Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overcoming barriers to intercultural communication
Uploaded by
Nadir Khattak Jr.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesOriginal Title
ELE 206 CH.1 -41-50
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesOvercoming barriers to intercultural communication
Uploaded by
Nadir Khattak Jr.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Barriers to Intercultural Communication
Four barriers to effectiveness in
intercultural communication:
1. Walking on eggs
Certain topics create tension for ethnic minorities
2. Hot buttons
words that invoke an emotional response in other
person.
3. Container myth
Is assumption that words mean the same thing across all
cultures
4. Language, vernacular ( (عاميهand
accent bias
Tools of diversity:
Overcome personal Biases
• Racism, stereotypes and discrimination negatively impact our
communication with others.
• These are the source of hurt feelings and result in
miscommunication, damaged relationships and loss in
productivity.
• Not only be sensitive to your own racisms but also develop
strategies to resist the racism that may occur in your
workspace.
Forms of racism:
• Overt racism ( (علني: such as “all… are lazy” or “they should go back
where they came from”.
• Symbolic racism: is attacking some symbol of importance to a particular
group of people.
• Arms – length racism: is suggesting that you don’t mind to work or know
minority people, but you oppose any closer relationship.
• Tokenism: believing that knowing one person from (different race….) is
enough to prove that he is not racist.
• Institutional Racism: Ideologies and structures that are used to
systematically legitimize unequal division of power and resources
between groups on the basis of race.
Some Important Definitions
Stereotype: negative beliefs about a particular group, it does not
consider people as individuals, it categorizes them as
members of a group who all think and behave in the same
way. We may pick up these stereotypes from what other
people say, from T.V or from what we read.
Prejudice: a set of rigid and unfavorable attitudes toward a
particular group. An unsupported judgment usually
accompanied by disapproval.
• Discrimination: the differential treatment based on unfair
categorization. It involves keeping people out of activities or
places because of the group to which they belong.
• Racism: the belief that one race is superior to another.
Scapegoating: The policy of blaming an individual or group when
the fault actually lies elsewhere. Those who we scapegoat
become objects of our aggression
Competence: Is an ability to accomplish goals while also
reducing misunderstanding and building strong interpersonal
relationships, these competencies will enhance your overall
quality of your life.
Effective Listening
Listening is important
Interesting facts and statistics that describe the importance of
listening in our lives:
• 85% of what we know we have learned by listening.
• We remember only 20% of what we hear
• Less than 2% of us have had any formal educational
experience with listening
• Being listened to spells the difference between feeling
accepted and feeling isolated
• People are fired, customer are lost and working relationship
are strained , friendship suffer, marriage and families fail
because of ineffective listening.
• Shared understanding, is the goal of effective communication.
Hearing VS. Listening
Hearing is sensory process Listening is a mental process
that includes: that includes:
•Conversion of acoustical •Choosing to attend
(mentally & physically)
energy
•Understanding thoughts and
•Sound reception
feelings
•Auditory sensation
•Confirming meaning
•Transfer to the brain
•Responding appropriately
Technicians of all kinds use Hearing skills to
Attending to the speaker (mentally and
monitor procedures, Judge the smoothness of
physically).Assigning meaning of both the
operations or locate problems.
verbal and non- verbal messages. Evaluating
the importance of message.
Why Bad Listening Occurs?
• Because we are poorly trained to listen:
• Through our formal
education, we rarely offered
listening.
• Mistaken belief that because
we are bombarded with a high
number of messages daily.
We somehow learn to
listen automatically.
• Because we disagree with speaker.
When we doubt what the speaker is saying, when we
begin to formulate a response before the speaker has
concluded, or when we are preoccupied with our own
personal problems.
• Because we overreact to emotional words (we can
not listen if we are angry, happy)
Our listening effectiveness drops as our emotional
responses increases.
• Because of falling to use the thought- speed
advantage (i.e. we think faster than any one can
talk).
You might also like
- Listening Skills Guide - Improve Comprehension & CommunicationDocument14 pagesListening Skills Guide - Improve Comprehension & CommunicationvivekNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument17 pagesListeningROHIT GARHWALNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Week-1 Lecture-1 Powr FleDocument53 pagesCommunication Skills Week-1 Lecture-1 Powr FleMusab AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Seven Magic Words For Better CommunicationDocument91 pagesSeven Magic Words For Better CommunicationKamran KhanNo ratings yet
- Active Listening 2Document30 pagesActive Listening 2Bhandari NivaNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: BY: Keerthana S MenonDocument26 pagesBusiness Communication: BY: Keerthana S Menonkeerthana menonNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: BY: Keerthana S MenonDocument26 pagesBusiness Communication: BY: Keerthana S Menonkeerthana menonNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: BY: Keerthana S MenonDocument26 pagesBusiness Communication: BY: Keerthana S Menonkeerthana menonNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: BY: Keerthana S MenonDocument26 pagesBusiness Communication: BY: Keerthana S Menonkeerthana menonNo ratings yet
- Business Communication SkillsDocument26 pagesBusiness Communication Skillskeerthana menonNo ratings yet
- International and Cross-Cultural NegotiationDocument39 pagesInternational and Cross-Cultural Negotiationdebjyoti77No ratings yet
- Direct File Topic DownloadDocument27 pagesDirect File Topic DownloadJass SidhuNo ratings yet
- ELE205 Communication Skills Chapter Three Effective ListeningDocument55 pagesELE205 Communication Skills Chapter Three Effective ListeningMohammed Abu TamamNo ratings yet
- 18.listening SkillsDocument29 pages18.listening SkillsMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- BCS 4.2 Final Active ListeningDocument31 pagesBCS 4.2 Final Active ListeningSaratha ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Final Active ListeningDocument31 pagesFinal Active Listeningjaiswalswatin87No ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument41 pagesCommunication BarriersMayankNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Listening: By-Tushar GuptaDocument12 pagesPresentation On Listening: By-Tushar GuptaRitika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills (RIU) Week-1 2-1Document49 pagesCommunication Skills (RIU) Week-1 2-1Muhammad TahirNo ratings yet
- Barriers TO Effective CommunicationDocument34 pagesBarriers TO Effective CommunicationSubratKumarNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal CommunicationDocument22 pagesInterpersonal CommunicationShazzy ShazzNo ratings yet
- Barriers to Effective CommunicationDocument35 pagesBarriers to Effective CommunicationShivu Yati100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Creation of Healthy and Caring Relationships: A Scientific Approach To Health AEC 26Document23 pagesUnit 3 - Creation of Healthy and Caring Relationships: A Scientific Approach To Health AEC 26akash DongeNo ratings yet
- Improve Listening Skills ModuleDocument32 pagesImprove Listening Skills ModuleRinki RolaNo ratings yet
- Role of Perception in Effective CommunicationDocument16 pagesRole of Perception in Effective CommunicationMecha0250% (2)
- Effective CommunicationDocument42 pagesEffective Communicationcandidagil2005No ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument22 pagesCommunicationG1 Bautista, Trishya Fatima I.No ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence ModuleDocument27 pagesEmotional Intelligence Modulediya.dsouza06No ratings yet
- Communication Skills AmityDocument69 pagesCommunication Skills Amityparmeet singhNo ratings yet
- NVC Compassionate Communication NonviolentDocument29 pagesNVC Compassionate Communication NonviolentSaadhvi NirmalNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument24 pagesCommunication Skillsamant100% (1)
- Effective Communication TechniquesDocument23 pagesEffective Communication TechniquesMihaelaSiVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Master Effective Communication with Powerful Listening Skills (40Document78 pagesMaster Effective Communication with Powerful Listening Skills (40Amit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument74 pagesBarriers To Effective CommunicationShiarica Mae NeriNo ratings yet
- Perspective Building On Life Skills DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPerspective Building On Life Skills DevelopmentRoopa Kothur100% (1)
- Behavioural CommunicationDocument13 pagesBehavioural Communicationk_09100% (2)
- Chap 4 HTF669Document38 pagesChap 4 HTF669Zzati Fida'iyNo ratings yet
- Listening Skill NewDocument26 pagesListening Skill NewshwtybeNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal and Conflict Management SkillsDocument34 pagesInterpersonal and Conflict Management SkillsrslapenaNo ratings yet
- Hearing vs Listening - Importance of Active Listening SkillsDocument19 pagesHearing vs Listening - Importance of Active Listening SkillsCandido MarjolienNo ratings yet
- Listening 2Document19 pagesListening 2Armando Shehi SayhellotogoodbyeNo ratings yet
- Barriers to Effective Communication and Their ManagementDocument36 pagesBarriers to Effective Communication and Their ManagementRuchika Duggal100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Self AwarenessDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Self AwarenessNAASC Co.No ratings yet
- NVC (Part 2)Document39 pagesNVC (Part 2)sanyam nayakNo ratings yet
- GROUP 11 Lesson 5 6Document37 pagesGROUP 11 Lesson 5 6riselle alfilerNo ratings yet
- Barriers of Communication FinalDocument22 pagesBarriers of Communication FinalHunain NadeemNo ratings yet
- Listening LctureDocument58 pagesListening LctureRashedul AlamNo ratings yet
- 2nd day Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument27 pages2nd day Non-Verbal Communicationhimanshu.koley4897No ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument13 pagesCommunication BarriersallanbuncadNo ratings yet
- Creating Effective OrganizatioDocument26 pagesCreating Effective OrganizatiomhsharieffNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document33 pagesUnit 5Aarav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Theory of Communication: Group 5Document44 pagesSubject: Theory of Communication: Group 5mawurldNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence TrainingDocument11 pagesEmotional Intelligence TrainingPan-African Shield College AfricaNo ratings yet
- Lesson III - ListeningDocument35 pagesLesson III - ListeningRomarc Bermudez CoronelNo ratings yet
- MoralDocument31 pagesMoralKharl Ashley PastorNo ratings yet
- Lva1 App6891Document23 pagesLva1 App6891saidikNo ratings yet
- Art of ListeningDocument14 pagesArt of Listeningmandanna11No ratings yet
- Types and Barriers of Listening ExplainedDocument27 pagesTypes and Barriers of Listening ExplainedArthy VenkatachalapathyNo ratings yet
- Ms Box 75x75x3mmDocument4 pagesMs Box 75x75x3mmNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
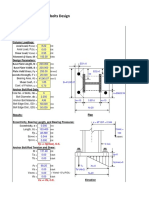
- Anchor Bolt DesignDocument8 pagesAnchor Bolt DesignNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- FLOOR PLAN-ModelDocument1 pageFLOOR PLAN-ModelNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Floor PlanDocument1 pageFloor PlanNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 100x50x5mm Channel SectionDocument4 pages100x50x5mm Channel SectionNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- MS Box.... 50x50x2mmDocument4 pagesMS Box.... 50x50x2mmNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 125x125x82mm Chequered Plate ColumnDocument3 pages125x125x82mm Chequered Plate ColumnNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 100x50x5mm Channel SectionDocument4 pages100x50x5mm Channel SectionNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- BASEPLT9Document4 pagesBASEPLT9Nadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 50x50x5mm Angle Section DesignDocument3 pages50x50x5mm Angle Section DesignNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Chequered Plate DesignDocument1 pageChequered Plate DesignNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Chequered Plate DesignDocument1 pageChequered Plate DesignNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Derivation of the heat equationDocument8 pagesDerivation of the heat equationNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 100x50x5mm Channel SectionDocument4 pages100x50x5mm Channel SectionNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Steel Beam Design & SizeDocument2 pagesSteel Beam Design & SizeNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Promax Stationary S130-TWNDocument4 pagesPromax Stationary S130-TWNNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Front 3DDocument1 pageFront 3DNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- 125x125x82mm Chequered Plate ColumnDocument7 pages125x125x82mm Chequered Plate ColumnNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Off-Base Concrete Batch PlantDocument4 pagesOff-Base Concrete Batch PlantNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering ReportDocument31 pagesGeotechnical Engineering ReportNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- MSc Proposal Research OutlineDocument13 pagesMSc Proposal Research OutlineNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Plan View DeckDocument1 pagePlan View DeckNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- PlansDocument5 pagesPlansNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Manzoor FPSCDocument1 pageManzoor FPSCNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Post design calculationsDocument3 pagesPost design calculationsNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Research ModelDocument1 pageResearch ModelNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Wa0036.Document1 pageWa0036.Nadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Just Read The Below Instruction and These Crack IsnDocument1 pageJust Read The Below Instruction and These Crack IsnNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Ringbeam DesignDocument21 pagesRingbeam DesignNadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- As Per Size of The Beam You Need To Place A 6Document1 pageAs Per Size of The Beam You Need To Place A 6Nadir Khattak Jr.No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Strategies of Nestle PakistanDocument16 pagesProduct Life Cycle Strategies of Nestle PakistanFahad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Waiver RightsDocument2 pagesAffidavit Waiver RightsMasa Lyn87% (47)
- wcl-20-24 11 2023Document15 pageswcl-20-24 11 2023Codarren VelvindronNo ratings yet
- Essay 3Document2 pagesEssay 3Rinna Trisha V. QuilinoNo ratings yet
- Life and General InsuranceDocument28 pagesLife and General InsuranceAravinda ShettyNo ratings yet
- Ingeus Restart Scheme Participant Handbook Cwl-19july2021Document15 pagesIngeus Restart Scheme Participant Handbook Cwl-19july2021pp019136No ratings yet
- Laws Affecting Nursing PracticeDocument65 pagesLaws Affecting Nursing PracticeDave MismanNo ratings yet
- 5081 PDFDocument159 pages5081 PDFTemp PersonNo ratings yet
- Il & MLDocument14 pagesIl & MLVIPIN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Nord Pool - The Nordic Power MarketDocument30 pagesNord Pool - The Nordic Power MarketVanádio Yakovlev FaindaNo ratings yet
- East Pakistan 1971 - Distortions and Lies - Revised Edition PDFDocument372 pagesEast Pakistan 1971 - Distortions and Lies - Revised Edition PDFHalqa e Yaran100% (2)
- The Historical Development of Teaching as a Profession in the PhilippinesDocument5 pagesThe Historical Development of Teaching as a Profession in the PhilippinesRichel Leola SumagangNo ratings yet
- The Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning - Lesson 2bDocument18 pagesThe Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning - Lesson 2bAnonymous lNV4yt0No ratings yet
- Nobody Does It Better and Indian Hospitality Will Leave You Feeling Better Too.Document2 pagesNobody Does It Better and Indian Hospitality Will Leave You Feeling Better Too.Abhijeet UmatheNo ratings yet
- Manchester Devt. Corp. vs. CA, GR No. 75919Document3 pagesManchester Devt. Corp. vs. CA, GR No. 75919Rodel Cadorniga Jr.No ratings yet
- Act 4103 - The Indeterminate Sentence LawDocument3 pagesAct 4103 - The Indeterminate Sentence LawRocky MarcianoNo ratings yet
- Business and Supply Chain Strategy of Flying Above The Dessert: A Case Study of Emirates AirlinesDocument17 pagesBusiness and Supply Chain Strategy of Flying Above The Dessert: A Case Study of Emirates AirlineskeerthiiNo ratings yet
- Ôn tập ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh cơ bản với bài tập To V VingDocument10 pagesÔn tập ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh cơ bản với bài tập To V Vingoanh siuNo ratings yet
- Los Del Camino #5 (Inglés)Document8 pagesLos Del Camino #5 (Inglés)benjaminNo ratings yet
- Punjab National Bank Punjab National Bank Punjab National BankDocument1 pagePunjab National Bank Punjab National Bank Punjab National BankHarsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Lease and HPDocument27 pagesLease and HPpreetimaurya100% (1)
- Herb Fitch 1993 Chicago SeminarDocument131 pagesHerb Fitch 1993 Chicago SeminarLeslie BonnerNo ratings yet
- Erp Cloud Global CatalogDocument124 pagesErp Cloud Global Catalogmaha AhmedNo ratings yet
- InDefend Data SheetDocument3 pagesInDefend Data Sheetabhijit379No ratings yet
- Web Search - People's Public Trust CVACDocument23 pagesWeb Search - People's Public Trust CVACVincent J. CataldiNo ratings yet
- Ffiitrsfrshq (Fthfraf) : LadingDocument1 pageFfiitrsfrshq (Fthfraf) : LadingNeo KnightNo ratings yet
- Kwarapoly Portal - Completed ApplicationDocument3 pagesKwarapoly Portal - Completed ApplicationosinoluwatosinNo ratings yet
- Aurengzeb The Throne or The GraveDocument10 pagesAurengzeb The Throne or The GravevstrohmeNo ratings yet
- Bank Asia - Annual Report - 2017 PDFDocument405 pagesBank Asia - Annual Report - 2017 PDFFahim KhanNo ratings yet
- Flaws in India's Coal Allocation ProcessDocument12 pagesFlaws in India's Coal Allocation ProcessBhaveen JoshiNo ratings yet