Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Numerical S
Uploaded by
HASSAN WASEEMOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Numerical S
Uploaded by
HASSAN WASEEMCopyright:
Available Formats
Hassan Waseem
2020-pe-19
Problem 1: An aluminium rod and a copper rod of equal length 2.0 m and
cross-sectional area 2 cm 2 are welded together in parallel. One end is kept
at a temperature of 10 °C and the other at 30 °C. Calculate the amount of
heat taken out per second from the hot end. (Thermal conductivity of
aluminium is 200 W ⁄ m °C and of copper is 390 W ⁄ m °C).
Solution:
Given:
Thermal conductivity of aluminum, K Al = 200 W ⁄ m °C
Thermal conductivity of aluminum, K Cu = 390 W ⁄ m °C
Combined thermal conductivity for parallel combination, K = 200 W ⁄ m °C + 390
W ⁄ m °C = 590 W ⁄ m °C
Length of rod, d = 2 m
Area of rod, A = 2 cm2 = 2 × 10-4 m2
Temperature difference, Th – Tc = 30 °C – 10 °C = 20 °C
The formula for heat transfer rate is given as:
q = K A (Th – Tc) ⁄ d
= (590 × 2 × 10-4 × 20) ⁄ 2 W
= 1.18 W
Hence, the total amount of heat transfer is 1.18 W.
2. The air in a room is at 25° c and outside temperature is 0° c. The window of the room has an area of
2m2 and thickness 2mm. Calculate the rate of loss of heat by conduction through window ? Thermal
conductivity for glass is 1 Wm– 1degree– 1.
Sol: Rate of loss of heat is given by
where Q is the quantity of heat that flows from hot area to cold area and is given by Q
Q =
=
Rate of loss
k is Thermal conductivity of glass = 1 Wm– 1deg– 1
A Area of the window = 2 m2
T1 Temperature in the room = 25° c
T2Temperature outside the room = 0° c
x is thickness of the window = 2mm = 2 × 10– 3
=
= 25 × 103 w/s
= 25 kw/s
You might also like
- CH 2-2Document203 pagesCH 2-2Aishahed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- TP ProblemsDocument4 pagesTP ProblemsNOUMAN AMJADNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument10 pagesHeat TransferRommel ArmentaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-02 - ME502 - Steady Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesProblem Sheet-02 - ME502 - Steady Heat ConductionYELSI YAJAIRA QUICENO VILLANUEVA100% (1)
- Problem Set 3Document10 pagesProblem Set 3Zainal AzrinNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document14 pagesHW 3Mark LutherNo ratings yet
- Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesSolved ProblemsMahir Mahmood33% (3)
- Lecture 5 - May 2014 Heat TrasferDocument19 pagesLecture 5 - May 2014 Heat TrasferAhmedHassan100% (12)
- Holman 1Document4 pagesHolman 1Kumar SamyanaikNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Steady State ConductionDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer: Steady State ConductionAnonymous 1VhXp1No ratings yet
- EjerciciosDocument24 pagesEjerciciosMarjorieNo ratings yet
- Assignment Week 1 CC PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment Week 1 CC PDFPushparaj MariaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thickness PDFDocument6 pagesCritical Thickness PDFSurya KiranNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Gate QuestionDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Gate QuestionSANDEEP GautamNo ratings yet
- Full Download Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manualwhinyard.around.vb2c100% (41)
- Ejercicios Transferencia de CalorDocument15 pagesEjercicios Transferencia de CalorWilliam Hernan HenaoNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Paper 3 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesMid Term Paper 3 Heat TransferAbdul GhaffarNo ratings yet
- HW#1Document2 pagesHW#1AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Problemas Resolvidos IDocument12 pagesProblemas Resolvidos IAdelia CristinaNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.1 KNOWN: Heat Rate, Q, Through One-Dimensional Wall of Area A, Thickness L, ThermalDocument8 pagesProblem 1.1 KNOWN: Heat Rate, Q, Through One-Dimensional Wall of Area A, Thickness L, ThermalMarco Antonio Salcedo HinojosaNo ratings yet
- NiceDocument18 pagesNicepamiNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de Calor Cengue Del 3.19 - 3.22Document10 pagesTransferencia de Calor Cengue Del 3.19 - 3.22Carlos Hernández JulioNo ratings yet
- ME5101 2020 Assignment 01Document2 pagesME5101 2020 Assignment 01palash_shrivastava6282058No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 NumericalsDocument11 pagesLesson 7 Numericalssurya kiranNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions Manualcuongviolet1or0zm0% (1)
- Heat Transfer ch-1Document1 pageHeat Transfer ch-1Fawazil NawesNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer: "Solved Problems"Document16 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: "Solved Problems"qiritical99No ratings yet
- 1 - Mechanisms - ExercisesDocument2 pages1 - Mechanisms - ExercisesIñigoAlberdiNo ratings yet
- YehshsDocument15 pagesYehshsNadiaNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument37 pagesHeat Transferjason1989No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Kunal YadavNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Heat TransferDocument12 pagesSolved Problems Heat TransferFaisal SadaatNo ratings yet
- Nama:Rofiatun Nurfaiza NIM:11521098 Tugas 1 Perpindahan PanasDocument5 pagesNama:Rofiatun Nurfaiza NIM:11521098 Tugas 1 Perpindahan PanasrofiatunnurfaizaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Mukul ParasharNo ratings yet
- Northern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesNorthern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferAj ZNo ratings yet
- Transferencia Cap 03-1-39Document22 pagesTransferencia Cap 03-1-39JONATHAN JUNIOR BARRETO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
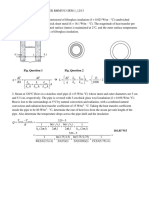
- L A K L A K L T RA T Q K K L K L Q T L: Fig. Question 1 Fig. Question 2 Fig. Question 3Document2 pagesL A K L A K L T RA T Q K K L K L Q T L: Fig. Question 1 Fig. Question 2 Fig. Question 3Bi100% (1)
- مثال فصل 3Document10 pagesمثال فصل 3mohammadNo ratings yet
- sm3 058Document2 pagessm3 058Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Eoal Perpindahan PanasDocument4 pagesEoal Perpindahan Panasmei fenti andrianiNo ratings yet
- ENG-S17-S18 - Heat Transfer Problems (Modes, Plane Wall, Thermal Resistances)Document4 pagesENG-S17-S18 - Heat Transfer Problems (Modes, Plane Wall, Thermal Resistances)fNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint PERPINDAHAN PANASDocument17 pagesPowerpoint PERPINDAHAN PANASDwipasaribuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 With AnswersDocument2 pagesSheet 2 With Answers01156295293cNo ratings yet
- Conducción EstacionariaDocument5 pagesConducción EstacionariaMILENKA ALISON SICCHA JARANo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument1 pagePractice ProblemsKenneth dimaandalNo ratings yet
- Conduction Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesConduction Tutorial Sheet 2Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Conduction Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesConduction Tutorial Sheet 2Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- ALL Problems - 230918 - 120556Document8 pagesALL Problems - 230918 - 120556Priyojit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Composite Walls Part 2Document10 pagesHeat Transfer Composite Walls Part 2Jershell Dumayao0% (1)
- Heat Conservation in Liquid IronDocument2 pagesHeat Conservation in Liquid Ironarnaldorcr8646No ratings yet
- Problem Sets DanioDocument9 pagesProblem Sets DanioMark Angelo DanioNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Document14 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Christopher MillerNo ratings yet
- Ch3 HeatTransfer 2Document27 pagesCh3 HeatTransfer 2Fernando EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Document2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Lucky 230503No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document10 pagesTutorial Sheet 3kushalNo ratings yet
- PPO Assignment 1 Group 1Document87 pagesPPO Assignment 1 Group 1HASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2583 Standard Testing Method of Measuring Hardness by Barcol Hardness MethodDocument8 pagesASTM D2583 Standard Testing Method of Measuring Hardness by Barcol Hardness MethodHASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- 2020-Pe-19 (Lab Report)Document36 pages2020-Pe-19 (Lab Report)HASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- Astm D1709-16ae1 Standard Test Methods For Impact Resistance of Plastic Film by The Free-Falling Dart MethodDocument9 pagesAstm D1709-16ae1 Standard Test Methods For Impact Resistance of Plastic Film by The Free-Falling Dart MethodHASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- Group # 05 Complex Engineering ProblemDocument6 pagesGroup # 05 Complex Engineering ProblemHASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- Astm D1709-16ae1 Standard Test Methods For Impact Resistance of Plastic Film by The Free-Falling Dart MethodDocument7 pagesAstm D1709-16ae1 Standard Test Methods For Impact Resistance of Plastic Film by The Free-Falling Dart MethodHASSAN WASEEMNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Culture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandCulture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Fire Protection in Chemical, Petrochemical, and Hydrocarbon Processing FacilitiesFrom EverandGuidelines for Fire Protection in Chemical, Petrochemical, and Hydrocarbon Processing FacilitiesNo ratings yet
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Last Days of the Concorde: The Crash of Flight 4590 and the End of Supersonic Passenger TravelFrom EverandLast Days of the Concorde: The Crash of Flight 4590 and the End of Supersonic Passenger TravelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Pre-Accident Investigations: An Introduction to Organizational SafetyFrom EverandPre-Accident Investigations: An Introduction to Organizational SafetyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Establishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001From EverandEstablishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)