Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Biologi F4 (Answers) #
Uploaded by
irdina qistinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Biologi F4 (Answers) #
Uploaded by
irdina qistinaCopyright:
Available Formats
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
JAWAPAN
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
ANSWER
1 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 1 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Unit Pengenalan kepada Biologi dan Peraturan Makmal 1.4
1 Introduction to Biology and Laboratory Rules Membuat hipotesis
Making a hypothesis
1.1
1 Genetik / Genetics Mengenal pasti dan
Mengumpul dan merekod
2 Sitologi / Cytology data
mengawal pemboleh ubah
Identifying and controlling
3 biologi / biology Collecting and recording data
variables
5 struktur / structure
6 penyakit / disease
Menganalisa dan mentafsir
7 Biokimia / Biochemistry data
Membuat kesimpulan
Making conclusions
8 Ekologi / Ecology Analysing and interpreting data
10 mikroorganisma / microorganisms
Rangka Laporan / Framework of a Report
1.2 • Pernyataan masalah
1 Problem statement
• Bahan dan Radas
Materials and Apparatus
• Prosedur
Procedure
• Pemerhatian / Keputusan
Observation / Results
• Perbincangan
Discussion
2 Larutan DCPIP Klorofom Unit Biologi Sel dan Organisasi Sel
3 7
DCPIP solution Chloroform
2 Cell Biology and Organisation
Ampaian yis Bahan sisa organik 2.1
3 7
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Yeast suspension Organic waste 1
Sisa pepejal Merkuri
7 7
Solid waste Mercury b Membran plasma
Plasma membrane
Bahan buangan Larutan metilena biru
c Sentriol
radioaktif 7 Methylene blue 3 Centrioles
Radioactive waste solution d Jalinan endoplasma kasar
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
3 (a) Sisa tajam / Sharp waste e Mitokondrion
(b) Kertas tisu, sarung tangan, piring petri Mitochondrion
f i
Tissue paper, glove, petri dish Sitoplasma Jalinan endoplasma licin
Cytoplasm Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
beg plastik autoklaf bio bahaya g h j
Ribosom Lisosom Jasad Golgi
autoclave biohazard plastic beg Ribosome Lysosome Golgi apparatus
(d) Cecair / Liquids
1.3
dimanipulasi / Manipulated
bergerak balas / Responding b Jalinan endoplasma licin
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
c
1 Satah sagital Satah frontal Satah melintang Dinding sel
Cell wall
Sagittal plane Frontal plane Tranverse plane
d Membran plasma
Plasma membrane
2 Keratan membujur Keratan rentas / melintang
e Vakuol
Longitudinal section Cross section Vacuole
g Mitokondrion f
3 Mitochondria Kloroplas
Chloroplast
Superior
Anterior Posterior
Ventral Dorsal
Lateral
Lateral
Inferior
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 2
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 2 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
SPM K3 3 Peta pemikiran / I-think map
(a) Sitoplasma Nukleus
Cytoplasm Nucleus
Mempunyai
Has
Membran sel
Cell membrane Tiada
Nukleus Dinding sel Sitoplasma No
Nucleus Cell wall Cytoplasm
Sel A / Cell A Sel B / Cell B
(b) Sampel Jenis sampel
Sample Type of sample
Mempunyai Mempunyai
Has Has
A Sel haiwan / Animal cell
B Sel tumbuhan / Plant cell
(c) Sel pipi / Cheek cell
1. Kikis bahagian dalam pipi secara perlahan-lahan
menggunakan sebatang pencungkil gigi. Mempunyai
Gently scrape the inside of the cheek with toothpick. Has
2. Pindahkan kikisan dalam titisan air suling di atas slaid kaca
dan tutup slaid kaca tersebut dengan penutup slaid kaca.
Transfer the scrapping into a drop of water on the glass slide and
cover with cover slip.
Tiada
3. Warnakan sel pipi dengan larutan metilena biru No
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
menggunakan penitis.
Stain the cheek cell with methylene blue solution using a dropper.
4. Pastikan tiada gelembung udara terbentuk di dalam slaid.
Make sure no air bubble formed in the slide.
Sel bawang / Onion cell 2.2
1. Potong bawang menjadi sampel lapisan nipis dengan 1
T Sitoplasma
menggunakan skalpel. P Cytoplasm
Nukleus
Cut the onion into a sample of thin layer using a scalpel. Nucleus U Membran plasma
2. Letakkan sampel ke atas slaid B dan titiskan air suling. Plasma membrane
Q Vakuol mengecut
Put the sample onto the slide B and drop a distilled water.
Contractile vacuole
3. Dengan berhati-hati, letakkan penutup kaca ke atas sampel V Vakuol makanan
R Lisosom Food vacuole
dengan menggunakan forsep. Lysosome
Carefully lower the cover slip onto the sample using forceps.
S
4. Pastikan tiada gelembung udara terbentuk di dalam slaid. Pseudopodium
Pseudopodium
Make sure no air bubble formed in the slide.
5. Titiskan larutan iodin pada tepi penutup kaca dan kertas
pseudopodium / pseudopodium
turas.
belahan dedua / binary fission
Drop iodine solution on one side of the slip and filter paper on
another side.
spora / spores
6. Gunakan kertas turas untuk menyerap iodin dan larutan membran plasma; mengecut; berlebihan
berlebihan di sekitar penutup kaca. plasma membrane; contractile; excess
Use filter paper to absorb excess iodine and solution around the pseudopodium / pseudopodium
cover slip. melingkungi; fagositosis / engulf; phagocytosis
(d) Sel bawang mempunyai bentuk yang teratur manakala sel pipi vesikel makanan; lisosom / food vacuole; lysosome
mempunyai bentuk yang tidak teratur. Enzim hidrolitik; glukosa / Hydrolytic enzymes; glucose
Onion cell has regular shape while cheek cell has irregular shape. sitoplasma / cytoplasm
Atau / Or resapan / diffusion
Sel bawang mempunyai dinding sel manakala sel pipi tidak rangsangan; menuju; jauh / stimulus; towards; away
mempunyai dinding sel.
Onion cell has cell wall while cheek cell do not has cell wall. Proses kehidupan Penerangan
(e) Tidak. Kloroplas tidak boleh diperhatikan dalam sel epidermis Living process Explanation
bawang kerana sel epidermis tidak menjalankan fotosintesis.
No. Chloroplasts can’t be observed in the epidermal cells of onions Habitat Di dalam kolam air tawar
because epidermal cells do not carry out photosynthesis. Habitat In fresh water ponds
3 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 3 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
tisu-tisu saraf untuk merawat penyakit Alzheimer dan Parkinson dan
• Di dalam keadaan sesuai, Paramecium
penghasilan otot-otot jantung baru untuk merawat masalah jantung.
sp. menjalani belahan dedua.
Stem-cell research is a research that is carried out on stem cells for use in
In a favourable condition, Paramecium sp.
medicine. The research is important in treating diseases. The stem cells can
carries out binary fission.
be used in treating blood cancer such as leukaemia and replacing damaged
• Di dalam keadaan tidak sesuai,
tissues and organs. For examples, the production of nerve tissues to treat
Paramecium sp. membiak secara
Pembiakan dan Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease and producing new heart muscles to treat
seksual yang dikenali sebagai
pertumbuhan heart problem.
konjugasi.
Reproduction and growth
In unfavourable condition, Paramecium sp.
reproduces sexually known as conjugation. 3 (ii) cahaya
• Paramecium sp. membesar dengan light
menggunakan nutrien yang diperolehi.
Paramecium sp. grows by using nutrients (iii) enzim; hormon
obtained. enzymes; hormones
• Bahan kumuh disingkirkan secara
resapan ringkas dan eksositosis AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
melalui membran plasma. Gangguan mitokondria disebabkan oleh mutasi yang berlaku kepada
Waste products are excreted by simple DNA mitokondria yang menyebabkan ianya gagal berfungsi untuk
diffusion and exocytosis across the plasma menghasilkan tenaga. Untuk terbang, seekor burung memerlukan
membrane. otot pektralis major dan minor untuk mengecut. Namun, apabila
• Ia mempunyai dua vakuol mengecut anak burung tersebut gagal menghasilkan lebih banyak tenaga, otot-
yang mengawal atur kandungan air otot tersebut tidak dapat mengecut dan mengendur. Oleh itu, anak
dalam sel. burung tersebut tidak dapat terbang.
Perkumuhan dan It has two contractile vacuoles which Mitochondrial disorder is caused by mutations in the mitochondrial DNA
pengosmokawalaturan regulate the water content in the cell.
that cause the mitochondria fail to generate energy. To fly, a bird requires the
Excretion and • Air akan memasuki vakuol mengecut
pectoralis major and minor muscles to contract and relax. However, when the
osmoregulation secara osmosis.
nestling fails to produce more energy, the muscles are not able to contract and
Water enters the contractile vacuoles by
relax. Therefore, the nestling cannot fly.
osmosis.
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
• Vakuol mengecut akan mengembang
sehingga mencapai saiz maksimum 2.4
dan seterusnya mengecut untuk
menyingkirkan air berlebihan. 2 Sistem
The contractile vacuoles expanded until peredaran
they reach a maximum size and later Sistem darah Sistem rangka Sistem saraf
contract to expel the excess water. System Blood Skeletal system Nervous system
circulatory
• Pukulan silia menggerakkan makanan system
ke dalam sitostoma.
The beating of cilia moves the food particle Jantung, salur
into cytostome. Organ / Tisu darah Tulang Otak
• Di dalam sitostoma, vakuol makanan Organs / Tissues Heart, blood Bones Brain
yang mengandungi makanan vessels
terbentuk.
Pemakanan
In the cytostome, food vacuoles containing nutrien, rangsangan,
Feeding
food are formed. hormon sokongan, impuls saraf,
• Makanan dicernakan oleh enzim Fungsi nutrient, dalaman gerak balas
dan nutrien yang terhasil meresap ke Function hormone support, stimuli,
dalam sitoplasma. bahan kumuh internal impulse,
The foods are digested by enzymes and waste substances responses
the nutrient produced diffuse into the
cytoplasm. Sistem Sistem
Sistem respirasi Sistem urinari pencernaan
System Respiratory Urinary system Digestive
2.3
system system
2 Tisu saraf Tulang ginjal, pundi Mulut,
Nerve tissue Bone
Organ / Tisu hidung, trakea kencing pankreas
Organs / Tissues nose, trachea kidneys, Mouth,
Tisu sklerenkima Tisu meristem Tisu xilem
bladder pancrease
Sclerenchyma tissue Meristematic tissue Xylem tissue
oksigen,
kompleks,
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY karbon
Fungsi urea nutrien
Penyelidikan sel stem adalah satu penyelidikan yang dijalankan ke dioksida
Function urea complex,
atas sel-sel stem untuk kegunaan perubatan. Penyelidikan ini adalah oxygen,
nutrients
penting untuk merawat sesuatu penyakit. Sel-sel stem ini boleh carbon dioxide
digunakan untuk merawat pesakit kanser darah seperti leukemia dan
menggantikan tisu dan organ yang rosak. Contohnya, penghasilan
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 4
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 4 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
SOALAN ESEI / ESSAY QUESTIONS
Sistem 1 (a) 1. Habitat. Di dalam kolam air tawar
Sistem limfa
Sistem Sistem otot endokrin Habitat. In fresh water ponds
Lymphatic
System Muscular system Endocrine 2. Pergerakan / Bergerak secara pukulan silium yang
system
system beritma yang membolehkan Paramecium sp. bergerak
ke hadapan secara berputar di paksinya.
Salur limfa Movement. Moves by means of the rhythmic beating of the
Organ / Tisu Otot rangka Kelenjar
Lymphatic cilia which enables the Paramecium sp. to move forward
Organs / Tissues Skeletal muscles Glands
vessels while rotating along its axis.
3. Pembiakan dan pertumbuhan
pengecutan, Reproduction and growth.
Fungsi pengenduran hormon penyakit Pembiakan secara belahan dedua dalam keadaan
Function contraction, hormones diseases sesuai dan secara konjugasi dalam keadaan tidak
relaxation sesuai.
Reproduce by binary fission in the favourable condition and
Sistem Sistem by conjugation in unfavourable condition.
pembiakan pembiakan Sistem 4. Perkumuhan dan pengosmokawalaturan. Bahan
Sistem lelaki perempuan integumen kumuh dibuang secara resapan ringkas dan eksositosis
System Male Female Integumentary melalui membran plasma dengan bantuan vakoul.
reproductive reproductive system Excretion and osmoregulation. Waste products are excreted by
system system simple diffusion and exocytosis across the plasma membrane
with the help of vacoules.
Organ / Tisu uterus Kulit 5. Pemakanan / Makanan dicernakan oleh enzim dan
Organs / Tissues uterus Skin nutrien yang terhasil di dalam vakoul makanan dan ia
meresap ke dalam sitoplasma.
Fungsi sperma ovum kecederaan Feeding. The foods are digested by enzymes and the
Function sperms ovum injuries nutrient produced in the food vacoules and it diffuse into the
cytoplasm.
(b) (i) Amoeba sp.
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise P : Vakoul mengecut / Contractile vacoule
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Q : Pseudopodium / Pseupodium
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS R : Membran plasma / Plasma membrane
1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 C 6 C (ii) Struktur Q membantu untuk Amoeba sp. bergerak.
Amoeba sp. akan bergerak menghampiri makanan
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS dengan pseudopodium. Kemudian, ia akan
1 (a) Selulosa / Cellulose mengunjurkan pseudopodium untuk melingkungi
(b) Mengawal kandungan air di dalam sel untuk membolehkan makanan melalui fagositosis. Makanan yang
sel sentiasa berkeadaan segah. Ini memberikan sokongan dibungkus dalam vesikel makanan bergabung
kepada tumbuhan herba. dengan lisosom. Enzim hidrolitik dalam lisosom
Controls the water content of the cells to enable the cells to always
menghidrolisiskan atau mencernakan zarah makanan
be turgid. This gives support to the herbaceous plants.
kepada nutrien seperti glukosa dan asid amino.
(c) Nutrien tersebut diserap ke dalam sitoplasma untuk
metabolisme.
Structure Q helps Amoeba sp. to move. Amoeba sp.
S approaches food by pseudopodium. Then, it extends its
pseudopodium to engulf the food by phagocytosis. The food
is packed into food vacuole fuses with lysosome. Hydrolytic
enzymes in the lysosome hydrolyse or digest food particles
into nutrients such as glucose and amino acids. The nutrients
2 (a) 2: Tisu / Tissue are absorbed into cytoplasm for metabolism.
3: Organ / Organ
(b) Pembezaan / Differentiation
(c) Struktur tersebut adalah otot licin. Tisu ini mengecut dan
Pergerakan Bahan Merentasi Membran Plasma
Unit
Movement of Substances Across a Plasma
mengendur untuk membolehkan peristalsis berlaku di 3 Membrane
dalam salur pencernaan.
The structure is smooth muscle. The tissue contracts and relaxes to 3.2
allow peristalsis to occur in the digestive tract.
(d) (i) Sistem pencernaan / Digestive system Peta pemikiran / I-think map
(ii) Mulut, hati, pankreas, usus kecil [mana-mana dua] 1 Asid lemak dan
gliserol / Fatty acid
Mouth, liver, pancrease, small intestine [any two] and glycerol
Bahan
(e) Sel dalam Rajah 2 tidak mempunyai kloroplas, tetapi sel Substances
Seperti Seperti
As Besar dan larut As
tumbuhan mempunyai kloroplas. Sel dalam Rajah 2 tidak lemak / Large
mempunyai dinding sel, tetapi sel tumbuhan mempunyai and lipid soluble
dinding sel.
Cell in Diagram 2 does not have chloroplast, but a plant cell has Air Asid amino
Water Amino acid
chloroplast. Cell in Diagram 2 does not have cell wall, but a plant Bahan
cell has cell wall. Substances
Seperti Seperti
Kecil dan berkutub As As Besar dan berkutub
Small and polar Large and polar
5 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 5 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
2 Asid lemak dan 1 Pengangkutan pasif / Passive transport:
gliserol / Fatty acid tinggi; rendah / high; low
and glycerol
Bahan
Substances
Seperti
As
Seperti
As
Pengangkutan aktif / Active transport:
Resapan ringkas
Simple diffusion
rendah; tinggi; / low; high
A Resapan ringkas / Simple diffusion
Air Asid amino tinggi; rendah; menuruni; dinamik
Water Amino acid high; low; down; dynamic
Bahan
Substances
Seperti Seperti
As As
Osmosis Resapan berbantu B Osmosis / Osmosis
Osmosis dan pengangkutan
aktif air; tinggi; rendah; menuruni; dinamik
Facilitated water; high; low; down; dynamic
and active transport
C Resapan berbantu / Facilitated diffusion
SPM K3 tinggi; rendah; protein pembawa
high; low; carrier protein
2 Masa (minit)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Time (minutes) D Pengangkutan aktif / Active transport
menentang; molekul ATP; protein pembawa; fosfat; bentuk
Aras larutan sukrosa (mm) against; ATP molecule; carrier protein; phosphate; shape
0 6 12 20 24 32 38
Level of sucrose solution (mm)
3 AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
Aras sukrosa (mm) / Level of sucrose (mm)
Herbisid akan memusnahkan enzim ATPase di dalam sel. Enzim
ATPase penting di dalam memangkinkan penguraian ATP kepada
ADP dan fosfat tak organik. Tanpa enzim ini, pengangkutan aktif
40 tidak dapat berlaku kerana tiada ion fosfat yang akan bergabung
dengan tapak aktif protein pembawa untuk membolehkannya
35
berubah bentuk dan membantu pergerakan garam mineral ke dalam
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
sel tumbuhan rumpai.
Herbicide destroys the ATPase enzymes in the cell. The ATPase enzymes
30 are important in catalysing the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and non-organic
phosphate. Without the enzyme, active transport cannot occur as there is no
phosphate ion to bind with the binding site of the carrier protein to allow it to
25
change its shape and assist the movement of mineral salts into the cells of the
weed plants.
20
Peta pemikiran / I-think map
15
keseimbangan pengumpulan;
protein
dinamik penyingkiran
10 pembawa
dynamic accumulation;
carrier protein
equilibrium elimination
5
0 Masa (minit)
2 4 6 8 10 12 Time (minutes)
membran plasma
4 Aras larutan sukrosa dalam kapilari tiub meningkat seiring the plasma membrane
dengan masa.
The level of sucrose solution in the capillary tube rises with time.
5 Aras larutan sukrosa / Level of sucrose solution
6 • Molekul air di dalam bikar meresap masuk ke dalam tiub
visking
Water molecules diffuses into the Visking tube tenaga tenaga
sel hidup
• Secara osmosis / By osmosis daripada ATP daripada ATP
living cells
• Melalui membran telap memilih energy from ATP energy from ATP
Through selectively permeable membrane
7 • Aras air di dalam tiub Visking akan berkurangan dari semasa
ke semasa.
The water level in the capillary tube will decrease over time. menuruni menentang
• Tiub Visking menjadi lembik dan isipadu air akan menurun. down against
The Visking tubing will become soft and the volume of water will
decrease.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 6
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 6 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
3.3 C
1 • tinggi; kapilari darah; resapan ringkas sama; mengekalkan
higher; the blood capillary; simple diffusion same; retains
• tinggi; alveolus; resapan ringkas 5 A
higher; the alveolus; simple diffusion osmosis; segah
2 • tinggi; osmosis osmosis; turgid
higher; osmosis B
keluar dari; mengecut; plasmolisis; deplasmolisis
out of; shrinks; plasmolysis; deplasmolysis
3 Larutan hipotonik keupayaan air
C
Hypotonic solution water potential
sama; mengekalkan
Larutan isotonik zat terlarut same; retains
Isotonic solution solute molecules
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
Larutan hipertonik keupayaan air; zat terlarut Air bersifat hipotonik terhadap sel-sel di bahagian dalam lada
Hypertonic solution water potential; solute molecules tersebut. Molekul air akan meresap masuk ke bahagian dalam secara
osmosis. Bahagian luar lada mempunyai lapisan berlilin yang tidak
membenarkan resapan air ke dalam sel-sel di bahagian tersebut. Sel-
SPM K3 sel di bahagian dalam menjadi segah dan menyebabkan lada
7 Kepekatan larutan natrium klorida membengkok ke luar.
The concentration of sodium chloride solution Water is hypotonic towards the cells of the inner part of the chillies. Water
8 Untuk mengelakkan darah ayam daripada beku molecules diffuse into the inner part by osmosis. The outer part of the chillies
To prevent the chicken blood from clotting has waxy layer which does not allow water to diffuse into the cells. Cells in the
9 Larutan hipotonik: Air suling inner part become turgid and cause the chillies to bend outward.
Hypotonic solution: Distilled water 3.4
Larutan isotonik: Larutan natrium klorida 0.8% EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
Isotonic solution: 0.8% sodium chloride solution Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
Larutan hipertonik: Larutan natrium klorida 5% Apakah kepekatan larutan yang isotonik terhadap sap sel tisu
Hypertonic solution: 5% sodium chloride solution tumbuhan?
10 Keadaan sel darah ayam pada akhir eksperimen What is the concentration of solution which is isotonic to cell sap of plant
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
The condition of red blood cell at the end of experiment tissues?
11
Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
B
C Kepekatan larutan yang isotonik terhadap sap sel tisu tumbuhan
(larutan
(larutan 5% adalah kepekatan yang tidak menyebabkan perubahan jisim pada tisu
Sel darah A 0.8%
natrium tumbuhan tersebut.
Slaid merah (air suling) natrium The concentration of solution which is isotonic to the plant tissues is the
klorida)
Slide Red blood (distilled klorida ) concentration which does not cause any changes in the mass of the plant
(5% sodium
cell water) (0.8% sodium tissues.
chloride
chloride solution)
solution) Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Kepekatan larutan sukrosa
Kembang Manipulated variable: The concentration of the sucrose solution
Bentuk Tidak
Pemerhatian dan pecah Mengecut Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Perubahan jisim tisu ubi kentang
normal berubah
Observation Expand and Shrink Responding variable: Changes in the mass of the potato tissue
Normal shape Not changed
burst Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu larutan sukrosa
Constant variable: The volume of the sucrose solution
Lakaran
bentuk sel Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
darah merah Hipotesis diterima.
Red blood cell Hypothesis is accepted.
sketch
hipertonik; keluar; osmosis; plasmolisis; layu
12 • Air suling adalah hipotonik kepada sel darah merah hypertonic; out of the; osmosis; plasmolysed; wilt
Distilled water is hypotonic to the red blood cell.
• Air meresap masuk ke dalam sel darah merah
Water diffuses into the red blood cell Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
• Sel darah merah mengalami hemolisis. SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Red blood cell undergoes hemolysis. 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 B 5 B 6 D
7 D 8 A 9 A 10 D
4 A
ke dalam; osmosis; membran plasma; mengembang; meletus; SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
hemolisis 1 (a) (i) Membran plasma / Plasma membrane
into; osmosis; plasma membrane; expands; bursts; haemolysis (ii) Separa telap / Telap memilih
B Partially permeable / Selectively permeable
keluar dari; mengecut; krenasi (iii) M: Protein liang / Channel protein
out of; shrinks; crenation N: Dwilapisan fosfolipid / Phospholipid bilayer
7 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 7 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(b) Asid lemak / Gliserol / Oksigen / Karbon dioksida / Air /
Disakarida
Vitamin A, D, E, K.
Disaccharides
Fatty acids / Glycerol / Oxygen / Carbon dioxide / Water / Vitamins
A, D, E, K.
• Glikogen
(c) Pengangkutan aktif / Active transport Glycogen
2 (a) 5% – 3 • Selulosa
(b) Larutan Y adalah bersifat hipotonik terhadap sel darah Cellulose
merah. Molekul air meresap ke dalam sel secara osmosis.
Sel akan mengembang dan seterusnya meletus disebabkan • paling ringkas • monosakarida • monosakarida
ketiadaan dinding sel. simplest monosaccharide monosaccharides
Solution Y is hypotonic towards the red blood cells. Water molecules • Larut • maltosa • Glikogen
diffuse into the cells by osmosis. The cells expanded and later burst Dissolve maltose Glycogen
due to the absence of cell wall. • penurun • sukrosa • Selulosa
3 (a) Tumbuhan akan layu. Baja berlebihan akan menyebabkan reducing sucrose Cellulose
air tanah bersifat hipertonik terhadap sel akar tumbuhan • laktosa
tersebut. Molekul air dari sel akar meresap keluar secara lactose
osmosis. Ini menyebabkan sel-sel tumbuhan tersebut • Maltosa; laktosa
menjadi flasid. Maltose; lactose
The plant will wilt. Excess fertiliser makes the soil water be • Sukrosa
hypertonic to the root cells of the plant. Water molecules from the Sucrose
root cells diffuse out by osmosis. This causes the cells of the plants
to be flaccid. AKTIVITI / ACTIVITY
(b) Dinding sel Pemerhatian / Observation:
Cell wall biru; merah bata / blue; brick-red
Vakuol Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
Vacuole
menurunkan; merah bata / reduce; brick red
Nukleus 4.3
Nucleus
oksigen (O); nitrogen (N); polipeptida; asid amino
Membran plasma oxygen (O); nitrogen (N); polypeptide; amino acid
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Plasma membrane
Peta pemikiran / I-think map
Sitoplasma
Cytoplasm
Membaiki
Repair Mensintesis
Synthesise
Unit Komposisi Kimia dalam Sel
4 Chemical Compositions in a Cell
4.1
hidrogen; oksigen
hydrogen; oxygen
Atom hidrogen
H H
Atom oksigen O Hydrogen atom pembahagian
Oxygen atom sel
cell division
hidrogen
Hydrogen
H
δ– O
δ+ H 4.4
H H hidrofobik; pelarut organik; polimer
O O hydrophobic; organic solvents; polymers
H H
2 Lilin / Wax; Fosfolipid / Phospholipid; Steroid / Steroids
1 molekul berkutub; separa negatif; separa positif; hidrogen;
pelarut semesta • satu molekul; tiga molekul
bipolar; partially negative; partially positive; hydrogen; universal solvent Lemak one molecule of; three molecules of
2 tinggi; 4 200 J; menyerap; memecahkan; mengekalkan Fats • tepu; tak tepu
high; 4 200 J; absorbing; break; maintaining saturated; unsaturated
3 hidrogen; lekitan; lekatan; mengangkut air
Hydrogen; cohesive; adhesive; transporting water Lilin • alkohol; asid lemak
Wax alcohol; fatty acid
4.2 Fosfolipid • hidrofilik; hidrofobik
karbon (C); hidrogen (H); oksigen (O); (CH2O)n Phospholipid hydrophilic; hydrophobic
carbon (C); hydrogen (H); oxygen (O); (CH2O)n
Steroid • jenis
Steroids types
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 8
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 8 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
3 (c) (i) Molekul air tidak ditunjukkan. Air merupakan
Peta pemikiran / I-think map substrat dalam proses hidrolisis dan merupakan hasil
dalam proses kondensasi.
The molecule of water is not shown. Water is the substrate for
hydrolysis process and product in condensation process.
trigliserida satu (ii) Dua asid amino bergabung menjadi dipeptida melalui
triglyceride one
kondensasi dengan menghasilkan satu molekul air.
Asid amino bergabung dengan dipeptida dengan
proses yang sama dan proses ini diulangi sehingga satu
polipeptida terbentuk.
gliserol; asid Two amino acids are combined to become dipeptide through
condensation by producing one water molecule. Amino acids
lemak
combine with dipeptide by the same process and repeated until
glycerol; fatty
one polypeptide is formed.
acids
(iii) Ribosom / Ribosome
(d) 1 Sebagai enzim / As enzyme
2 Sebagai antibodi / As an antibody
2 (a) (i) Selulosa / Cellulose
rantai (ii) Glukosa / Glucose
tinggi rendah
hidrokarbon (iii) Selulosa terbentuk daripada ratusan monomer yang
high low
hydrocarbon chains dikenali sebagai glukosa melalui proses kondensasi.
Cellulose are formed by hundreds monomers, known as
glucose through condensation process.
(b) (i) Ikatan hidrogen yang terbentuk antara molekul air
Pepejal Cecair menghasilkan daya lekitan, manakala ikatan hidrogen
Solid Liquid yang terbentuk antara molekul air dengan permukaan
lain berpolar menghasilkan daya lekatan.
Hydrogen bonds formed among water molecules generates
4 kondensasi; hidrolisis / condensation; hydrolysis a cohesive force, whereas hydrogen bonds formed between
water molecules and polar surface generate an adhesive
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
4.5 force.
1 asid deoksiribonukleik; nitrogen (N); fosforus (P); dua; satu; (ii) Air adalah pelarut terbaik bagi bahan tak organik.
monomer; bes bernitrogen Garam mineral dapat terlarut dalam air. Garam
deoxyribonucleic acid; ribonucleic acid; nitrogen (N); phosphorus (P);
mineral membentuk ikatan dengan molekul air.
two; one; monomer; nitrogenous base
Apabila air diangkut dalam salur xilem dari akar ke
pucuk, mineral yang terlarut dalam air juga diangkat
2 Kumpulan fosfat bersama.
Phosphate group
Water is the best solvent for inorganic materials. Mineral
Bes bernitrogen salts can be dissolved in water. Mineral salts form bonds with
Nitrogenous base
water molecules. When water is transported through the xylem
channel from root to tip, the water-soluble minerals are lifted
Ribosa atau deoksiribosa together.
Ribose or deoxyribose
(c) (i) Nukleotida / Nucleotides
3 guanina; sitosina; timina (ii) DNA terdiri daripada dua rantai yang berpintal,
guanine; cytosine; thymine membentuk struktur heliks ganda dua.
DNA consists of two spiral strands, forming a double helix
4 urasil / uracil
structure.
Struktur RNA / Structure of RNA
satu / one
ribosom / Ribosomal Unit Metabolisme dan Enzim
pemindah / Transfer 5 Metabolism and Enzymes
5.1
1 RNA pengutus / messenger RNA
2 penguraian / breaking down
ribosom; polipeptida / Ribosomal; polypeptide
pembentukan / forming
ciri-ciri / characteristics
2 kromatin; kromosom / chromatin; chromosome
5.2
1 pemangkin biologi; mempercepatkan
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise biological catalyst; speeds up
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS 2
1 B 2 C 3 D 4 B 5 D 6 B
7 B 8 C 9 C 10 B Sukrase Laktase Protease Lipase Amilase Selulase
Sucrase Lactase Protease Lipase Amylase Cellulase
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
2 (a) M: Hidrolisis / Hydrolysis 3 (a) kecil / small
N: Kondensasi / Condensation (b) terurai / broken down
(b) Monomer / Monomer: Asid amino / Amino acids (c) spesifik / specific
Polimer / Polymer: Polipeptida / Polypetides
9 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 9 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(d) berbalik / reversible EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
(e) pH; suhu / pH; temperature Kesan suhu ke atas tindak balas enzim.
(f) kofaktor / cofactors Effect of temperature on the enzymatic reactions.
(g) perencat / inhibitors
4 nukleus; mRNA; ribosom; jasad Golgi; rembesan; membran Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
plasma Apakah kesan suhu ke atas aktiviti amilase air liur terhadap kanji?
nucleus; mRNA; ribosome; transport; Golgi apparatus; secretory; plasma What are the effects of temperature on the activity of salivary amylase on
membrane starch?
5 mangga dan kunci; kunci; mangga; tapak aktif; kompleks enzim-
substrat; hasil; tidak berubah Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
lock and key; key; lock; active site; enzyme-substrate complex; products; Aktiviti enzim amilase air liur adalah paling tinggi pada suhu
unchanged optimum 37 °C.
6 The activity of salivary amylase is the highest at the optimum temperature of
37 °C.
Kepekatan substrat
Substrate concentration Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Suhu medium tindak balas
Manipulated variable: Temperature of the reaction
Kepekatan enzim Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kadar tindak balas enzim
pH Responding variable: Rate of enzymatic reaction
Enzyme concentration
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu air liur, isi padu ampaian kanji,
kepekatan ampaian kanji, pH medium tindak balas
Suhu / Temperature Constant variable: Volume of saliva, volume of starch suspension,
• rendah / low concentration of starch suspension, pH of the reaction
• meningkat; kinetik; perlanggaran; enzim-substrat
increases; kinetic; collision; enzyme-substrate Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
• tinggi / highest Enzim amilase air liur paling aktif pada suhu 37 °C. Enzim ini tidak
• menurun; ternyahasli; terurai; tapak aktif; enzim-substrat aktif pada suhu 0 °C dan ternyahasli pada suhu 60 °C.
decreases; denatured; broken down; active site; enzyme-substrate Salivary amylase is very active at 37 °C. The enzyme is inactive at temperature
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY of 0 °C and denatured at temperature of 60 °C.
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
(i) Baju akan rosak // terbakar
The dress will be damaged // burned EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
(ii) Sutera adalah protein. Suhu yang tinggi akan menyebabkan Kesan pH ke atas tindak balas enzim.
Effect of pH on the enzymatic reactions.
protein dinyahasli. Ini menyebabkan struktur protein akan
terurai / berubah bentuk.
Silk is protein. High temperature will cause the protein to be denatured. Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
This causes the structure of the protein will be destroyed / changed. Apakah kesan pH terhadap aktiviti pepsin?
What is the effect of pH on the activity of pepsin?
pH / pH
• optimum / Optimum Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
• ternyahasli; tapak aktif ; enzim-substrat Pepsin aktif dalam medium berasid (pH 1.5-2.5).
denatured; active site; enzyme-substrate Pepsin is active in an acidic medium ( pH 1.5-2.5).
• 2
Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
• 7
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: pH medium tindak balas
• 8.5
Manipulated variable: pH of medium of reaction
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kejernihan larutan
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
Responding variable: Clarity of solution
(i) Dengan menambahkan asid hidroklorik.
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu dan kepekatan ampaian
By adding hydrochloric acid.
albumen, isi padu dan kepekatan larutan pepsin, suhu medium tindak
(ii) Asid hidroklorik ditambah kerana pepsin bertindak paling aktif
balas
dalam medium berasid. Oleh itu, hidrolisis albumen berlaku
Constant variable: Volume and concentration of albumen suspension, volume
dengan lebih cepat seterusnya mempercepatkan pengurangan and concentration of pepsin solution, temperature of medium
panjang jalur albumen tersebut.
Hydrochloric acid is added because pepsin reacts the most active in
Keputusan / Results:
acidic medium. Therefore, hydrolysis of albumen occurs faster and
therefore speeds up the decreases in the length of the albumen strip.
Keruh Jernih
P
Cloudy Clear
Kepekatan substrat / Substrate concentration
• tinggi; tapak aktif; enzim-substrat Keruh Keruh
Q
higher; active sites; enzyme-substrate Cloudy Cloudy
• perlahan; tapak aktif; pengehad
low; active sites; limiting Keruh Keruh
R
Cloudy Cloudy
Kepekatan enzim / Enzyme concentration
• tinggi; tapak aktif ; enzim-substrat Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
higher; active sites; enzyme-substrate Medium berasid merupakan medium yang paling sesuai untuk pepsin
• perlahan; substrat berfungsi dengan efisien.
low; substrate An acidic medium is the most suitable medium for pepsin to function efficiently.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 10
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 10 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
5.3
2 Profasa / Prophase
kanji / starch pendek; tebal; sentromer; nukleolus
Amilase shorter; thicker; centromere; nucleolus
Amylase
kain / fabrics Metafasa / Metaphase
Protease / Protease rerambut / hair satah khatulistiwa; Gentian gelendong
metaphase plate; spindle fibres
Laktase / Lactase laktosa / lactose
Anafasa / Anaphase
Pektinase / Pektinase pektin / pectin
membahagi; kromosom anak; kutub bertentangan;
memeram / ripen pengecutan
Lipase divides; daughter chromosomes; opposite poles; contraction
Lipase
lemak / lipid
Telofasa / Telophase
panjang; halus; Membran nukleus; nukleolus; Dua;
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise kromosom; genetik
long; thin; nuclear membrane; nucleolus; Two; chromosomes;
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
genetic
1 D 2 A 3 C 4 A 5 C
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
3 Sitokinesis dalam sel haiwan
2 (a) Molekul / Molecule P: Maltosa / Maltosa Cytokinesis in animal cells
Molekul / Molecule Q: Glukosa / Glucose
(b) Kompleks maltase-maltosa / Maltase-maltose complex mikrofilamen; mengecut; gelang pencerutan
(c) I. Tidak berubah di akhir tindak balas. microfilament; contract; cleavage furrow
Does not change at the end of the reaction.
II. Tindakan enzim adalah amat spesifik. Sitokinesis dalam sel tumbuhan
The action of enzyme is highly specific. Cytokinesis in plant cells
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
(d) Kunci / Key: Molekul P // Maltosa / Molecule P // Maltose Vesikel; plat sel; membran plasma; Dinding sel
Mangga / Lock: Enzim // Maltase / Enzyme // Maltase vesicles; cell plate; plasma membrane; cell wall
(e) Kadar tindak balas menurun dan lalu berhenti. Suhu
melebihi 60 °C menyebabkan enzim dinyahasli. Ikatan-
ikatan yang membentuk enzim terurai. Oleh itu, bentuk AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
tapak aktif akan berubah menyebabkan substrat tidak boleh (a) Kebun A. Anak-anak pokok dihasilkan secara pembiakan
melekat padanya. seks yang melibatkan persenyawaan gamet. Terdapat variasi
The rate of reaction decreases and then stops. The temperature pada anak-anak pokok. Oleh itu, anak-anak pokok tersebut
above 60 °C causes the enzyme to be denatured. The bonds that mempunyai daya rintangan terhadap penyakit yang berbeza
form enzyme break down. Therefore, the shape of the active site will serta dapat menyesuaikan diri dengan perubahan yang berlaku
change and disable the substrates to bind to it. di persekitaran. Ini dapat memastikan anak-anak pokok tersebut
dapat hidup dengan lebih lama.
Farm A. The plantlets are produced by sexual reproduction which
involves fertilisation of gametes. There are varieties of plantlets produced.
Unit Pembahagian Sel Therefore, the plantlets have resistance towards different diseases as well
6 Cell Division as able to adapt to the changes in the environment. This will ensure the
plantlets can live longer.
6.1 (b) 1. Pilih tumbuhan yang mempunyai daya rintangan terhadap
Kromosom homolog / Homologous chromosomes pelbagai jenis penyakit.
• struktur; maklumat genetik / structure; genetic information Choose a plant that is resistant to various types of diseases.
• soma / somatic 2. Pilih tumbuhan yang telah diubah suai secara genetik.
Choose a plant which has been genetically modified.
6.2 3. Pilih tumbuhan yang mempunyai daya rintangan yang
tinggi terhadap racun serangga dan racun rumpai.
1 Interfasa Fasa M Choose a plant that has high resistant to insecticides and pesticides.
Interphase M phase
• baharu; protein • mitosis; sitokinesis 6.3
new; protein mitosis; cytokinesis 1 gamet; separuh
• kromatin / chromatin • profasa; metafasa; anafasa; gametes; half
• Replikasi; kromatid telofasa
kembar prophase; metaphase;
Replication; sister chromatids anaphase; telophase
• enzim; protein • sitoplasma
enzymes; proteins cytoplasm
11 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 11 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
2
diploid Mitosis / Mitosis Meiosis / Meiosis
diploid
soma / Somatic pembiakan / reproductive
pertumbuhan; mati gamet
growth; dead gametes
gamet variasi profasa I / prophase I
gametes variation
profasa I / prophase I
3 Meiosis I Dua / Two
Profasa I / Prophase I sama / similar separuh / half
Pindah silang; kiasma; nukleolus Berbeza / Different
Crossing over; chiasmata; nucleolus
Tidak berlaku / Not occur
Metafasa I / Metaphase I
satah khatulistiwa; sentromer 6.4
metaphase plate; centromere 1 (a) • tidak terkawal; tidak berfungsi; mutasi; abnormal; tumor
uncontrolled; not function; mutation; abnormal; tumor
Anafasa I / Anaphase I
• malignan; kanser / barah; nutrien; maut
kromosom homolog; kutub bertentangan; gentian malignant; cancerous; nutrients; death
gelendong • benigna / benign
homologous chromosomes; opposite poles; spindle fibres
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
Telofasa I / Telophase I
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
kutub bertentangan; nukleolus; haploid 1 B 2 A 3 B 4 B 5 C 6 B
opposite poles; nucleolus; haploid
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
Meiosis II
1 (a) (i) Q: Sentromer / Centromere
Profasa II / Prophase II R: Kromosom / Chromosome
S: Membran nukleus / Nuclear membrane
menghilang / disappear T: Membran plasma / Plasma membrane
(ii) Menyimpan maklumat // bahan genetik
Metafasa II / Metaphase II
Store genetic information // material
satah khatulistiwa / metaphase plate (b) (i) Mitosis / Mitosis
(ii) I. Menambahkan bilangan sel untuk membolehkan
Anafasa II / Anaphase II pertumbuhan berlaku.
Increase the number of cells to allow growth to occur.
kromosom anak; kutub bertentangan; gentian gelendong
daughter chromosomes; opposite poles; spindle fibre II. Menggantikan sel-sel yang telah mati.
Replace dead cells.
Telofasa II / Telophase II III. Membaiki tisu-tisu rosak.
Repair injured tissues.
kutub bertentangan; kromatin; muncul semula
(c) (i) 2
opposite poles; chromatin; reappear
(ii) 4
Empat; berlainan
Four; different 2 (a) Sel P / Cell P: Mitosis
Sel Q / Cell Q: Meiosis
4 • diploid / diploid (b) Sel P / Cell P
• nukleus; sitoplasma I. Menambahkan bilangan sel untuk membolehkan
nucleus; cytoplasm pertumbuhan berlaku.
• replikasi / replication Increase the number of cells to allow the growth to occur.
II. Mengganti sel-sel yang telah mati.
Replace dead cells.
III. Membaiki tisu-tisu rosak.
Repair injured tissues.
Sel Q / Cell Q
I. Menghasilkan gamet.
Produce gametes.
II. Menghasilkan variasi.
Produce variation.
III. Mengekalkan bilangan kromosom dalam zigot.
Maintain the number of chromosomes in a zygote.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 12
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 12 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(c) Sel P / Cell P: Metafasa / Metaphase Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
Sel Q / Cell Q: Metafasa I / Metaphase I Gas oksigen digunakan dalam proses respirasi aerob.
(d) Di dalam sel P, setiap kromosom tersusun di satah Oxygen gas is used in aerobic respiration process.
khatulistiwa, manakala di dalam sel Q, pasangan kromosom
Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
homolog tersusun di satah khatulistiwa.
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Keadaan biji benih
In cell P, each chromosome align at the metaphase plate, while in
cell Q, the homologous chromosomes pairs align at the metaphase Manipulated variable: Condition of germinating seeds
plate. Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kehadiran oksigen
Responding variable: Presence of oxygen
(e) Kutub bertentangan Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Suhu kukus air
Opposite pole Constant variable: Temperature of water bath
Prosedur / Procedure:
Kromosom anak 1 Sediakan susunan radas seperti rajah di atas.
Daughter chromosome Prepare set-up of apparatus as shown in the diagram above.
2 Tandakan titik mula pada tiub kapilari di mana penanda berada.
Mark initial points where the markers are.
3 Perhatikan pergerakan penanda dalam tiub kapilari.
Observe the movement of markers in the capillary tubes.
4 Hentikan eksperimen apabila kedua-dua penanda telah berhenti
Sel P / Cell P
bergerak.
Stop the experiment when both markers stop to move.
Kromatid kembar 5 Tandakan titik akhir penanda.
Sister chromatids Mark final points where the markers are.
6 Catatkan jarak pergerakan penanda.
Record the distance moved by the markers.
7 Ujikan kehadiran gas oksigen pada kedua-dua tabung didih
dengan menggunakan kayu uji menyala.
Test the presence of oxygen in both boiling tubes with burning wooden
splinter.
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Sel Q / Cell Q 8 Catatkan pemerhatian anda.
Record your observation.
Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
Unit Respirasi Sel Gas oksigen diperlukan dalam proses respirasi aerob.
7 Cellular Respiration Oxygen gas is needed in aerobic respiration process.
7.1
7.3
2
1 menguraikan; oksigen
Fermentasi breaking down; oxygen
Fermentation 2 tidak lengkap; sitoplasma
incomplete; cytoplasm
• oksigen; • Menguraikan; • tidak lengkap; 3 manusia / human
glukosa; karbon karbon dioksida; oksigen
dioksida tenaga incompletely; 4 Asid laktik / Lactic acid:
oxygen; glucose; Break down; oxygen
Glukosa + Air
carbon dioxide carbon dioxide; ➝
Glucose Water
energy
• Sel otot manusia
Human muscle cells
7.2
• Lactobacillus
1 Glukosa; glikolisis
Glucose; glycolysis Alkohol / Alcohol:
2 ATP
3 mitokondrion / mitochondrion Etanol + Karbon dioksida +
➝
Ethanol Carbon dioxide
4 dioksidakan; karbon dioksida
oxidised; carbon dioxide
5 mitokondrion EKSPERIMEN TIDAK BERPANDU / UNGUIDED EXPERIMENT
mitochondrion Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
6 Apakah hasil respirasi anaerob dalam yis?
Glukosa + + Air + ATP What are the products of anaerobic respiration in yeast?
➝
Glucose Water ATP
Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT Yis menghasilkan karbon dioksida, etanol dan tenaga apabila
Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement: menjalankan respirasi secara anaerob.
Apakah gas yang digunakan dalam proses respirasi aerob? Yeast produces carbon dioxide, ethanol and energy when it carries out
What is the gas used in aerobic respiration process? anaerobic respiration.
13 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 13 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Pemboleh ubah / Variables: (b) Bakteria Lactobacillus ditambahkan ke dalam susu dan
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Kehadiran yis ditutup dengan ketat. Dalam keadaan tanpa oksigen,
Manipulated variable: The presence of yeast Lactobacillus menukarkan glukosa dalam susu kepada asid
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Perubahan pada air kapur / Suhu laktik. Kehadiran asid laktik akan menukarkan susu kepada
larutan minuman yogurt.
Responding variable: Changes in the lime water / Temperature of the solution Lactobacillus bacteria are added to milk and tightly closed. In the
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Keadaan anaerob absence of oxygen, Lactobacillus converts glucose in milk to lactic
Constant variable: Anaerobic condition acid. The presence of lactic acid will convert milk to yogurt drinks.
(c) Dalam keadaan tanpa oksigen, yis menjalankan fermentasi
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: alkohol dengan menukarkan glukosa kepada alkohol dan
Tanpa oksigen, yis berespirasi secara anaerob dan menghasilkan karbon dioksida. Penghasilan karbon dioksida membentuk
karbon dioksida, etanol dan tenaga. rongga dalam adunan roti.
Without oxygen, yeast respire anaerobically and produces carbon dioxide, In the absence of oxygen, yeast carry out alcohol fermentation by
ethanol and energy. converting glucose to alcohol and carbon dioxide. The production of
carbon dioxide forms a cavity in the bread dough.
(d) (i) T
Peta pemikiran / I-think map (ii) U
Respirasi aerob / Aerobic respiration:
Penguraian glukosa secara lengkap
Complete breakdown of glucose
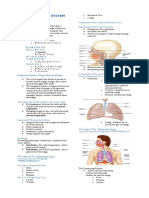
Unit Sistem Respirasi dalam Manusia dan Haiwan
Fermentasi / Fermentation: 8 Respiratory Systems in Humans and Animals
Tanpa oksigen / Without oxygen
8.1
Berlaku di sitoplasma / Occurs in cytoplasm
Menghasilkan sedikit ATP / Produce less ATP 1
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise Seperti Seperti Seperti
As Trakeol As Filamen dan As Kulit dan peparu
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS Tracheoles lamela insang Skin and lungs
1 D 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 B 6 C Filaments and
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
7 D 8 D gills lamellae
2
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
1 (a) (i) M: Glikosis / Glycolysis
luas permukaan
N: Fermentasi / Fermentation surface area
(ii) Membolehkan organisma atau sel dalam organisma
dapat berfungsi buat sementara dalam keadaan tanpa
oksigen.
Allow the organism or cell in the organism to function
temporarily in an oxygen-free state. lembap; melarut pertukaran gas
(b) P diangkut ke dalam mitokondrion melalui resapan Moist; dissolve exchange of gases
berbantu. P diangkut menurun kecerunan kepekatan
dengan protein pengangkut.
P is transported into the mitochondrion through facilitated diffusion. 3
P is transported down the concentration gradient with the transport
protein. Manusia Serangga Amfibia
(c) (i) Karbon dioksida dan air. Human Insect Amphibian
Carbon dioxide and water.
(ii) P dioksidakan dengan membebaskan karbon dioksida. Alveolus Kulit dan peparu
T menerima hidrogen dan diturunkan menjadi air. Alveoli Skin and lungs
Dalam pengoksidaan P, tenaga dihasilkan dalam
Tiada
bentuk S.
None
P is oxidised by releasing carbon dioxide. T accept hydrogen
and reduced into water. In oxidation of P, energy is produced Dinding dalam peparu
in the form of S.
berlipat-lipat dan kulit
(d) (i) P akan ditukarkan menjadi asid laktik dalam Bilangan alveolus Bilangan trakeol yang berpermukaan
sitoplasma sel otot. yang banyak yang banyak besar
P is converted into lactic acid in the cytoplasm of muscle Numerous alveoli Numerous tracheoles The inner wall of the lung
cells.
is folded and the skin
(ii) P akan ditukarkan kepada etanol dan karbon dioksida with large surface area
dalam sitoplasma sel yis.
P is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide in the
cytoplasm of yeast cell. 8.2
2 (a) Fermentasi asid laktik dan fermentasi alkohol 1 (a) Tarikan nafas / Inhalation
Asid lactic and alcohol fermentation ❶ mengecut / contract
❷ mengecut; mendatar / contract; flattens
❸ atas; luar / upwards; outwards
❹ menambahkan; berkurang / increases; decrease
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 14
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 14 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(b) Hembusan nafas / Exhalation 2 • tercerai; oksigen / dissociates; oxygen
❶ mengendur / relax • tinggi; oksigen / higher; oxygen
❷ mengendur; atas / relax; upwards • respirasi sel / cellular respiration
❸ bawah; dalam / downwards; inwards • tinggi; resapan ringkas / higher; simple diffusion
❹ mengurangkan; bertambah / decreases; increase 3 • hemoglobin; oksihemoglobin / haemoglobin; oxyhaemoglobin
ion bikarbonat / bicarbonate ions
2 Trakeol / Tracheol
karbaminohemoglobin / carbaminohaemoglobin
• banyak; luas permukaan / N umerous; surface area
karbon dioksida / carbon dioxide
• nipis; resapan / Thin; diffusion
Tarikan nafas / Inhalation 8.4
• mengendur / relax paru-paru; emfisema / lungs; emphysema
• berkurang / decreases
• spirakel / spiracles Bronkitis kronik / Chronic bronchitis
Keradangan; batuk / inflammation; coughing
Hembusan nafas / Exhalation
• mengecut / contract Emfisima / Emphysema
• bertambah / increases kekenyalan; mengurangkan / elasticity; reduces
• keluar / out
3 Insang / Gills Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
• lamela; nipis; luas permukaan SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
thin; lamella; surface area 1 A 2 A 3 C 4 A
Tarikan nafas / Inhalation
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
• menurun / lowers
1 (a) (i) Gas X: Oksigen / Oxygen
• tertutup; bertambah; berkurang
Gas Y: Karbon dioksida / Carbon dioxide
closes; increase; decreases
(ii) • Mempunyai dinding nipis untuk membolehkan
• oksigen / oxygen
proses pertukaran gas yang cepat.
Hembusan nafas / Exhalation Have thin wall to allow rapid exchange of gases.
• menaik / rises • Permukaan lembap untuk membolehkan oksigen
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
• terbuka; berkurang; bertambah / opens; decrease; increase dan karbon dioksida melarut.
Moist surface to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to
4 Peparu / Lungs dissolve.
• berlipat-lipat / f olded • Dikelilingi jaringan kapilari darah untuk
• nipis; lembap / thin; moist mengangkut gas dengan lebih berkesan.
Surrounded by a network of blood capillaries to transport
Kulit / Skin more efficient gases.
• nipis; lembap / thin; moist (b) Tekanan separa gas Y adalah lebih tinggi berbanding
• kapilari darah / blood capillaries tekanan separa gas X dalam salur darah Q. Gas X adalah
Tarikan nafas / Inhalation rendah kerana telah digunakan oleh sel-sel badan untuk
• lubang hidung; diturunkan; tertutup respirasi sel yang menghasilkan karbon dioksida. Justeru,
nostrils; lowered; closes tekanan separa gas Y adalah lebih tinggi di salur Q untuk
• berkurang / decreases diangkut ke alveolus untuk disingkirkan.
The partial pressure of gas Y is higher than the partial pressure of
• terbuka; dinaikkan / opens; raised
gas X in blood vessel Q. Gas X is low because it has been used by
• bertambah; peparu / increases; lungs
body cells for cellular respiration which produces carbon dioxide.
Hembusan nafas / Exhalation Therefore, the partial pressure of gas Y is high in blood vessel Q to
• mengecut; keluar / contract; out be transported to alveoli to be expelled.
• tertutup / closes 2 (a) Kedua-dua mempunyai permukaan yang lembap untuk
membolehkan oksigen dan karbon dioksida melarut.
Both have moist surface to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
dissolve.
Ikan belacak akan membesarkan ruang insangnya dan
(b) • Asap rokok mengandungi haba yang tinggi. Ini akan
memenuhkannya dengan air. Apabila berada di darat, ia bergantung
mengeringkan permukaan struktur X. Justeru, oksigen
kepada “tangki oksigen” ini untuk membekalkan darah dengan
tidak boleh melarut.
oksigen. Ia juga boleh bernafas melalui kulit yang lembap yang Cigarette smokes contains a lots of heat. This will dry up the
mengandungi jaringan kapilari darah yang kompleks. surface of structure X. Therefore, oxygen cannot be dissolved.
The mudskippers enlarge their gill chambers and fill them with water. Once on
• Tar dalam asap rokok akan berkumpul di dinding dalam
land, they rely on these “oxygen tanks” to supply their blood with oxygen. They
alveolus dan mengurangkan luas permukaan untuk
can also breathe through their moist skin that contains a complex network of
blood capillaries. pertukaran gas. Ini menyebabkan pertukaran gas berlaku
secara perlahan.
Tar in cigarette smoke accumulates in the inner wall of the
8.3 alveoli and reduces the surface area for gases exchange. This
1 • melarut / d issolves causes exchange of gases to occur slowly.
• tinggi; meresap / higher; diffuses
• hemoglobin; oksihemoglobin / haemoglobin; oxyhaemoglobin
• tinggi; meresap / higher; diffuses
15 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 15 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(c) Mekanisme ini dikenali sebagai tukar ganti lawan arus. Ia 5 Hati / Liver
memaksimakan pertukaran gas kerana air mengalir melalui hempedu; pundi hempedu
insang pada satu arah, manakala darah mengalir pada bile; gallbladder
arah yang bertentangan. Resapan gas berlaku pada seluruh
Pundi hempedu / Gallbladder
filamen insang.
duktus hempedu / bile duct
The mechanism is known as counter current exchange. It maximises
the exchange of gases as water flows over the gills in one direction, Duodenum / Duodenum
while blood flows in the opposite direction. Diffusion of gases • lemak; asid lemak; gliserol / fats; fatty acids; glycerol
occurs along all gill filaments.
• polipeptida; peptida / polypeptides; peptides
(d) Mekanisme pernafasan yang ditunjukkan adalah
mekanisme hembusan nafas. Dasar rongga mulut Pankeras / Pancreas
dinaikkan untuk mengurangkan isi padu rongga mulut amilase pankreas; tripsin; lipase; duktus pankreas
dan meningkatkan tekanan di dalamnya. Pada masa yang pancreatic amylase; trypsin; lipase; pancreatic duct
sama, ruang operkulum menjadi kecil dan ianya terbuka. Ini
Usus kecil / Small intestine
membolehkan air mengalir keluar melalui operkulum.
• laktosa / lactose
The breathing mechanism shown is an exhalation process. The floor
of the mouth cavity is raised to lower the volume of the mouth cavity • sukrosa; glukosa / sucrose; glucose
and increase the pressure in it. At the same time, the operculum • peptida; asid amino / peptides; amino acids
cavity becomes smaller and it is open. This allows water to flow out
through the operculum. AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN / REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
Dia dinasihatkan untuk mengurangkan pengambilan makanan
berlemak. Apabila pundi hempedunya dibuang, jus hempedu tidak
dapat disimpan dan dirembeskan ke duodenum. Oleh itu, lemak di
Unit Nutrisi dan Sistem Pencernaan Manusia dalam duodenum tidak dapat diemulsifikasi menjadi titisan lemak
9 Nutrition and the Human Digestive System dan menyebabkan luas permukaan bagi tindakan enzim ke atas lemak
9.1 tersebut adalah kecil. Akibatnya, pencernaan lemak tidak dapat
1 berlaku dengan lengkap.
He is advised to reduce the fatty food intake. When the gallbladder is removed,
bile cannot be stored and secreted to the duodenum. Therefore, lipid in the
Mulut duodenum cannot be emulsified into tiny droplets of lipid and causes the
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Mouth surface area for the enzyme action on the lipid to be small. As a result,
digestion of lipid is incomplete.
Esofagus
Oesophagus EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
Hati Kanji / Starch
Liver Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
Enzim amilase air liur menghidrolisiskan kanji kepada gula penurun.
Duodenum Salivary amylase hydrolyzes starch into reducing sugar.
Duodenum
Pundi hempedu Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
Gallbladder Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Kehadiran enzim amilase air liur
Manipulated variable: The presence of salivary amylase
Usus besar Perut
Large intestine Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kehadiran gula penurun
Stomach
Responding variable: The presence of reducing sugar
Ileum Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Suhu
Ileum Constant variable: Temperature
Rektum
Rectum Bahan / Materials:
Ampaian kanji 1%, air liur, air suling, larutan Benedict, larutan iodin
Dubur 1% starch suspension, saliva, distilled water, Benedict solution, iodine solution
Anus
Radas / Apparatus:
9.2 Tabung uji, penitis, penunu Bunsen, pemegang tabung uji, penitis,
termometer, kasa dawai, rod kaca, bikar 250 ml dan tungku kaki tiga.
1 mekanikal; luas permukaan
Test tubes, Bunsen burner, test tube holder, thermometer, wire gauze, glass rod,
mechanical; surface area
250 ml beaker and tripod stand.
2 diangkut; hidrolisis
transported; hydrolysis
Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
3 amilase air liur; maltosa
Enzim amilase air liur menghidrolisiskan kanji kepada gula penurun.
salivary amylase; maltose
Salivary amylase hydrolyzes stach into reducing sugar.
4 Sel mukus / Mucous cell
mukus; asid hidroklorik EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
mucus; hydrochloric acid
Protein / Protein
Sel parietal / Parietal cell Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
asid hidroklorik; berasid; pepsin Pepsin menghidrolisiskan protein dalam medium berasid.
hydrochloric acid; acid medium; pepsin Pepsin hydrolyzes protein in an acidic medium.
Sel utama / Chief cell
pepsinogen; pepsin; polipeptida
pepsinogen; pepsin; polypeptide
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 16
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 16 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Pemboleh ubah / Variables: 2
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Kehadiran enzim pepsin Makanan tercerna
Manipulated variable: The presence of pepsin Digested food
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Keadaan campuran selepas 20 minit Seperti Seperti
As As
Responding variable: The condition of the mixture after 20 minutes Pengangkutan Resapan berbantu
Proses terlibat
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Suhu Process involved aktif Facilitated
Active transport diffusion
Constant variable: Temperature
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: Makanan tercerna Air
Digested food Water
Pepsin menghidrolisiskan protein dalam medium berasid.
Pepsin hydrolyzes protein in an acidic medium. Seperti Seperti
As As
Pengangkutan Diserap bersama Osmosis
Proses terlibat
aktif air / Absorbed Osmosis
EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT Process involved
Active transport with water
Lemak / Fats
Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
Makanan tercerna
Enzim lipase menghidrolisiskan lemak kepada asid lemak dan Digested food
gliserol. Seperti
Lipase hydrolyzes fat into fatty acid and glycerol. Proses terlibat Resapan ringkas As Resapan ringkas
Process involved Simple diffusion Simple diffusion
Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Kehadiran enzim lipase 9.4
Manipulated variable: The presence of lipase 1 I. vena portal hepar; hati; asimilasi
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Perubahan warna kertas litmus hepatic portal vein; liver; assimilation
Responding variable: Changes in the colour of litmus paper II. sel-sel badan / body cells
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Suhu III. salur limfa; duktus toraks; vena subklavian kiri
Constant variable: Temperature lymphatic vessels; thoracic duct; left subclavian vein
2 Penyahtoksinan / Detoxification
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: toksik / toxic
Enzim lipase menghidrolisiskan lemak kepada asid lemak dan
gliserol. Sintesis protein plasma / Synthesis of plasma protein
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Lipase hydrolyzes fat into fatty acid and glycerol. Asid amino; enzim / Amino acids; enzyme
Penyimpanan nutrien / Storage of nutrients
9.3 glukosa; glikogen / glucose; glycogen
Microvilli
Lakteal Microvilli Pendeaminan / Deamination
Lacteal
asid amino; urea / amino acids; urea
Sel epitelium
Epithelial cell
Kapilari darah 9.5
Blood capillary
Sel goblet / Sel mukus 1 kolon; rektum; dubur / colon; rectum; anus
Goblet cell / Mucous cell
2 serat; peristalsis / fibers; peristalsis
Arteri 3 aliran darah / blood stream
Artery Kelenjar usus
Intestinal gland 4 tinja / faeces
5 sel-sel mati; pigmen hempedu; bahan toksik
Salur limfa Vena dead cells; bile pigments; toxic substances
Lymphatic vessel Vein
6 mukus / mucus
7 rektum / rectum
1 Terdapat lakteal dalam setiap vilus untuk mengangkut titisan 8 dubur; penyahtinjaan / anus; defaecation
asid lemak dan gliserol.
Lacteal are present in each vilus to transport drops of fatty acids and 9.6
glycerol. 1 tujuh; nisbah / seven; proportions
Bersaiz panjang untuk pencernaan yang lebih lama dan 2 tenaga / energy
penyerapan nutrien yang lebih baik
The size is long for longer digestion and better absorption of nutrients Peta pemikiran / I-think map
Banyak kapilari darah di dalam vilus untuk memudahkan
Tujuh kelas makanan / Seven classes of food
pengangkutan hasil pencernaan.
Lots of blood capillaries in the villi to facilitate the transportation of
digestive products. Protein Karbohidrat Lipid Garam mineral
Protein Carbohydrate Lipids Minerals salt
Serat Air Vitamin
Dietray fibres Water Vitamins
3 • gram; dioksidakan / gram; oxidised
• kilojoule per gram (kJ g–1); kalori (kal)
kilojoules per gram (kJ g–1); calories (cal)
17 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 17 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kandungan vitamin C
Menentukan nilai tenaga dalam sampel makanan Responding variable: Vitamin C content
Determining the energy value of the food sample Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu larutan DCPIP
Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement: Constant variable: Volume of DCPIP solution
Apakah nilai tenaga dalam kacang gajus dan kacang tanah? Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
What is the energy value of a cashew nut and a peanut?
Pada suhu tinggi, kandungan vitamin C jus buah-buahan adalah
Hipotesis / Hypothesis: rendah.
Kacang tanah mempunyai nilai tenaga yang lebih tinggi berbanding At high temperature, the vitamin C content of fruit juices is low.
gajus.
Peanut contains higher energy value than cashew nut.
1 Punca Obesiti Kesan Obesiti
Pemboleh ubah / Variables: Cause of Obesity Effect of Obesity
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Jenis sampel makanan
Manipulated variable: Type of food sample Kurang bersenam Kolestrol tinggi
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Nilai tenaga Lack of exercise High cholestrol
Responding variable: Energy value
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu air Genetik Tekanan darah tinggi
Constant variable: Volume of water Genetic High blood pressure
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: Cara hidup tidak sihat Kencing manis
Hipotesis diterima. Kacang tanah mempunyai nilai tenaga yang lebih Unhealthy lifestyle Diabetes
tinggi berbanding gajus.
Hypothesis is accepted. Peanut contains higher energy value than cashew nut.
9.7
EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT
Menentukan kandungan vitamin C jus buah-buahan. 1 gaster; berat badan / Gastric; weight
Determining the vitamin C content of fruit juices. 2 pengecilan; pembedahan / reducing; surgical
Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
Gastritis / Gastritis
Antara jus betik, nanas dan limau, yang manakah mengandungi
kepekatan vitamin C yang lebih tinggi? lapisan epitelial perut; asid hidroklorik
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Among papaya, pineapple and lime juices, which one contains a higher stomach epithelial lining; hydrochloric acid
concentration of vitamin C?
Anoreksia nervosa / Anorexia nervosa
Hipotesis / Hypothesis:
Jus limau mengandungi kepekatan vitamin C yang lebih tinggi makan; kurus / eating; thin
berbanding jus betik dan nanas.
Lime juice has a higher concentration of vitamin C compared to papaya and Bulimia nervosa / Bulimia nervosa
pineapple juices.
memuntahkannya semula / purging
Pemboleh ubah / Variables:
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Jenis jus buah-buahan Dismorfia otot / Muscle dysmorphia
Manipulated variable: Type of fruit juices
kecil; tidak cukup / small; underdeveloped
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas: Kepekatan vitamin C
Responding variable: Vitamin C concentration
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan: Isi padu larutan DCPIP
Constant variable: Volume of DCPIP solution Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Hipotesis diterima. Jus limau mengandungi kepekatan vitamin C yang 1 A 2 A 3 C 4 D 5 D
lebih tinggi berbanding jus nanas dan betik.
Hypothesis is accepted. Lime juice has a higher vitamin C concentration SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
compared to pineapple and papaya juices. 1 (a) Penyerapan / Absorption
(b) Berdinding nipis iaitu setebal satu sel / Mengandungi
EKSPERIMEN BERPANDU / GUIDED EXPERIMENT banyak kapilari darah / Mengandungi lakteal
Mengkaji kesan suhu ke atas kandungan vitamin C jus buah- Thinned wall which is one cell thick / Contain lots of blood
buahan atau sayur-sayuran. capillaries / Contain a lacteal
Studying the effect of temperature on the vitamin C content in fruit juices or (c) Salur P / Vessel P: Vena portal hepar / Hepatic portal vein
vegetables. Salur Q / Vessel Q: Salur limfa / Lymphatic vessels
(d) Kepekatan glukosa dalam salur P lebih tinggi daripada
Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement:
dalam salur Q. Glukosa diangkut ke dalam kapilari darah
Apakah kesan suhu terhadap kandungan vitamin C jus buah-buahan?
What is the effect of temperature on the vitamin content of fruit juices?
lalu ke hati melalui salur P. Manakala salur R mengangkut
lipid dari usus kecil dan limfa dari bendalir tisu.
Hipotesis / Hypothesis: The concentration of glucose in vessel P is higher than in vessel Q.
Pada suhu tinggi, kandungan vitamin C jus buah-buahan adalah Glucose is transported into blood capillary then to liver via vessel P.
rendah. While vessel R transports lipids from small intestine and lymph from
At high temperature, the vitamin C content of fruit juices is low. tissue fluid.
(e) Asid amino berlebihan akan diuraikan kepada urea melalui
Pemboleh ubah / Variables: proses pendeaminan.
Pemboleh ubah dimanipulasikan: Suhu Excess amino acids are broke down into urea by a deamination
Manipulated variable: Temperature process.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 18
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 18 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Unit Pengangkutan dalam Manusia dan Haiwan 10.2
10 Transport in Humans and Animals Darah / Blood
Eritrosit / Erythrocytes
10.1 Platlet / Platelets
Peta pemikiran / I-think map Eosinofil / Eosinophils
Monosit / Monocytes
Keperluan nutrien dan oksigen yang
Plasma / Plasma
tinggi
High requirement of nutrients and oxygen
Air / Water
Kadar resapan rendah Jarak yang jauh antara sel badan dan
Low rate of diffusion persekitaran luar / Long distance between
Sel darah merah Sel darah putih
body cells and external environment Keterangan (eritrosit) (leukosit)
Mengandungi sel yang banyak Description Red blood cells White blood cells
Consists of lots of cells Bersaiz besar / The size is big
(erythrocytes) (leucocytes)
Ciri-ciri 1 dwicekung / Biconcave 1 tidak sekata / Irregular
Characteristics 3 nukleus / nucleus 2 Lebih besar / Larger
Bongkah 1 cm 3 cm
4 Hemoglobin 3 berlobus; bergranul
Cube 1 cm 3 cm Haemoglobin lobed; granular
1 cm
3 cm 4 tidak berlobus; tidak
Saiz / Size Kecil / Small Besar / Large bergranul
not lobed; non-granular
Jumlah luas permukaan
(JLP) 6 54 Fungsi oksigen; karbon 1 heparin / heparin
Total surface area (TSA) Functions dioksida; 3 Fagositosis
Isi padu (I) / Volume (V) 1 27 oksihemoglobin Phagocytosis
6 =6 54 = 2 oxygen; carbon dioxide; 5 antibodi
Nisbah JLP/I
oxyhaemoglobin antibodies
Ratio TSA/V 1 27
Kadar resapan Fungsi darah / Functions of blood
Diffusion rate
Tinggi / Higher Rendah / Lower
Mengangkut oksigen / Transport oxygen
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Mengangkut haba / Transport heat
Contoh bahan buangan Mengangkut nutrien / Transport nutrient
Contoh bahan keperluan sel
dikumuh oleh sel
Examples of required substances
Example of waste substances Ciri-ciri Arteri Kapilari Vena
by cells
excreted by cells Characteristics Artery Capillary Vein
• Nutrien / Nutrient • Karbon dioksida Saiz lumen Besar
• Garam mineral Carbon dioxide Size of lumen Large
Mineral salts • Air berlebihan / Excess water
Dinding
Tebal
1 Darah mengalir di dalam salur darah dari jantung ke sel-sel berotot Thick
badan. Muscular wall
Blood flows inside blood vessels from the heart to body cells.
Kehadiran
2
injap Ada
Presence of Present
Banyak segmen
Serangga valves
ruang / Many
Insect
segments of space
Tekanan darah Tinggi
Blood pressure High
Peredaran tunggal
Ikan tertutup terdeoksigen;
Fish Single closed Kandungan
beroksigen pertukaran pulmonari
circulatory system darah oxygenated exchange deoxygenated;
Blood contents pulmonary
Peredaran ganda Bercampur di
Amfibia dua tertutup Tiga ventrikel Pengaliran
Amphibian Double closed Three Mixing in seluruh vena jantung
circulatory system the ventricle darah entire veins heart
Blood flow
Tiada
Peredaran ganda
percampuran
Manusia dua tertutup Empat
Four berlaku
Human Double closed
No mixing
circulatory system
occurs
19 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 19 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Struktur Jantung Manusia / The Structures of the Human Heart
A, B, AB dan O
Aorta / Aorta Arteri pulmonari A dan O B dan O A, B, AB and O O sahaja
Pulmonary artery A and O B and O Penerima universal O only
Vena kava superior Universal recipients
Superior vena cava Vena pulmonari
Pulmonary vein
Isu bagi faktor Rhesus / Issue with Rhesus factor
Atrium kanan • Rh-negatif; Rh-positif / Rh-negative; Rh-positive
Right atrium Atrium kiri • merangsang / s timulates
Left atrium • anak kedua yang Rh-positif / Rh-positive second baby
Injab sabit • kematian / death
Semi-lunar valve Injap bikuspid
Bicuspid valve
Injap trikuspid 10.6
Tricuspid valve
Ventrikel kiri 1 • pertumbuhan sel / growth of cells
Vena kava inferior Left ventricle • respirasi sel / c ellular respiration
Inferior vena cava • disingkirkan / e xcreted
Ventrikel kanan Septum / Septum
Right ventricle
10.7
Struktur Jantung / The Structures of Heart 1 ❶ tekanan darah / blood pressure
2 toraks; sangkar rusuk / thoracic; rib cage ❷ hujung arteriol kapilari darah; tinggi
3 ia mengecut dan mengendur secara automatik end of arteriole capillary blood; higher
it contracts and relaxes automatically ❸ plasma darah / blood plasma
4 perikardium; tisu / pericardium; tissue 1 darah merah / Red blood
5 sehala; pengaliran balik / one direction; backflow 2 Protein / proteins
6 (a) atrium; ventrikel / Atrium; ventricle 3 Platlet / Platelets
(b) kiri; kanan / Left; right ❹ bendalir tisu / tissue fluid
(c) kiri; seluruh badan / left; whole body 2
(d) Ventrikel kanan / Right ventricle
Kandungan Darah Bendalir tisu Limfa
Contents Blood Interstitial fluid Lymph
10.3
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
1 Eritrosit,
leukosit dan
Sel-sel platlet Limfosit
Nodus sinoatrium Cells Erythrocytes, Lymphocytes
Sinoartrial node leucocytes and
platelets
Nodus atrioventrikel Lemak Rendah Tinggi
Atrioventricular node Low High
Fats
Oksigen Tinggi
Oxygen High
2 Nodus sinoatrium (nodus SA); nodus atrioventrikel (nodus AV)
Sinoartrial node (SA node); atrioventricular node (AV node) Karbon
Tinggi Tinggi
3 perentak / pacemaker dioksida
High High
Carbon dioxide
saraf / Nervous
endokrin / Endocrine 3 (a) (i) Duktus toraks / Thoracic duct
(ii) Duktus limfa kanan / Right lymphatic duct
5 mengecut; terbuka / contract; opens (b) kiri; vena subklavikel kiri
6 mengendur; tertutup / relaxed; closed left; left subclavian vein
(c) kanan; vena subklavikel kanan
right; right subclavian vein
10.5
(d) nipis; besar
A B AB O thin; large
(e) injap; satu arah sahaja
Tiada antigen valve; one direction only
Antigen B Antigen AB
No antigen (f) resapan; duktus limfa
diffusion; lymphatic ducts
Anti-B Anti-A Anti-A & Anti-B
(g) penapis bakteria / mikroorganisma
A, B, AB dan O bacterial / microorganisms filter
A dan AB AB sahaja A, B, AB and O (h) sel darah putih; sel darah merah
A and AB AB only Penderma universal white blood cells; red blood cells
Universal donor (i) sel limfosit / lymphocytes
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 20
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 20 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(d) Otot kardiak adalah miogenik yang membolehkan ia
• 85% mengecut dan mengendur sendiri tanpa rangsangan.
• limfa / lymph Pengecutan jantung dimulakan oleh perentak jantung
(nodus SA).
Cardiac muscles are myogenic which enable them to contract and
relax without stimulation by nerve impulses. Heart contractions are
bakteria // mikroorganisma initiated by pacemakers (SA node).
bacteria // microorganisms (e) Pada cabang arteriol-kapilari, tekanan hidrostatik darah
yang mengalir adalah tinggi. Ini memaksa bendalir terturas
keluar dari plasma ke ruang antara sel dan dikenali sebagai
(a) Duktus toraks / Thoracic duct cecair interstis. 15% dari cecair interstis akan meresap ke
(b) Duktus limfa kanan dalam kapilari limfa membentuk P.
Right lymphatic duct At the arteriole-capillary branch, the hydrostatic pressure of the
flowing blood is very high. This forces some of the fluid to seep out
4 from the plasma into the intercellular spaces and thus referred to as
tekanan darah; isi padu darah interstitial fluid. 15% of the interstitial fluid would diffuse into the
blood stream; blood volume lymph capillaries to form P.
(f) Pengumpulan bendalir tisu. Tekanan di ruang antara sel
meningkat. Pembengkakan (edema)
Tissue fluid would accumulate which will increase pressure in
intercellular spaces. This results in swelling (oedema).
2 Persamaan: Kedua-duanya ialah sistem peredaran tertutup.
Similarities: Both are closed circulatory systems.
Perbezaan M dan N:
Differences between M and N:
M N
limfosit titisan lemak; vitamin larut lemak (a) Sistem peredaran ganda (a) Sistem peredaran tunggal
lymphocytes lipid droplets; lipid soluble vitamins
dua – darah mengalir dalam – darah beredar dalam
jantung dua kali dalam satu jantung sekali dalam satu
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
10.8 peredaran lengkap peredaran lengkap
Double circulatory system – Single circulatory system –
blood flows through the heart blood flows through the
twice in one complete cardiac heart once in a complete
cycle cardiac cycle
(b) Jantung terdapat 4 ruang – 2 (b) Jantung terdapat 2 ruang –
atrium dan 2 ventrikel 1 atrium dan 1 ventrikel
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise Heart has 4 chambers – 2 atria Heart has 2 chambers – 1
and 2 ventricles atrium and 1 ventricle
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1 D 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 D 6 C (c) Darah beroksigen mengalir (c) Darah beroksigen mengalir
7 A dari paru-paru ke jantung dari insang ke tisu badan
ke tisu badan – Organisma N bernafas
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS – Organisma M bernafas melalui insang (adalah
1 (a) R: Peredaran pulmonari / Pulmonary circulation melalui paru-paru sistem yang membekalkan
S: Peredaran sistemik / Systemic circulation (ialah sistem respirasi yang oksigen ke dalam darah)
(b) Peredaran S membawa darah terdeoksigen dari seluruh membekalkan oksigen ke Oxygenated blood flows from
dalam darah) the gills to body tissues
badan kembali ke jantung melalui vena kava dan membawa
darah beroksigen dari jantung melalui aorta ke seluruh Oxygenated blood flows through – Organism N breathes through
the lungs to the heartthen to the gills (a system that supplies
badan. oxygen to the blood).
body tissues
Circulation S transports deoxygenated blood from the whole body
– Organism M breathes through
back to the heart through vena cava and brings oxygenated blood
the lungs (a respiratoy system
from the heart to the whole body through aorta.
that supplies oxygen to the
(c) blood)
(d) Bahagian kanan jantung (d) Jantung hanya
mempunyai darah mengandungi darah
R
terdeoksigen dan bahagian terdeoksigen. Tiada septum
kiri jantung mempunyai The heart only has
darah beroksigen deoxygenated blood. No septum
– Septum membahagi
jantung kepada kiri dan
kanan
Right side of the heart has
S
deoxygenated blood while
left side of the heart has
oxygenated blood
– Septum separates the heart to
left and right side
21 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 21 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Unit Keimunan Manusia Penguraian / Decomposition:
11 Immunity in Humans Lisin / Lysin
11.1 Peneutralan / Neutralisation:
meneutralkan / neutralise
1 antibodi / antibodies
permukaan patogen; limfosit Pengaglutinan / Agglutination:
surface of a pathogen; lymphocyte aglutinin / Agglutinin
2 patogen / pathogen
3 (b) Peneutralan / Neutralization
mukus (c) Penguraian / Lysis
Mucous (d) Pengopsoninan / Opsonination
(e) Pemendakan / Precipitation
kedua
Second 11.3
memori 1 Limfosit / Lymphocytes perlahan / slowly
memory cepat; banyak / faster; greater antibodi / antibodies
plasenta / placenta berkurang / decrease
Barisan Pertahanan Pertama / First Line of Defence
lisozim
lysozymes
2 Keimunan aktif Keimunan pasif
Active immunity Passive immunity
Kulit (epidermis) Limfosit dirangsang untuk
Skin (epidermis) menghasilkan antibodi
Lymphocytes are stimulated to
produce antibodies
Mukus
Mucus Tindak balas adalah cepat
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
The action is fast
Keimunan adalah sementara
The immunity is temporary
Asid hidroklorik 11.4
Hydrochloric acid 2 imun; sihat / immune; healthy
Mekanisma pembekuan
darah Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
Blood clotting mechanism
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1 A 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 B 6 B
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
1 (a) Individu P / Individual P:
Barisan Pertahanan Ketiga / Third Line of Defence Keimunan aktif buatan / Artificially acquired active immunity
spesifik / specific Individu Q / Individual Q:
Keimunan pasif buatan / Artificially acquired passive immunity
Keimunan Rintangan (b)
Immunity resistance
Individu P / Individual P Individu Q / Individual Q
Imunisasi Proses
Immunisation process Diperolehi menerusi suntikan Diperolehi menerusi suntikan
vaksin antiserum
Antigen Molekul; luar Obtained through an injection of Obtained through an injection of
Antigen molecules; outer vaccine antiserum
Antibodi Protein; bergabung; antigen Keimunan kekal lama Keimunan adalah sementara
Antibody protein; binds; antigen The immunity lasts longer The immunity is temporary
Limfosit antibodi; Sel limfosit T; sel memori Antibodi dihasilkan oleh Antibodi tidak dihasilkan oleh
Lymphocyte antibodies; T cell lymphocyte; memory cells limfosit individu P limfosit individu Q
The antibody is produced by The antibody is not produced by
individual P’s lymphocytes individual Q’s lymphocytes
11.2
Pengopsoninan / Opsonination: Keimunan lambat diperolehi Keimunan segera diperolehi
The immunity is slowly obtained The immunity is immediately
antigen / antigens
obtained
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 22
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 22 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(c) (i) Antiserum / Antiserum 2
Otak
(ii) Antibodi di dalam antiserum akan bertindak ke atas Brain Saraf
antigen dari virus yang terkandung dalam air liur kranium
Cranial nerves
anjing tersebut secara penyahtoksinan. Sistem saraf
periferi
The antibody found in the antiserum will react on the antigen Peripheral
from the virus in the saliva of the dog by neutralising the nervous system
toxin.
(d) Saya bersetuju dengan tindakan ibu tersebut. Susu ibu
Saraf tunjang
membekalkan keimunan pasif semula jadi kepada bayi Spinal cord
kerana ia mengandungi kolostrum yang kaya dengan
antibodi. Ini akan melindungi bayi dari penyakit.
I agree with the mother’s action. Breast milk provides naturally
passive immunity as the milk contains colostrum which is rich in
antibody. This protects the baby against diseases.
Unit Koordinasi dan Gerak Balas dalam Manusia
12 Coordination and Response in Humans
12.1
1 bergerak balas / respond
2 rangsangan / stimuli Struktur dan fungsi otak / Structure and functions of the brain
3 luar / External
Hipotalamus / Hypothalamus Serebrum / Cerebrum
4 dalam / Internal
• Mengawal atur • terbesar; hemisfera
6 impuls saraf / impulse Regulates Largest; hemispheres
7 pusat integrasi / integration centre • maklumat
information
8 efektor / effectors
9 tisu otot; kelenjar / muscular tissues; glands
12
Rangsangan Reseptor Pusat integrasi Efektor Gerak balas Talamus / Thalamus
Stimuli Receptors Integration centre Effectors Response
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
• Mengintegrasi
Kelenjar pituitari / Pituitary gland
Integrates
• hipotalamus
Peta pemikiran / I-think map hypothalamus
• hormon
hormones
Menyesuaikan diri
homeostasis Adapt
homeostasis
Bergerak Medula oblongata / Medulla oblongata Serebelum / Cerebellum
Move • luar kawal • Mengkoordinasi
involuntary Coordinates
Mendapat pasangan Mendapat sumber makanan • refleks • keseimbangan
Obtain partners Obtain food sources Reflex balance
Struktur dan fungsi saraf tunjang
12.2
Structure and function of the spinal cord
1 (a) turus vertebra / vertebral column
Otak / Brain
(b) tindakan refleks; isyarat; otak
Saraf tunjang / Spinal cord reflexes; signals; brain
(c) bendalir serebrospinal / cerebrospinal fluid
deria; efektor
sensory; effectors Jirim kelabu / Grey matter Akar dorsal / Dorsal root
Ganglion akar dorsal
Saraf spina / Spinal nerves Dorsal root ganglion
• ventral / ventral
spina / spinal Neuron geganti
Relay neurone
Akar ventral / Ventral root
Sistem Saraf Periferi / Peripheral Nervous System
1 soma; autonomi / somatic; autonomic
2 terkawal / voluntary
3 luar kawal; denyutan jantung / involuntary; heartbeat
4 reseptor deria; efektor / sensory receptors; effectors
23 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 23 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
12.3 Kesan penyalahgunaan dadah terhadap koordinasi dan gerak balas
Struktur Neuron / Structure of a Neurone manusia / Effects of drug abuse on human coordination and response
❶ impuls / impulse 1 Mempercepatkan / Accelerates
❷ tunjang / spinal 2 Melambatkan / Delays
❸ eferen / Efferent 3 berfikir / think
Sinaps dan Penghantaran Maklumat 12.6
Synapse and Transmission of Information 1 tidak berduktus; hormon / ductless; hormone
❷ Vesikel sinaps / Synaptic vesicle 2 protein; mengawal atur / protein; regulate
❺ reseptor / receptors
Kelenjar tiroid
Thyroid gland
12.4
Tindakan Terkawal / Voluntary Action Pankreas / Pancreas
korteks serebrum / cerebral cortex
kemahuan / will
soma / somatic
Adrenalina / Adrenaline
Tindakan Luar Kawal / Involuntary Action Aldosteron / Aldosterone
medula oblongata / medulla oblongata Ovari / Ovary
automatik / automatically
kelenjar / gland Testosteron
autonomi / autonomic Testosterone
1 (a) luar kawal / involuntary
(b) reseptor; saraf tunjang; efektor / receptor; spinal cord; effectors Kelenjar Tisu / Organ
(c) arka refleks / reflex arc endokrin Hormon sasaran Fungsi
Endocrine Hormone Target tissue / Functions
gland organ
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Kelenjar
Hipotalamus
pituitari
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Hormon
pertumbuhan
(GH)
Growth hormone
(GH)
❷ Reseptor deria / Sensory receptor
❸ Neuron deria / Sensory neurone Testis • folikel
Testis follicle
(e)
Hormon
Kelenjar peluteinan • testosteron
pituitari (LH) ovari testosterone
(Lobus Luteinising ovary • pengovulan
anterior) hormone ovulation
Pituitary gland (LH)
(Anterior lobe)
Hormon
perangsang
tiroid (TSH) • tiroksina
Thyroid thyroxine
stimulating
12.5 hormone (TSH)
Faktor Kesan • korteks
Factors Effects adrenal
adrenal cortex
imun / immune
Kelenjar uterus • uterus
otak / Brain ingatan / Memory pituitari Uterus uterus
(Lobus
menggeletar / Shaking
posterior) Ginjal
Pituitary gland Kidney
Neuron / neurone
(Posterior lobe)
hiperaktif / hyperactive
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 24
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 24 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Sensory neurons are transformed into motor neurons and
Kelenjar tiroid Tiroksina relay neurons are also involved in the transmission of
Thyroid gland Thyroxine information.
P: P adalah reseptor yang mengesan rangsangan dan
(ii)
• berlebihan;
Insulin Hati menghasilkan impuls saraf.
glikogen P is receptor that detect stimuli and produce nerve impulses.
Insulin Liver
excess; glycogen
Pankreas S: S adalah efektor yang menerima impuls saraf dari
Pancrease • glikogen; pusat integrasi dan menghasilkan gerak balas.
glukosa S is effector that receive nerve impulses from the integration
glycogen; centre and produce response.
glucose (b)
Adrenalina • Meningkatkan
Kelenjar Adrenaline Rises
adrenal
Adrenal gland • garam mineral (c) Apabila impuls saraf tiba di hujung prasinaps neuron,
mineral salt neurotrasmiter dihasilkan oleh prasinaps neuron ke dalam
celahan sinaps. Neurotransmiter meresap ke arah postsinaps
Testis Testosteron neuron dan bergabung dengan protein reseptor. Ini
Testis Testosterone mencetuskan postsinaps neuron menghasilkan impuls saraf.
When the nerve impulse arrives at the end of the presynaptic neuron,
• haid the neurotransmitter is produced by the presynaptic neuron into the
menstruation
Ovari synaptic cavity. The neurotransmitters penetrate the postsynaptic
Ovary neuron and join the receptor protein. This triggers the postsynaptic
Progesteron • plasenta
of neurons to produce nerve impulses.
Progesterone placenta
(d) Tindakan terkawal / Voluntary action
2 (a) (i) Kelenjar pituitari / Pituitary gland
Persamaan / Similarities (ii) Kelenjar K tidak mempunyai duktus. Ia merembeskan
• rangsangan / stimulus hormon terus ke dalam darah.
• aktiviti / activities The K gland does not have a duct. It secretes hormones
directly into the bloodstream.
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Sistem saraf / Nervous system (b) Hormon L adalah hormon perangsang tiroid yang
• neuron / neurone merangsangkan kelenjar tiroid merembeskan tiroksina ke
• pantas / rapid dalam darah. Kekurangan hormon L yang dirembeskan oleh
• berbalik / reversible kelenjar K, kelenjar tiroid kurang dirangsang dan kurang
• terkawal / voluntary merembeskan tiroksina. Ini akan menyebabkan isu Q, iaitu
goiter.
Sistem endokrin / Endocrine system
The hormone L is a thyroid stimulating hormone that stimulates
• kelenjar endokrin / endocrine gland the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine into the blood. L-deficient
• hormon / hormone hormones are secreted by the K gland, the thyroid gland is less
• perlahan / slow stimulated and less secreted by the thyroid. This will cause the Q
• luar kawal / involuntary issue, the goitre.
(c) Hormon M adalah hormon perangsang folikel yang
12.7 merangsangkan perkembangan folikel dalam ovari. Sel
folikel yang berkembang akan menghasilkan hormon
2 Kekurangan Rembesan berlebihan N, iaitu estrogen yang merangsang pertumbuhan dan
Deficiency Over secretion penebalan endometrium ATAU Hormon M adalah hormon
peluteinan yang merangsangkan ovulasi di mana oosit
Kekerdilan / Dwarfism Kegergasian / Gigantism sekunder (ovum) dibebaskan dari folikel Graaf. Korpus
luteum yang terbentuk menghasilkan hormon N, iaitu
Hipertiroidisme
Goiter / Goitre progesteron yang merangsang dan mengekalkan penebalan
Hyperthyroidism
endometrium.
Diabetes melitus The hormone M is a follicle-stimulating hormone that promotes
Diabetes mellitus follicle development in the ovaries. The developing follicle cells
produce the hormone N, an oestrogen that stimulates endometrial
Edema / Oedema growth and thickening OR The hormone M is a lethal hormone that
stimulates ovulation where the secondary oocyte (ovum) is released
from the follicle of the Grave. The formed corpus luteum produces
the hormone N, a progesterone that stimulates and maintains
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise endometrial thickening.
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (d) (i) Kekerdilan pituitari / Pituitary dwarfism
1 C 2 B 3 C 4 B 5 D 6 D (ii) Suntikan hormon pertumbuhan sebelum akil baligh
7 D 8 C 9 A 10 A Injection of growth hormones before puberty
(e) Kuantiti air kencing yang banyak dan cair dihasilkan.
Large quantities of urine and fluid are produced.
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
1 (a) (i) Neuron deria telah ditukar jadi neuron motor dan
neuron geganti juga terlibat dalam penghantaran
maklumat.
25 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 25 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Unit Homeostasis dan Sistem Urinari Manusia Tindakan kelenjar tiroid / Actions of thyroid glands
13 Homeostasis and the Human Urinary System
• tidak dirangsang • Banyak / More
13.1 not stimulated
1 dalaman; optimum / internal; optimal
Faktor fizikal / Physical factors Pengawalaturan aras gula darah / Regulation of blood sugar level
• Suhu / Temperature 1 gula; normal / normal; sugar
• Tekanan darah / Blood pressure 2 (a) • glukagon / glucagon
• insulin / insulin
Faktor kimia / Chemical factors 3 75 – 110 mg
• Kepekatan garam mineral / Mineral salt concentration 4 glikogen / glycogen
Homeostasis / Homeostasis glukosa / glucose
• suap balik / feedback Mekanisme pengawalaturan tekanan separa karbon dioksida
2 menterbalikkan; pembetulan / reverse; corrective dalam darah
Mechanism of regulation of carbon dioxide partial pressure in blood
3 (a) sistem saraf; sistem endokrin
nervous system; endocrine system
2 tekanan separa / partial pressure
(b) tekanan osmosis darah; sistem endokrin; sistem urinari; 3 kemoreseptor / chemoreceptors
julat normal 4 medula oblongata / medulla oblongata
blood osmotic pressure; endocrine system; urinary system; normal 7 meningkatkan; lebihan / increases; excess
range 8 kawalan respirasi; kawalan kardiovaskular
(c) separa; sistem respirasi respiratory control; cardiovascular control
partial; respiratory system
Mekanisme kawal atur tekanan darah
(d) pH darah; sistem peredaran darah Mechanism of regulation of blood pressure
blood pH; blood circulatory system
2 baroreseptor / baroreceptors
(e) sistem endokrin 3 kawalan kardiovaskular / cardiovascular control
endocrine system
4 nodus sinoatrium / sinoatrium node
Pengawalaturan suhu badan / Regulation of body temperature kardiovaskular / Cardiovascular
1 julat normal; termoreseptor; impuls saraf; deria; mengintegrasi; Efektor / Effector
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
efektor; gerak balas; suap balik negatif medula oblongata / medulla oblongata
normal range; thermoreceptors; nerve impulse; sensory; integrates; Baroreseptor / Baroreceptor
effectors; response; negative feedback
2 Pusat kawal aturan suhu / Thermoregulating center 13.2
Efektor / Effector
1 ginjal / kidney
normal / Normal
2 (a) air; garam / water; salts
3 (a) perubahan; luar
(c) air kencing / urine
change; external
5 (a) Kapsul Bowman / Bowman’s capsule
(b) hipotalamus; dalam
hypothalamus; internal
(b) Tubul berlingkar proksimal / Proximal convoluted tubule
(c) (c) Liku Henle / Loop of Henle
6 glomerulus / glomerulus
Tindakan kelenjar peluh / Action of sweat glands 7
• aktif / active • Kurang / Less
Glomerulus Kapsul Bowman
• Lebih / More Bowman’s capsule
Arteriol aferen / Afferent arteriole Tubul berlingkar distal
Tindakan kapilari darah pada kulit Distal convoluted tubule
Arteri renal / Renal artery
Action of blood capillaries on skin Kapilari
Capillaries
• mengendur / relax • mengecut / contract Liku Henle / Loop of Henle
• Pemvasodilatan / Vasodilation • Pemvasocerutan
Vasoconstriction
Proses Pembentukan Air Kencing / Process of Urine Formation
Tindakan otot regang rambut / Action of hair erector muscle 1
• mengendur / relax • penebat / insulator
• condong / slanted • Kurang / Less Kapsul Bowman
Bowman's capsule Glomerulus
Tindakan otot rangka / Action of skeletal muscles Glomerulus
• menggigil / Shivering • dihasilkan / generated
(d)
(a) aferen; eferen / Afferent; efferent
Tindakan kelenjar adrenal / Action of adrenal glands (b) tinggi / high
(c) kapsul Bowman / Bowman’s capsule
• dirangsang / stimulated • meningkat / increases
(d) (ii) Sel darah merah / Red blood cells
• Banyak / More
(iii) Platlet / Platelets
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 26
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 26 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
2 (b) kapilari darah / blood capillaries (b) (i) Glomerulus
3 (a) kapilari darah; tubul renal / blood capillaries; renal tubule (ii) Ultraturasan berlaku di mana bendalir dituraskan dari
darah dalam H ke dalam kapsul Bowman disebabkan
Pengosmokawalaturan / Osmoregulation
tekanan hidrostatik yang tinggi.
garam; air; osmosis / salt; water; osmotic Ultrafiltration taken place in which fluid is filtered from blood
(a) air; kurang / water; less in H into Bowman’s capsule due to high hydrostatic pressure.
rendah / Low (c) H mengandungi sel darah, platlet dan protein plasma
(b) garam; kurang / salt; less manakala J tidak mengandungi sel darah, platlet dan protein
tinggi / High plasma.
H contains blood cells, platelets and plasma proteins while J does
Mekanisme Pengosmokawalaturan / Osmoregulation Mechanism
not contain those components.
(a) Hormon antidiuresis (ADH) / Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
(d) Osmoreseptor di hipotalamus mengesan tekanan osmosis
(b) Aldosteron / Aldosterone
darah yang tinggi lalu merangsangkan lobus posterior
Pengosmokawalaturan oleh ginjal / Osmoregulation by kidney kelenjar pituitari membebaskan lebih ADH ke dalam darah.
1 (a) hormon antidiuresis (ADH) / antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ADH meningkatkan ketelapan tubul berlingkar distal dan
(b) tubul pengumpul / collecting duct duktus pengumpul terhadap air. Banyak air diserap semula
(c) air / water dari tubul berlingkar distal dan duktus pengumpul ke dalam
2 (a) aldosteron / aldosterone darah melalui osmosis.
(b) garam / salt Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect the high blood osmotic
1 (a) Tidak / Not pressure, then stimulate posterior lobe of pituitary gland to release
more ADH into blood. ADH increases permeability of distal
(b) air / water
convoluted tubule and collecting duct toward water. More water is
2 (a) aldosteron / aldosterone reabsorbed from distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct into
(b) Tubul berlingkar distal / distal convoluted tubule blood via osmosis.
(e) Dapat menyerap banyak air dari K // Lebih menyesuaikan
EKSPERIMEN / EXPERIMENT diri di habitat yang kering dan panas.
Pernyataan masalah / Problem statement: Able to absorb more water from K // More adapt to dry and hot
Adakah kuantiti air yang diminum mempengaruhi kuantiti air habitat.
kencing yang dihasilkan? 2 (a) (i) K: Termoreseptor / Thermoreceptor
Does the amount of water intake affect the amount of urine produced? L: Pusat kawal atur terma / Thermoregulating center
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
(ii) K menghasilkan impuls saraf dan menghantar ke L
Hipotesis / Hypothesis: melalui saraf deria.
banyak; banyak / larger; larger K generates nerve impulse and send to L via sensory nerve.
(b) Otot erektor rambut mengendur mencondongkan bulu
Pemboleh ubah / Variables: roma untuk memperangkapkan lapisan udara yang nipis
Dimanipulasikan: Kuantiti air yang diminum supaya lebih haba dapat disingkirkan dari badan. // Kelenjar
Manipulated: Amount of water consumed peluh diaktifkan untuk menghasilkan peluh. Banyak haba
Bergerak balas: Kuantiti air kencing yang dihasilkan diserap dari badan untuk menyejatkan peluh.
Responding: Amount of urine produced Hair erector muscle relaxes to slant the hair for trapping a thin
layer of air so that more heat can be removed from body. // Sweat
Perbincangan / Discussion: gland is activated to produce sweat. More heat is absorbed from
1 banyak; banyak / larger; larger body to evaporate the sweat.
2 menurun; banyak / decreases; more (c) Otot licin arteriol afferen mengendur untuk membenarkan
3 kurang; banyak / less; more lebih darah mengalir ke dalam kapilari darah di permukaan
kulit. Lebih haba disingkirkan dari badan melalui perolakan
Kesimpulan / Conclusion: dan sinaran.
banyak; banyak / larger; larger Smooth muscle of afferent arteriole relaxes to allow more blood
flows into blood capillaries nearer to skin surface. More heat can be
removed from body via convection and radiation.
13.3
(d) (i) Kelenjar tiroid / Thyroid gland
2 (a) penghabluran / crystallisation
(ii) Kelenjar tiroid yang terangsang menghasilkan
(b) berdarah / blood
lebih hormon tiroksina. Hormon tiroksina akan
merangsangkan sel-sel badan untuk meningkatan
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise kadar metabolisme. Semakin tinggi kadar metabolisme
sel, semakin banyak haba dihasilkan untuk
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
meningkatkan suhu badan ke julat normal.
1 B 2 B 3 C 4 D 5 A 6 D
The stimulated thyroid gland produces thyroxine. The
thyroxine will stimulate body cells to increase metabolic
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS rate. The higher the cell metabolic rate, the more heat will be
1 (a) (i) F: Korteks renal / Renal cortex generated to increase body temperature to a normal range.
G: Medula renal / Renal medulla (e) Gerak balas yang dihasilkan mempunyai kesan suap balik
(ii) G mempunyai tekanan osmosis yang lebih tinggi negatif terhadap K.
daripada F sebab ion natrium, ion klorida dan urea The response produced had a negative feedback effect on K.
diangkut keluar dari tubul ke dalam medula renal.
G has a higher osmotic pressure than G because sodium ions,
chloride ions and urea are transported out from tubule into
renal medulla.
27 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 27 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
2
Sokongan dan Pergerakan dalam Manusia dan
Unit
Haiwan
14 Support and Movement in Humans and Animals
Vertebra
Vertebra
Ciri-ciri dan fungsi
Characteristics and functions
14.1 (c) salur arteri vertebra / foramen
1 hidrostatik / Hydrostatic melintang; arteri
2 Atlas (1) vertebrarterial canals / transverse
Atlas (1) foramen; arteries
berat (d) mengangguk / Nodding
weight tengkorak / skull
bentuk Melindungi (a) Cuaran odontoid
shapes Protects Odontoid process
(b) salur arteri vertebra / foramen
Axis (1)
Axis (1) melintang
sel darah perlekatan vertebrarterial canals / transverse
blood cells attachment foramen
(d) sisi ke sisi / Side-to-side
pertumbuhan (c) salur arteri vertebra / foramen
pergerakan growth melintang
movements Serviks (7)
vertebrarterial canals / transverse
kalsium; fosfat Cervical (7)
foramen
calcium; phosphate
(d) cuaran spina / spinous process
(a) cuaran spina; belakang
14.2 spinous process; backwards
(b) sangkar rusuk / rib cage
Toraks (12)
Tengkorak / Skull Klavikel / Clavicle kepala dan leher / head and neck
Thoracic (12)
Sentrum / centrum
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Skapula / Scapula
Cuaran melintang
transverse process
Sternum
Sternum
(a) kuat / strongest
Tulang rusuk Turus vertebra Lumbar (5)
Vertebral column (b) tebal / thick
Ribs Lumbar (5)
(e) berat / weight
Humerus / Humerus Sakrum (5) dan kaudal (4) (a) segi tiga / triangular
Sacrum (5) and caudal (4) (c) duduk / sitting
Ilium Radius / Radius
Ilium
Ulna / Ulna
Vertebra serviks Vertebra toraks Vertebra lumbar
Pubis
Pubis
Karpus / Carpals Cervical vertebrae Thoracic vertebrae Lumbar vertebrae
Iskium Metakarpus Pendek Panjang
Ischium Metacarpals
Short Long
Falanks
Phalanges Kecil Besar
Small Large
Femur / Femur
Mempunyai sepasang
Patela / Patella
foramen melintang
Tibia / Tibia Has a pair of transverse
foramen
Fibula / Fibula
Sendi / Joint
1 (a) sendi / joints
(b) otot rangka / skeletal muscles
Tarsus / Tarsals
Metatarsus / Metatarsals
Falanks / Phalanges
1 7 serviks / Cervical
12 toraks / Thoracic
5 lumbar / Lumbar
5 sakrum / Sacral
4 kaudal / Caudal
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 28
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 28 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
2 4
Membengkokkan kaki Meluruskan kaki
Jenis sendi Ciri-ciri Contoh Bending of the leg Straightening of the leg
Types of joint Characteristics Examples
mengecut; kuadriseps Kuadriseps; mengendur
Sendi tidak bergerak • sutur • lengkungan pelvis contract; quadriceps Quadriceps; relaxes
Immovable joints sutures pelvic girdle
fibula / fibula tibia / tibia
Sendi bergerak • rawan • vertebra
sedikit cartilage vertebrae belakang / backward hadapan / forward
Slightly moveable joints • sternum
sternum
Pergerakan cacing tanah / Locomotion in earthworm
Sendi bebas bergerak • bendalir sinovia • engsel (a) Otot lingkar / Circular muscles
Freely moveable joints synovial fluid Hinge Otot membujur / Longitudinal muscles
• lesung (b) Rangka hidrostatik / Hydrostatic skeleton
Ball-and-socket
(c) Keta / Chaetae
1 • menyerap / absorbs A
• kehausan / wearing away • mengecut; membujur / contract; longitudinal
pelincir; geseran / lubricant; friction • mengunjur ke depan / extend forward
bendalir sinovia / synovial fluid
B
Sendi lesung / A ball-and-socket joint • mengendur; mengecut / relax; contract
• semua satah / all planes • tertarik ke depan / to be pulled forward
• humerus / humerus
Pergerakan ikan / Locomotion in fish
Sendi engsel / A hinge joint (a) larus / Streamlined
• femur / femur (b) rintangan air / water resistance
(c) miotom / myotomes
Peranan Otot Rangka, Ligamen dan Tendon dalam Pergerakan (d) Pundi renang / Swim bladder
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Roles of the Skeletal Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons in Movement
• keapungan / buoyancy
(e) sirip / fins
Struktur Ciri-ciri Fungsi
ke kanan / to the right
Structure Characteristics Functions
mengendur; mengecut / relax; contract
Tendon • Tidak / Not • otot; tulang daya tujah ke hadapan / forward thrust
Tendons • penghubung muscles; bones
Pergerakan belalang / Locomotion in grasshopper
Connective • Menghantar; tulang
Otot berantagonis / Antagonistic muscles
Transmits; bone
(a) fleksor / Flexor
Ligamen • penghubung • tulang; tulang / (b) ekstensor / Extensor
Ligaments Connective rawan • belakang / rear
bone; bone / cartilage • pengecutan / contraction
• sendi / joints Otot ekstensor
• terseliuh / dislocation Extensor muscle
• terhad / limited
Otot • Sepasang otot • tarikan Otot fleksor
Muscles A pair of muscles pulling Flexor muscle
• mengendur • gerak alih
relaxes locomotion
Melompat / Jumping
(a) otot fleksor / flexor muscles
14.3 (b) Otot ekstensor / Extensor muscles
3
Membengkokkan lengan Meluruskan lengan 14.4
Bending of the arm Straightening of the arm Isu kesihatan yang berkaitan dengan sistem otot rangka manusia
Health issues related to the human skeletal muscle system
Biseps; triseps Triseps; biseps
Biceps; triceps Triceps; biceps Osteoporosis • kalsium • fosfat
Osteoporosis calcium phosphate
Menghantar; radius Menghantar; triseps; ulna
Transmits; radius Transmits; triceps; ulna Osteomalasia • lembut / soft • tulang / bone
Osteomalacia • rikets / rickets • bersenam / Exercise
ke atas / upwards ke bawah / downwards
Artritis (Osteoartritis)
sendi / joint tulang / bones
Arthritis (Osteoarthritis)
ke atas; membengkokkan ke bawah; meluruskan
upwards; bend downwards; straighten Skoliosis • genetik
Scoliosis genetic
29 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 29 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Amalan untuk menjaga kesihatan sistem otot rangka (b)
The practice of maintaining the health of the skeletal muscle system Otot berlingkar Otot berlingkar
gizi seimbang / diet consumption mengendur
Circular muscle
mengecut
Circular muscle
Rongga berisi Rongga berisi
ketat / tight relaxes bendalir contracts bendalir
Otot membujur Cavity filled Otot membujur Cavity filled
Postur / postures mengecut with fluid mengendur with fluid
Longitudinal Longitudinal
muscle contracts muscle relaxes
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise (c) Apabila otot berlingkar mengecut, struktur U diangkat dari
tanah dan segmen anterior badan cacing tanah memanjang
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS ke hadapan. Apabila otot membujur mengecut, struktur U
1 A 2 C 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 A mencengkam tanah dan menggerakkan segmen posterior
7 A 8 D badan cacing tanah ke hadapan.
When the circular muscles contract, structure U retracted from soil
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS and the anterior segments of earthworm body are extended forward.
1 (a) (i) Cuaran spina / Spinous process When the longitudinal muscles relaxes, structure U anchored to soil
(ii) Perlekatan otot / Attachment of muscle and move the posterior segments of earthworm body forward.
(iii) Vertebra toraks / Thoracic vertebra (d) Gerak alih cacing tanah dan ikan melibatkan pengecutan
dan pengenduran selang-seli pasangan otot yang
(iv) 1
berantagonistik.
2
3 Locomotions in earthworm and fish involved contraction and
4
relaxation of antagonistically pair of muscles intervally.
5
6
7
1
2
3
4 Pembiakan Seks, Perkembangan dan Pertumbuhan
5 Unit
dalam Manusia dan Haiwan / Sexual Reproduction,
6
7
8
X 15 Development And Growth in Humans and Animals
9
10 15.1
11
12 Sistem Pembiakan Lelaki / Male Reproductive System
1
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
2 Vesikel semen Duktus sperma
3 Seminal vesicle Sperm duct
4
5
Kelenjar prostat
Prostate gland
Skrotum
Scrotum
Epididimis
Zakar Epididymis
(b) J adalah muka sendi yang bersendi dengan tulang rusuk Penis
J are articulating surface that joint to ribs Testis Tubul seminiferus
(c) L perlu memberi sokongan dan menahan daya mampatan Testes Seminiferous tubule
yang menjadi semakin besar daripada berat badan
L required to provide support and withstand greater compression
Sistem Pembiakan Perempuan / Female Reproductive System
from the body weight
(d) (i) Sendi Rajah 1(a) / Joint Diagram 1(a):
Sendi bergerak sedikit / Slightly moveable joint
Sendi Rajah 1(c) / Joint Diagram 1(c): Folikel Graaf
Graafian follicle
Sendi bebas bergerak / Freely moveable joint
(ii) 1 Sendi bergerak sedikit menyambungkan dua tulang
Tiub Falopio
dengan cakera rawan (cakera intervertebra) Fallopian Tube
manakala sendi bebas bergerak menyambungkan
dua tulang dengan bendalir sinovia
Ovari / Ovary
Slightly moveable joint joins two bones with cartilage disc
(intervertebral disc), whereas freely moveable joint joins
Serviks / Cervix
two bones with synovial fluid Uterus / Uterus
2 Sendi bergerak sedikit tidak mempunyai membran Faraj / Vagina
sinovia manakala sendi bebas bergerak mempunyai
membran sinovia
Slightly moveable joint does not have synovial membrane, 15.2
whereas freely moveable joint has synovial membrane 1 gametogenesis / gametogenesis
2 (a) (i) Rangka hidrostatik / Hydrostatic skeleton 2 spermatogenesis; oogenesis / spermatogenesis; oogenesis
(ii) Otot berlingkar dan otot membujur
Circular muscle and longitudinal muscle Keperluan gametogenesis / Necessity of gametogenesis
• gamet; haploid / gametes; haploid
• variasi / variation
• zigot / zygote
• zuriat / offspring
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 30
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 30 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Spermatogenesis / Spermatogenesis 15.3
1 spermatogonium; spermatosit primer 1 28
spermatogonium; primary spermatocyte
3 embrio / embryo
meiosis I; spermatosit sekunder pengovulan / ovulation
meiosis I; secondary spermatocytes
meiosis II / meiosis II 4 Hormon perangsang folikel (FSH) perkembangan folikel
pembezaan / differentiation Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) follicle development
2 epididimis / epididymis
3 – ovulasi / ovulation
Ekor / Tail Kepala / Head
– korpus luteum
Hormon peluteinan (LH) corpus luteum
Luteinising hormone (LH)
– progesteron
progesterone
4 nukleus / nucleus
5 mitokondrion; tenaga / mitochondria; energy Estrogen – endometrium
6 Ekor / tail Oestrogen endometrium
– endometrium
Oogenesis / Oogenesis Progesteron endometrium
1 mitosis / mitotically Progesterone
– Merencat / Inhibits
4 folikel primer / primary follicle
5 perangsang folikel / follicle stimulating
6 folikel Graaf / Graafian follicle Perhubungan antara Aras Hormon, Perkembangan Folikel dan
7 oosit sekunder / secondary oocyte Keadaan Dinding Uterus semasa Kitar Haid
The Relationship between Hormone Levels, Follicle Development and the
oogonium / oogonia
Thickness of Endometrium in the Menstrual Cycle
oosit primer / primary oocyte
tidak lengkap / incomplete meningkat Endometrium
oosit sekunder / secondary oocyte increase Endometrium
sel folikel / follicle cells
folikel Graaf / Graafian follicle meningkat oosit sekunder semakin menebal
increases secondary oocyte thicken
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
oosit sekunder / secondary oocyte
jasad kutub; ovum / polar body; ovum Korpus luteum;
merencat persenyawaan terurai
Perbandingan antara spermatogenesis dengan oogenesis inhibits Corpus luteum; break
Comparison between spermatogenesis and oogenesis fertilisation
pembiakan / reproductive
5 – Membaik pulih / Repair
gamet / gametes
– endometrium / endometrium
persenyawaaan / fertilisation
– ovulasi / ovulation
– Merangsang / Stimulates
Testis / Testis Ovari / Ovary – Merencatkan / Inhibit
Sperma / Sperm Ovum / Ovum
1 sebelum / before
Berbentuk sfera
Spherical shape
2 • Sakit kepala / Headache • Mudah marah
Boleh bergerak dengan ekor • Mudah letih / Feeling tired Irritability
Can move with tail
Sel folikel menyelaputi 3 berhenti / stops
gamet
Follicle cells surrounding • 46 hingga 54 umur • tidur • emosi
the gamete 46 till 54 year-olds Sleep Mood
• FSH dan LH
Empat / Four Satu / One
FSH and LH
Tiada Satu atau tiga • rendah / Low
None One or three
Kecil / Small Besar / Large 15.4
Perkembangan Awal Zigot dalam Manusia
Early Development of a Human Zygote
Berlaku secara berterusan 1 sperma; ovum / sperm; ovum
tanpa berhenti 2 tiub Falopio / Fallopian tube
Occurs continuously without
break 3 sperma / sperms
Tidak melibatkan proses
Melibatkan proses Perkembangan Awal Embrio / Early Embryo Development
pembezaan
pembezaan 1 mitosis / mitosis
Does not involve
Involves differentiation
differentiation 2 morula / morula
31 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 31 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
3 blastosista / blastocyst Rawatan Kemandulan / Infertility treatment
4 Blastosista / Blastosista • disenyawakan; piring kultur / fertilised; culture plate
embrio / embryo • dimasukkan semula; penempelan / re-inserted; implantation
5 plasenta / placenta • tabung uji / test tube
Peranan hormon gonadotrofin korion manusia (HCG) ketika 15.7
proses kehamilan 1 tidak berbalik; jisim badan / irreversible; body mass
Role of human chorionic gonadotrotin (HCG) during pregnancy process
2 pertumbuhan / growth
1 (a) korpus luteum / corpus luteum
(b) progesteron; estrogen / progesterone; oestrogen
(c) plasenta / placenta
Fungsi plasenta dan tali pusat dalam perkembangan fetus
Function of placenta and umbilical cord in the development of foetus
3 pertukaran / exchange • Ketinggian / Height • Jisim kering / Dry mass
5 darah ibu / maternal blood
6 urea; karbon dioksida / urea; carbon dioxide
7 arteri; vena / arteries; vein Pertumbuhan Serangga / Growth in Insect
(a) plasenta / placenta 1 berangka luar / exoskeleton
8 (a) menapis / filters 2 metamorfosis / metamorphosis
(b) melekatkan / attaches 4 metamorfosis lengkap / complete metamorphosis
(c) merembeskan; progesteron / secretes; progesterone 5 metamorfosis tidak lengkap / incomplete metamorphosis
(d) memisahkan / separates
Lengkung Pertumbuhan Sigmoid bagi Sesuatu Organisma
Keperluan sistem peredaran darah fetus berasingan dengan sistem Sigmoid Growth Curve of an Organism
peredaran darah ibu 1 berbentuk S / S-shaped
Necessity of having separate foetal and maternal circulatory system 2 ❶ Fasa permulaan / Lag phase
1 tekanan darah / blood pressure ❷ Kadar pertumbuhan paling cepat
2 pengaglutinan / agglutination Fastest growth rate
❸ Fasa pertumbuhan perlahan / Slow growth phase
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
3 fetus / foetal
❹ mati atau rosak / dead or damaged
15.5 ❺ Fasa penuaan dan kematian / Senescence and death phase
Pembentukan Kembar / The Formation of Twins 3 berbentuk tangga / staircase shaped
• rangka luar; kitin / exoskeleton; chitin
2 ovum; 2 sperma • ekdisis / ecdysis
2 ova; 2 sperms • instar / instars
Jantina yang sama Jantina yang sama atau berbeza
Same sex Same or different sex Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise
Berbeza SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Different 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 D 5 B 6 B
7 A 8 D 9 B 10 B 11 C
Serupa Berbeza
Identical Different SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
1 (a) (i) V: Meiosis I / Meiosis I
W: Meiosis II / Meiosis II
15.6 (ii) Proses V berlaku dalam pembentukan sel R
menghasilkan dua spermatosit sekunder manakala
kurang pembentukan sel S menghasilkan satu oosit sekunder
Less dan satu jasad kutub. Dua spermatosit sekunder
yang terhasil mempunyai saiz yang sama manakala
Lelaki tidak normal saiz oosit sekunder adalah lebih besar daripada jasad
Male Abnormal kutub.
V process took place in the formation of cell R produces
Falopio two secondary spermatocytes whereas the formation of
Fallopian cell S produces one secondary oocyte and one polar body.
Two secondary spermatocytes produced have the same size
persenyawaan whereas size of secondary oocyte is bigger than the polar
fertilisation body.
(b) Oosit sekunder mengalami proses W untuk membahagi dan
Perempuan tersumbat menghasilkan satu ovum dan satu jasad kutub manakala
Female Blockage jasad kutub pertama membahagi dan menghasilkan dua
jasad kutub.
tidak normal Secondary oocyte undergoes process W to divide into an ovum and
Irregular a polar body whereas the first polar body is divided into two polar
bodies.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 32
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 32 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(c) Pembezaan sel berlaku. (iii) Oosit sekunder (ovum) dibebaskan ke dalam tiub
Cell differentiation took place. Falopio. Sel folikel tertinggal dirangsangkan oleh
(d) Sel P adalah spermatosit sekunder yang mengandungi LH untuk membentuk korpus luteum. Korpus
bilangan kromosom haploid. luteum merembeskan progesteron dan estrogen
Cell P is secondary spermatocyte containing haploid number of untuk mengekalkan ketebalan endometrium demi
chromosome. penempelan jika persenyawaan berlaku.
(e) Sel S melengkapkan meiosis II dan nukleus sel S bercantum Secondary oocyte (ovum) is released into Fallopian tube.
dengan nukleus sel R untuk membentuk zigot diploid. The remaining follicle is stimulated by LH to form corpus
Cell S completes meiosis II and the nucleus of cell S fuses with luteum. Corpus luteum secretes progesterone and oestrogen
nucleus of cell R to form a diploid zygote. to maintain thickness of endometrium for implantation if
fertilisation taken place.
2 (a) (i)
(c) Aras hormon peluteinan menurun dengan pantas.
(a) (i) FSH Pembentukan korpus luteum meningkatkan aras estrogen
dan progesteron. Aras progesteron yang tinggi merencatkan
penghasilan FSH daripada kelenjar pituitari. Jadi, aras FSH
(ii) Hormon perangsang folikel (FSH) dirembeskan oleh adalah rendah.
lobus anterior kelenjar pituitari untuk merangsang Level of luteinising hormone decrease sharply. The formation of
perkembangan folikel dalam ovari. corpus luteum increase the levels of oestrogen and progesterone.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by anterior High progesterone level inhibits production of FSH from pituitary
lobe of pituitary gland to stimulate the development of follicle gland. Hence, FSH level is low.
in ovary.
(b) (i) Ovulasi / Pengovulan // Ovulation
(ii)
(b) (ii) LH
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
33 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Biologi F4 (answers)csy2p.indd 33 17/03/2022 8:36 AM
You might also like
- Full Download Test Bank For Structure and Function of The Body 16th Edition Kevin T Patton PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Structure and Function of The Body 16th Edition Kevin T Patton PDF Full Chapterprimityguanabjy1095% (21)
- 2006 MRSM With AnswerDocument70 pages2006 MRSM With AnswerccffyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 f4 KSSMDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 8 f4 KSSMEtty Saad0% (1)
- Amali Wajib - Modul A+1 Fizik Tg4Document32 pagesAmali Wajib - Modul A+1 Fizik Tg4joplaysroblox14No ratings yet
- 106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsDocument3 pages106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsThooi Joo WongNo ratings yet
- 091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26Document21 pages091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26risya mariaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Halus Struktur Atom PDFDocument30 pagesSoalan Halus Struktur Atom PDFNur Irdina HaniNo ratings yet
- Force&Motion II Skor A+ AnswerDocument13 pagesForce&Motion II Skor A+ AnswerAisyatul AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Number Bases: 2. Asas NomborDocument3 pagesNumber Bases: 2. Asas NomborRaidah AdhamNo ratings yet
- KBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2Document9 pagesKBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2kancil416670No ratings yet
- 04 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4Document26 pages04 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4yannNo ratings yet
- SKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewDocument8 pagesSKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewZulkefliNo ratings yet
- Fizik PAPER 3Document8 pagesFizik PAPER 3Roszelan Majid100% (2)
- Accounting 2 Second EditionDocument152 pagesAccounting 2 Second EditionFatin AinaNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Project Work - Statistics and Index NumberDocument26 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project Work - Statistics and Index NumberNur Syahirah90% (10)
- Kebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q (Z) Bagi Taburan Normal N (0, 1)Document1 pageKebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q (Z) Bagi Taburan Normal N (0, 1)Anonymous nv1tUv6cNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Physics Pelangi Form 4Document63 pagesJawapan Physics Pelangi Form 4Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- 02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4Document20 pages02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4ONG TEIK MING -100% (1)
- Soalan EseiDocument7 pagesSoalan EseiAinFatihahNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING TEST - Module 6Document8 pagesSPEAKING TEST - Module 6SYAHRUNIZA BINTI ABDUL GHAFOOR KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Function and EquationDocument16 pagesQuadratic Function and EquationAlia AdrianaNo ratings yet
- 12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4Document10 pages12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4izrulNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDocument19 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- Dwibahasa - Modul Latihan Asas Persediaan Maths Tingkatan 3Document26 pagesDwibahasa - Modul Latihan Asas Persediaan Maths Tingkatan 3Manik SobriNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Analysing Momentum Paper 2 - Essay Question (Section B)Document2 pages2.4 Analysing Momentum Paper 2 - Essay Question (Section B)fungchernNo ratings yet
- Biologi Tingkatan 4 Bab 3: Pergerakan Bahan Merentas Membran SelDocument4 pagesBiologi Tingkatan 4 Bab 3: Pergerakan Bahan Merentas Membran SeleimNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDocument9 pagesSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Document28 pagesPaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Modul Bio Smart A+ K2 SPM 2023 - ExcellentDocument66 pagesModul Bio Smart A+ K2 SPM 2023 - Excellentdeannabatrisyia2405No ratings yet
- Selangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)Document17 pagesSelangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)SITI RAIHANI BINTI KAMSO MoeNo ratings yet
- Asid, Bes Dan GaramDocument6 pagesAsid, Bes Dan GaramTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Add Math SPM Trial 2018 SBP P1&Ans PDFDocument25 pagesAdd Math SPM Trial 2018 SBP P1&Ans PDFKataba MyTutorNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- Module Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments (Form 4 &form 5) With Analysis SPM QuestionsDocument38 pagesModule Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments (Form 4 &form 5) With Analysis SPM QuestionsEncikMohdNNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 Kertas 2 (2018) Set 2 (1) - CalonDocument15 pagesBio Form 4 Kertas 2 (2018) Set 2 (1) - CalonHuda TahaNo ratings yet
- Teknik Menjawab Kertas 2 FizikDocument41 pagesTeknik Menjawab Kertas 2 FizikCikgu Mohamad Esmandi HapniNo ratings yet
- Revision SPM 2018 Paper 2Document70 pagesRevision SPM 2018 Paper 2Azie Nurul Akhtar75% (4)
- SIRI 3 MODUL Bio Ting 4 BAB 1-7 TG4 GURUDocument10 pagesSIRI 3 MODUL Bio Ting 4 BAB 1-7 TG4 GURUMALISA BINTI CHE OTHMAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Teknik Menjawab Kimia 3 SPM...Document31 pagesTeknik Menjawab Kimia 3 SPM...Aini AliNo ratings yet
- 02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1Document9 pages02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1ZazaNo ratings yet
- Set 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)Document20 pagesSet 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)NajwaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- F5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Document13 pagesF5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Alia Qistina Mara KasmedeeNo ratings yet
- Tg4 Praktis 3 PDFDocument23 pagesTg4 Praktis 3 PDFMarhamah Kamaludin100% (1)
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k2Document24 pagesSPM 4551 2005 Biology k2pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Dn. BHD .: Jirim Dan Struktur AtomDocument18 pagesDn. BHD .: Jirim Dan Struktur AtomlhmooNo ratings yet
- MRSM 2018 - JawapanDocument14 pagesMRSM 2018 - JawapanbeaveralterNo ratings yet
- Buah AgregatDocument3 pagesBuah AgregatNawasasi Laksmita MahananiNo ratings yet
- Meth HybridDocument80 pagesMeth HybridRuthneta JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Document19 pagesKertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Mastura Hussin0% (1)
- 2022 Selangor Chemistry K2 Set - 2 JawapanDocument14 pages2022 Selangor Chemistry K2 Set - 2 JawapanNuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Soalan Program Kecemerlangan Fizik Daerah KP 2016 Fasa 1Document64 pagesSoalan Program Kecemerlangan Fizik Daerah KP 2016 Fasa 1azila805671No ratings yet
- 2 We Had Never Laugh So Much in Our LifeDocument4 pages2 We Had Never Laugh So Much in Our LifeTutor ConnieNo ratings yet
- ITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanDocument7 pagesITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanNur Ain Fitriah Mohamad KholibNo ratings yet
- SOALAN STRUKTUR Form 5Document9 pagesSOALAN STRUKTUR Form 5Willey TaluanNo ratings yet
- Report Marking KeyDocument1 pageReport Marking KeyDavid LyeluNo ratings yet
- Group 1 RevisionDocument72 pagesGroup 1 RevisionMCortez Joshua F.No ratings yet
- Basic Procedure in Research ProcessDocument21 pagesBasic Procedure in Research ProcessJILPA86% (7)
- Neuro-Urologie - EAU GuidelinesDocument32 pagesNeuro-Urologie - EAU GuidelinesstefangoagleNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - Overview Qualitative Research - Prof Adi UtariDocument32 pagesMateri 1 - Overview Qualitative Research - Prof Adi UtariDodik TugasworoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - TransesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - TransesMLS1C - PLARISAN, VALENT DAVENo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransportation in AnimalskrovrainkNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant CellDocument4 pagesTypes of Plant CellKathleen Castañeda FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bones That Protect The Internal OrgansDocument16 pagesBones That Protect The Internal OrgansMirasol GamilongNo ratings yet
- Skin of Amphibians and ReptilesDocument9 pagesSkin of Amphibians and ReptilesHussaynNo ratings yet
- 5b9f87df82236UG Syllabus (MBBS) AIIMS RaipurDocument8 pages5b9f87df82236UG Syllabus (MBBS) AIIMS RaipurBri MinNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal SystemChatterley OlanoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemMN NgọcNo ratings yet
- Hhis Obe MidtermDocument5 pagesHhis Obe MidtermHANNAH DARLED BALIADNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument88 pagesMuscular SystemLewis RamosNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Anatomy)Document11 pagesDigestive System (Anatomy)Akash SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Common Rodent Surgical ProceduresDocument32 pagesCommon Rodent Surgical ProceduresMuzi Valentina RojasNo ratings yet
- Le Fort FracturesDocument8 pagesLe Fort FracturesSeiska RbNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 12Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 12Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJakeOwensbnpm100% (10)
- Anatomy of The Pancreas and SpleenDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas and SpleenSanjaya SenevirathneNo ratings yet
- Struktur Anatomi Batang Tiga Jenis Rotan Genus Calamus Dari Kawasan Tembawang Kabupaten Kubu RayaDocument6 pagesStruktur Anatomi Batang Tiga Jenis Rotan Genus Calamus Dari Kawasan Tembawang Kabupaten Kubu RayaZahra Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Aad Abdomen WorksheetDocument15 pagesAad Abdomen WorksheetAchNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 1 QN by Zta MalappuramDocument3 pagesHsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 1 QN by Zta MalappuramNiharika SRNo ratings yet
- PlanttissuesDocument25 pagesPlanttissuesphuongchi53100% (1)
- Background Lesions in Laboratory Animals, A Color AtlasDocument134 pagesBackground Lesions in Laboratory Animals, A Color AtlasHugo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Writing History ThesisDocument29 pagesWriting History ThesisSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Ana 231 - General EmbryologyDocument20 pagesAna 231 - General EmbryologyAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Skeletal SystemDocument20 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Skeletal Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Long Test g7Document2 pagesLong Test g7Earn cruzNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab TransesDocument57 pagesAnaphy Lab TransesCarl Axel AzurNo ratings yet
- Diaphragmatic StructuresDocument7 pagesDiaphragmatic StructuresTameemNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument16 pagesOrganisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPNatalie RossetteNo ratings yet
- Mauseth Chapter 05 PDFDocument2 pagesMauseth Chapter 05 PDFCharlotte AmanteNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Understanding Anatomy and Physiology by ThompsonDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Understanding Anatomy and Physiology by ThompsonBecky Ramirez100% (27)