Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A) Oral Language: Analyzed in 3-Angle Perspective by Linguistis
Uploaded by
Celeste NarvaezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A) Oral Language: Analyzed in 3-Angle Perspective by Linguistis
Uploaded by
Celeste NarvaezCopyright:
Available Formats
1st
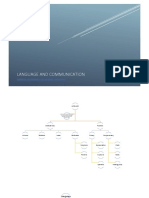
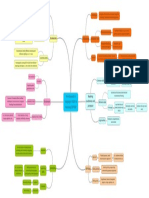
- LANGUAGE AS COMMUNICATION: ORAL AND WRITTEN LANGUAGE. FACTORS WHICH DEFINE A COMUNICATIVE SITUATION: SPEAKER, LISTENER, FUNCTIONALITY AND CONTEXT. 1st - LANGUAGE AS COMMUNICATION: ORAL AND WRITTEN LANGUAGE. FACTORS WHICH DEFINE A COMUNICATIVE SITUATION: SPEAKER, LISTENER, FUNCTIONALITY AND CONTEXT.
1. INTRODUCTION
Unnamed area
Unnamed area
3. FACTORS THAT DEFINE A COMMUNICATIVE SITUATION: SPEAKER, LISTENER, FUNCTIONALITY, AND CONTEXT.
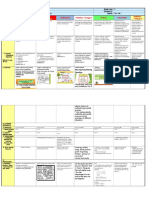
A) ORAL LANGUAGE
Doubtlessly , primary means of developed 30.000 - presented ALL human societies
naturally acquired - essential in family/social/working activities.
A dynamic inf. transformation interact constantly - roles often interchangeables
tone
Expressive posibilities due the inmmediacy can
accent vary to emphasize words or attitude.
3.1. LANGUAGE AS COMMUNICATION.
speed
Use of gestures +body
analyzed in 3-angle perspective by linguistis.
constantly companion W , reinforcing
Unnamed area
Simple constructions : spontaneity and speed of // no time -as-product phonology, syntactic, morphlogical and semantic rules - analyzed This is a title...
= identifying parts of speech dialectical variation
2. LANGUAGE AS COMMUNICATION: ORAL AND WRITTEN LANGUAGE. Pause, repetition and rephrasing: expected - depending speaker´s understanding This is a title...
Erors: frequently - uttering word, hesitating / incompleted sentences -as- Emphasized how A can be used - to operate upon environment.
feelings learning a imples internalizing potentialities as an instrument.
signs Dialectal and regional varieties shown in
distinctly human - aids in trasmiting Through arbitrary words convey
postures a specific meaning.
thoughts -as-activity-language-as-process into pragmatics +social pyschology how
gestures
THE ORAL LANGUAGE IN PE initiate conversations or formality used -different situa.
Most importan means of a to express complex + abstract
Communicative emphasizes + real-life situ.
is of transferring a us better understand different
goal their needs + / X worring pertfect grammar. A) COMPONENTS OF SPEECH ACTS C) PHASES
In all act- 4 clear defined phases:
talking less / listening more / Dell Hymes´s speaking model most well-known of speech act components within the field of pragmatics.
Whereas active facilitators of students´learning (Larsen -Freeman, 1986)
Hymes simultaneous interaction setting forces + continuous decisions
Codification Carried out - addresser - turns idea/message into a gropu of linguistic signs-
according code share with addressee
scene This is a title...
participants lexis Emission transmitted through channel. use speech organs message / muscles - allow us to write. This is a title...
This is a title...
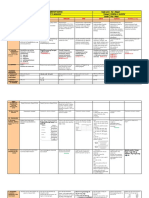
B) WRITTEN LANGUAGE ends selecting grammar
phonological features Reception received in this phases through the auditory organs+ eyes.
act sequence,
appeared in 3,500 BC. Each own features + rules - has to be taught
C essencial intrumentalities Decoding consists of interpretation by decoding.
norms
interpreted
complex task - entails new signs - form words- must be to genre inverted for the addresser + addressee
connected
Canale is and negotiation of inf. + o/w modes + and processes
Precise: permanent/ + for its preparation / promoting neat+careful organi. +complex expre.
words correctly , sentences internal cohesión + well finished. simple
Personality psychology However, model components of speech art completed
implies will to + inf. gap = negotiation meaning is mandatory. come into play
Socio-cultural sociology generally accepted
from semiotic
Clarity : are not usually present; ambiguities must be avoided.
3.2. LANGUAGE AS COMMUNICATION.
The use of implies knowledge of reality + to represent it. Formed by
to linguistic. Unique graphics features - exclusively used in . puntuation, spelling, capitalization, space organization or calligraphy. Swedish lingustic Roman Jacobson proposed comprehensive theory of involve describing and functions
This is a title...
Porpose intention / interacts other elements /influences language form choices How takes place in the can be explained following way: This is a title...
mainly by cognitive psychology This is a title...
codify
The existence of required complex cognitive skill to simultaneously This is a title...
decode to a lesser exten pedagogy + applied linguistic.- Formality than spoken / provides standard valued by society. Addresser person orignates
Audience person (s) to whom sent
Addressee person to whom addressed
Voice mainly refers varieties +styles / level formality used according other components of act.
Perception: pay sounds + graphemes to extract meaning
THE WRITTEN LANGUAGE IN PE Channel medium through travels
Analysis: reconstructing of previous schemas. Genre kind of speech act / whether leter/ conversation/ narative/ poem
Message content + particular ggrammatical + lexical choices of
Utilization: Elaborating inf. + creating new schemas. purpose of is often lacking in the English classroom.
Medium channel through transmitted
Code language or dialect
create engaging context . addressed to a person/reason + expected response = + Context Most relevant = determines + of the rest. time + space act + socual/cultural conventons Context social + pysical circumstances of
Construction: intention from which can be deduced. alongside knowledge
Transformation: applying gramm. rules to formulate
Execution: expressing physically. relevant + realistic encourage to publish in blogs or writing notes, recipes / e-mails / pen friend
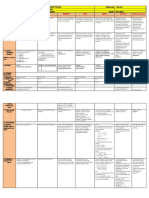
3.3. FUNCTIONALITY
B) MODELS
This is a title...
Jakobson´s description process allowed to define functions .
2.2. ORAL AND WRITTEN LANGUAGE 2.3. ORAL LANGUAGE VS WRITTEN LANGUAGE
literature In any situa. serie elements make possible.
spontaneous
Supremacy of over remained 19th - due to medium standard of linguistic excellence. Paying to spontaneity criterion planned
all ellements necessary for inf. to take place
20th new aprroach - more imp.
ancient - developed naturally
spontaneous planned (henceforth PL) many modesl of hum have been proposed over centuries.
artificially taugh - trasncription of sound / speech
simple/ coordinated complex subordinated
juxtaposed Analysts classify as:
purpose
Whenever we to attend same factors ( ) audience medium chosen to inf. connectors/ introductory structures
voice/style chosen carefully + elaborated Linear models : cronologically speaking the oldest.
+accesible/repeated
genre not consider presence of feedback
context repetition avoided present it as ocurring in 1 direc.
repetitions + parallelism = cohesion
However, differences between - charactersitics + elaborated parallelism
Interactional models: inclu. cosideration of
self-corrections/ repairs/ plenty of time to avoid them
doubt markers Transacional models : admit any process can be either a sender / a receiver
- changing roles during process
You might also like
- Relations Among Subglottal Resonances VoDocument1 pageRelations Among Subglottal Resonances VoAbderrahmaneAbdouNo ratings yet
- Week 1111Document25 pagesWeek 1111Bing GemenaNo ratings yet
- Language and DialectDocument1 pageLanguage and DialectSantiago MoralesNo ratings yet
- Language and Communication: Daniela Alejandra Villalobos GuarachiDocument4 pagesLanguage and Communication: Daniela Alejandra Villalobos GuarachiDaniela VillalobosNo ratings yet
- DLL wk7Document31 pagesDLL wk7Marie Ann Añonuevo100% (1)
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W9 - D1Document8 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W9 - D1Rezeile LazarusNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter: - News Reports - Speeches - Informative Talks - Panel DiscussionsDocument2 pages1 Quarter: - News Reports - Speeches - Informative Talks - Panel DiscussionsCarrie Alyss P Eder-Ibacarra100% (2)
- Estructura Estandar AIPM Professional Competency Standards For Project Management, Australian Instit...Document1 pageEstructura Estandar AIPM Professional Competency Standards For Project Management, Australian Instit...Maleja SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Lenguaje y Comunicación: Guía Cursos AnualesDocument16 pagesLenguaje y Comunicación: Guía Cursos AnualesHernàn Gonzàlez ParraNo ratings yet
- Intro To Study On Language 1002Document7 pagesIntro To Study On Language 1002sammietungNo ratings yet
- Instrument For Diagnostic For Academic & Bilingual High Schools V.F 16-2-22Document81 pagesInstrument For Diagnostic For Academic & Bilingual High Schools V.F 16-2-22Michael FaerronNo ratings yet
- WEEK1 June - 4 8 - 2018 DLL - BenjDocument37 pagesWEEK1 June - 4 8 - 2018 DLL - BenjHarlyn GayomaNo ratings yet
- EDST2100 Notes 2Document4 pagesEDST2100 Notes 2Steph DowneyNo ratings yet
- Settings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormDocument3 pagesSettings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormJhessa May CanuelNo ratings yet
- 30 Minute Activity 43Document1 page30 Minute Activity 43MustaqueNo ratings yet
- Residencia Inferior 9Th Ward - Elemental: El DiseñoDocument1 pageResidencia Inferior 9Th Ward - Elemental: El DiseñoMaria Natalia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- WEEK1 June 5-9-2017 DLL - BenjDocument35 pagesWEEK1 June 5-9-2017 DLL - BenjLaarni Kiamco Ortiz EpanNo ratings yet
- Updated - WEEK 3Document40 pagesUpdated - WEEK 3Nguyễn Đan NhiNo ratings yet
- Lingüística Aplicada - ApuntesDocument30 pagesLingüística Aplicada - ApuntesJose ALCONCHEL IRANZONo ratings yet
- ArwoodEllynLuca 2010 Chapter3TheStudyOfLan LanguageFunctionAnIntDocument13 pagesArwoodEllynLuca 2010 Chapter3TheStudyOfLan LanguageFunctionAnIntCorreo imprimirNo ratings yet
- Disco AnalsisDocument28 pagesDisco AnalsisAjiNo ratings yet
- Rekod Semakan Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah: Listening and Speaking SkillsDocument7 pagesRekod Semakan Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah: Listening and Speaking Skillsnasrie_kelateNo ratings yet
- Đề Chính Thức TS 10.2023-2024Document2 pagesĐề Chính Thức TS 10.2023-2024Phạm NguyênNo ratings yet
- SPEEEEEECHDocument4 pagesSPEEEEEECHRemedios BianesNo ratings yet
- Eccd / Kindergarten Education Record SY - : Fruits of Faith School IncDocument1 pageEccd / Kindergarten Education Record SY - : Fruits of Faith School IncLiezl ValtiendazNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log ESP A.P English MTB Math Filipino MapehDocument8 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log ESP A.P English MTB Math Filipino MapehAnonymous bCxoR3jqEfNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies:: . Basic Competencies Indicators Aspects/DomainsDocument7 pagesCore Competencies:: . Basic Competencies Indicators Aspects/DomainsJonni Hendika HarianjaNo ratings yet
- Communicative Competence: Noam ChomskyDocument2 pagesCommunicative Competence: Noam ChomskyKiara Denise SuarezNo ratings yet
- CMPT 413/713: Natural Language Processing: Nat LanglabDocument43 pagesCMPT 413/713: Natural Language Processing: Nat LanglabWenpei LiNo ratings yet
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W9 - D1Document1 pageDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W9 - D1Jela Marie CandaNo ratings yet
- DLL Q1 Week1 Day3Document6 pagesDLL Q1 Week1 Day3Manila Hankuk AcademyNo ratings yet
- DLL English Grade1 Quarter3 Week1Document4 pagesDLL English Grade1 Quarter3 Week1Stephanie AbutatilNo ratings yet
- Teaching Language in Context. Chapter 1 SummaryDocument6 pagesTeaching Language in Context. Chapter 1 SummarySC Zoe100% (6)
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W1 - Feb 13-17Document45 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q3 - W1 - Feb 13-17helen caseriaNo ratings yet
- Bladder AnatomuDocument1 pageBladder AnatomuCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- Rekod Semakan Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah: Listening and Speaking SkillsDocument8 pagesRekod Semakan Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah: Listening and Speaking Skillsnasrie_kelateNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 1Document26 pagesDLL Week 1EdilyndeGuzmanNo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Grammar and Text AnalysisDocument23 pagesSystemic Functional Grammar and Text AnalysisBobak Mohi33% (3)
- PPD Meradong Progressive Test (Responses) PDFDocument2 pagesPPD Meradong Progressive Test (Responses) PDFIbuHafiziqalisya ZulfizalNo ratings yet
- Programa Nacional de Inglés en Educación BásicaDocument2 pagesPrograma Nacional de Inglés en Educación BásicadavidNo ratings yet
- Annual Teaching Plan 4o P ImprimirDocument6 pagesAnnual Teaching Plan 4o P ImprimirmaggielisabNo ratings yet
- Annual Planning A1 - 1 PDFDocument10 pagesAnnual Planning A1 - 1 PDFAnonymous ibSRqUNo ratings yet
- Para Saxo BaritonoDocument5 pagesPara Saxo BaritonoJuan Manuel Jaramillo LlerasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 y 19 by RoachDocument1 pageChapter 18 y 19 by RoachPizza te amoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Week 1 Day 2 2019Document11 pages1ST Quarter Week 1 Day 2 2019FiLresh OcLarit - LlorenNo ratings yet
- Development of Language Skills in Teaching ESPDocument1 pageDevelopment of Language Skills in Teaching ESPLUIS IVAN LLUMIQUINGA GUAMANNo ratings yet
- File4aroundtheworld 3amlevel Accordingtotheatfaefcompet 150502161711 Conversion Gate02Document18 pagesFile4aroundtheworld 3amlevel Accordingtotheatfaefcompet 150502161711 Conversion Gate02Rida NaniNo ratings yet
- Language in Communication: What Is World Englishes (WE)Document3 pagesLanguage in Communication: What Is World Englishes (WE)Jennifer DimaporoNo ratings yet
- BiographyBookReportRubric 1Document6 pagesBiographyBookReportRubric 1Latifah SaadNo ratings yet
- DLL June Week 1Document28 pagesDLL June Week 1Fcgs Francis FrancesNo ratings yet
- Annual TrimestralDocument28 pagesAnnual TrimestralHeydi SaucedoNo ratings yet
- 3° y 4° - Texto Del EstudianteDocument156 pages3° y 4° - Texto Del EstudiantePablo TorresNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics Mid-Term ExamDocument2 pagesEnglish Phonetics Mid-Term Examnohemy20No ratings yet
- Primero U 1Document2 pagesPrimero U 1davidNo ratings yet
- NCCK Job Application FormDocument4 pagesNCCK Job Application Formsolocheruic100% (3)
- English Language Scheme of Work FORM 3 2018Document16 pagesEnglish Language Scheme of Work FORM 3 2018Ct Sabaya SaadNo ratings yet
- Hello, Everyone!Document28 pagesHello, Everyone!Dilshad ShahNo ratings yet
- Cold War Broadcasting: Impact on the Soviet Union and Eastern EuropeFrom EverandCold War Broadcasting: Impact on the Soviet Union and Eastern EuropeNo ratings yet
- Milliken's Complete Book of Instant Activities - Grade 4: Over 110 Reproducibles for Today's Differentiated ClassroomFrom EverandMilliken's Complete Book of Instant Activities - Grade 4: Over 110 Reproducibles for Today's Differentiated ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Reward CardsDocument6 pagesReward CardsCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Pink and Black Cute Playful School TimetableDocument1 pagePink and Black Cute Playful School TimetableCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Didactica Del InglesDocument30 pagesDidactica Del InglesCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Tema8 ICTDocument18 pagesTema8 ICTCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Tema4 ICTDocument21 pagesTema4 ICTCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Tema6 ICTDocument23 pagesTema6 ICTCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Preguntas Exámen English 2021 DidacticsDocument2 pagesPreguntas Exámen English 2021 DidacticsCeleste NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Deviation Control MethodsDocument4 pagesDeviation Control MethodsLazuardhy Vozicha FuturNo ratings yet
- Lattner HRT Power Plus Operations ManualDocument42 pagesLattner HRT Power Plus Operations Manualsabir_munnaNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. - CSE - R13-Syllabus JntuaDocument132 pagesB. Tech. - CSE - R13-Syllabus JntuaVasim AkramNo ratings yet
- SCI Annual Report 2017Document32 pagesSCI Annual Report 2017The Seamen's Church Institute100% (2)
- ITR-C (Instrument) 16cDocument1 pageITR-C (Instrument) 16cMomo ItachiNo ratings yet
- Clavija L5-30P Ref 2611Document3 pagesClavija L5-30P Ref 2611CristianDuarteSandovalNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein ExtractDocument1 pageFrankenstein ExtractAnneNo ratings yet
- The Art of Starting OverDocument2 pagesThe Art of Starting Overlarry brezoNo ratings yet
- PL SQL Exercise6Document2 pagesPL SQL Exercise6Nishant AndhaleNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare Ubd Unit PlanDocument16 pagesShakespeare Ubd Unit Planapi-239477809No ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering-Chapter 11Document3 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering-Chapter 11JurgenNo ratings yet
- Monster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionDocument9 pagesMonster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionMark JaffeNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainDocument49 pagesDNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainKhalid HussainNo ratings yet
- XIInfo Pract H Y 416Document4 pagesXIInfo Pract H Y 416Neelima VijayanNo ratings yet
- Hyperinflation of Zimbabwe and The Lesson For Zimbabwe: Foreign Trade University Faculty of Banking and FinanceDocument38 pagesHyperinflation of Zimbabwe and The Lesson For Zimbabwe: Foreign Trade University Faculty of Banking and FinancePham Việt AnhNo ratings yet
- Awareness On Stock MarketDocument11 pagesAwareness On Stock MarketBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Krunker SettingsDocument2 pagesKrunker SettingsArsyad DanishNo ratings yet
- The USP AdvantageDocument30 pagesThe USP AdvantageGabriel A. RamírezNo ratings yet
- Assembling Your Antenna SystemDocument27 pagesAssembling Your Antenna SystemKam MusNo ratings yet
- Basic Definition of Manufacturing SystemDocument18 pagesBasic Definition of Manufacturing SystemRavenjoy ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetDocument3 pagesEcological Pyramids Worksheetapi-26236818833% (3)
- Body Wash Base Guide Recipe PDFDocument2 pagesBody Wash Base Guide Recipe PDFTanmay PatelNo ratings yet
- TTD Accommodation ReceiptDocument2 pagesTTD Accommodation ReceiptDharani KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MethodologyDocument22 pagesChapter 3 MethodologySiva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Radiant Protection Force Pvt. LTD.,: Col David DevasahayamDocument13 pagesRadiant Protection Force Pvt. LTD.,: Col David Devasahayamabhilash0029No ratings yet
- JapanDocument15 pagesJapanceazar BugtongNo ratings yet
- Leading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesDocument3 pagesLeading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesAhmed AbboudNo ratings yet
- WestIntroToSSB PDFDocument100 pagesWestIntroToSSB PDFnaval_05No ratings yet
- Va797h 15 Q 0019 A00001003Document35 pagesVa797h 15 Q 0019 A00001003Hugo GranadosNo ratings yet
- Cell Signaling - The ComponentsDocument7 pagesCell Signaling - The Componentsk10 Lớp Dinh DưỡngNo ratings yet