 Hydraulics - HOMEWORKDocument2 pages14ENV212 Hydraulics - HOMEWORKAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Selector: Energy Is Obtained From Oxidation of COD Using ODocument2 pagesAerobic Selector: Energy Is Obtained From Oxidation of COD Using OAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIDocument5 pagesCourse Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV302 - Unit Operations IIDocument1 pageCourse Name: ENV302 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIDocument6 pagesCourse Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIDocument4 pagesCourse Name: ENV3002 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIDocument5 pagesCourse Name: 14ENV302 - Unit Operations IIAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: 14ENV305 - Soil and Groundwater Pollution: Ckantar@comu - Edu.tr Signature: SignatureDocument4 pagesCourse Name: 14ENV305 - Soil and Groundwater Pollution: Ckantar@comu - Edu.tr Signature: SignatureAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- 14ENV212 Hydraulics - FINAL EXAMDocument4 pages14ENV212 Hydraulics - FINAL EXAMAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Env2007 - Final ExamDocument4 pagesEnv2007 - Final ExamAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 FinalpdfDocument2 pagesHomework 2 FinalpdfAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Env2007 - Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesEnv2007 - Midterm ExamAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Questions: Course Name: Current Topics in Environmental EngineeringDocument1 pageMidterm Questions: Course Name: Current Topics in Environmental EngineeringAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV304 - Biological Processes: Ayman Öz SignatureDocument3 pagesCourse Name: ENV304 - Biological Processes: Ayman Öz SignatureAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- AB Is The Last Two Digits of Your Student Number.: Course Name: ENV 2016 - Strength of MaterialsDocument4 pagesAB Is The Last Two Digits of Your Student Number.: Course Name: ENV 2016 - Strength of MaterialsAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV1015 - General Physics I: Midterm Examination Question-Answer Sheet Instructor'S Name & Title: SignatureDocument2 pagesCourse Name: ENV1015 - General Physics I: Midterm Examination Question-Answer Sheet Instructor'S Name & Title: SignatureAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: ENV1014 - General Physics II: Homework Instructor'S Name & Title: SignatureDocument2 pagesCourse Name: ENV1014 - General Physics II: Homework Instructor'S Name & Title: SignatureAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Env304 - Biological Processes: QuestionsDocument3 pagesCourse Name: Env304 - Biological Processes: QuestionsAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Questions: Course Name: Env206 - Environmental Microbiology LabDocument2 pagesMidterm Questions: Course Name: Env206 - Environmental Microbiology LabAslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument1 pageFinal Projectpravalika lakkakulaNo ratings yet
- Salient Feature:: Right Main Canal Left Main CanalDocument4 pagesSalient Feature:: Right Main Canal Left Main CanalSephali MoharanaNo ratings yet
- Section 1Document28 pagesSection 1Chuck JacksonNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Sanitary EngineeringDocument12 pagesWater Supply and Sanitary Engineeringash100% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesSeminar ReportTanmoy Chandra100% (2)
- M7S1 Flood Gates and Pump StationsDocument19 pagesM7S1 Flood Gates and Pump StationsEunnice PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Max FajardoDocument175 pagesPlumbing Max FajardoayeNo ratings yet
- Presentation Dialogue Water Purification and Water SupplyDocument1 pagePresentation Dialogue Water Purification and Water SupplyK A M I K A Z ENo ratings yet
- LetterDocument5 pagesLetterSameer NaveenaNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument6 pagesWater PollutionRichu NNo ratings yet
- Effects of Industrial Waste On STPDocument11 pagesEffects of Industrial Waste On STPManu JainNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations Symbols Demolition Notes: 1 09/07/2018 Issue For Bid 2 09/13/2018 Addendum 1Document9 pagesAbbreviations Symbols Demolition Notes: 1 09/07/2018 Issue For Bid 2 09/13/2018 Addendum 1Md. Farid UddinNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument6 pagesSyllabusAbhishek GondNo ratings yet
- 1-1-Over View of PlumbingDocument30 pages1-1-Over View of PlumbingCalvin Paulo MondejarNo ratings yet
- RRL OutlineDocument4 pagesRRL OutlineKirsten SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 0128 PDFDocument8 pages0128 PDFNimish GoyalNo ratings yet
- ISSS AC Program (For Participants)Document3 pagesISSS AC Program (For Participants)Dien NoelNo ratings yet
- G.S BirdieDocument172 pagesG.S BirdieVishal Kumar100% (1)
- 3257, Case Study Mars NL 1Document1 page3257, Case Study Mars NL 1Ryan PasupathyNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Kemira FennoPol Composite Polymer ABTCP Tres Lagoas Brazil - Final - 2Document14 pages2020 - Kemira FennoPol Composite Polymer ABTCP Tres Lagoas Brazil - Final - 2Carlos UngarettiNo ratings yet
- Ijert Ijert: Proposed Wastewater Treatment Plant Design of Harihar CityDocument8 pagesIjert Ijert: Proposed Wastewater Treatment Plant Design of Harihar CityTushar KambleNo ratings yet
- Storm Drainage System Group 5Document20 pagesStorm Drainage System Group 5Shanica Rosaldo CariñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Aquifer Hydraulic Properties: Grain Size and Sorting Aquifers - Unconfined Versus ConfinedDocument15 pagesChapter 9 - Aquifer Hydraulic Properties: Grain Size and Sorting Aquifers - Unconfined Versus ConfinednimcanNo ratings yet
- Consent Decree in Baykeeper v. City of San JoseDocument37 pagesConsent Decree in Baykeeper v. City of San JoseBayAreaNewsGroupNo ratings yet
- Government of Telangana Rural Water Supply and Sanitation DepartmentDocument3 pagesGovernment of Telangana Rural Water Supply and Sanitation DepartmentvarunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internal Erosion in Dams and Their Foundations 12 20 21Document78 pagesIntroduction To Internal Erosion in Dams and Their Foundations 12 20 21Renathielly Fernanda da SilvaNo ratings yet