Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spread Spectrum Techniques
Uploaded by
Harsh Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views18 pagesOriginal Title
spread spectrum techniques
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views18 pagesSpread Spectrum Techniques
Uploaded by
Harsh KumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Spread Spectrum in Mobile Computing
• Spread spectrum is a technique used for wireless communications in
telecommunication and radio communication. In this technique, the
frequency of the transmitted signal, i.e., an electrical signal,
electromagnetic signal, or acoustic signal, is deliberately varied and
generates a much greater bandwidth than the signal would have if its
frequency were not varied.
• In other words, "Spread Spectrum is a technique in which the transmitted
signals of specific frequencies are varied slightly to obtain greater
bandwidth as compared to initial bandwidth."
• Now, spread spectrum technology is widely used in radio signals
transmission because it can easily reduce noise and other signal issues.
Spread Spectrum Concept
• Input fed into channel encoder
• Produces narrow bandwidth analog signal around central frequency
• Signal modulated using sequence of digits
• Spreading code/sequence
• Typically generated by pseudonoise/pseudorandom number generator
• Increases bandwidth significantly
• Spreads spectrum
• Receiver uses same sequence to demodulate signal
• Demodulated signal fed into channel decoder
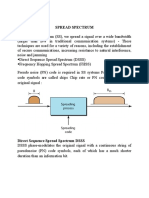
General Model of Spread Spectrum System
In this conventional wireless communication
model, you can face at least two problems:
1.A signal whose frequency is constant is subject to catastrophic
interference. This interference occurs when another signal is
transmitted on or near the frequency of a specified signal.
2.A constant-frequency signal can easily be intercepted. So, it is not
suitable for the applications in which information must be kept
confidential between the source (transmitting party) and the receiver.
• The spread spectrum model is used to overcome with this
conventional communication model. Here, the transmitted signal
frequency is deliberately varied over a comparatively large segment of
the electromagnetic radiation spectrum. This variation is done
according to a specific but complicated mathematical function.
• If the receiver wants to intercept the signal, it must be tuned to
frequencies that vary precisely according to this function.
Types of Spread Spectrum
• Spread Spectrum can be categorized into two types:
• Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
• Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum(DSSS)
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
• The Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum or FHSS allows us to utilize
bandwidth properly and maximum. In this technique, the whole
available bandwidth is divided into many channels and spread
between channels, arranged continuously.
• The frequency slots are selected randomly, and frequency signals are
transmitted according to their occupancy.
• The transmitters and receivers keep on hopping on channels available
for a particular amount of time in milliseconds.
• It implements the frequency division multiplexing and time-division
multiplexing simultaneously in FHSS.
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum(FHSS)
• The Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum or FHSS can also be
classified into two types:
• Slow Hopping: In slow hopping, multiple bits are transmitted on a
specific frequency or same frequency.
• Fast Hopping: In fast hopping, individual bits are split and then
transmitted on different frequencies.
Slow and Fast Frequency Hopping
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
• The Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) is a spread-spectrum
modulation technique primarily used to reduce overall signal
interference in telecommunication.
• The Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum modulation makes the
transmitted signal wider in bandwidth than the information
bandwidth.
• In DSSS, the message bits are modulated by a bit sequencing process
known as a spreading sequence. This spreading-sequence bit is
known as a chip. It has a much shorter duration (larger bandwidth)
than the original message bits.
Following are the features of Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum or DSSS.
• In Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum or DSSS technique, the data that
needs to be transmitted is split into smaller blocks.
• After that, each data block is attached with a high data rate bit sequence
and is transmitted from the sender end to the receiver end.
• Data blocks are recombined again to generate the original data at the
receiver's end, which was sent by the sender, with the help of the data rate
bit sequence.
• If somehow data is lost, then data blocks can also be recovered with those
data rate bits.
• The main advantage of splitting the data into smaller blocks is that it
reduces the noise and unintentional inference.
DSSS
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
• Each bit represented by multiple bits using spreading code
• Spreading code spreads signal across wider frequency band
• In proportion to number of bits used
• 10 bit spreading code spreads signal across 10 times bandwidth of 1 bit code
• One method:
• Combine input with spreading code using XOR
• Input bit 1 inverts spreading code bit
• Input zero bit doesn’t alter spreading code bit
• Data rate equal to original spreading code
• Performance similar to FHSS
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Example
You might also like
- Spread Spectrum ModulationDocument75 pagesSpread Spectrum ModulationA21126512117 SUKALA ABHIRAMNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- DC Module 4Document66 pagesDC Module 4Quartz DeepNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum TechniquesDocument21 pagesSpread Spectrum TechniquesShahid جنيدNo ratings yet
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Spread Spectrum: Unit - 5 Presented by Mrs. M.P.SasirekhaDocument26 pagesSpread Spectrum: Unit - 5 Presented by Mrs. M.P.SasirekhasasirekhaNo ratings yet
- Optimize Bandwidth With Multiplexing TechniquesDocument29 pagesOptimize Bandwidth With Multiplexing TechniquesVeena Gadad100% (1)
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Analytical Study Of: FHSS and DsssDocument30 pagesAnalytical Study Of: FHSS and DsssLalita GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument11 pagesUnit 5 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum in Mobile Computing - JavatpointDocument9 pagesSpread Spectrum in Mobile Computing - Javatpointjulie MNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum: By: Rahat Ullah Associate Professor CS - IT, SUIT PeshawarDocument26 pagesSpread Spectrum: By: Rahat Ullah Associate Professor CS - IT, SUIT PeshawarAhsan JameelNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum and CDMA TechnologyDocument31 pagesSpread Spectrum and CDMA TechnologyAltayeb Ibn AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum: Fhss DsssDocument26 pagesSpread Spectrum: Fhss DsssvinithemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 1 33155!spreadspectrumDocument28 pages1 33155!spreadspectrumSri RAM ReloadedNo ratings yet
- Cst476 Mobile Computing 2Document41 pagesCst476 Mobile Computing 2Ajin JosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Physical LayerDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - Physical Layerhenok metaferiaNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum: Presented By:-Ramjee Prasad 10804900 RH68T2B54Document24 pagesSpread Spectrum: Presented By:-Ramjee Prasad 10804900 RH68T2B54ramjee26No ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Techniques for Multiple AccessDocument31 pagesSpread Spectrum Techniques for Multiple Accesspapayee lakshmananNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum: Ss SsDocument11 pagesSpread Spectrum: Ss SsBindhya BibinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document20 pagesLecture 12sohaib hashmatNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum SystemDocument27 pagesSpread Spectrum SystemTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Spread SpectrumDocument27 pagesLecture 7 - Spread SpectrumMohamed Mostafa elnahasNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum in Spread Spectrum (SS), We Spread A Signal Over A Wide BandwidthDocument9 pagesSpread Spectrum in Spread Spectrum (SS), We Spread A Signal Over A Wide BandwidthTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum FundamentalsDocument27 pagesSpread Spectrum FundamentalsSharland GodinhoNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Modulation SystemsDocument27 pagesSpread Spectrum Modulation SystemsKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Data and Computer Communications Chapter 9 – Spread SpectrumDocument30 pagesSpread Spectrum Data and Computer Communications Chapter 9 – Spread Spectrumalbin paul100% (1)
- Chapter FourDocument20 pagesChapter FourDere JesusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Edited) Wireless Area NeworksDocument132 pagesChapter 2 (Edited) Wireless Area NeworksDawit AndargachewNo ratings yet
- Spread SpectrumDocument25 pagesSpread SpectrumaloksanjayNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer 4Document23 pagesPhysical Layer 4soumen maityNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueThasleema BanuNo ratings yet
- Spread spectrum techniques for telecommunicationsDocument2 pagesSpread spectrum techniques for telecommunicationsmanikandanNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey of Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum SystemDocument10 pagesLiterature Survey of Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum SystemDheyauldeen NajimNo ratings yet
- MC Answer Key 1Document47 pagesMC Answer Key 1Neeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document33 pagesCH 1Hamze Ordawi1084No ratings yet
- 09 SpreadSpectrumDocument28 pages09 SpreadSpectrumChandan SasamalNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum and Multiple Access T Chniqu S: UNIT-5Document30 pagesSpread Spectrum and Multiple Access T Chniqu S: UNIT-5makNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum: Submitted By: Vikas Sharma M.Tech (Part Time)Document19 pagesSpread Spectrum: Submitted By: Vikas Sharma M.Tech (Part Time)sunilNo ratings yet
- Week01 FundamentalsDocument43 pagesWeek01 FundamentalsSara El-GendyNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing (DC)Document64 pagesMultiplexing (DC)akrNo ratings yet
- Lec 4-2 Spread Spectrum2Document27 pagesLec 4-2 Spread Spectrum2Ajmal EnsanahNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: Lecture - 6Document51 pagesData Communication and Networking: Lecture - 6HaroonĦammadiNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Techniques for Secure Wireless CommunicationDocument11 pagesSpread Spectrum Techniques for Secure Wireless CommunicationSandra MariaNo ratings yet
- CDMA SlidesDocument37 pagesCDMA SlidesAnkush GoyalNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum by SamDocument15 pagesSpread Spectrum by SamSameer TiwariNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument14 pagesProgress ReportWarren CarlsonNo ratings yet
- Cdma Code Division Multiple Accses and Radio ComDocument43 pagesCdma Code Division Multiple Accses and Radio Commuhannad aljazaerliNo ratings yet
- Fhss DsssDocument5 pagesFhss DsssAhmed IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Why Are Waves of Very Low Frequency Not Used For Data Transmission in Computer Networks?Document11 pagesWhy Are Waves of Very Low Frequency Not Used For Data Transmission in Computer Networks?danielNo ratings yet
- Direct Sequence Spread-Spectrum With Frequency HoppingDocument30 pagesDirect Sequence Spread-Spectrum With Frequency HoppingMaki-Bum MaharotNo ratings yet
- Tugas Spread SpectrumDocument7 pagesTugas Spread SpectrumShidqi PranitiNo ratings yet
- Paper-4 - Simulation and Analysis of Spread Spectrum Techniques Using MATLABDocument6 pagesPaper-4 - Simulation and Analysis of Spread Spectrum Techniques Using MATLABRachel Wheeler100% (2)
- Course Work #3 Discussiong Spread Spectrum & Multiple Access TechniquesDocument10 pagesCourse Work #3 Discussiong Spread Spectrum & Multiple Access TechniqueswahahahhasiafiadgNo ratings yet
- Direct Sequence Spread SpectrumDocument6 pagesDirect Sequence Spread SpectrumKhandai SeenananNo ratings yet
- ListOf PHD Students OngoingDocument5 pagesListOf PHD Students OngoingBiswajit DebnathNo ratings yet
- XPT Igbt 600V Genx3 W/ Diode Ixxh50N60B3D1: V 600V I 50A V T 135NsDocument7 pagesXPT Igbt 600V Genx3 W/ Diode Ixxh50N60B3D1: V 600V I 50A V T 135Nsali ülküNo ratings yet
- Sensor and Actuator QuestionsDocument9 pagesSensor and Actuator Questionsvaishnav kNo ratings yet
- Variasi Jumlah Elektroda Dan Besar Tegangan Dalam Menurunkan Kandungan Cod Dan Tss Limbah Cair Tekstil Dengan Metode ElektrokoagulasiDocument7 pagesVariasi Jumlah Elektroda Dan Besar Tegangan Dalam Menurunkan Kandungan Cod Dan Tss Limbah Cair Tekstil Dengan Metode ElektrokoagulasiDwiki RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Earthing (Check-1) PDFDocument4 pagesEarthing (Check-1) PDFZin BoNo ratings yet
- Format 8 Synchronizing ReportDocument4 pagesFormat 8 Synchronizing ReportSameerNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Antennas Assignment BankDocument2 pagesMicrowave and Antennas Assignment Bankvijayarani.katkamNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument13 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringTirth MasarwalaNo ratings yet
- Report On RelayDocument27 pagesReport On RelayDeepakVyas67% (3)
- List of Qa Equiptment For CalibrationDocument26 pagesList of Qa Equiptment For CalibrationVincent EbdaniNo ratings yet
- 20G00117 Electrical CompressedDocument13 pages20G00117 Electrical CompressedYvette Claire MagbualNo ratings yet
- IG Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesIG Datasheet PDFHoang GiangNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Resistors, Ohm's Law, Power Rating and I-V Caharacteristic (2012)Document10 pagesExp 2 Resistors, Ohm's Law, Power Rating and I-V Caharacteristic (2012)usmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Volumn 3 of 3Document186 pagesVolumn 3 of 3Rohan MalikNo ratings yet
- Vibxpert II Technical DataDocument1 pageVibxpert II Technical DataLuis GonzaloNo ratings yet
- PV Box ST Technical Specification - V01 PDFDocument24 pagesPV Box ST Technical Specification - V01 PDFMarioMur100% (1)
- 570Document205 pages570Brijendra Singh100% (1)
- Introduction to Electronic Components and DevicesDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Electronic Components and DevicesVincent AveryNo ratings yet
- 1 AC Voltage Controllers ICCDocument15 pages1 AC Voltage Controllers ICCMuhammad Nazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesPN Junction Diode CharacteristicssrinathlalNo ratings yet
- Review of Comparative Analysis of Speed Control Techniques of BLDC & PMSM MotorDocument9 pagesReview of Comparative Analysis of Speed Control Techniques of BLDC & PMSM MotorIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Miller TM-2206 INVISION 304PDocument106 pagesMiller TM-2206 INVISION 304PLila WeldingNo ratings yet
- Microwave EnggDocument4 pagesMicrowave EnggasiffarookiNo ratings yet
- BJT Small SignalDocument56 pagesBJT Small SignalasiffarookiNo ratings yet
- Manual / Handbuch Spare Parts List / ErsatzteillisteDocument59 pagesManual / Handbuch Spare Parts List / Ersatzteillisteneno111No ratings yet
- Brochure ICS Repeater (20W) WCDMADocument3 pagesBrochure ICS Repeater (20W) WCDMAHoàng Anh DũngNo ratings yet
- Load SheddingDocument5 pagesLoad SheddingAdhyartha KerafNo ratings yet
- RIS Comem 2Document8 pagesRIS Comem 2tanniayulianaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Excitation System Control Modes OnDocument7 pagesInfluence of Excitation System Control Modes OnailsonmouraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesLesson 1 IntroductionShiela Amiral BisanaNo ratings yet