Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Almanda Gitta Puspa
Uploaded by
Almanda Gitta PuspaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Almanda Gitta Puspa
Uploaded by
Almanda Gitta PuspaCopyright:
Available Formats
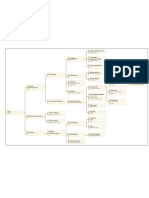
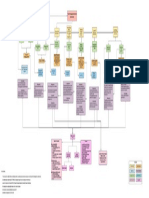
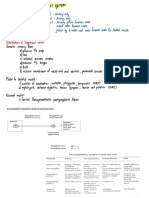
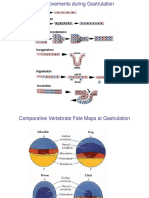
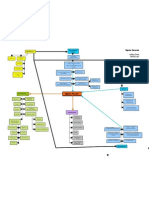
coping guidance through PJOK
mechanism educational system olfactory
BK
optic
affects cellular orientation oculomotor
chronic changes in gene
metabolism of trochlear
stress expression
neuron trigeminal
abducens
increased production of increases facial
glucocorticosteroids hippocampus
vestibulo
sensitivity
epithalamus cochlear agonist
glosso
amygdala cholinergic
subthalamus pharnygeal antagonist
vagus receptor
cognition memory spinal
thalamus
dien-- hypoglossal accessory adrenergic
neurodegene- cervical agonist
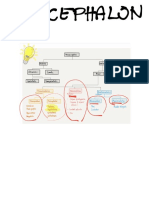
hypothalamus cephalon receptors
rative process limbic antagonist
activation thoracic somatic
system basal ganglia telen- forebrain
decreased
reduced dendritic cephalon lumbar visceral pharma
cogniton hippocampus dura cology
branches
sacral cranial sensoric somatic sympathetic
behavioral, cerebral arach
decreased cerebrum
cognitive, and cortex brain noid coccygeal spinal motoric autonomic division parasympathetic
neurons midbrain
mood disorders stem pia
altered frontal peripheral nerve injury
nerve fiber pathology
disordered synaptic
temporal meninges
spatial memory terminals myasthenia gravis DCML
cerebellum meten- hindbrain
decreased altered LTP
parietal cephalon CSF PNS
reaction time pons tracts ascending conscious anterolateral
reduced occipital
hippocampus medulla myenle- white descending unconscious spinocerebellar
brain spinal cord
volume oblongata cephalon
gray corticospinal
declarative pyramidal
cerebral corticobulbar
memory pathology organ matter extrapyramidal
disorders
edema
herniation vestibulospinal
reduced spatial ipsilateral reticulospinal
memory poliomyelitis hydrocephalus CNS
tetanus infection contralateral rubrospinal
weakened
verbal memory
multiple diseases nervous tectospinal
sclerosis of myelin system components number of
neuromyelitis multipolar
processes
optica dementia
central bipolar
neurobehavior
neurons parts
pontine ADHD unipolar
myelinolysis
soma anaxonic
special senses
opioids and dendrite
drugs of myelinated
alcohols & sedative-hypnotics axon /
abuse unmyelinated
amphetamines nerve fiber
neuroglia
presynaptic synapses astrocytes
special
axon CNS oligodendrocytes
synaptic senses
components
cleft postsynaptic ependymal cells
axon electrical types eye microglia
axosomatic structure chemical
PNS satellite cells
axodendritic resultant ionotropic neuro- anatomy physiology
Schwann cells
transmitter sclera
axoaxionic
metabotropic ear
receptors
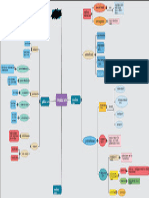
cornea layers structures principles eye visual
excitatory
of optics movement pathways
inhibitory anatomy physiology fibrous vitreous
temporal
body refraction inferior superior light ray
semicircular hemiretina
internal middle auditory choroid vascular rectus rectus
canalis external
lens focal nasal
pathway iris retina
vestibula inner length lateral medial hemiretina
bony tympanic auricle chamber
cochlea ciliary rectus rectus
labyrinth membrane retina image optic ipsilateral
external inner hair body anterior
formation superior inferior nerve fiber
ear canal cells
membranous ossicles muscles posterior
ciliary oblique oblique contralateral
labyrinth cochlear muscle pigmented depth of optic
fiber
malleus stapedius nerve layer focus chiasm
ciliary
cochlear
incus tensor process neural
labyrinth spiral accomodation
stapes tympani layer optic
ganglion
vestibular tract
labyrinth cochlear
nuclei lateral
utricle & sacule
geniculate
urticolassacular Myer's temporal
midbrain nucleus
duct loop lobe
thalamus
semicircular optic Baram's parietal
ducts radiation loop lobe
primary
endolymphatic auditory primary
ducts cortex occipital
visual
lobe
cortex
You might also like
- Brain StructureDocument1 pageBrain StructurevvargasencisoNo ratings yet
- 7.0 (Micro Mynotes Prelim 2) Diencephalon - Thalamus, HypothalamusDocument5 pages7.0 (Micro Mynotes Prelim 2) Diencephalon - Thalamus, HypothalamusDeepbluexNo ratings yet
- Brain SummaryDocument1 pageBrain SummaryKanisorn VoraratchaikulNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument2 pagesSeptic ShockmeNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Document1 pageConcept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Hazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hormones and The Endocrine System: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument68 pagesHormones and The Endocrine System: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- Ent Osce AssembledDocument5 pagesEnt Osce AssembledPrathamNo ratings yet
- 4250 Lec21 15Document10 pages4250 Lec21 15Carlos Enrique Pijo PerezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Senses QuickStudy Reference Guide - (HEARING)Document2 pagesAnatomy of The Senses QuickStudy Reference Guide - (HEARING)statsoNo ratings yet
- Brain CirculationDocument1 pageBrain CirculationNoisy KenNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - Keyranag59100No ratings yet
- EstomihMtuiGreg 2012 CerebralTopography ClinicalNeuroanatomyADocument23 pagesEstomihMtuiGreg 2012 CerebralTopography ClinicalNeuroanatomyANastya PapounidouNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument6 pagesLimbic Systemi gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- 100 Concepts 2Document1 page100 Concepts 2api-371857395No ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document5 pagesLecture 11bibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve Head and Neck - 311220224436-١Document1 pageTrigeminal Nerve Head and Neck - 311220224436-١mkomyu088No ratings yet
- Mindmap Digestive AnatomyDocument2 pagesMindmap Digestive Anatomyapi-535582646No ratings yet
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsDocument18 pagesGlossopharyngeal Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsNorawaylandNo ratings yet
- Filmkard PDFDocument81 pagesFilmkard PDFCamilaNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon, Brainstem & CerebellumDocument1 pageDiencephalon, Brainstem & CerebellumwinNo ratings yet
- Psywar PDFDocument1 pagePsywar PDFmrelfeNo ratings yet
- Resumão, Resumo, Articulações e Ligamentos, Anatomia - Passei DiretoDocument3 pagesResumão, Resumo, Articulações e Ligamentos, Anatomia - Passei DiretoPablo FranzoniNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- MindmapDocument1 pageMindmapChoco MousseNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Jasmine PraveenNo ratings yet
- 3876 NI Fig25-1Document1 page3876 NI Fig25-1paige4pattonNo ratings yet
- Reviewsheet12Document5 pagesReviewsheet12villafrancatin8No ratings yet
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDocument2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Tumor, Orbit & ReconstructionDocument31 pagesTumor, Orbit & ReconstructionZaskiyahNo ratings yet
- ThalamusDocument4 pagesThalamusi gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- Zoo 113 Selected SlidesDocument29 pagesZoo 113 Selected SlidesSheila Marie CuananNo ratings yet
- Imaging The Anatomy of The Brachial Plexus: Review And: Self-Assessment ModuleDocument9 pagesImaging The Anatomy of The Brachial Plexus: Review And: Self-Assessment ModuleAjversonNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedDocument1 pageFigure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin: GlanglionDocument1 pageImmunoglobulin: Glanglionธีรนัย เสารางทอยNo ratings yet
- DIPRINTDocument1 pageDIPRINTAnonymous wRiKUO07DHNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGYDocument3 pagesZOOLOGYJackelyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- MRCS Upper Limb Till Forearm - IoDocument3 pagesMRCS Upper Limb Till Forearm - IoZaeem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapashleydean100% (1)
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument1 pageDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationAnn Justine OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Complete PPDocument103 pagesPharma Complete PPHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- KINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Document40 pagesKINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Gonzalo RetamalNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument4 pagesReproductiveJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- A&P II - Unit II - Power PointDocument17 pagesA&P II - Unit II - Power PointSteve Sullivan75% (4)
- Parkland Trauma Soft TissueDocument14 pagesParkland Trauma Soft TissueJulieNo ratings yet
- Cog09 24Document33 pagesCog09 24genesis serominesNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Machinic Intelligence MDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Machinic Intelligence MMariana Campos CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Kidneys - FactRecallDocument2 pagesKidneys - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- DPW (Paralisis Pada Anak)Document31 pagesDPW (Paralisis Pada Anak)Muhammad HerryNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination in Spinal Cord Injury NewDocument18 pagesNeurological Examination in Spinal Cord Injury NewPratyush RanjanNo ratings yet
- Adrenal CortexDocument8 pagesAdrenal CortexEdward Xiam100% (1)
- Jan-Dec2016 เชื้อดื้อยาไทยDocument2 pagesJan-Dec2016 เชื้อดื้อยาไทยKook-kigNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and Its Role in PsychiatryDocument46 pagesSerotonin and Its Role in PsychiatryAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- EpicardiumDocument2 pagesEpicardiumŠhâh NawazNo ratings yet
- Histo Final2-1Document4 pagesHisto Final2-1Ook ChayapornNo ratings yet
- iOoAzKpa2P2DAOFbutAh PDFDocument5 pagesiOoAzKpa2P2DAOFbutAh PDFAhxhsNo ratings yet
- Posterior PituitaryDocument1 pagePosterior PituitaryfocussedlearnerNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument37 pagesNervous System Powerpointapi-302936823No ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument20 pagesModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- Ch.3 Quiz BDocument22 pagesCh.3 Quiz BSultan AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Development of Midbrain and HindbrainDocument58 pagesDevelopment of Midbrain and HindbrainBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic NotesDocument4 pagesAutonomic NotesYeyeth Jabaybay TabolongNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument40 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueSHARON MARIA SUNNYNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon Thalamus and EpithalamusDocument19 pagesDiencephalon Thalamus and EpithalamusIgme Mocke StraussNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesNervous System Practice QuestionsOsama AlhumisiNo ratings yet
- Architectonic Mapping Amunts 2015Document22 pagesArchitectonic Mapping Amunts 2015Andra-Amalia ArmulescuNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination in HumansDocument14 pagesCo-Ordination in HumansRahulBansumanNo ratings yet
- ch3 PretestDocument7 pagesch3 Pretestapi-245307240No ratings yet
- Neurobiology Exam II Study GuideDocument3 pagesNeurobiology Exam II Study GuideStacy BrenesNo ratings yet
- Auditory PathwayDocument33 pagesAuditory PathwayAnusha Varanasi100% (1)
- Lim Tze Ying 184661 Fce3204Document19 pagesLim Tze Ying 184661 Fce3204Tze YingNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1-YASHDEEP-Behavioral PhysiologyDocument4 pagesQuiz 1-YASHDEEP-Behavioral PhysiologyManvendra JhalaniNo ratings yet
- Revised ScheduleDocument20 pagesRevised ScheduleMiguelito GuballaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Hadzics Peripheral Nerve Blocks and Anatomy For Ultrasound Guided Regional Anesthesia PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Hadzics Peripheral Nerve Blocks and Anatomy For Ultrasound Guided Regional Anesthesia PDF Full Chapter PDFdonald.mortensen170100% (26)
- Brain BeeDocument2 pagesBrain Beebubblegumlover96No ratings yet
- Tela Choroidea - WikipediaDocument11 pagesTela Choroidea - WikipediaAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Module 5Document12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Module 5JayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonDocument5 pagesHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Organisation and Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesOrganisation and Functions of The Nervous SystemBoemo BolaaneNo ratings yet
- Higher Cortical Functions and Basis of LanguageDocument78 pagesHigher Cortical Functions and Basis of Languagelovelots1234No ratings yet
- WEEK 8 LAB EXERCISE - Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesWEEK 8 LAB EXERCISE - Nervous SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Basic Neuroanatomical MethodsDocument11 pagesBasic Neuroanatomical Methods88jnfNo ratings yet
- Localisation in NeurologyDocument19 pagesLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument65 pagesCranial Nervessarguss14100% (13)
- HHBS1HBB Workshop Activities Wk8 2022Document5 pagesHHBS1HBB Workshop Activities Wk8 2022Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument2 pagesNervous System WorksheetRoda Aranquez RabinoNo ratings yet
- L23 The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesL23 The Nervous SystemGemma Wrigley100% (2)