Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Blood Disease:: Causes of Enlarged Spleen
Uploaded by
home0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesThe document discusses various causes of an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) including blood diseases, infections, tumors, tissue deposits, and circulatory or storage issues. It then focuses on bilharzial splenomegaly caused by schistosomiasis infection, describing the pathogenesis involving hyperplasia and venous congestion, pathological features of fibrosis, atrophy, and hemorrhage, and effects like compression and hypersplenism where the enlarged spleen destroys blood cells. Finally, it briefly discusses acute splenic swelling seen in sepsis.
Original Description:
Original Title
باثو ١
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various causes of an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) including blood diseases, infections, tumors, tissue deposits, and circulatory or storage issues. It then focuses on bilharzial splenomegaly caused by schistosomiasis infection, describing the pathogenesis involving hyperplasia and venous congestion, pathological features of fibrosis, atrophy, and hemorrhage, and effects like compression and hypersplenism where the enlarged spleen destroys blood cells. Finally, it briefly discusses acute splenic swelling seen in sepsis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pages1-Blood Disease:: Causes of Enlarged Spleen
Uploaded by
homeThe document discusses various causes of an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) including blood diseases, infections, tumors, tissue deposits, and circulatory or storage issues. It then focuses on bilharzial splenomegaly caused by schistosomiasis infection, describing the pathogenesis involving hyperplasia and venous congestion, pathological features of fibrosis, atrophy, and hemorrhage, and effects like compression and hypersplenism where the enlarged spleen destroys blood cells. Finally, it briefly discusses acute splenic swelling seen in sepsis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
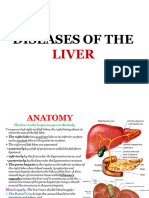
Spleen
Splenomegaly
Causes of enlarged spleen:
1- Blood disease:
a) Hemolytic anemia
b) Leukemia
c) Polycythemia
2- Infectious:
- Septicemia (acute splenic swelling)
- Typhoid fever
- Subacute bacterial endocarditis
- Granulomas: TB, syphilis, sarcoidosis
- Parasitic: bilharziasis, malaria, leishmaniasis
3- Neoplasia: malignant lymphoma, secondaries
4- Tissue deposits: amyloidosis
5- Circulatory disturbance:
a) CHF
b) Portal hypertension
6- Storage diseases: lipid storage, glycogen storage diseases
IBL Pioneer in pathology
Spleen
Bilharzial splenomegaly:
Definition:
Enlarged spleen associated with advanced bilharzial hepatic
fibrosis
Pathogenesis:
1- Early:
Hyperplasia of the splenic reticuloendothelial cells (littoral cells)
in response to bilharzial antigens
2- Chronic venous congestion of the spleen:
Due to portal hypertension resulting in progressive
enlargement of the spleen
Pathological features:
Grossly:
- Size : markedly enlarged
- Consistency: firm
- The capsule: is thick and greyish white due to fibrosis
- Subcapsular hemorrhage and accentuated splenic notch are
found
- The cut surface shows dark brown color and pinpoint white
spots of Atrophic lymphoid follicles
IBL Pioneer in pathology
Spleen
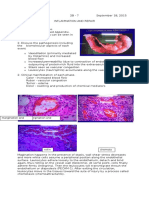
Microscopic picture:
- The capsule and trabeculae are thickened due to fibrosis
- Dilated sinusoids with interstitial hemorrhage (hemosiderin)
- Pressure atrophy of lymphoid follicles and hyalinosis of center
arterioles
- Fibroblastic proliferation forming fibro-siderotic modules
(Gandy-Gumna modules)
Effects of bilharzial splenomegaly:
1- Pressure effect: compression of surrounding organs
2- Hypersplenism (wild spleen): destruction of all blood
elements (pancytopenia)
Hypersplenism:
- Enlargement of spleen→ sequestration of large number of
RBCs → anemia
platelets→ thrombocytopenia
leukocytes →leucopenia
- Activation of macrophages→ fibrosis
- Splenectomy results in a marked improvement
IBL Pioneer in pathology
Spleen
Acute splenic swelling:
Splenic enlargement in case of septicemia
Pathological features:
- Spleen ➔ moderately enlarged and soft in consistency
- Red pulps ➔ soft and congested
- White pulps ➔ necrotic
- The splenic tissue are infiltrated by neutrophils
IBL Pioneer in pathology
You might also like
- Hemodynamic DisordersDocument34 pagesHemodynamic DisordersLiesel Illyry100% (1)
- Lecture 7 (Diseases of Urinary System)Document26 pagesLecture 7 (Diseases of Urinary System)Logyn SamNo ratings yet
- Pathology Slides by Organ 2Document25 pagesPathology Slides by Organ 2Lin AdutNo ratings yet
- Klinik ÖzetDocument10 pagesKlinik ÖzetEllaNo ratings yet
- 7.hematology SummaryDocument91 pages7.hematology SummaryPeter Shirima100% (1)
- Diseases of The Kidney-ClassificationDocument21 pagesDiseases of The Kidney-ClassificationAsha dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Sindroame MieloproliferativeDocument7 pagesSindroame MieloproliferativeBogdan Marian SorohanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Slides by Organ 1-1Document36 pagesPathology Slides by Organ 1-1Lin AdutNo ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument83 pagesAnaemiaMohammad_Islam87100% (2)
- ST 09 Selected Slides HaematopathologyDocument43 pagesST 09 Selected Slides HaematopathologyMuhammad Harmen Reza SiregarNo ratings yet
- 15 LivernDocument45 pages15 LivernDrAbdullrabAlmarwanyaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Internship: Hematology: WBC AnomaliesDocument8 pagesClinical Internship: Hematology: WBC AnomaliesNaomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersDocument25 pagesHemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersKlein’s Gaming ChannelNo ratings yet
- Diseases Involving Blood Vessels of The KidneysDocument34 pagesDiseases Involving Blood Vessels of The KidneysAma SatharasingheNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloproliferative DisorderDocument25 pagesChronic Myeloproliferative DisorderJilycamae COSMODNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DiseasesDocument2 pagesHematologic Diseasessun shineNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders AnemiaDocument6 pagesBlood Disorders AnemiaFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument27 pagesAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisAlokh Saha RajNo ratings yet
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483No ratings yet
- BloodDocument27 pagesBloodbody fayezNo ratings yet
- Kidney - 1Document4 pagesKidney - 1eutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan UKDI CLINIC 3 Batch Mei 2016Document662 pagesPembahasan UKDI CLINIC 3 Batch Mei 2016widi kusumaNo ratings yet
- Hematologic SystemDocument39 pagesHematologic SystemESPINOSA JHANNANo ratings yet
- The Liver and The Biliary TractDocument109 pagesThe Liver and The Biliary TractKw ChanNo ratings yet
- Triệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3Document58 pagesTriệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3trungNo ratings yet
- Margination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionDocument3 pagesMargination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionKat JolejoleNo ratings yet
- Hepatosplenomegaly: - Question: - AnswerDocument7 pagesHepatosplenomegaly: - Question: - AnswerSyximsh FPNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Heart Failure and CardiomyopathiesDocument33 pagesPathology of Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathiesciyace7849No ratings yet
- GNM 1st Year Trhering Topic Handout 2020Document13 pagesGNM 1st Year Trhering Topic Handout 2020shapan biswaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Disease and Their Oral ManifestationsDocument80 pagesSystemic Disease and Their Oral ManifestationsRakshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera ReportDocument31 pagesPolycythemia Vera ReportAdrianNo ratings yet
- Histology & Cell BiologyDocument33 pagesHistology & Cell BiologyMohSen100% (1)
- A. Inflammation and Repair: I. Disease Process (6 Questions)Document17 pagesA. Inflammation and Repair: I. Disease Process (6 Questions)Anonymous Sw4Pk9fNo ratings yet
- Curs 12 Semiologie MedicalaDocument54 pagesCurs 12 Semiologie MedicalaLia PopaNo ratings yet
- 5.nephritic SyndromeDocument64 pages5.nephritic Syndromeyeni100% (1)
- WBC BasicsDocument70 pagesWBC BasicsZoe ZillaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Prof - Univ.Dr. Zorilă CorinaDocument60 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Prof - Univ.Dr. Zorilă CorinaCasiana GuiNo ratings yet
- Cns PathologyDocument18 pagesCns Pathologysunnyorange8No ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument33 pagesJaundiceRahulNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 1Document14 pagesOxygenation 1Riño Roland RexNo ratings yet
- 3 Liver Biliary TractDocument141 pages3 Liver Biliary Tractandreea0deyNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document27 pagesLec 7helenyakhyNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument29 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemHassan.shehri100% (9)
- Chronic Liver DiseasesDocument43 pagesChronic Liver DiseasesDickson Luvi100% (1)
- Manifestarile Hematologice in Cursul Bolilor SistemiceDocument7 pagesManifestarile Hematologice in Cursul Bolilor SistemiceLaurențiu AcostioaeiNo ratings yet
- Lecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceDocument36 pagesLecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceEl Farouk100% (1)
- WSU Renal ReviewDocument100 pagesWSU Renal ReviewLeticia BornsteinNo ratings yet
- GLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Document8 pagesGLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Anjitha K. JNo ratings yet
- Tubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaDocument48 pagesTubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaThomas McconnellNo ratings yet
- 2020 Lecture Liver Pathology AnglDocument89 pages2020 Lecture Liver Pathology AnglRinkiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Blood VesselsDocument12 pagesLec 2 - Blood VesselsJeffrey LübbertNo ratings yet
- View A Negative Experience in Your Life Like You'd Look at A Photo Negative. A Single Negative Can Create An Unlimited Number of Positive Prints.Document90 pagesView A Negative Experience in Your Life Like You'd Look at A Photo Negative. A Single Negative Can Create An Unlimited Number of Positive Prints.madhuNo ratings yet
- Pathology Revision Practicals: Presented by Roll No. 061-090Document60 pagesPathology Revision Practicals: Presented by Roll No. 061-090PeaceNo ratings yet
- Dr. Fairuz Quzwain, Sppa, M.Kes: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Universitas JambiDocument119 pagesDr. Fairuz Quzwain, Sppa, M.Kes: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Universitas JambiAlfian DaudNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Extra NotesDocument5 pagesMyeloproliferative Extra NotesRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Renal PathologyDocument108 pagesRenal PathologyKedir jemalNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument23 pagesHemolytic AnemiaRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Reversible Intra - and Extracellular Lesions (Accumulations) - Seminar.Document24 pagesReversible Intra - and Extracellular Lesions (Accumulations) - Seminar.ТатьянаБабийNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Glomerulopathies and Nephrotic SyndromeDocument35 pagesLecture-Glomerulopathies and Nephrotic SyndromeJames StiltonNo ratings yet
- CDHO Factsheet LupusDocument3 pagesCDHO Factsheet LupusWayan Sutresna YasaNo ratings yet
- Ais Student Medical and Health Declaration Form 2023-24Document7 pagesAis Student Medical and Health Declaration Form 2023-24hafizvy6No ratings yet
- April 2021 Monthly Accomplishment ReportDocument36 pagesApril 2021 Monthly Accomplishment ReportReinald Raven GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis Nejm 2022 ReviewDocument13 pagesMyocarditis Nejm 2022 ReviewNox ÁtroposNo ratings yet
- Persons Living With Hiv AidsDocument19 pagesPersons Living With Hiv AidsAllona Zyra Cambronero0% (1)
- Blood Grouping 1690574753Document30 pagesBlood Grouping 1690574753willowmaecayabyabNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: PresentationDocument17 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: PresentationBonface NdunguNo ratings yet
- German Gov't Bombshell - Alarming Number of Vaccinated Are Developing AIDS' - News PunchDocument8 pagesGerman Gov't Bombshell - Alarming Number of Vaccinated Are Developing AIDS' - News PunchKarla VegaNo ratings yet
- MutrakrikshDocument5 pagesMutrakrikshPriya singhNo ratings yet
- Immunology Study Sheet For The Final ExamDocument3 pagesImmunology Study Sheet For The Final ExamDenizDerenNo ratings yet
- Symposiumbooklet CareerDocument36 pagesSymposiumbooklet Careerroh009No ratings yet
- Ma120 SpecDocument28 pagesMa120 SpecSkylake CoffeelakeNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus EpidermidisDocument12 pagesStaphylococcus EpidermidisSim M ChangNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument25 pagesHepatitis BJevon AndraNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument55 pagesVirologySelvenThirumalai100% (4)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument70 pagesLymphatic SystemMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- 2009 Article 9164Document170 pages2009 Article 9164Amir Surya HidayahNo ratings yet
- 13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsDocument14 pages13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsWillSmathNo ratings yet
- 8A Nosocomial InfectionDocument15 pages8A Nosocomial InfectionSuminaShrestha100% (1)
- Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and InflammationDocument15 pagesNociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and InflammationRogerio MachadoNo ratings yet
- C OP Y: Office of The SecretaryDocument5 pagesC OP Y: Office of The SecretaryJonathan LegionNo ratings yet
- DysenteryDocument7 pagesDysenterymukulpjrNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument14 pagesMonoclonal AntibodiesGAJENDRA RATHORNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sumait Hospital: Final Investigation ReportDocument10 pagesDr. Sumait Hospital: Final Investigation ReportShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Immnunology Notebook Chapter One: Innate ImmunityDocument45 pagesImmnunology Notebook Chapter One: Innate ImmunityJavier Alejandro Daza GalvánNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Blood Groups, Transfusion, RH Incompatibility by Dr. RoomiDocument41 pagesLecture On Blood Groups, Transfusion, RH Incompatibility by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Plasmapheresis For AutoimmunityDocument14 pagesPlasmapheresis For AutoimmunityEliDavidNo ratings yet
- JSW MA1 TetanusDocument2 pagesJSW MA1 TetanusTâlHa SafDârNo ratings yet
- Im Case Presentation: PGI Avery Carol BartolomeDocument61 pagesIm Case Presentation: PGI Avery Carol BartolomeAvery CarolNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Aps OrangDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka Aps OrangAlexander DickyNo ratings yet