Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
api-4063079330 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views26 pagesOriginal Title
7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views26 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
api-406307933Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Osmosis and Diffusion
Movement through Cell Membranes
◦ Selective permeability of membranes surrounding
the cells and within the cells.
◦ Definition of the terms “diffusion” and “osmosis”.
Examples of each.
◦ Describe the application of high salt or sugar
concentration in food preservation.
◦ Definition of “turgor”. Simple explanation of
turgidity in plant cells.
Selectively Permeable Hypertonic Solution
Diffusion Hypotonic Solution
Active Transport Osmoregulation
Osmosis Turgor
Isotonic Solution Plasmolysis
Membranes can be:
◦ Permeable – allows all substances in and out.
◦ Semi/Selectively Permeable – allows some
substances in and out.
◦ Impermeable – does not allow substances to move
through it.
Substances move in and out of cells in two
ways:
◦ Diffusion is the movement of molecules from areas
of high concentration to areas of lower
concentration.
Diffusion is a passive process.
◦ Active Transport is the movement of molecules
from areas of low concentration to areas of higher
concentration.
Active transport requires energy.
Examples of diffusion include:
◦ The smell of perfume.
◦ Food colouring in water.
◦ Sugar in tea.
◦ Diffusion of gases in leaves/animal cells.
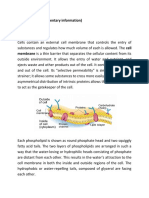
Osmosis is the movement of water from an
area of high water concentration to an area of
lower water concentration across a semi-
permeable membrane.
Note: The higher the solute concentration the
lower the water concentration and vice versa.
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion and is
passive.
Animal cells are enclosed only by a cell
membrane.
Isotonic means two solutions have the same
solute concentration.
If an animal cell is surrounded by an isotonic
solution water will move in and out at the
same rate and the cell will remain intact.
Our kidneys make sure the fluid in our bodies
that surrounds our cells (plasma) has a stable
concentration.
This process is called osmoregulation.
Many animals that live in the sea have
cytoplasm with similar concentration to sea
water.
Hypotonic means a solution has a lower
solute concentration than another solution.
If an animal cell is surrounded by a hypotonic
solution water will move into the cell and may
cause it to burst.
An Amoeba is a single-celled organism that
lives in freshwater pools and ponds.
The cytoplasm of the Amoeba is more
concentrated than the water surrounding it,
this means that Amoeba must have a way of
controlling osmosis or it will burst.
Amoeba contain a contractile vacuole which
expels water.
Amoeba species that live in seawater don’t
have this contractile vacuole as the seawater
has the same concentration as their
cytoplasm.
Hypertonic means a solution has a higher
solute concentration than another solution.
If an animal cell is surrounded by a
hypertonic solution water will move out of the
cell and may cause it to shrivel up and die.
Plants have a cell wall which surrounds their
membrane.
The cell wall is fully permeable and will allow
all substances in and out of the cell.
If a plant cell is surrounded by a less
concentrated solution then water will move
into the cytoplasm and vacuole of plant cells.
This is how roots absorb water (osmosis).
When water enters the plant cell the vacuole
and cytoplasm swell.
This causes the membrane to be pushed out
towards the cell wall.
When cells are fully ‘swelled’ like this they are
said to be turgid.
Turgor, or turgor pressure, is the pressure of
the cytoplasm and vacuole against the cell
wall of a plant.
This turgor pressure gives plants their
strength.
Plants would wilt without this turgor
pressure.
Non-woody plants, such as lettuce and house
plants, rely on turgor pressure for strength
and support.
If a plant cell is surrounded by a more
concentrated solution then water will move
out of the cytoplasm and vacuole of plant
cells.
When this happens the cell wall stays intact
but the membrane shrivels away from it.
Cells in this condition are called plasmolysed
cells.
Plasmolysis is the loss of water from the
cytoplasm and the movement of the
membrane away from the cell wall.
We can easily see plasmolysis in red onion
cells left in a salt solution.
Osmosis is often used to prevent
microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi
from growing on food.
If foods are placed in a sugary or salty
solution then any bacteria or fungi present
will lose the water from their cells and they
will shrivel and die.
◦ This prevents food spoilage.
Examples of food preservation using osmosis
include:
◦ Fish and meat (bacon) being soaked in a salty
solution.
◦ Jams, marmalades and tinned fruit being stored in a
sugary solution.
Active transport uses energy to take
chemicals into a cell against the
concentration gradient i.e. from a low
concentration to a high concentration.
Proteins in the cell membrane undertake
active transport.
You might also like
- Biology Info Sheet 18.11.23Document5 pagesBiology Info Sheet 18.11.23jhoyvanNo ratings yet
- What Is OsmosisDocument4 pagesWhat Is OsmosisMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- 2 2 OsmosisDocument25 pages2 2 OsmosisAyah FNo ratings yet
- MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS: DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS, ACTIVE TRANSPORTDocument10 pagesMOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS: DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS, ACTIVE TRANSPORTMoni VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Osmosis and Togor PressureDocument12 pagesLecture 3 Osmosis and Togor Pressuremichael328wanjiruNo ratings yet
- LO: - Define Osmosis and Explain How Does It Work: Starter: (In The Back of Your Book)Document21 pagesLO: - Define Osmosis and Explain How Does It Work: Starter: (In The Back of Your Book)nidhiNo ratings yet
- CELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDocument6 pagesCELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDENIS KIPKOSGEINo ratings yet
- Cell Boundaries Module 2Document17 pagesCell Boundaries Module 2Vedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Water Relations Explained in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesPlant Water Relations Explained in 40 CharactersalekhyaNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 XII (From Email)Document27 pagesChapter-01 XII (From Email)Larkana ssmNo ratings yet
- DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS: KEY CELLULAR PROCESSESDocument3 pagesDIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS: KEY CELLULAR PROCESSESshaniah100% (1)
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)Document3 pagesGRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)EleinaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Into and Out of CellsDocument9 pagesMovement of Substances Into and Out of CellsethanNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument32 pagesDiffusionAce Mhac TeñidoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9Document5 pagesBiology Notes Class 9lalitha muraliNo ratings yet
- TitleDocument10 pagesTitleWei Loon100% (1)
- Cells: Diffusion and OsmosisDocument22 pagesCells: Diffusion and OsmosisjmgardnerNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - TonicityDocument1 pageModule 1 - TonicitySam TagardaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1Jonathan ObejaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 3Document15 pagesBio CH 3SourabhiNo ratings yet
- Ch3 OL RevisionDocument11 pagesCh3 OL Revisionzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument11 pagesOsmosisIscariot PriestNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterDocument60 pages4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterankurbiologyNo ratings yet
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocument40 pagesGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Written ReportDocument4 pagesGroup 6 Written ReportLuckyGuy25No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells - NOTESDocument5 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells - NOTESAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFDocument47 pagesUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraNo ratings yet
- Effect of Water Potential On Plant CellDocument2 pagesEffect of Water Potential On Plant CellWalwin HareNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventDocument3 pagesOsmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventCHIEF VISHAAL 45No ratings yet
- Gene103Lab_DiffusionandOsmosis (2)Document5 pagesGene103Lab_DiffusionandOsmosis (2)bodurr571No ratings yet
- MOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportDocument4 pagesMOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportTshepo O MotsemmeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport ExplainedDocument4 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis & Active Transport ExplainedgulminaNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Cell Content 2Document34 pagesOsmosis and Cell Content 2Ñïà ǸìæNo ratings yet
- 3 Movement Into & Out of CellsDocument4 pages3 Movement Into & Out of CellsmeerzasarahNo ratings yet
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDocument6 pagesNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTSDocument19 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTSnihalbolla2023No ratings yet
- Pergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanDocument36 pagesPergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanSitiKomariahAgustinaNo ratings yet
- OSMOSISDocument4 pagesOSMOSISsuwethajNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport: Diffusion, Osmosis, Active TransportDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Transport: Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transportaby251188No ratings yet
- Biological ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiological ProcessesIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Semipermeable MembranesDocument4 pagesOsmosis and Semipermeable MembranesAarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- MOVEMENT INTO AND OUT OF CELLSDocument12 pagesMOVEMENT INTO AND OUT OF CELLSf8sdh6xvzyNo ratings yet
- CELL TRANSPORT Notes SY 2022 2023Document36 pagesCELL TRANSPORT Notes SY 2022 2023Olitres, John Vincent A.No ratings yet
- Movement of MoleculesDocument16 pagesMovement of MoleculeslibanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion in Living Organisms ExplainedDocument11 pagesDiffusion in Living Organisms ExplainedRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and osmoregulation in animals and plantsDocument57 pagesHomeostasis and osmoregulation in animals and plantsShafia Batool100% (3)
- 04 NotesDocument6 pages04 NotesAirus SamaNo ratings yet
- First Year ScienceDocument46 pagesFirst Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: First Year ScienceDocument16 pagesAcids and Bases: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Skeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year ScienceDocument15 pagesSkeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- States of Matter: First Year ScienceDocument34 pagesStates of Matter: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: First Year ScienceDocument28 pagesSeparating Mixtures: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds & Mixtures: First Year ScienceDocument11 pagesElements, Compounds & Mixtures: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Third Year EventsDocument1 pageThird Year Eventsapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Fifth Year EventsDocument1 pageFifth Year Eventsapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Solutions & Crystallisation: First Year ScienceDocument18 pagesSolutions & Crystallisation: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Sixth Year EventsDocument1 pageSixth Year Eventsapi-406307933No ratings yet
- First Year EventsDocument1 pageFirst Year Eventsapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Density and Flotation: Third Year ScienceDocument20 pagesDensity and Flotation: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument53 pagesThe Human Reproductive Systemapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Second Year EventsDocument1 pageSecond Year Eventsapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Genetics: Third Year ScienceDocument15 pagesGenetics: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Electronics: Third Year ScienceDocument11 pagesElectronics: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Microbiology & Biotechnology: Third Year ScienceDocument19 pagesMicrobiology & Biotechnology: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Pressure: Third Year ScienceDocument23 pagesPressure: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Uses and Effects of Electricity: Third Year ScienceDocument20 pagesUses and Effects of Electricity: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Static and Current Electricity: Third Year ScienceDocument68 pagesStatic and Current Electricity: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Third Year ScienceDocument14 pagesAcids and Bases: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Sound: Third Year ScienceDocument23 pagesSound: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Sound: Third Year ScienceDocument23 pagesSound: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Ecology: Third Year ScienceDocument46 pagesEcology: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Ecology: Third Year ScienceDocument46 pagesEcology: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Motion: Third Year ScienceDocument59 pagesMotion: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Moments, Levers and Centre of Gravity: Third Year ScienceDocument44 pagesMoments, Levers and Centre of Gravity: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Motion: Third Year ScienceDocument59 pagesMotion: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Microbiology & Biotechnology: Third Year ScienceDocument19 pagesMicrobiology & Biotechnology: Third Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Light: Second Year ScienceDocument34 pagesLight: Second Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- l3 Immunization & Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl3 Immunization & Cold ChainNur AinaaNo ratings yet
- Kim Hoff PAR 117 JDF 1115 Separation AgreementDocument9 pagesKim Hoff PAR 117 JDF 1115 Separation AgreementlegalparaeagleNo ratings yet
- Foreign AidDocument4 pagesForeign AidJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Titanium Plates and Screws For Open Wedge HtoDocument6 pagesTitanium Plates and Screws For Open Wedge HtoDaniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- STS Lesson 1-2Document23 pagesSTS Lesson 1-2zarnaih SmithNo ratings yet
- Protective & Marine Coatings: Hi-Solids Alkyd Metal PrimerDocument4 pagesProtective & Marine Coatings: Hi-Solids Alkyd Metal PrimerAna CabreraNo ratings yet
- EasyGreen ManualDocument33 pagesEasyGreen ManualpitoupitouNo ratings yet
- The Power of Prayer English PDFDocument312 pagesThe Power of Prayer English PDFHilario Nobre100% (1)
- Kent Thiry IndictmentDocument10 pagesKent Thiry IndictmentMichael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- SMEspdfDocument13 pagesSMEspdflilpumpdidnothingwrong dNo ratings yet
- Diseñadores Del Siglo XX - Las Figuras Clave Del Diseño y - Dormer, Peter - 1993 - Barcelona - Ceac - 9780747202684 - Anna's ArchiveDocument264 pagesDiseñadores Del Siglo XX - Las Figuras Clave Del Diseño y - Dormer, Peter - 1993 - Barcelona - Ceac - 9780747202684 - Anna's ArchiveSilvina RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Surrealismo TriplevDocument13 pagesSurrealismo TriplevVictor LunaNo ratings yet
- Researching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureDocument1 pageResearching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureJithin gtNo ratings yet
- Weekly Capital Market Report Week Ending 22.07.2022 2022-07-22Document2 pagesWeekly Capital Market Report Week Ending 22.07.2022 2022-07-22Fuaad DodooNo ratings yet
- CV HannahDocument3 pagesCV HannahRoxan DosdosNo ratings yet
- Sponsor A Child With E-Tuition 2022Document19 pagesSponsor A Child With E-Tuition 2022nuur xiemaNo ratings yet
- Target products to meet 20% demandDocument12 pagesTarget products to meet 20% demandAlma Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For American Pageant Volume 1 16th EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For American Pageant Volume 1 16th Editionzoonwinkfoxyj8100% (48)
- Water As A Weapon - Israel National NewsDocument11 pagesWater As A Weapon - Israel National NewsJorge Yitzhak Pachas0% (1)
- Integrate Payments Direct Post APIDocument31 pagesIntegrate Payments Direct Post APIAnjali SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Case of Haemochromatosis and Diabetes A Missed OpportunityDocument111 pagesA Case of Haemochromatosis and Diabetes A Missed Opportunitymimran1974No ratings yet
- NEW HOLLAND - Trucks, Tractor & Forklift Manual PDDocument14 pagesNEW HOLLAND - Trucks, Tractor & Forklift Manual PDAjjaakka0% (2)
- Time To Get SeriousDocument354 pagesTime To Get SeriousEdmond Blair100% (1)
- Learning, Perception, Attitudes, Values, and Ethics: Fundamentals of Organizational Behavior 2eDocument21 pagesLearning, Perception, Attitudes, Values, and Ethics: Fundamentals of Organizational Behavior 2eJp AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Types of Motivation in Language LearningDocument8 pagesTypes of Motivation in Language LearningAlya IrmasyahNo ratings yet
- Free Easy Autopilot BTC Method 2Document4 pagesFree Easy Autopilot BTC Method 2Adderall 30MG XRNo ratings yet
- Anne Frank Halloween Costume 2Document5 pagesAnne Frank Halloween Costume 2ive14_No ratings yet
- Landman Training ManualDocument34 pagesLandman Training Manualflashanon100% (2)
- Agility Logistics SolutionsDocument5 pagesAgility Logistics SolutionsWagner MontielNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Purpose - TitusDocument46 pagesModule 2 - The Purpose - TitusEnp Titus VelezNo ratings yet