Professional Documents
Culture Documents
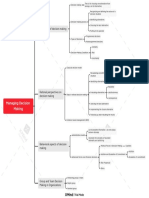
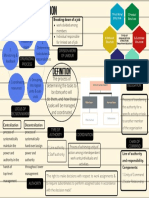
Organization Structure and Design: The Basic Elements of Organizing
Organization Structure and Design: The Basic Elements of Organizing
Uploaded by
Le Nhu Y (K17 DN)Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organization Structure and Design: The Basic Elements of Organizing
Organization Structure and Design: The Basic Elements of Organizing
Uploaded by
Le Nhu Y (K17 DN)Copyright:
Available Formats
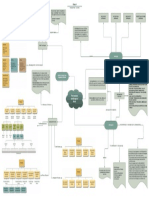
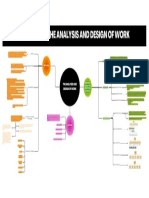
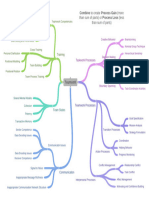
Job rotation
Job enlargement
Job enrichment
Skill variety
Job specialization (Designing jobs) Task identity
Job characteristics approach Task significance
Autonomy
Feedback
Work teams
Grouping jobs involving the same or similar
Functional Departmentalization
activities
Grouping activities around products or
Product Departmentalization
product groups
Departmentalization (Grouping jobs)
Grouping activities to respond to and
Customer Departmentalization interact with specific customers or
customer groups
The basic elements of Grouping jobs on the basis of defined
Location Departmentalization
Organizing geographic sites or areas
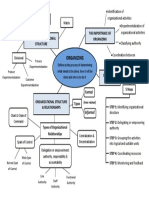
Unity of command
Chain of command
Scalar principle
Establishing reporting relationships
Span of management
Tall versus Flat organizations
Power that has been legitimized by the
Delegation
organization
Distribution of Authority
Decentralization and Centralization
Pooled interdependence
three major forms of interdependence Sequential interdependence
Reciprocal interdependence
Coordination
Structural Coordination Techniques
Electronic Coordination
The Bureaucratic Model of
Organization Design
Organization
Structure and Design Unit or small-batch technology
Conversion process used to transform
Technology Large-batch or mass-production technology
inputs to outputs
Continuous-process technology
Situational Influences on Mechanistic organizations stable environments.
Environment
Organization Design Organic organizations unstable and unpredictable environments.
Total number of full-time or full-time
Organizational size
equivalent employees
Organizational size and life cycle
Organizational life cycle
Functional (U-form) design
Conglomerate (H-form) design
Basic Forms of Organization
Divisional (M-form) design
Design
Matrix design
Hybrid Designs
Team organization
Emerging issues in
Virtual organization
Organization Design
Learning organization
You might also like
- SSAT Prep Guide: Tips and Strategies For Every Section of The TestDocument64 pagesSSAT Prep Guide: Tips and Strategies For Every Section of The Testthomson100% (1)
- Grade and Pay StructuresDocument23 pagesGrade and Pay Structuresprince_RGF100% (10)
- Copyright Infringement Notice LetterDocument2 pagesCopyright Infringement Notice LetterTanya CharlesNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Speaking TemplatesDocument12 pagesTOEFL Speaking TemplatesKatieSalsbury100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Le Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Mindmap - Week 3 SystemologyDocument1 pageMindmap - Week 3 SystemologyMuhammad Zaid SahakNo ratings yet
- Strategic Healthcare Management Planning and Execution Second Edition Full ChapterDocument38 pagesStrategic Healthcare Management Planning and Execution Second Edition Full Chapterbobby.theiss375100% (26)
- Hi 60881Document2 pagesHi 60881Mohamed RafihNo ratings yet
- Oxide Scale Measurement Application SolutionDocument20 pagesOxide Scale Measurement Application Solutionนูโน่ โกเมซNo ratings yet
- HR Consulting - Road - MapDocument1 pageHR Consulting - Road - MapGVS RaoNo ratings yet
- Service-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureFrom EverandService-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- Drama SyllabusDocument57 pagesDrama Syllabusclaracheung100% (1)
- Hg4000tx+ (Sn101 Servise ManualDocument526 pagesHg4000tx+ (Sn101 Servise ManualWabcoNo ratings yet
- TOGAF 9.1 MetamodelDocument1 pageTOGAF 9.1 Metamodelcreamz100% (1)
- Petronas Besar ProjectDocument12 pagesPetronas Besar ProjectMarlon MoncadaNo ratings yet
- X10834 (Oce751)Document2 pagesX10834 (Oce751)Chockalingam100% (4)
- Job Characteristics ModelDocument14 pagesJob Characteristics ModelAnivesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument1 pageOrganization StructureAysza IrtantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Aisyah Nabihah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure: The Formal Arrangement of Jobs Within An OrganizationDocument1 pageOrganizational Structure: The Formal Arrangement of Jobs Within An OrganizationNguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument6 pagesOrganizingczarleen catapangNo ratings yet
- Organizing: Engineering ManagementDocument7 pagesOrganizing: Engineering Managementsha mNo ratings yet
- Minggu 09 OrganizingDocument18 pagesMinggu 09 OrganizingGunawan MarbunNo ratings yet
- 9 StructuralimplementationDocument1 page9 Structuralimplementationdayabilung9451No ratings yet
- The 2 Core Management FunctionDocument46 pagesThe 2 Core Management FunctionPalwinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Dora Research ProgramDocument1 pageDora Research ProgramtutumeNo ratings yet
- Foundations of OrganizingDocument51 pagesFoundations of OrganizingJoshua Danielino RahajaanNo ratings yet
- MGT162 Chapter 4Document1 pageMGT162 Chapter 4Aina AshNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Business Studies Chapter - 5 Organisation Revision NotesDocument14 pagesCbse Class 12 Business Studies Chapter - 5 Organisation Revision NotesRohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document1 pageChap 4Nhứt Phú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Agile Coaching Growth Wheel Self-AssessmentDocument1 pageAgile Coaching Growth Wheel Self-AssessmentFlorinManolescuNo ratings yet
- Bùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Document1 pageBùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Huong Bui Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- Alyaa Natasha Section69 - Mind MapDocument9 pagesAlyaa Natasha Section69 - Mind MapALYAA NATASHA (BG)No ratings yet
- BB 50Document6 pagesBB 50Gerson Antonio MocelimNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 OB 28pgs - RotatedDocument28 pagesUnit 5 OB 28pgs - Rotatedsasithar jaisankaranNo ratings yet
- Designing Organizational Structures: The Future of BusinessDocument65 pagesDesigning Organizational Structures: The Future of BusinessDani QureshiNo ratings yet
- Is Retail-ContentDocument2 pagesIs Retail-ContentSivaNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Organizing: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie CookDocument32 pagesBasic Elements of Organizing: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie CookNURUN NABINo ratings yet
- Sixth/ Seventh Semester B.E (All Branches) Essentials of Management HSS-302/401Document62 pagesSixth/ Seventh Semester B.E (All Branches) Essentials of Management HSS-302/401Ayesha SheikhNo ratings yet
- POM - s2Document3 pagesPOM - s2AlbaneNo ratings yet
- MCQ CH - 5 OrganisingDocument17 pagesMCQ CH - 5 OrganisingSharanya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Government Business Process TransformationDocument39 pagesGovernment Business Process TransformationsheicyNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Organization DevelopmentDocument2 pagesJob Description - Organization DevelopmentandrieNo ratings yet
- T4 SummaryDocument1 pageT4 SummaryMuhamad AdibNo ratings yet
- A10 - The Secrets To Successful Strategic ExecutionDocument8 pagesA10 - The Secrets To Successful Strategic ExecutionPHANI SAI VAMSI KRISHNA GUNTURUNo ratings yet
- 2 Balancing: Differentiation IntegrationDocument28 pages2 Balancing: Differentiation IntegrationNurNo ratings yet
- Mapa en InglesDocument1 pageMapa en Inglesmarinaza13No ratings yet
- c4 DrawioDocument1 pagec4 DrawioChi BongNo ratings yet
- Brendah Oduori OutDocument1 pageBrendah Oduori OutWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Kisii University Main CampusDocument1 pageKisii University Main CampusWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 Part2Document3 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 Part2avishaNo ratings yet
- TeamworkDocument1 pageTeamworkaliarefnezhad2022No ratings yet
- Bsr307 Building Maintenance Ii: Organisation StructureDocument19 pagesBsr307 Building Maintenance Ii: Organisation Structurenur sheNo ratings yet
- Actividades de AdministracionDocument14 pagesActividades de AdministracionAnita Gómez HernándezNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping MKKPDocument1 pageMind Mapping MKKPErita ShafiraNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organization DesignDocument5 pages2 - Organization DesigngülraNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document20 pagesCH 10abeernabilabdNo ratings yet
- SFRLO SecB Group1 v2Document9 pagesSFRLO SecB Group1 v2Priyanka Kambli100% (1)
- Introduction To Project ManagementDocument66 pagesIntroduction To Project ManagementAhmad Muzakkir Ahmad FauziNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument46 pagesOrganizingsneha sasidharanNo ratings yet
- LD - Oracle Labor Distribution Student GuideDocument96 pagesLD - Oracle Labor Distribution Student GuideChary MadarapuNo ratings yet
- SCM - Oracle Cloud Maintenance Enhancements To Maintenance ProgramsDocument28 pagesSCM - Oracle Cloud Maintenance Enhancements To Maintenance ProgramsMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- c5 Mgt420 Yong SlideDocument33 pagesc5 Mgt420 Yong SlideNurul SakinahNo ratings yet
- 07 Organising AddendumDocument3 pages07 Organising AddendumAbubakarNo ratings yet
- ES-MGMT Handout 3.1Document15 pagesES-MGMT Handout 3.1Lorenzo Igot IvNo ratings yet
- Modern Management ToolsDocument1 pageModern Management ToolsJohanna HolzerNo ratings yet
- Organization Theory, Design and Change Summary Chapter 4: KoenspaansenDocument6 pagesOrganization Theory, Design and Change Summary Chapter 4: KoenspaansenLeena MehtaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structures: Types of Organizational StructureDocument1 pageOrganizational Structures: Types of Organizational Structuremarinaza13No ratings yet
- SBP InfographicDocument1 pageSBP Infographickhesviny.vijayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Order Management and Customer Service-2Document38 pagesLecture 3 Order Management and Customer Service-2Edward TrầnXDNo ratings yet
- IT and Business ProcessesDocument1 pageIT and Business ProcesseselliotttateNo ratings yet
- Planning and Strategic ManagementDocument1 pagePlanning and Strategic ManagementLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- The Organization's Environments: External EnvironmentDocument1 pageThe Organization's Environments: External EnvironmentLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Organization Change and InnovationDocument1 pageOrganization Change and InnovationLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Assignment Front Sheet Student Name / FPT Roll Number Lecturer NameDocument20 pagesAssignment Front Sheet Student Name / FPT Roll Number Lecturer NameLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Management: Understanding The Manager's JobDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Management: Understanding The Manager's JobLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- FPT University - Da Nang: Assignment Front SheetDocument4 pagesFPT University - Da Nang: Assignment Front SheetLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Outline - Individual AssignmentDocument6 pagesOutline - Individual AssignmentLe Nhu Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Effect of Organic Solvents Antigen Antibody InteractionsDocument7 pagesEffect of Organic Solvents Antigen Antibody InteractionsMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Edtpa Lesson Plan 5Document4 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan 5api-612046340No ratings yet
- EC6403 Electromagnetic FieldsDocument13 pagesEC6403 Electromagnetic Fieldssrinureddy2014No ratings yet
- A Study On The Attitude of B.ed. Teacher Trainees Towards Internal AssessmentDocument5 pagesA Study On The Attitude of B.ed. Teacher Trainees Towards Internal AssessmentAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Manufacturer LIST 8th October, 2013Document176 pagesManufacturer LIST 8th October, 2013boopelectraNo ratings yet
- Aw y Gin 2011 - Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Waterborne Pathogenic Viruses in Surface Waters of Tropical Urban CatchmentsDocument13 pagesAw y Gin 2011 - Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Waterborne Pathogenic Viruses in Surface Waters of Tropical Urban CatchmentsYoNo ratings yet
- ĐỀDocument34 pagesĐỀThành PhátNo ratings yet
- Proposal ArgumentDocument8 pagesProposal ArgumentbeccaslowikNo ratings yet
- QR25DE Timing ChainDocument21 pagesQR25DE Timing ChainDONALDO CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Presenting The Data SL&HLDocument6 pagesPresenting The Data SL&HLAlishaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 3 Formative-2Document3 pagesTopic 5 3 Formative-2api-296446683No ratings yet
- C & C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDocument24 pagesC & C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant PublishersNo ratings yet
- Using Office Backstage: Lesson 3Document35 pagesUsing Office Backstage: Lesson 3Емил БогдановNo ratings yet
- Ekrv PDFDocument28 pagesEkrv PDFvickraj100% (1)
- Do Animals Talk?: Understanding Language - Maja Brala VukanovićDocument2 pagesDo Animals Talk?: Understanding Language - Maja Brala VukanovićAelNo ratings yet
- Science 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Document4 pagesScience 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Ferdinand James PascuaNo ratings yet
- Tidalenergy 150109025117 Conversion Gate01Document7 pagesTidalenergy 150109025117 Conversion Gate01Mir Mustafa AliNo ratings yet
- M39a Body Wiring SystemDocument21 pagesM39a Body Wiring SystemAnurag AwasthiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Concurrent ProgrammingDocument28 pages1 - Concurrent ProgrammingBunny HoneyNo ratings yet
- Ready Aim Firefinal 2011Document19 pagesReady Aim Firefinal 2011Mohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet