100% found this document useful (1 vote)
445 views10 pagesHelicopter Long Line Operations SOP
This document outlines standard operating procedures for helicopter long line and external load operations. It details roles and prerequisites for pilots and personnel, required tools and equipment, and the procedures to follow. The procedures section provides a high level flowchart and requirements for communication, operations, load handling, and emergency response. It aims to ensure the safe completion of light, intermediate and medium helicopter long line operations.
Uploaded by
Ramesh BajracharyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
445 views10 pagesHelicopter Long Line Operations SOP
This document outlines standard operating procedures for helicopter long line and external load operations. It details roles and prerequisites for pilots and personnel, required tools and equipment, and the procedures to follow. The procedures section provides a high level flowchart and requirements for communication, operations, load handling, and emergency response. It aims to ensure the safe completion of light, intermediate and medium helicopter long line operations.
Uploaded by
Ramesh BajracharyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- 1.0 Purpose
- 2.0 Roles and Prerequisites
- 3.0 Tools and Equipment
- 4.0 Procedure
- 2.0 Cargo Hook Inspections
- 3.0 Load Pick Up Procedure
- 4.0 Receiving a Load
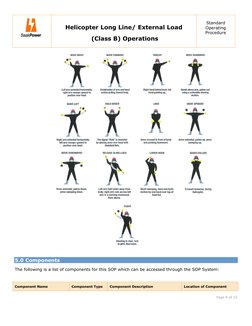
- 5.0 Components
- 6.0 Acronyms, Definitions and Symbols
- 7.0 Policies and Regulatory Requirements
- 8.0 References