Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water and Osmotic Regulation
Uploaded by
PNU Kristine Garcia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageAnimal cells must regulate their water content to avoid bursting or dehydration when placed in hypertonic or hypotonic environments. If placed in a hypertonic environment, a cell will lose water but gain solute and shrink. If placed in a hypotonic environment, solute will exit the cell while water enters, causing swelling and potential bursting. Organisms have developed ways to regulate their body's fluid concentration including being osmotic conformers, stenohaline, or euryhaline. Freshwater fish in particular regulate their salt balance to prevent water from continually diffusing into their cells and causing swelling.
Original Description:
Lecture notes about water and osmotic regulation.
Original Title
WATER AND OSMOTIC REGULATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnimal cells must regulate their water content to avoid bursting or dehydration when placed in hypertonic or hypotonic environments. If placed in a hypertonic environment, a cell will lose water but gain solute and shrink. If placed in a hypotonic environment, solute will exit the cell while water enters, causing swelling and potential bursting. Organisms have developed ways to regulate their body's fluid concentration including being osmotic conformers, stenohaline, or euryhaline. Freshwater fish in particular regulate their salt balance to prevent water from continually diffusing into their cells and causing swelling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageWater and Osmotic Regulation
Uploaded by
PNU Kristine GarciaAnimal cells must regulate their water content to avoid bursting or dehydration when placed in hypertonic or hypotonic environments. If placed in a hypertonic environment, a cell will lose water but gain solute and shrink. If placed in a hypotonic environment, solute will exit the cell while water enters, causing swelling and potential bursting. Organisms have developed ways to regulate their body's fluid concentration including being osmotic conformers, stenohaline, or euryhaline. Freshwater fish in particular regulate their salt balance to prevent water from continually diffusing into their cells and causing swelling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
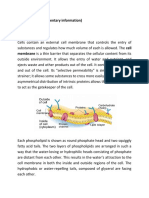
WATER AND OSMOTIC - if animal cell is put in a hypertonic environment, it will
lose water but gain solute, the cell will shrink/be
REGULATION dehydrated
- important because animal cells in general, are not
protected by cell walls, are sensitive in increase and case. b) 1 is Extracellular Fluid which is hypotonic
decrease in osmotic pressure. if the water gets in too fast while 2 is the animal cells which is hypertonic
or if too much water gets in, it might burst. decrease in - solute will exit, water will enter
water can cause dehydration and death. - result to swelling and bursting
- classify organisms based on their ability to thrive in
different environments case. c) concentration of solute and solvent are equal
- called isotonic/isosmotic
Osmotic conformers - organisms incapable of - no swelling nor shrinking through maintaining the
regulating their body's fluid concentration concentration of cytoplasm relatively to the
(marine invertebrates), they tend to conform w/ concentration of the solute in ECF
the environments’ osmotic balance/pressure
Stenohaline - organisms with narrow range of
tolerance to salinity (can be marine or fresh
water organism but a slight change can be a risk
to their survival); they can be mostly found on
eco zones or estuaries
Euryhaline - organisms with wide range of
tolerance to salinity (fluctuating changes in the
environment/salinity is still tolerable for these
organisms)
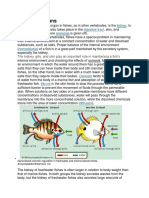
Hyperosmotic Regulations
- refers to fishes or living organisms living in a specific
aquatic environment Hypoosmotic Regulation
- body fluids less concentrated than the surrounding
(how can a freshwater fish regulate its body’s medium
salt/osmotic balance? the tendency is for the
environment to be less salty than the body, if that is the
case, thinking of diffusion, you know that the water will
keep on entering the cell, so that would result to swelling
or bursting of the cell if not controlled. overcoming that
challenge is the fish’s way of evolving.)
*diffusion – movement of material from an area of
greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration
*tonicity – concentration of solute
1 (ratio of solute to solvent)
- 1 (with greater concentration of
solute but lesser concentration of
2 solvent) is called hypertonic
environment/solution
- 2 (with lesser concentration of
solute but higher concentration of solvent) is called
hypotonic environment
case. a) 1 is Extracellular Fluid (any fluid present in the
external environment of the cell) while 2 is the animal
cells
- through diffusion, the solute is more likely to enter the
cell but the solvent (greater concentration of water on the
animal cell) will move outward
You might also like
- ZOOLFUN Breathing NotesDocument2 pagesZOOLFUN Breathing NotesKirsten Elry AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Diffusion & Osmosis LabDocument17 pagesDiffusion & Osmosis LabDee Mar0% (1)
- BlobfishDocument17 pagesBlobfishapi-34604020550% (2)
- Lab Report: I. TitleDocument13 pagesLab Report: I. TitleCatherine Marie Tucker100% (2)
- BiologyDocument80 pagesBiologyAmp100% (6)
- Group 6 Written ReportDocument4 pagesGroup 6 Written ReportLuckyGuy25No ratings yet
- 7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalDocument58 pages7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalAhmed Oraby81% (16)
- Chapter-01 XII (From Email)Document27 pagesChapter-01 XII (From Email)Larkana ssmNo ratings yet
- Bio 306 General Physiology-2Document143 pagesBio 306 General Physiology-2Bi AnhNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis FSC Biology Notes Part 2 Chapter 15Document18 pagesHomeostasis FSC Biology Notes Part 2 Chapter 15yaseen shahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 30: Homeostasis: Internal Fluids and RespirationDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 30: Homeostasis: Internal Fluids and RespirationGlen Arthur Villarisco DolleteNo ratings yet
- 2018 G12 Biology E PDFDocument402 pages2018 G12 Biology E PDFAli Shahzad25% (4)
- 12th BiologyDocument402 pages12th BiologyMarush KhanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Biology NotesDocument30 pages2nd Year Biology NotesTaleem City75% (4)
- Topic GRP 1 5Document12 pagesTopic GRP 1 5Jade Lawrence IgnacioNo ratings yet
- What Is HomeostasisDocument2 pagesWhat Is HomeostasisChidinma Glory EjikeNo ratings yet
- Transport Mind MapDocument49 pagesTransport Mind MapMiryaNo ratings yet
- Final OsmosisDocument2 pagesFinal Osmosisapi-523278684No ratings yet
- Module 1 - TonicityDocument1 pageModule 1 - TonicitySam TagardaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document21 pagesChapter 15 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Suffa Academy100% (3)
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument4 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsIndah ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Notes 2023 Osmoregulation - 1968568183Document12 pagesLecture 10 Notes 2023 Osmoregulation - 1968568183Modupe OlunugaNo ratings yet
- Session 5 OsmoregulatonDocument16 pagesSession 5 OsmoregulatonNadeem aslamNo ratings yet
- Document 333pDocument3 pagesDocument 333pbyxctdyv67No ratings yet
- CH 44 OutlineDocument17 pagesCH 44 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Q4 Week 3Document27 pagesGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 3Sherry Macalalad Garcia50% (2)
- Keypoints Xii Bio RO WatermarkDocument57 pagesKeypoints Xii Bio RO WatermarkShafia Batool100% (3)
- Document PDFDocument1 pageDocument PDFKhansa AlizaiNo ratings yet
- How Plant and Animal Adapt To Aquatic HabitatDocument16 pagesHow Plant and Animal Adapt To Aquatic HabitatCharles Amaechi100% (2)
- Chapter 8 BioDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Biosgangwar2005sgNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsDocument16 pagesRegulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsPaopao Macalalad100% (4)
- Osmosis and DiffusionDocument26 pagesOsmosis and Diffusionapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Osmoregulation - Part OneDocument24 pagesOsmoregulation - Part OneMohamadNajmiNo ratings yet
- Biology-Cell MemraneDocument3 pagesBiology-Cell Memranekrbedes.pboxNo ratings yet
- 2 D Movement in and Out of CellsDocument39 pages2 D Movement in and Out of Cellsyippee.ndi13No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Major Fluid CompartmentDocument9 pagesOsmosis: Major Fluid CompartmentMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- OSMOREGULATIONDocument24 pagesOSMOREGULATIONGEETA MOHAN100% (3)
- Osmoregulation, Lecture 2Document24 pagesOsmoregulation, Lecture 2amuyawtheophilusNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory SystemPrecious BucayNo ratings yet
- 5 DiffusionDocument37 pages5 Diffusionrezamaulana100% (1)
- Theory: 1 Plant Water RelationsDocument11 pagesTheory: 1 Plant Water RelationsalekhyaNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument2 pagesOsmosissajmirNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: 1 MechanismDocument6 pagesOsmosis: 1 MechanismsnowflomanNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument12 pagesAbsorption by Rootsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)Document3 pagesGRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)EleinaNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiologyChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- Cells: Diffusion and OsmosisDocument22 pagesCells: Diffusion and OsmosisjmgardnerNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab VocabularyDocument3 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Lab Vocabularydannyf09No ratings yet
- First Semester 2020/2021Document37 pagesFirst Semester 2020/2021low luffecussNo ratings yet
- OSMOSISDocument4 pagesOSMOSISsuwethajNo ratings yet
- Excretory OrgansDocument4 pagesExcretory OrgansEstela Benegildo100% (1)
- Bio560 OsmoregulationDocument110 pagesBio560 OsmoregulationNuratika OthmanNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulatory Systems in Fishes: Maintaining Homeostasis With Respect To Solute Concentrations and Water ContentDocument24 pagesOsmoregulatory Systems in Fishes: Maintaining Homeostasis With Respect To Solute Concentrations and Water ContentBella utariNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Adaptations - Poonam SinghDocument46 pagesAquatic Adaptations - Poonam Singhaksahu01234No ratings yet
- Limiting Factors and ToleranceDocument18 pagesLimiting Factors and Tolerancearvinric83% (6)
- The Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishFrom EverandThe Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Pharmaceutical Calculation Lec 2Document41 pagesPharmaceutical Calculation Lec 2Christine Mae Mina CablingNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis WSDocument4 pagesDiffusion Osmosis WSCamila ValerioNo ratings yet
- Osmosis & Orbeez CERDocument3 pagesOsmosis & Orbeez CERVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- 1 Osmosis DialysisDocument5 pages1 Osmosis DialysisRio SurNo ratings yet
- Chapter at A Glance: Study Key PointsDocument14 pagesChapter at A Glance: Study Key PointssatishNo ratings yet
- CLIN PHARM - Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument11 pagesCLIN PHARM - Fluids and ElectrolytesAlodia RazonNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - Week 4Document20 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - Week 4Anime KISSANIME100% (1)
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument20 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesWyn Agustin100% (1)
- Menselijke Biologie en Ziekteleer SamenvattingDocument167 pagesMenselijke Biologie en Ziekteleer SamenvattingLotte WoutersNo ratings yet
- OSPE Physiology Lap (Osmosis)Document6 pagesOSPE Physiology Lap (Osmosis)layla abdullahNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Cell (Prashant Kirad)Document17 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Cell (Prashant Kirad)chinkavarshaved100% (1)
- 1.tonicity & Osomlarity - LabDocument14 pages1.tonicity & Osomlarity - LabSairee AbianNo ratings yet
- Experiments in Physiology 11th Edition Woodman Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesExperiments in Physiology 11th Edition Woodman Solutions Manualvolapukbubalevoju2100% (15)
- Sea As Biological EnvironmentDocument19 pagesSea As Biological EnvironmentAamir Khan0% (1)
- Lecture Notes - Chem 16 LE3Document8 pagesLecture Notes - Chem 16 LE3Alexander Gordon InesNo ratings yet
- Biophysics-Lectures-2012-3 (Physiology) PDFDocument107 pagesBiophysics-Lectures-2012-3 (Physiology) PDFNedelcuGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia From HarrisonDocument3 pagesHypernatremia From HarrisonNobel LaureateNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat SheetPatrick Formoso0% (1)
- ScienceDocument103 pagesScienceWisdom AbotsiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Summative Test 4Document2 pagesGen Bio Summative Test 4Kennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument13 pagesPlant PhysiologyIdasari DewiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Body Fluids-1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Body Fluids-1Lazuardi FadhullahNo ratings yet
- FullDocument139 pagesFullsendtomicahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab ReportDocument9 pagesAnatomy Lab ReportAndre VilliersNo ratings yet
- Date: 27/11/2020 Lab# 2 Title: Osmosis in Onion Rings. Aim: To Investigate Osmosis Using Onion Rings. Materials: ApparatusDocument5 pagesDate: 27/11/2020 Lab# 2 Title: Osmosis in Onion Rings. Aim: To Investigate Osmosis Using Onion Rings. Materials: ApparatusTabitha Darrell100% (1)
- 1.4 NotesDocument12 pages1.4 Notesyara hazemNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDocument69 pagesFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceJoshua KellyNo ratings yet
- Biology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Document60 pagesBiology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Azure Fikadu100% (1)