Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Principals of Genetic Inheritance: Cells Tissues Organs Body
Uploaded by
Daniel Dowding0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Plant Genetics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThe Principals of Genetic Inheritance: Cells Tissues Organs Body
Uploaded by
Daniel DowdingCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Principals of Genetic Inheritance
The basic structure of all organisms is the cell. Some
CELLS
organisms, such as bacteria, are unicellular and
consist of only one cell. Most organisms are
TISSUES
multicellular and consist of large numbers of
different cells organized into tissues and organs.
ORGANS
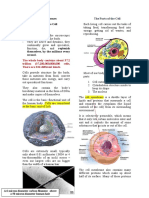
Cells
All cells have the following features: BODY
● A cell membrane surrounding the living material of the cell
● The cytoplasm: the living material of the cell
● A nucleus containing chromosomes
Plant cells
Plant cells differ from animal cells in that they have:
● A cellulose cell wall
● A vacuole (space surrounded by a membrane) containing cell sap
● Chloroplasts containing the green pigment chlorophyll
Questions:
● State the function of the labelled
parts from the
diagram
● Name parts that
are found in the plant cell but not
in the animal cell
Cell Division
New cells are formed by cell division, it is vital that genetic information in the
parent cell gets passed on to the new cells.
There are two types of nuclear division:
● Mitosis: in mitosis chromosomes in the nucleus of the parent cell are divided
into two equal sets so that the nucleus in each new cell has exactly the same
number of chromosomes as the parent cell; this type of division occurs when
new cells are produced throughout the life of an living organism.
● Meiosis: this involves the formation of gametes (sex cells) in the
reproductive organs; the nucleus of each gamete has half the number of
chromosomes as the parent cell; when fertilization occurs the zygote has
the correct number of chromosomes restored.
Questions
● How much chromosomes does a cell normally contain in
humans?
You might also like
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cells The Building Blocks (Part 1)Document11 pagesCells The Building Blocks (Part 1)Areeha KashafNo ratings yet
- GsciDocument9 pagesGscimahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Cell PortfolioDocument7 pagesCell PortfolioChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cell Class 9 Cbse Biology - CompleteDocument42 pagesCell Class 9 Cbse Biology - Completenayshajain63No ratings yet
- Inside CellsDocument31 pagesInside CellsWill GarciaNo ratings yet
- Life Chapter 3 From A Cell To An OrganismDocument39 pagesLife Chapter 3 From A Cell To An OrganismvaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 0 - The CellDocument5 pagesUnit 0 - The CellDavid ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Biology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Document14 pagesBiology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Jaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- CMB PPT 2 Borja JayvenDocument17 pagesCMB PPT 2 Borja JayvenJayven BorjaNo ratings yet
- PRPLLLDocument19 pagesPRPLLLPraveen KolaganiNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument5 pagesRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 The CellDocument75 pages1 The CelllorenzegeneblaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Number. 8 Notes ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Number. 8 Notes ScienceVinod PursaniNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Del Tema 5Document44 pagesEjercicios Del Tema 5Natalia Ricoy CallejaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Biology PDFDocument29 pages1 Cell Biology PDFRashad AlamNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4Document2 pagesBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- CO1Document42 pagesCO1KitNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Document27 pagesZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1Document27 pagesPlant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1Reinalyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Body Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesBody Cells and TissuesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument4 pagesThe CellsSlaheddineNo ratings yet
- S4en Biology Chapter 1Document59 pagesS4en Biology Chapter 1MeharNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure & Function 02 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023Document38 pagesCell - Structure & Function 02 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023wigiye6232No ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- Grade VIII-Biology - Lesson Notes & Thinksheet Solutions - Chapter-8 - CELLSDocument7 pagesGrade VIII-Biology - Lesson Notes & Thinksheet Solutions - Chapter-8 - CELLSkedar vatsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Cell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceDocument48 pagesCell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- 1 CellBiologyDocument37 pages1 CellBiologyBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BWDocument33 pagesChapter 2 BWmiek ThomasNo ratings yet
- Cells: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaDocument27 pagesCells: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaNafees Hasan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CELLS For Class8Document15 pagesCELLS For Class8cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument13 pagesLecture 1 - Cells - The Building Blocks of Lifekinza yasirNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNo ratings yet
- 1-The Eukaryotic CellDocument23 pages1-The Eukaryotic Cellmichaelkingtz01No ratings yet
- Topic1-Lesson 2-Cell Structue Part 1Document22 pagesTopic1-Lesson 2-Cell Structue Part 1Afreen ImranNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - OutputDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Function - OutputRaghav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- NCS211 CellsDocument4 pagesNCS211 CellsOrtiz, Jazmyn Q.No ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell and Its FunctionDocument24 pagesParts of The Cell and Its FunctionErnest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- CELLS BiologyDocument8 pagesCELLS BiologyKYLENE ABELLANANo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsDocument14 pagesLesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellcmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- "Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology IDocument23 pages"Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology ITeacher Ella MorillaNo ratings yet
- Cells, Viruses and BacteriaDocument39 pagesCells, Viruses and BacteriaAsawni McDowell100% (1)
- 025adeadc8376-Cell The Unit of LifeDocument44 pages025adeadc8376-Cell The Unit of Lifepallavivermabt21No ratings yet
- What Is CellDocument2 pagesWhat Is CellRose Marie ArendainNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesJairhiz AnnNo ratings yet
- All About Cells: Ms. Dzwil'S 8Th Grade Biology ClassDocument15 pagesAll About Cells: Ms. Dzwil'S 8Th Grade Biology Classapi-550034646No ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument51 pagesMicroorganismsAchira DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- From Cells To Organisms: Learning ObjectivesDocument39 pagesFrom Cells To Organisms: Learning ObjectivesJoanneNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1 Cells As Basic Unit of LifeDocument30 pagesModule 1 Unit 1 Cells As Basic Unit of LifeMonique scheepersNo ratings yet
- Cropping Systems: What Is A Cropping System?Document4 pagesCropping Systems: What Is A Cropping System?Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Machinery in Crop HusbandryDocument6 pagesMachinery in Crop HusbandryDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Pre Health Course ScoreDocument1 pagePre Health Course ScoreDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Selection in Plants: The Brassicas (Family Name) - A Wide Range of Vegetables Have BeenDocument4 pagesSelection in Plants: The Brassicas (Family Name) - A Wide Range of Vegetables Have BeenDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Land Preparation MethodsDocument2 pagesLand Preparation MethodsDaniel Dowding100% (2)
- Sowing Seeds and Seedling ProductionDocument2 pagesSowing Seeds and Seedling ProductionDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Weeds What Is A Weed?: Why Are Weeds So Successful?Document3 pagesWeeds What Is A Weed?: Why Are Weeds So Successful?Daniel Dowding100% (1)
- Plant Processes: 1. PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPlant Processes: 1. PhotosynthesisDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Section B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesSection B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Plant QuarantineDocument1 pageThe Importance of Plant QuarantineDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Roles and Careers in AgricultureDocument3 pagesRoles and Careers in AgricultureDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Classical Antiquity (In Which The Sport Was Largely Greco-Roman Influenced) New Track andDocument6 pagesClassical Antiquity (In Which The Sport Was Largely Greco-Roman Influenced) New Track andDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- (Kelly Sankar) Business PlanDocument17 pages(Kelly Sankar) Business PlanDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Non-Conventional Farming Cont'dDocument3 pagesNon-Conventional Farming Cont'dDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- What Is Organic Farming?Document2 pagesWhat Is Organic Farming?Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Challenges Affecting Agriculture (Cont'd)Document2 pagesChallenges Affecting Agriculture (Cont'd)Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- What Is Asexual Reproduction?Document5 pagesWhat Is Asexual Reproduction?Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Challenges in AgricultureDocument5 pagesChallenges in AgricultureDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Vershanie Goberdhan SBA (CROP)Document39 pagesVershanie Goberdhan SBA (CROP)Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Fruit CropDocument8 pagesFruit CropDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Liturature ReviewDocument2 pagesLiturature ReviewDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Anna Regina Secondary School School Based Assessment (2020-2022) EnglishDocument17 pagesAnna Regina Secondary School School Based Assessment (2020-2022) EnglishDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Duncans Realty & Property Management Services Employee Time SheetDocument2 pagesDuncans Realty & Property Management Services Employee Time SheetDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- English A&B Sba Mark Scheme: Areas Marks Assigne D Marks CommentsDocument2 pagesEnglish A&B Sba Mark Scheme: Areas Marks Assigne D Marks CommentsDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Heat Treatment Processes Powerpoint PresentationDocument14 pagesHeat Treatment Processes Powerpoint PresentationDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Cyril Potter College of Education: EssayDocument4 pagesCyril Potter College of Education: EssayDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- E.D.P.M PracticeDocument3 pagesE.D.P.M PracticeDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Anna Regina Secondary School Lesson PlanDocument1 pageAnna Regina Secondary School Lesson PlanDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Cyril Potter College of Education: EssayDocument4 pagesCyril Potter College of Education: EssayDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet