Professional Documents
Culture Documents
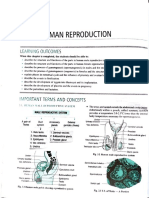
Concept Map On Reproductive System (Final)
Uploaded by
Hazel Ann GonzalesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map On Reproductive System (Final)
Uploaded by
Hazel Ann GonzalesCopyright:
Available Formats
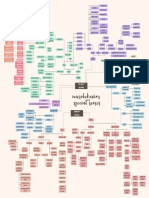
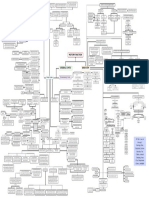
Reproductive
System
produce have experience are
children gametes gonads maturation Homologous
exocrine
function
endocrine
dartos muscle
scrotum
cremaster muscle
vas deferens
testicular artery testes
pampiniform plexus
consist of spermatic cord
autonomic nerves
Lymphatic vessels
cremaster muscles
associated structure
inguinal canal
broad ligament
tunica vaginalis
supporting
structure supensory ligament
tunica albuginea
ovarian ligament
contains 23 chromosomes
(haploid) formation of sperm which is spermatogenesis site of ovaries
ovarian medulla inner portion
Sperm forming cells Spermatogenic cells
divided outer portiom
nourishing the cells into
diploid
Seminiferous tubules
primordial follicles contain oogonia chromosomes
moving the cell to
tubule lumen assist sperm ovarian cortex
production through Sertori/Sentacular Cells primary follicles contain primary oocyte
secrete testicular
fluid secondary follicles contain primary oocyte
contains
ovarian follicles
release inhibin Graafian follicle which is mature follicle
Leydig/Interstitial progesterone
Testosterone produce Cells
estrogen
receive sperm from corpus luteum release
seminiferous tubule relaxin
which Rete testis
convey sperm into inhibin
epididymis
interstitial portion lies w/in uterine wall
ductus epididymis aka
isthmus cute during tubal ligation
comma-shaped organ MALE
Epididymis
divided into
ampulla fertilization occur
site of maturation of
sperm which is
lies near ovary;opens pelvoc cavity
infundibulum
temporarily storage of
fimbriae catch eggs
sperm
mucosa innermost
ductus deferens aka
vas deferens Ducts Fallopian Tube
has layers namely muscularis middle
conveys sperm from the
epididymis toward the urethra which
serosa outer
carry sperm from the vas
deferens to the urethra which Ejaculatory ducts uterine tubes/
aka oviducts
prostatic urethra
secondary oocyte from
fxn ovaries to uterus
membranous urethra Urethra
pathway to fallopian tube
spongy urethra
which womb
helps neutralize acid in
female reproductive tract
FEMALE site of fetus development
provide fructose
upper portion
alkaline, viscous fluid secrete seminal vesicles REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM fundus which is
contribute to sperm motility
and vitality can be palpated
uterus
divided into
coagulate semen body which form bulk or organs
accessory glands
helps semen coagulate prostate gland cervix which opening to vagina
Cowper’s glands aka perimetrium outer
Bulbourethral glands
neutralize acids from urine layers myometrium middle
which
lubricates the urethra endometrium inner
scrotum aka birth canal
deliver sperm into the female protective surfac
external genetilia
reproductive tract which
vagina mucosa inner
most of the mass of the penis corpora cavernosa Penis
cause acidity of vagina
surround the spongy urethra corpus spongiosum made up of
layer mons pubis coarse hair appears
end of the corpus spongiosum glans penis muscularis
labia majora pigmented skin
labia minora hair-free fold
clitoris homologous to penis
urethral meatus
external urethral orifice
external opening of urethra
vaginal orifice
Bartholin's Glands lubricate external genetilia
Perineum danger of being torn in labor
vulva collective term of EFG and structures
Areola surrounds nipple
lobes
breast
lactiferous gland contain milk-secreting cell
lactiferous duct convey milk to nipple
You might also like
- Self-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience PleasingDocument2 pagesSelf-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience PleasingHazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summative Test 1 Quarter3 With AnswerDocument3 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 1 Quarter3 With AnswerRowena Nim100% (7)
- BarCharts QuickStudy Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesBarCharts QuickStudy Reproductive SystemRUDY792100% (4)
- Endocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - Keyranag59100No ratings yet
- Reproductive System MMDocument1 pageReproductive System MMKhaled Abdel-saterNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve Head and Neck - 311220224436-١Document1 pageTrigeminal Nerve Head and Neck - 311220224436-١mkomyu088No ratings yet
- Microanatomy PracticalsDocument1 pageMicroanatomy Practicalsaferdita xhepaNo ratings yet
- Almanda Gitta PuspaDocument1 pageAlmanda Gitta PuspaAlmanda Gitta PuspaNo ratings yet
- Female InfertilityDocument1 pageFemale InfertilityHawraa AbbasNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Kidneys - FactRecallDocument2 pagesKidneys - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- PeriniumDocument11 pagesPeriniumTahaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Concept MapDocument1 pageAnimal Tissue Concept MapBeyonce C. SIBALNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Jasmine PraveenNo ratings yet
- Bio 057Document1 pageBio 057Ari SterlingNo ratings yet
- Brain SummaryDocument1 pageBrain SummaryKanisorn VoraratchaikulNo ratings yet
- KINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Document40 pagesKINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Gonzalo RetamalNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024Document4 pagesHsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024ajithaprabhath123No ratings yet
- Bio 2Document30 pagesBio 2Pauline Jade TrespecesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledSwitzel Smyle Goh PuyaoanNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument19 pagesEndocrineIsabel Bibat DavidNo ratings yet
- Level of Organisation QPDocument10 pagesLevel of Organisation QPApdiweli AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Senses QuickStudy Reference Guide - (HEARING)Document2 pagesAnatomy of The Senses QuickStudy Reference Guide - (HEARING)statsoNo ratings yet
- Some Answers For ANATOMY RGHUSDocument4 pagesSome Answers For ANATOMY RGHUSIsha RaghuNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument1 pageEpitheliumhawdeng xalitNo ratings yet
- Digestive (DONE)Document1 pageDigestive (DONE)Aoun Sial60No ratings yet
- Anmal Skin (Chart)Document3 pagesAnmal Skin (Chart)Mark Anthony Nieva RafalloNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFRDocument8 pagesUrogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFROloruntomi AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept MaphaafizaNo ratings yet
- Traducir 20 PDFDocument1 pageTraducir 20 PDFNora Maricela Cavazos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyne ReviewerDocument2 pagesOb Gyne ReviewerDaphneNo ratings yet
- Resumão, Resumo, Articulações e Ligamentos, Anatomia - Passei DiretoDocument3 pagesResumão, Resumo, Articulações e Ligamentos, Anatomia - Passei DiretoPablo FranzoniNo ratings yet
- Concept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)Document1 pageConcept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)lu.justina100% (8)
- Vestibular RehabilitationDocument4 pagesVestibular RehabilitationFlaviaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal Celljustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument1 pageAnatomy NotesJoe hoeNo ratings yet
- Development of The Spinal CordDocument4 pagesDevelopment of The Spinal CordSri MaheshNo ratings yet
- A Visual Guide To A Chicken NecropsyDocument2 pagesA Visual Guide To A Chicken NecropsyalrezaNo ratings yet
- Cells Concept MapDocument1 pageCells Concept MapprameetaNo ratings yet
- PostersDocument8 pagesPostersVictoria CristobalNo ratings yet
- General Stem Cell Biology BrochureDocument32 pagesGeneral Stem Cell Biology BrochureSigma-AldrichNo ratings yet
- ObstetricDocument4 pagesObstetricIsabel Bibat DavidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - EukaryoticDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 5 - EukaryoticYuume YuuNo ratings yet
- PSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)Document24 pagesPSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)kadiatou konateNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument75 pagesThe Nervous SystemChris ZantiraNo ratings yet
- MindmapDocument1 pageMindmapChoco MousseNo ratings yet
- Biology?Document7 pagesBiology?JenniferNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument4 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationSipranjali SubudhiNo ratings yet
- (Netter) Atlas of Human Anatomy. 8° (2023) - 4Document9 pages(Netter) Atlas of Human Anatomy. 8° (2023) - 4ALEXIS SEDERAPNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document5 pagesLecture 11bibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- Otic Ganglion: Schema: Plate 145Document8 pagesOtic Ganglion: Schema: Plate 145Andreea LăzăroiuNo ratings yet
- Small Exotic Mammals: Oral CavityDocument2 pagesSmall Exotic Mammals: Oral CavityNisrina ZhafirahNo ratings yet
- Case 5 Concept MapDocument1 pageCase 5 Concept MapdreamedyyyNo ratings yet
- (#5) Benign and Malignant Ovariaan TumorsDocument35 pages(#5) Benign and Malignant Ovariaan Tumorsmarina_shawkyNo ratings yet
- Histo Final2-1Document4 pagesHisto Final2-1Ook ChayapornNo ratings yet
- Histology Note of MuscleDocument11 pagesHistology Note of Muscle陳碩璠No ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument2 pagesSeptic ShockmeNo ratings yet
- Posterio Approach Subaxial Cervical Spine + Anterior Approach Cervical Spine +aplied Surgical AnatomyDocument28 pagesPosterio Approach Subaxial Cervical Spine + Anterior Approach Cervical Spine +aplied Surgical AnatomywidapnNo ratings yet
- Local Media5855473667819953112Document3 pagesLocal Media5855473667819953112Hazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Concept Map in Pakinsons DiseaseDocument1 pageConcept Map in Pakinsons DiseaseHazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in Nursing ExamDocument16 pagesFundamentals in Nursing ExamHazel Ann Gonzales100% (2)
- The Physical/Sexual Self 1. Physical SelfDocument4 pagesThe Physical/Sexual Self 1. Physical SelfHazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PNLE - FON Pract-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesPNLE - FON Pract-WPS OfficeHazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- My Module 08Document46 pagesMy Module 08Hazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Everyone Who Needs To Access The Internet and Don't Have The Previledge To Own A Wifi, Especially Students Who Needs To Attend Online ClassesDocument1 pageEveryone Who Needs To Access The Internet and Don't Have The Previledge To Own A Wifi, Especially Students Who Needs To Attend Online ClassesHazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemcorpuzxyleneyaraNo ratings yet
- Product Active IngredientDocument2 pagesProduct Active IngredientOuamrouche SouheilNo ratings yet
- Cf+oym FT Te PlannerDocument8 pagesCf+oym FT Te Plannerharshvardhan singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - 30.12.2022Document17 pagesLecture 8 - 30.12.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- English For MidwiferyDocument27 pagesEnglish For MidwiferyRetno AW100% (1)
- Garbha & Garbha Sambhava SaamagriDocument12 pagesGarbha & Garbha Sambhava SaamagriManojNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Development: Ob NotesDocument2 pagesReproductive System Development: Ob NotesLykee PadillaNo ratings yet
- Immature Oocyte Incidence Contributing Factors and Effects OnDocument7 pagesImmature Oocyte Incidence Contributing Factors and Effects OnTrang Nguyễn NhưNo ratings yet
- Midterms ObDocument29 pagesMidterms ObMary Grace Bañes100% (1)
- Mestrual CycleDocument15 pagesMestrual CycleMary-Ann SanchezNo ratings yet
- Antenatal ExaminationDocument18 pagesAntenatal ExaminationAnonymous 0C4OZmR100% (1)
- Soal Ujian Tengah Semester GanjilDocument5 pagesSoal Ujian Tengah Semester GanjilNovia FaizatiwahidaNo ratings yet
- DeciduaDocument14 pagesDeciduaashphoenix32No ratings yet
- Betty Dodson The G Spot RevisitedDocument7 pagesBetty Dodson The G Spot Revisitedaskmayajohnson100% (1)
- Female Repro Part3 - GomezDocument53 pagesFemale Repro Part3 - GomezMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty A Case ReportDocument8 pagesIdiopathic Central Precocious Puberty A Case ReportCarolyn CapisnonNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science 10 Third QuarterDocument16 pagesDLL in Science 10 Third QuarterAlfred NeriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionDocument108 pagesAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Health TeachingDocument3 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis Health Teachinggenellemaarte100% (1)
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Reproduction and DevelopmentroiveryepesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument53 pagesReproduction and DevelopmentJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Class 12 Biology 202324Document27 pagesReproduction Class 12 Biology 202324Janet RoyNo ratings yet
- Exam Mdwifery 101Document3 pagesExam Mdwifery 101invictus044688% (16)
- GAMETOGENESISDocument6 pagesGAMETOGENESISFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- Masteron Enanthate The Longer Acting Androgenic Anabolic Steroid (AAS)Document12 pagesMasteron Enanthate The Longer Acting Androgenic Anabolic Steroid (AAS)AASrawNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemOre Perez CañeteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Male GenitaliaDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Male GenitaliaWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBurni GuevaraNo ratings yet