Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biological Basis of Psychology: Structures, Functions and Cells
Uploaded by
Nurul Hasanah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesOriginal Title
BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF PSYCHOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesBiological Basis of Psychology: Structures, Functions and Cells
Uploaded by
Nurul HasanahCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Today
• Structures involved in thinking
• Functioning
Biological Basis of Psychology
• Organization
Intro Psychology
Georgia Tech
Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker
Recall the “Machine” Analogy Seeing Structure and Function
• The brain is the key to cognition • Structure:
• So how is the brain structured? – Dissection, MRI
• How does it operate? • Function:
• What else do we need to know? – Case studies, ablation,
PET, fMRI, EEG
Recall the Neuron Doctrine Nervous System
• Neurons do the work
• Fissures/Sulci
• Actually, networks of neurons do the work
• Gyri
• Neurons are connected by synapses
• Nerves
• So we need to know how these “building
blocks” work, and how they form “networks” • Tracts
• Ganglia
• Nuclei
Nervous System Nervous System
• Fissures/Sulci • Fissures/Sulci
• Gyri • Gyri
• Nerves • Nerves
• Tracts • Tracts
• Ganglia • Ganglia
• Nuclei • Nuclei
Cellular Anatomy of the Nervous
Gray & White Matter
System
• Hard to study! • Neurons are small…
• Billions of cells in NS – Cell body 1-100 mm
– ~1010 in brain • Same color
• 2 categories • Complicated
– Neurons connections
– Glial cells
Myelin Glial Cells
• White – leading to distinction between • “Support system” for neurons
“white” and “grey” matter • ~50% of cells in brain are glia
• 2 Basic functions • Astrocytes (Astroglia)
– Speeds nerve conduction – Physical matrix for neurons
• Neural depolarization occurs at nodes, then jumps – Metabolic support
to next node Glucose - Lactate
• Can increase conduction from 30 to 120 ms/sec. Glycogen
– Phagocytosis
OUTSIDE CELL INSIDE CELL
Cell Membrane + -
osmotic pressure
• Lipid bilayer
K+ K+
+ - membrane is
• Semipermeable + osmotic pressure relatively
• Membrane potential
Na Na+
impermeable
+ - to Na+
• Membrane proteins osmotic pressure
– Pumps Cl- + -
Cl-
– Ion channels electrostatic pressure
• Leak channels
+ -
• Mechanically gated
• Voltage gated A-
• Chemically gated + - cannot
• Many types
cross
membrane
Firing of a neuron Firing of a neuron
• Signal of a neuron is carried by an electrical • Concept of Threshold
charge that moves from one end of the – All or None – Neurons fire or they don’t
neuron to the other – “Intensity” information carried by frequency of
• Electrical activity firing
– Resting potential – Firing may increase or decrease likelihood of
connected neurons firing
– Action potential
• Neural “Inhibition”
Where the action is at
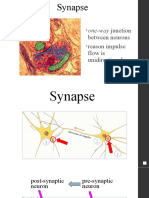
• Synapse
– Connection point between neurons
– Electrical activity carrying neural signal along
axon is converted into chemical signals to
transfer to the next neuron
Neurotransmitters Upcoming
• Acetylcholine – one of the most common • Brain regions & organization
• Norepinephrine – important to bodily and
psychological arousal/alertness – released by
• Vision as an example of neural computation
amphetamine • Motivation & learning
• Dopamine – central in schizophrenia, depleted in • Sensation & perception
Parkinson’s disease, important in higher cognitive
functions
• Endorphins – stimulate certain neurons that
disrupt messages from pain centers – placebo
effects, acupuncture
You might also like
- CH 7 Nervous Tissue PDFDocument6 pagesCH 7 Nervous Tissue PDFIbra TutorNo ratings yet
- Ch28 Nervous SystemsDocument18 pagesCh28 Nervous Systems鄭心美No ratings yet
- Psyc 372 – Synapses, Neurotransmitters, and ReceptorsDocument6 pagesPsyc 372 – Synapses, Neurotransmitters, and ReceptorsHarindra DunuwilaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 CoordinationDocument25 pagesTopic 10 CoordinationKaushalya PeoplezzNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Guide - CNS, PNS, Neurons, Reflexes (Part 2Document13 pagesNervous System Guide - CNS, PNS, Neurons, Reflexes (Part 2Llyana paula SuyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Neurons, Synapses, and NeurotransmissionDocument44 pagesLecture 3: Neurons, Synapses, and NeurotransmissionYiping HuangNo ratings yet
- B05 L4 NeurotransmissionDocument54 pagesB05 L4 Neurotransmissionspotifymailhamza12No ratings yet
- Overview of The Nervous System Overview of The Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesOverview of The Nervous System Overview of The Nervous Systemarlinie100% (1)
- NCERT Based KT’s PowerNotes for Neural Control and CoordinationDocument2 pagesNCERT Based KT’s PowerNotes for Neural Control and CoordinationSushmit Srivastava100% (1)
- Nervous IDocument20 pagesNervous Iaji50No ratings yet
- Week13 Lecture Spring2023Document22 pagesWeek13 Lecture Spring2023Rusting StardustNo ratings yet
- Drugs and The Nervous System: Pharmacodynamics of A DrugDocument28 pagesDrugs and The Nervous System: Pharmacodynamics of A DrugSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Nervous TissueDocument58 pagesNervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Nervous TissueSUTHANNo ratings yet
- BA Psychology: Neurons and Neural Information FlowDocument21 pagesBA Psychology: Neurons and Neural Information FlowAteesh SagarNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemJustGellaiNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4ADocument5 pagesDay 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4AAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle Physiology: An Overview of Nervous and Muscular TissuesDocument34 pagesNerve Muscle Physiology: An Overview of Nervous and Muscular TissuesMahfooz Nisar100% (1)
- Woreta Health Science and Business College Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesWoreta Health Science and Business College Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- TA Session 7-1Document31 pagesTA Session 7-1viviannaNo ratings yet
- The Brain Hypothesis The Neuron HypothesisDocument10 pagesThe Brain Hypothesis The Neuron HypothesisAbraham WalkthewokNo ratings yet
- CH 3 AP Psychology Biological School. (2) PDFDocument9 pagesCH 3 AP Psychology Biological School. (2) PDF朱颖No ratings yet
- Cell Adaptation - CNSDocument13 pagesCell Adaptation - CNSClaraNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsDocument5 pagesNervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- lecture 1Document30 pageslecture 1Osama adel Mohamed SmadiNo ratings yet
- Biology and BehaviorDocument72 pagesBiology and BehaviorCarlee MayesNo ratings yet
- Upload 9.06 Nerve Impulse Notes To EbackpackDocument24 pagesUpload 9.06 Nerve Impulse Notes To EbackpackPAMELA CASTILLONo ratings yet
- 03 Biological PsychologyDocument20 pages03 Biological PsychologyTunahan OğuzNo ratings yet
- The Richest Man in BabylonDocument36 pagesThe Richest Man in BabylonDHARMENDRANo ratings yet
- The Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesThe Nervous TissueRO OMNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing OverviewDocument64 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing OverviewRAYMUND IAN ABALOS100% (2)
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Neuron: Neurons Vs Somatic CellsDocument10 pagesOverview of The Neuron: Neurons Vs Somatic CellsAbraham WalkthewokNo ratings yet
- What is a BiosensorDocument8 pagesWhat is a BiosensorManh Trung TranNo ratings yet
- Nerve Physiology 1718 PracticalDocument18 pagesNerve Physiology 1718 PracticalMichael TobilobaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument67 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pinoyalfred31191% (23)
- Nrevious and Special SenseDocument232 pagesNrevious and Special SenseMani Raj DhakalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Part 1Document4 pagesNervous System Part 1Cyrill Denise CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33-1 The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 33-1 The Nervous Systemnancie8No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Applying Research To Everyday Exercise and Sport: Neuroscience: Exploring The Brain, 4eDocument7 pagesChapter 1: Applying Research To Everyday Exercise and Sport: Neuroscience: Exploring The Brain, 4eKevin LamNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021Document43 pagesKuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021rifkaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Organization and Function of the Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesUnderstanding the Organization and Function of the Nervous SystemShreya AnandNo ratings yet
- Functional Neuroanatomy: Mazyar FallahDocument21 pagesFunctional Neuroanatomy: Mazyar FallahgeorgefrombaNo ratings yet
- Optogenetics 1Document40 pagesOptogenetics 1120420314No ratings yet
- Muscle tissue types and functionsDocument6 pagesMuscle tissue types and functionscristine antonioNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument77 pagesNervous Tissuemarjanggyamar7No ratings yet
- Neural Control N Coordination-NotesDocument5 pagesNeural Control N Coordination-Notessudeep27krNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueSilvia FierroNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTDocument25 pagesNervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTZahid Mehmood100% (1)
- Introduction to the Nervous System and NeuronsDocument18 pagesIntroduction to the Nervous System and NeuronsSudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Musculo-Skeletal Notes The Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesWeek 2 Musculo-Skeletal Notes The Structure of The Nervous SystemjhnnolanNo ratings yet
- L1 SBM Neuro 1Document88 pagesL1 SBM Neuro 1Sohil PatelNo ratings yet
- 2 - Synapse and Reflex ArcDocument15 pages2 - Synapse and Reflex ArcRashpal SidhuNo ratings yet
- When Neurons Tell Stories A Layman's Guide to the Neuroscience of Mental Illness and Health Erin Hawkes-From EverandWhen Neurons Tell Stories A Layman's Guide to the Neuroscience of Mental Illness and Health Erin Hawkes-No ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Metaphysics of Infinity: The Problem of Motion and the Infinite BrainFrom EverandMetaphysics of Infinity: The Problem of Motion and the Infinite BrainNo ratings yet
- The Kybernetics of Natural Systems: A Study in Patterns of ControlFrom EverandThe Kybernetics of Natural Systems: A Study in Patterns of ControlNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsFrom EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate Neuroanatomy: Evolution and AdaptationFrom EverandComparative Vertebrate Neuroanatomy: Evolution and AdaptationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Visa Vertical and Horizontal Analysis ExampleDocument9 pagesVisa Vertical and Horizontal Analysis Examplechad salcidoNo ratings yet
- How To Cook Indian: More Than 500 Classic Recipes For The Modern KitchenDocument431 pagesHow To Cook Indian: More Than 500 Classic Recipes For The Modern Kitchenbingoteam100% (1)
- Advertising and Imc Principles and Practice 11th Edition Moriarty Solutions ManualDocument28 pagesAdvertising and Imc Principles and Practice 11th Edition Moriarty Solutions Manualcemeteryliana.9afku100% (19)
- Stone Fox BookletDocument19 pagesStone Fox Bookletapi-220567377100% (3)
- IMU 25,26 Oct 2014 (Other) ResultDocument2,582 pagesIMU 25,26 Oct 2014 (Other) ResultMuhammadFarhanShakee100% (1)
- Paths To Mastery Lesson 17 Speaking Tips From Dale Carnegie The Quick and Easy Way To Effective SpeakingDocument10 pagesPaths To Mastery Lesson 17 Speaking Tips From Dale Carnegie The Quick and Easy Way To Effective SpeakingZelic NguyenNo ratings yet
- PETDocument4 pagesPETMaria Dolores Barrionuevo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Plattischemic Stroke Lesson PlanDocument18 pagesPlattischemic Stroke Lesson Planapi-216258123100% (3)
- CUCM BK F3AC1C0F 00 Cucm Features Services Guide 100Document1,158 pagesCUCM BK F3AC1C0F 00 Cucm Features Services Guide 100shan76palNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Kinematics FundamentalsDocument31 pagesTheory of Machines Kinematics FundamentalsmungutiNo ratings yet
- SGT Vacancy ListDocument196 pagesSGT Vacancy ListSusheelabaiNo ratings yet
- ICT4D - Richard Heeks (2305843009216382716)Document307 pagesICT4D - Richard Heeks (2305843009216382716)Jeff GeoffNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Project: Made By: Rahil JainDocument29 pagesBusiness Studies Project: Made By: Rahil JainChirag KothariNo ratings yet
- Importers - Dry Fruits and NutsDocument5 pagesImporters - Dry Fruits and Nutsankit0% (1)
- PROGRAM DESIGN TOOLS LESSONDocument10 pagesPROGRAM DESIGN TOOLS LESSONDun kithekaNo ratings yet
- Sam's Melancholic MorningDocument4 pagesSam's Melancholic Morningali moizNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris LJ Congratulating and ComplimentingDocument7 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris LJ Congratulating and ComplimentingAmalia Rhmdani100% (4)
- StudenttextDocument29 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- pmwj93 May2020 Omar Fashina Fakunle Somaliland Construction IndustryDocument18 pagespmwj93 May2020 Omar Fashina Fakunle Somaliland Construction IndustryAdebayo FashinaNo ratings yet
- STELEX PrO (E) FinalDocument4 pagesSTELEX PrO (E) FinalGhita-Mehedintu GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Manocha Icile Feasibility StudyDocument95 pagesManocha Icile Feasibility StudyAlmadin KeñoraNo ratings yet
- Partnership Dissolution QuizDocument8 pagesPartnership Dissolution QuizLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- An Essay For The Glass Menagerie PDFDocument11 pagesAn Essay For The Glass Menagerie PDFBily ManNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and WoundsDocument15 pages2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and Woundsnovia100% (2)
- National Power Corporation vs. Teresita Diato-Bernal 2Document3 pagesNational Power Corporation vs. Teresita Diato-Bernal 2mickcarpioNo ratings yet
- CAE Proposal Expressions and SamplesDocument6 pagesCAE Proposal Expressions and SamplesKimLiênNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Sec. Gr. To BT History Temp Panel 2013Document50 pagesSec. Gr. To BT History Temp Panel 2013edwin_prakash75No ratings yet
- Mil STD 1365bDocument49 pagesMil STD 1365bprakki123No ratings yet
- B IngDocument2 pagesB IngsyfnanyNo ratings yet
- Jack Turner - Not On Any MapDocument13 pagesJack Turner - Not On Any MapormrNo ratings yet