Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 4
Chap 4
Uploaded by
sharmine adiba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageADS514 MIND MAP
Original Title
CHAP 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentADS514 MIND MAP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageChap 4
Chap 4
Uploaded by
sharmine adibaADS514 MIND MAP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
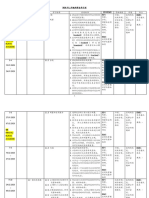
1.
To plan for the best possible course of action
Policy Forecasting among the various alternatives which the future may 1. Quantitative methods: Time Series, Regression
Analysis
offer
Process of predicting future direction / action - Method that relies on hard data / statistics and
towards a problem (policy agenda): 2. To use the past and present situation to determine statistical model to predict and project future
- What kind of option is suitable to solve a the future states of a problem. direction
particular policy problem? Problem Process
- What action to take? – new policy, 3. To shape the future in an active manner in relations 2. Qualitative Methods (Judgmental)
modifying policy, terminating policy to what has happened in the past. - Methods that relies on the opinions and judgments
of human being (individual or group of panel) to
predict future direction.
- The panels make decision based on their expert
judgment (knowledge, personal experience, and
intuition)
Purpose of Methods of
Forecasting Forecasting
Definition of
Terms 1. In-accuracy of info / data
2. Data is expensive & difficult to
access
CHAPTER 4 : 3. Limitation of forecasting methods
POLICY and techniques
1. Inducement: either positive such as tax 4. Invalid expert opinion
FORECASTING &
credit holiday or negative in nature such as 5. Personal bias
FORMULATION
fines and charges impose for pollution. 6. In-accuracy of forecast
2. Regulatory: to control and regulate Problems of
behavior of people such as regulation Types / Category
Forecasting
governing pollution. of Policy Options
3. Enforcement: involves giving (enforcing) - Process of formulating (drafting) /
certain people rights or duties they deserve. Policy developing acceptable courses of action
Formulation / options for the selected policy agenda
For example, human rights legislation.
4. Allocation of power: where certain body - It involves 2 main elements/ activities
is charged with power to improve certain
situation, e.g. Parliamentary legislations,
executive orders, judicial decisions etc
5. Distributive: extends goods and services
to members of an organization as well as Authorization Analysis
distributing the cost of the goods among the -At this stage, assuming the course of action is In deciding which courses of action / policy
members of the organization. able to resolve problem and is cost effective, option to choose for a selected policy agenda,
E.g. government policies that impact now the political actor / policy maker will be policy maker (administrators) will be doing 2
spending for welfare, public education, deciding on which policy recommendation / main tasks:
highway and public safety causes of action proposed to be accepted / i. Analyzing the courses of action
authorized. ii. Deciding which type / category of policy
- This is done through political process (first option to introduce
reading)
You might also like
- 二年级科学全年教学计划Document19 pages二年级科学全年教学计划TEO KIA YING Moe100% (1)
- 2023年三年级科学全年教学计划Document10 pages2023年三年级科学全年教学计划CHANG MIN JING KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 公共政策課本考點摘要筆記Document138 pages公共政策課本考點摘要筆記Lan HsiehNo ratings yet
- TTQS訓練機構版指標課程大綱Document3 pagesTTQS訓練機構版指標課程大綱Ekiane WangNo ratings yet
- 公共政策Document83 pages公共政策姚立國No ratings yet
- ㅁㅊㅇㅁㅇㅈㅂㅈㅇDocument14 pagesㅁㅊㅇㅁㅇㅈㅂㅈㅇElaine TianNo ratings yet
- RPT Y2 SainsDocument15 pagesRPT Y2 SainsYIN KAI YI MoeNo ratings yet
- 2020年2年级科学全年计划 PDFDocument8 pages2020年2年级科学全年计划 PDFShu YiNo ratings yet
- SN T2Document19 pagesSN T2WONG SONG JIE MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter8:政策評估Document48 pagesChapter8:政策評估bca543785No ratings yet
- PMP答题套路及关键词整理 -于秀 2020版Document11 pagesPMP答题套路及关键词整理 -于秀 2020版ZhanKun YangNo ratings yet
- SN Tahun 2 RPTDocument11 pagesSN Tahun 2 RPTArics ChiengNo ratings yet
- 838fad08-b053-4f76-8ee1-efc505146340Document9 pages838fad08-b053-4f76-8ee1-efc505146340666 happyNo ratings yet
- RPT SN Tahun 2 KSSR SemakanDocument10 pagesRPT SN Tahun 2 KSSR SemakanSiew YinNo ratings yet
- PMP 工具与技术Document18 pagesPMP 工具与技术Qian GuoNo ratings yet
- 2024-2025 二年级科学全年教学计划Document18 pages2024-2025 二年级科学全年教学计划Jenny ChoungNo ratings yet
- 4 环境分析与理性决策Document57 pages4 环境分析与理性决策wuyang254029No ratings yet
- 2022 運用資料分析輔助內部稽核Document87 pages2022 運用資料分析輔助內部稽核ALEX JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- 二年级科学全年计划Document6 pages二年级科学全年计划陈惠任No ratings yet
- 临床监查心得体会Document8 pages临床监查心得体会炟炟No ratings yet
- 2. 三年级科学全年教学计划Document10 pages2. 三年级科学全年教学计划Arics ChiengNo ratings yet
- 六年级科学全年教学计划Document12 pages六年级科学全年教学计划LOW KAH YEE MoeNo ratings yet
- 6年级科学全年教学计划Document15 pages6年级科学全年教学计划LAU TZE SHENG MoeNo ratings yet
- 2年级科学全年教学计划Document9 pages2年级科学全年教学计划g-80130228No ratings yet
- 六年级科学全年教学计划Document20 pages六年级科学全年教学计划Richard Hughes100% (1)
- 第1章計畫作業Document12 pages第1章計畫作業Weichiann YangNo ratings yet
- Lo 2Document10 pagesLo 2berhanezemichaelNo ratings yet
- 三年级科学全年计划Document15 pages三年级科学全年计划Jenny ChoungNo ratings yet
- 老年人能力评估系统可视化设计策略研究 许晓云Document7 pages老年人能力评估系统可视化设计策略研究 许晓云yanny songNo ratings yet
- TTQS企業機構版指標課程大綱Document3 pagesTTQS企業機構版指標課程大綱Ekiane WangNo ratings yet
- 三年级全年教学计划Document10 pages三年级全年教学计划TAN LEE MING MoeNo ratings yet
- 如何做一名出色的部门经理Document28 pages如何做一名出色的部门经理SeanNo ratings yet
- 六年级科学全年教学计划2021Document12 pages六年级科学全年教学计划2021sc sungaiduaNo ratings yet
- Y6 科学全年计划Document20 pagesY6 科学全年计划Lee Ai FangNo ratings yet
- 2019年二年级科学全年教学计划Document12 pages2019年二年级科学全年教学计划Li Ting77% (48)
- 06第六课 教育调查(问卷调查法)PptDocument18 pages06第六课 教育调查(问卷调查法)PptShiMin MoonNo ratings yet
- 2019年三年级科学全年教学计划KSSR SemakanDocument10 pages2019年三年级科学全年教学计划KSSR SemakanTKN100% (10)
- 2020- 6年级科学全年教学计划Document21 pages2020- 6年级科学全年教学计划Amanda LawNo ratings yet
- 六年级科学全年教学计划.docx · 版本 1Document14 pages六年级科学全年教学计划.docx · 版本 1hunNo ratings yet
- 二年级科学全年计划Document14 pages二年级科学全年计划Jenny ChoungNo ratings yet
- 第二章 作业治疗评定Document50 pages第二章 作业治疗评定Joan YangNo ratings yet
- 4 语文教学研究的基本方法之一 行动研究Document11 pages4 语文教学研究的基本方法之一 行动研究cheng khNo ratings yet
- T3 SCDocument9 pagesT3 SCsjkcsanmin 芙蓉三民华小No ratings yet
- 附件5 执行依据样板Document7 pages附件5 执行依据样板rip1971No ratings yet
- 六年级科学全年计划 KSSR SEMAKANDocument15 pages六年级科学全年计划 KSSR SEMAKANTONG LI XIANG MoeNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains THN3Document16 pagesRPT Sains THN3PBD AIKTHEENo ratings yet
- 三年级科学全年教学计划Document9 pages三年级科学全年教学计划Kai Hui TanNo ratings yet
- 提议的研究方法论Document15 pages提议的研究方法论afoddlkrjjapgw100% (1)
- 五年级科学全年计划Document21 pages五年级科学全年计划sjkcyeokcheeNo ratings yet
- 数据安全改进大致方案Document2 pages数据安全改进大致方案vontinqinNo ratings yet
- 教育研究:1 目的、特征、方法Document6 pages教育研究:1 目的、特征、方法WONGNo ratings yet
- T3 SainsDocument12 pagesT3 SainsWong DylanNo ratings yet
- 比較政府一課程介紹與研究途徑20210927Document12 pages比較政府一課程介紹與研究途徑20210927Anderson LinNo ratings yet
- SN Tahun 1 RPT 2023 2024 LKLDocument6 pagesSN Tahun 1 RPT 2023 2024 LKLkuoklinNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning On Medical ImageDocument15 pagesDeep Learning On Medical ImageJUN WENNo ratings yet
- 行动研究Document9 pages行动研究Sarah LeeNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Tahun 2 2024Document12 pagesRPT Sains Tahun 2 2024santanjeffNo ratings yet
- 大数据治理的概念及其参考架构Document8 pages大数据治理的概念及其参考架构汪凡No ratings yet
- 2022年2年级科学全年教学计划Document11 pages2022年2年级科学全年教学计划CHUAH HERNG WEN MoeNo ratings yet