Professional Documents
Culture Documents
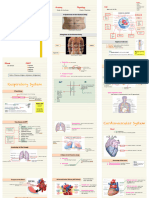
Pneumonia Concept Map
Uploaded by
haafizaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pneumonia Concept Map
Uploaded by
haafizaCopyright:
Available Formats
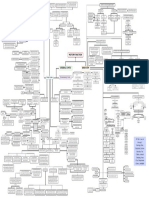
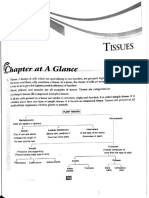
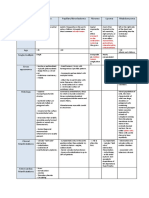
Simple Squamous Single layer of flat scale-shaped cells.
SImple Single unbranching ducts. lines the interior of the circulatory vessels and heart.
Exocrine Glands Endothelium
Simple Simple Cuboidal Single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells.
also known as the "Endocardium"
Compound Ducts are branching.
Simple Columnar Single row of tall, closely packed cells, aligned in a row.
Interspersed among epithelial tissue. Goblet cells
Mucous Membrane It lines body cavities that opens to the outside.
Unicellular Glands Protects and acts as a barrier.
Ductless glands
Stratified Squamous
Also known as "serous tissue" Layer of flat, tile-like cells.
Secretes hormones
Mesothelium
Endocrine Glands It lines great cavities of the body which
have no openings to the outside. Cube-like shaped cells arranged in
Found in thyroid and pituitary glands. Glandular Epithelium Stratified Stratified Cuboidal multiple layers.
Classification based on Functions
Stratified Columnar Column-shaped cells arranged in multiple layers.
flattened cells Squamous Have several layers due to various positioning of cell nucleic.
Classification based on Arrangement Pseudostratified Columnar
Classification based on Shape Layers of tall narrow cells, appears stratified but is not.
Gel-like matrix with all three types of fibers; cube-like cells Columnar
Areolar
Consist of several layers of cells.
Easily stretched but resist tearing.
column-like cells Cuboidal Transitional
Designed to stretch and return to normal
Loaded with fat droplets. state without damage.
Adipose
The nucleus and cytoplasm are pushed Loosely dispersed individual fibers. Loose Connective Tissue
against the cell membrane. spindle-shaped, have a single, centrally located nucleus,
2 Epithelial Tissue Smooth Muscle and lack striations. They are called involuntary muscles.
It is mainly composed of reticular fibers
Reticular
Fibers that support other cell types such as
white blood cells, macrophages, and mast cells.
cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control.
Skeletal Muscle
no visible fibers
resistant to stretching, intervertebral
Hyaline Cartilage
1 Connective TIssue Human Tissues 3 Muscle Tissue
It is composed of cells that can shorten
or contact to move the body parts.
pull bones causing movements of the body.
Fibrocartilage gelatinous around substance Cartilage
disks, and public symphysis
easily stretched and flexible. Elastic Cartilage
calcified ground substance Bone Bone Connective Tissue
One nucleus per cell, striations, and intercalated disks.
4 Nervous Tissue Cardiac Muscle Its contraction is not under voluntary control.
a fluid matrix called plasma,
Blood
and no fibers.
Tendons
controls the body and coordinates with body parts.
parallel arrangement of fibers
Ligaments Dense Regular Connective Tissue
(flexible but not elastic)
Aponeuroses Dense Connective Tissue
Neuron Neuroglia
irregular arrangement of fibers Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Group of cells that provide support and nourishment
to the neurons.
Responsible for conducting nerve impulses throughout Oligodendrocytes Ependymal
the nervous system.
Astrocytes
form myelin in brain and spinal cord. allow diffusion between interstitial
Dendrites Axon
and cerebrospinal fluid
Microglia
Cell Body attach to blood vessels, star-shaped cells,
receives the stimuli/nerve impulses the transmitting part of the neuron provide nourishment and support.
from the sense organs or the surrounding help fight brain damage
neuron.
the neuron's core. carries genetic information and
maintains the neuron's structure.
You might also like
- Cay, COAIFDocument3 pagesCay, COAIFSapphire RedNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - RamosDocument1 pageConcept Map - RamosJedd Kaamiño RamosNo ratings yet
- Colin Wilhelm, Marcus Del Bianco, Siavash Mojibian, Minkyung Kim, Grant MastickDocument1 pageColin Wilhelm, Marcus Del Bianco, Siavash Mojibian, Minkyung Kim, Grant MastickColin WilhelmNo ratings yet
- Binder 3 (Natural Lens and Cataract) - RemovedDocument20 pagesBinder 3 (Natural Lens and Cataract) - RemovedAyouvNo ratings yet
- Case 5 Concept MapDocument1 pageCase 5 Concept MapdreamedyyyNo ratings yet
- Histology Male-1Document1 pageHistology Male-1Yu Tung TsaiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Concept MapDocument1 pageAnimal Tissue Concept MapBeyonce C. SIBALNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology by 6Document8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology by 6Emmanuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartDocument1 pageCbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartAMit100% (1)
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell Structureadhit46No ratings yet
- Exercise 7E (Dwarf Tapeworm) I. Draw and Label The Different Structures Speci5iedDocument2 pagesExercise 7E (Dwarf Tapeworm) I. Draw and Label The Different Structures Speci5iedMemeowwNo ratings yet
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDocument1 pageBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Mind Map - 202346 - 21249Document1 pageMind Map - 202346 - 21249love bhagatNo ratings yet
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- Prac 1 Histology of Oral Cavity, Oesophagus & StomachDocument17 pagesPrac 1 Histology of Oral Cavity, Oesophagus & StomachSleepyHead ˋωˊNo ratings yet
- Development of The Spinal CordDocument4 pagesDevelopment of The Spinal CordSri MaheshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Muscular System NotesDocument3 pagesAnatomy Muscular System NotesrincyNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument65 pagesCytoskeletonapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Locomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFDocument2 pagesLocomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFANKITA MANDAVI67% (3)
- Flowering: Anatomy OlsDocument19 pagesFlowering: Anatomy Olsnashwa s.pNo ratings yet
- Ajr 101 1 34 PDFDocument13 pagesAjr 101 1 34 PDFGiuseppe RojasNo ratings yet
- Nashra U. Sindatoc Concept Map of Cells 20212244873: Cell TypesDocument1 pageNashra U. Sindatoc Concept Map of Cells 20212244873: Cell TypesiamNashix22No ratings yet
- Janoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)Document1 pageJanoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)maxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Janoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)Document1 pageJanoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)maxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Lab SheetDocument3 pagesSpecial Senses Lab SheetKelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial TissueDocument1 pageBody Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial Tissuemaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- GP Exer 9 Caseous NecrosisDocument1 pageGP Exer 9 Caseous NecrosisClyde HinloNo ratings yet
- Interpreting PDX Dot BlotsDocument2 pagesInterpreting PDX Dot BlotsSpy CameraNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 09 Feb 2024Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 09 Feb 2024shradhasharma2101No ratings yet
- Tissue CTDocument1 pageTissue CTAditi MishraNo ratings yet
- Lasercyte DX Dot Plot Poster enDocument2 pagesLasercyte DX Dot Plot Poster enSpital Veterinar AndivetNo ratings yet
- 22 Lecture PresentationDocument88 pages22 Lecture PresentationLeilaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 04 Aug 2021Jasmine PraveenNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Section: Faculty-in-ChargeDocument2 pagesName: Date: Section: Faculty-in-ChargeMaria StephanieNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types PPTDocument25 pagesTissue Types PPTAiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals Mind MapDocument3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals Mind MapAstha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Creatinina Renal (017-066) PDFDocument50 pagesCreatinina Renal (017-066) PDFEdison Huaman MorveliNo ratings yet
- Jerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsDocument1 pageJerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsCBR UBCNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - RespiratoryDocument1 pageAnatomy - Respiratorydead yrroehNo ratings yet
- T2 Histology of Epithelial, Connective, and Muscle TissueDocument86 pagesT2 Histology of Epithelial, Connective, and Muscle TissueretterateNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimiliaDocument1 pageKingdom AnimiliaNoman ZakiNo ratings yet
- TISSUES WORKSHEET (Till Epithelial Tissue)Document4 pagesTISSUES WORKSHEET (Till Epithelial Tissue)Mohammad Saif RazaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Bio SyllabusDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Bio SyllabusChamsNo ratings yet
- Primary Cardiac Tumors SummaryDocument2 pagesPrimary Cardiac Tumors SummaryMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- 2-HEAD AND NECK PrintDocument30 pages2-HEAD AND NECK Printsaddam hussain100% (1)
- Plant Growth & DifferentiationDocument25 pagesPlant Growth & DifferentiationAntarnet AntarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 NeuroDocument1 pageWeek 1 NeuroMuhammad SoudanNo ratings yet
- DR Gargi Singh - 2 Page Notes - Animal TissueDocument8 pagesDR Gargi Singh - 2 Page Notes - Animal TissueSuccessfactors TrainerNo ratings yet
- 人脑图谱 PDFDocument1 page人脑图谱 PDFzmNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Ana Lec 2Document53 pagesNervous System Ana Lec 2hey lolNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Levels - of - Organisation 1b Igcse - 9 1 - Edexcel BiologyDocument11 pages3.1 Levels - of - Organisation 1b Igcse - 9 1 - Edexcel BiologyIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyJRNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024thakur.shrish.singhNo ratings yet
- Chemokine ReceptorDocument1 pageChemokine ReceptorSNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 4Document8 pagesLab Rep 4Korreine BuccatNo ratings yet
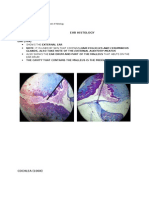
- Ear HistologyDocument3 pagesEar HistologyGrace Shan Bernus100% (1)
- PH Calculations and BufferDocument5 pagesPH Calculations and BufferhaafizaNo ratings yet
- M2 Lipids: Biochem LecDocument7 pagesM2 Lipids: Biochem LechaafizaNo ratings yet
- QC 12Document68 pagesQC 12haafizaNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Centro Escolar Integrated School, IncDocument29 pagesGenetics: Centro Escolar Integrated School, InchaafizaNo ratings yet
- Landscaping CatalogueDocument8 pagesLandscaping CatalogueDipti AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis LabDocument4 pagesEnzyme Catalysis LabMeera KumarNo ratings yet
- PCR ManualDocument74 pagesPCR ManualMARDHIANo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument342 pagesThesisAna CalmîșNo ratings yet
- 1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalDocument27 pages1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalAshar AbilowoNo ratings yet
- APTTDocument2 pagesAPTTApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- KLD Company Profile (Primary)Document60 pagesKLD Company Profile (Primary)Sukhman ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Calendula 8Document7 pagesCalendula 8Zeila OmarNo ratings yet
- Bioluminescence PDFDocument34 pagesBioluminescence PDFArup DasNo ratings yet
- Class - 9 Science Sample Paper - 1 FOR Summative AssesmentDocument16 pagesClass - 9 Science Sample Paper - 1 FOR Summative AssesmentApex Institute100% (1)
- Cell Organelles: Classify Different Cell Types (Plant and Animal Tissues) and Specify The Functions of EachDocument42 pagesCell Organelles: Classify Different Cell Types (Plant and Animal Tissues) and Specify The Functions of EachTatingJainarNo ratings yet
- Mind Does Really Matter: Evidence From Neuroimaging Studies of Emotional Self-Regulation, Psychotherapy, and Placebo EffectDocument19 pagesMind Does Really Matter: Evidence From Neuroimaging Studies of Emotional Self-Regulation, Psychotherapy, and Placebo Effectseagoddess_simoNo ratings yet
- 2016 Black Soldier Fly WartazoaDocument11 pages2016 Black Soldier Fly WartazoaghotamaNo ratings yet
- Ejhg 201324Document7 pagesEjhg 201324sssssNo ratings yet
- FCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 27 3 2020 PDFDocument75 pagesFCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 27 3 2020 PDFdchunNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Medicine, An Issue of Physical MedicineBook (The Clinics - Orthopedics) - Santos F. MartinezDocument646 pagesRegenerative Medicine, An Issue of Physical MedicineBook (The Clinics - Orthopedics) - Santos F. MartinezChung Tze YangNo ratings yet
- Development Psychology - Chapter 6 (Santrock)Document78 pagesDevelopment Psychology - Chapter 6 (Santrock)Shaine C.No ratings yet
- Leaflet Silliver TabsDocument2 pagesLeaflet Silliver TabsadnanjamilNo ratings yet
- Milno Et AlDocument9 pagesMilno Et AlLara SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Biology 2009 STPMDocument37 pagesBiology 2009 STPMPiDi DaeNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsEdward OllingerNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary SystemDocument36 pagesIntergumentary SystemKudzai MashayaNo ratings yet
- MLS 044 - Clinical Bacteriology (LABORATORY) Staining TechniquesDocument3 pagesMLS 044 - Clinical Bacteriology (LABORATORY) Staining Techniqueslorraine del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism & ReapirationDocument9 pagesCellular Metabolism & ReapirationAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rabun PDFDocument4 pagesJurnal Rabun PDFliana computerNo ratings yet
- Disease of Ornamental CropsDocument19 pagesDisease of Ornamental CropsPooja BhusalNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.0 Introduction/Literature Review 1.1 Background of StudyDocument62 pagesChapter One 1.0 Introduction/Literature Review 1.1 Background of StudySolomonNo ratings yet
- Gauk 1 Picture1 PDFDocument1 pageGauk 1 Picture1 PDFIshak Ika KovacNo ratings yet