Professional Documents
Culture Documents
XP (X) P (X) Yp (Y) P (Y)
Uploaded by
Vika BodokiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
XP (X) P (X) Yp (Y) P (Y)
Uploaded by
Vika BodokiaCopyright:
Available Formats
7.
54 a Refrigerators, x P(x)
1 0.22
1 0.49
2 0.29
b Stoves, y P(y)
0 0.34
1 0.39
2 0.27
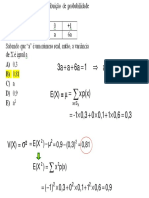
c ∑ xP( x ) = 0(0.22) + 1(0.49) + 2(0.29) = 1.07
μ x = E(X) =
σ = V(X) = ∑ (x−μ) P( x) = (0–1.07) (0.22) + (1–1.07) (0.49) + (2–1.07)
2 2 2 2 2
(0.29) = 0.505
d y = E(Y) = ∑
μ yP( y) = 0(0.34) + 1(0.39) + 2(0.27) = 0.93
σ = V(Y) = ∑ ( y−μ) P( y ) = (0–0.93) (0.34) + (1–0.93) (0.39) + (2–0.93)
2 2 2 2 2
(0.27) = 0.605
∑ ∑ xyP( x, y)
e all x all y = (0)(0)(0.08) + (0)(1)(0.09) + (0)(2)(0.05) + (1)(0)(0.14) + (1)(1)(0.17)
+ (1)(2)(0.18) + (2)(0)(0.12) + (2)(1)(0.13) + (2)(2)(0.04) = 0.95
∑ ∑ xyP( x, y) μ x μ y = 0.95 – (1.07)(0.93) = –0.045
COV(X, Y) = all x all y –
√
σ x =√ σ 2x=√ 0 . 505 = 0.711, σ y= σ 2y =√ 0 .605 = 0.778
COV ( X , Y ) −0.045
ρ=
σxσ y = (0.711 )(0.778 ) = –0.081
7.55 a P(X = 1 | Y = 0) = P(X =1 and Y = 0)/P(Y = 0) = 0.14/0.34 = 0.412
b P(Y = 0 | X = 1) = P(X =1 and Y = 0)/P(X = 1) = 0.14/0.49 = 0.286
c P(X = 2 | Y = 2) = P(X =2 and Y = 2)/P(Y = 2) = 0.04/.27 = 0.148
7.56 a P(CMD = 0 and SD = 2) = 0.06
b P(CMD = 2 and SD = 0) = 0
c P(CMD ≥ 1 and SD ≥ 1) = 0.07 + 0.01 + 0.10 + 0.15 + 0.04 + 0.02 = 0.39
6.67 Define events: A = heart attack, B = periodontal disease
P(A) = 0.10, P(B | A) = 0.85, P(B | AC ) = 0.29
P(B ) = 0.085 + 0.261 = 0.346
P( A and B ) 0 . 085
= =0 . 246
P(A | B) = P(B ) 0 . 346
6.70 Define events: A, B, C = airlines A, B, and C, D = on time
P(A) = 0.50, P(B) = 0.30, P(C) = 0.20, P(D | A) = 0.80, P(D | B) = 0.65, P(D | C) = 0.40
P(D) = 0.40 + 0.195 + 0.08 = 0.675
P( A and D ) 0 . 40
= =0 . 593
P(A | D) = P( D ) 0. 675
8.81 μ=1/ λ = 125 seconds; λ = 0.008 transactions/second = 0.48 transactions/minute
P( X >3 )=e−0 . 48( 3)=e−1. 44 = 0.2369
8.82 μ=1/ λ = 6 minutes; λ = 0.167 customers/minute
−0 .167( 10 ) −1 .67
P( X >10 )=e =e = 0.1889
8.83 x = 30 and P(X > x) = 0.10
−ln[ P ( X > x)] −ln[ 0.10] −(−2.303)
λ= x = 30 = 30 = 0.0768
The service rate should be 0.0768 cars per minute or 4.61 cars per hour.
p^ −p 0 .73−0 . 70
z=
12.54 a √ p(1−p )/n = √0 . 70(1−0. 70)/100 = 0.65, p-value = P(Z > 0.65) = 1 – 0.65=0.35
p^ −p 0. 72−0.70
z=
b √ p(1−p )/n = √0. 70(1−0. 70)/100 = 0.44, p-value = P(Z > 0.44) = 1 – 0.44=0.56
p^ −p 0 .71−0 .70
z=
c √ p(1−p )/n = √ 0.70(1−0 .70)/100 = 0.22, p-value = P(Z > 0.22) = 1 – 0.22=0.78
d The z statistic decreases and the p-value increases.
12.62 ^p = 259/373 = 0.69
^p±z α /2 √ ^p (1− ^p )/n
= 0.69 ± 1.96 √ 0.69(1−0.69)/373 = 0.69 ± 0.0469; LCL = 0.6431, UCL = 0.7369
12.63 H0: p = 0.25
H1: p < 0.25
^p = 41/200 = 0.205
p^ −p
z=
√ p(1−p )/n =0.47 , 1-0.47=0.53 there is enough evidence to support the officer’s belief.
You might also like
- 216032J - Group 04Document10 pages216032J - Group 04Uresh FernandoNo ratings yet
- 7 1Document24 pages7 1khrid3No ratings yet
- (Mai 4.11) Normal Distribution - SolutionsDocument5 pages(Mai 4.11) Normal Distribution - SolutionsSonia AroraNo ratings yet
- (MAA 4.11) NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - SolutionsDocument10 pages(MAA 4.11) NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - SolutionsAli HalawiNo ratings yet
- SOA Course 3 SolutionsDocument40 pagesSOA Course 3 SolutionsHông HoaNo ratings yet
- Final SBE-FINALSDocument11 pagesFinal SBE-FINALSVika BodokiaNo ratings yet
- Calculul Presiunii Vantului: β=4 - 50−0 - 856⋅ln (z I (z) = β z z c z) =1+g⋅ c z) =k z z c z) =c z) ⋅c z) w (z) =q c z) ⋅cDocument2 pagesCalculul Presiunii Vantului: β=4 - 50−0 - 856⋅ln (z I (z) = β z z c z) =1+g⋅ c z) =k z z c z) =c z) ⋅c z) w (z) =q c z) ⋅cBogdan FocsaneanuNo ratings yet
- Tut 15A Normal Distn and Sample Mean - SolutionsDocument5 pagesTut 15A Normal Distn and Sample Mean - SolutionsselmerparisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesTutorial - 1 Solutionssedobi1512No ratings yet
- Calculating sample size for a binomial proportionDocument11 pagesCalculating sample size for a binomial proportionMAIQUEL VELOSONo ratings yet
- P O Solutions To Exercises: ART NEDocument13 pagesP O Solutions To Exercises: ART NEDavid Santiago LagoNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Topic 3 Tutorial Solutions (Q1-Q10)Document4 pagesBusiness Statistics Topic 3 Tutorial Solutions (Q1-Q10)Beryl ChanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesProblem Set 2 - Solutionshoi chingNo ratings yet
- Statistics Tutorial Questions on Probability DistributionsDocument3 pagesStatistics Tutorial Questions on Probability DistributionsThảo PhươngNo ratings yet
- Statistik BAB2 Jilid2Document10 pagesStatistik BAB2 Jilid2Emil Agusta AsyrofNo ratings yet
- MLC Sample SolutionDocument169 pagesMLC Sample SolutionLoh Hui YinNo ratings yet
- Numerical MethodsDocument18 pagesNumerical MethodsAbed MasaudNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Questions Week 1Document15 pagesSolutions To Practice Questions Week 1YUPING GUONo ratings yet
- 19ECE - 29 - Trương Công Thắng - Lesson 3 - contDocument3 pages19ECE - 29 - Trương Công Thắng - Lesson 3 - contTrương ThắngNo ratings yet
- Iit Model Paper Answer 6Document9 pagesIit Model Paper Answer 6studysteps.inNo ratings yet
- Jan 2015 - Mock Paper - Solution Q3-5Document5 pagesJan 2015 - Mock Paper - Solution Q3-5jimmychillsNo ratings yet
- Tarea #3 - Litardo. DanielaDocument6 pagesTarea #3 - Litardo. DanielaDaniela FernandaNo ratings yet
- Formato Actividad 01 - S5 - Clase 2Document12 pagesFormato Actividad 01 - S5 - Clase 2Paul JHNo ratings yet
- CHP 6Document13 pagesCHP 6Mittal Kirti MukeshNo ratings yet
- EPIB 650 Homework 4 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsDocument4 pagesEPIB 650 Homework 4 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsDureyeNo ratings yet
- Lembar Perhitungan 1. Perhitungan Reagen: Asam AsetatDocument8 pagesLembar Perhitungan 1. Perhitungan Reagen: Asam AsetatRizky Ardias DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesExercise Sheet 4 SolutionsRyantyler13No ratings yet
- Tutorial chapters probability distributionsDocument5 pagesTutorial chapters probability distributionsHuiru ChuaNo ratings yet
- Teorema Del Limite CentralDocument14 pagesTeorema Del Limite CentralmodestorosNo ratings yet
- Calculo y Simulación Cto. RLC ParaleloDocument4 pagesCalculo y Simulación Cto. RLC Paralelophono.vozNo ratings yet
- s39 57 PDFDocument23 pagess39 57 PDFBreno EnricoNo ratings yet
- QM 161 Assignment 2Document8 pagesQM 161 Assignment 2Lana RoelandtsNo ratings yet
- Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value ProblemsDocument7 pagesSturm-Liouville Boundary Value ProblemsmahmuthuysuzNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Ingeniería Escuela Académico Profesional de Ingeniería CivilDocument10 pagesFacultad de Ingeniería Escuela Académico Profesional de Ingeniería CivilAntony Huaracha AbantoNo ratings yet
- masDocument3 pagesmasNguyễn DuyNo ratings yet
- Equivalant Moment of InertiaDocument13 pagesEquivalant Moment of InertiaYasiru KaluarachchiNo ratings yet
- Batch MEDocument3 pagesBatch MEYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- Figure X 0:0.1:1 y X. Exp (2) Plot (X, Y) : p1 (U) (1-U) P P PDocument3 pagesFigure X 0:0.1:1 y X. Exp (2) Plot (X, Y) : p1 (U) (1-U) P P PLawrence WafulaNo ratings yet
- Control Por Computador: November 12, 2013Document17 pagesControl Por Computador: November 12, 2013turbodilanNo ratings yet
- Taller EstadisticaDocument4 pagesTaller EstadisticaLaura PerezNo ratings yet
- PS2 Key - Stat 370Document2 pagesPS2 Key - Stat 370srikanthNo ratings yet
- Funkcje Bessela Najlepszy Art Z 1957Document3 pagesFunkcje Bessela Najlepszy Art Z 1957Baja BajabajasziNo ratings yet
- Skoog Chapter 22 JawabanDocument11 pagesSkoog Chapter 22 JawabanmarisaaaNo ratings yet
- 09 SM - Ch07Document26 pages09 SM - Ch07Ashish BhallaNo ratings yet
- 8Q SolutionDocument4 pages8Q SolutionMohammed YahyaNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Moment of InertiaDocument12 pagesEquivalent Moment of InertiaYasiru KaluarachchiNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Business Statistics 3e by Norean D Sharpe 0133866912Document13 pagesSolutions Manual For Business Statistics 3e by Norean D Sharpe 0133866912TimothyHilldpgoa100% (75)
- RincianperhitunganDocument6 pagesRincianperhitunganKucing PilekNo ratings yet
- B.6 Design of ForebayDocument12 pagesB.6 Design of ForebaysandeepNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5EmadNo ratings yet
- B I Tëp CH NG Ii: Longtkt - TK 1Document21 pagesB I Tëp CH NG Ii: Longtkt - TK 1longtkt198367% (3)
- Solution Manual For Introductory Statistics 9th by MannDocument25 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Statistics 9th by MannKatelynWebsterikzj100% (43)
- Practica de Clase Distrib - Binom y PoissonDocument4 pagesPractica de Clase Distrib - Binom y PoissonALDAHYR YOHELNo ratings yet
- Phase Behavior Analysis and CalculationsDocument8 pagesPhase Behavior Analysis and CalculationsAntonio ChissanoNo ratings yet
- Deber EstadisticaDocument4 pagesDeber EstadisticaDIANA CAMILA FERNANDEZ MEDINANo ratings yet
- Let The Required Sales Quantity Be X: Quantitative MethodsDocument8 pagesLet The Required Sales Quantity Be X: Quantitative MethodsUmer RehmanNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- HumanResourceManagement TheoryPractice PDFDocument35 pagesHumanResourceManagement TheoryPractice PDFYuga NayakNo ratings yet
- Statistics: 3.3 Number of Classes 1+3.3 Log300 9 Class Width 241-147 / 9 10.4Document8 pagesStatistics: 3.3 Number of Classes 1+3.3 Log300 9 Class Width 241-147 / 9 10.4Vika BodokiaNo ratings yet
- Final SBE-FINALSDocument11 pagesFinal SBE-FINALSVika BodokiaNo ratings yet
- Upstream Partner Means A Third Party That Sources and Supplies Downstream Partner Means Any Person, Organisation, Company or AgreementDocument3 pagesUpstream Partner Means A Third Party That Sources and Supplies Downstream Partner Means Any Person, Organisation, Company or AgreementVika BodokiaNo ratings yet
- Answers 2Document4 pagesAnswers 2Vika BodokiaNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument13 pagesMarketingquintupleNo ratings yet
- Social Studies For Brunei Darussalam Year 8 TextbookDocument152 pagesSocial Studies For Brunei Darussalam Year 8 TextbookChai Wei Chen100% (1)
- Appointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDocument1 pageAppointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDarwin Competente LagranNo ratings yet
- You Said It's Called Supreme Mathematics RightDocument2 pagesYou Said It's Called Supreme Mathematics RightAuMatu89% (9)
- Business PlanDocument15 pagesBusiness PlanAwel OumerNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Dbms PDFDocument66 pagesUnit4 Dbms PDFRS GamerNo ratings yet
- The Most Efficient and Effective Ways To Address New Literacies FDocument61 pagesThe Most Efficient and Effective Ways To Address New Literacies FAlpha MoontonNo ratings yet
- Montageanleitung sf25 35 enDocument20 pagesMontageanleitung sf25 35 enPaulo santosNo ratings yet
- Ej18 DetailsDocument6 pagesEj18 Detailsdaniel FerreiraNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 5Document24 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 5Anonymous wirViz1tyoNo ratings yet
- Ant Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesAnt Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFIwan Arinta100% (1)
- Postgraduate Prospectus 2021: World ChangersDocument35 pagesPostgraduate Prospectus 2021: World ChangersSKNo ratings yet
- 74HCT00Document8 pages74HCT00Sadikul FuadNo ratings yet
- HA RLE WS 24 Assessing Female Genitalia and Rectum Copy 1Document16 pagesHA RLE WS 24 Assessing Female Genitalia and Rectum Copy 1Katreena Barcelona GonzalesNo ratings yet
- XETEC 4g300 / 4g600Document6 pagesXETEC 4g300 / 4g600Harun ARIKNo ratings yet
- Visulas Yag III User ManualDocument126 pagesVisulas Yag III User ManualTomNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Thesis MaritimeDocument43 pagesBachelor Thesis MaritimeMiriam PedersenNo ratings yet
- 4880 AnsiDocument0 pages4880 AnsiabualamalNo ratings yet
- Appendix A. Second QuantizationDocument24 pagesAppendix A. Second QuantizationAgtc TandayNo ratings yet
- Stock TakeDocument14 pagesStock Takesafare2222No ratings yet
- Three Phase Traffic Theory PDFDocument11 pagesThree Phase Traffic Theory PDFKocic GradnjaNo ratings yet
- Philo Q1module 4Document18 pagesPhilo Q1module 4Abygiel Salas100% (1)
- Illuminism - The Occult Force Behind Globalization - by Wes PenreDocument98 pagesIlluminism - The Occult Force Behind Globalization - by Wes Penrebreiard100% (1)
- Moana Taka PartnershipDocument2 pagesMoana Taka Partnershipself sayidNo ratings yet
- General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument28 pagesGeneral Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJulie MerrillNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: by Asaye Gebrewold (PHD Candidate)Document17 pagesResearch Methodology: by Asaye Gebrewold (PHD Candidate)natnael haileNo ratings yet
- Mechanik Lammert ContentDocument3 pagesMechanik Lammert Contentapi-129423309No ratings yet
- House (Sometimes Known As House, M.D.) Is An American TelevisionDocument17 pagesHouse (Sometimes Known As House, M.D.) Is An American Televisionpichi94No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper IIDocument1 pageReflection Paper IIHazel Marie Echavez100% (1)
- D117/D118 Service ManualDocument75 pagesD117/D118 Service ManualJohn JuquenNo ratings yet
- Degrees of ComparisonDocument3 pagesDegrees of ComparisonThiru MoorthyNo ratings yet