Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MESL 3 Final Coaching Solution
Uploaded by
Ff ElevenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MESL 3 Final Coaching Solution
Uploaded by
Ff ElevenCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
MESL 3 Final Coaching Solution
Mechanical engineering (University of Southeastern Philippines)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
1
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
INSTRUCTION: Solve the following very probable problems. DO
NOT WRITE ANYTHING ON THE QUESTIONAIRES!
Problem 1 through Prob. 3 refer to a particle whose curvilinear
motion is represented by the equation S = 20t + 4t2 – 3t3.
Problem 1. What is particle’ s initial velocity?
A. 20 m/s * C. 30 m/s
B. 25 m/s D. 32 m/s
Problem 2. What is the acceleration of the particle at time t = 0?
A. 2 m/s2 C. 5 m/s2
B. 3 m/s2 D. 8 m/s2 *
6. A projectile is fired from a cannon with an initial velocity of 1000
Problem 3. What is the maximum speed reached by the particle? m/s and at an angle of 30 from the horizontal. What distance
A. 21.8 m/s * C. 34.6 m/s from the cannon will the projectile strike the ground if the point
B. 27.9 m/s D. 48.00 m/s of impact is 1500 m below the point of release?
A. 8200 m C. 78 200 m
B. 67 300 m D. 90 800 m *
Answer: D
Problem 4. Choose the equation that best represents a rigid body or
particle under constant acceleration.
A. a = 9.81 m/s2 + Vo/t The time: t :
B. V = ao(t – to) + Vo *
C. V = Vo + s(t)dt
D. a = Vt2 /r
7. What is the magnitude of the particle’s velocity at t = 4 rad?
s ( t ) = (2 sin t) i + (4 cos t ) j [ t in radians]
A. 2.61 C. 3.30 *
B. 2.75 D. 4.12
Answer: C
5. A roller coaster trains climbs a hill with a constant gradient.
Over a 10 s period, the acceleration is constant ta 0.4 m/s 2, and 8. What is the magnitude of the particle’s acceleration at t = ?
the average velocity of the train is 40 km/h. Find the final s ( t ) = (2 sin t) i + (4 cos t ) j [ t in radians]
velocity? A. 2.00 C. 3.14
A. 9.31 m/s C. 13.1 m/s * B. 2.56 D. 4.00 *
B. 11.1 m/s D. 15.1 m/s Answer: D
Answer: C
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
2
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
9. For the reciprocating pump the radius of the crank is r = 0.3 m,
and the rotational speed is n = 350 rpm. What is the tangential
velocity of point A on the crank corresponding to an angle of
= 35 from the horizontal?
A. 0 m/s C. 10 m/s
B. 1.1 m/s D. 11 m/s *
Answer: D
12. A stone is dropped down a well. 2.47 s after the stone is
released, a splash is heard. If the velocity of the sound in air is
342 m/s, find the distance to the surface of the water in the
well?
A. 2.4 m C. 28 m *
10. A golfer on level ground at the edge of a 50 m wide pond B. 7.2 m D. 30 m
attempts to drive a golf ball across the pond, hitting the ball so Answer: C
that it travels initially at 25 m/s. The ball travels at an initial
angle of 45 to the horizontal plane. How will the golf ball travel,
and does it clean the pond?
A. 32 m; the ball does not clear the pond
B. 45 m; the ball does not clear the pond
C. 58 m; the ball clears the pond
D. 64 m; the ball clear the pond *
Answer: D
11. A particle has a tangential acceleration of at (represented by the
13. A motorist is travelling at 70 km/h when he sees a traffic light in
equation given) when it moves around a point in a curve with
an intersection 250 m ahead turn red. The light’s red cycle is 15
instantaneous angular velocity (in rad/s ) of the particle?
s. The motorist wants to enter the intersection without stopping
at = 2 t - sin t + 3 cot t in m/s2 his vehicle, just as the light turns green. What uniform
deceleration of the vehicle will just put the motorist in the
A. t 2 + cos t + 3 In csct C. t 2 - cos t + 3 In sint intersection when the light turns green?
B. t 2 - cos t + 3 In csct D. t 2 + cos t + 3 In sint * A. 0.18 m/s2 C. 0.37 m/s2 *
B. 0.25 m/s2 D. 1.3 m/s2
Answer: C
Answer: D
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
3
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
18. A flywheel rotates at 7200 rpm when the power is suddenly cut
off. The flywheel deceleration at a constant rate of 2.1 rad / s 2
and comes to rest 6 min later. How many revolutions does the
flywheel make before coming to rest?
A. 18 000 rev C. 72 000 rev
B. 22 000 rev * D. 390 000 rev
Answer: B
14. A motorist is travelling at 70 km/h when he sees a traffic light in
an intersection 250 m ahead turn red. The light’s red cycle is 15
s. The motorist wants to enter the intersection without stopping
his vehicle, just as the light turns green. If the vehicle
19. A projectile has an initial velocity of 110 m/s and a launch angle
deceleration at a constant rate of 0.5 m/s 2, What will be its
20 from the horizontal. The surrounding terrain is level, and air
speed when the light turns green?
friction is to be disregarded. What is the flight time of the
A. 43 km / h * C. 59 km / h
projectile?
B. 52 km / h D. 63 km / h
A. 3.8 s C. 8.9 s
Answer: A
B. 7.7 s * D. 12 s
Answer: B
15. The position ( in radians ) of a car travelling around a curve is
described by the following function of time ( in seconds ).
( t ) = t 3 - 2t 2 - 4t + 10. What is the angular velocity at t = 20. A projectile has an initial velocity of 110 m/s and a launch angle
3 s? 20 from the horizontal. The surrounding terrain is level, and air
A. -16 rad/s C. 11 rad /s * friction is to be disregarded. What is the horizontal distance
B. – 4 rad/s D. 15 rad/s traveled by the projectile?
Answer: C A. 80 m C. 800 m *
B. 400 m D. 1200 m
Answer: C
16. The position ( in radians ) of a car travelling around a curve is
described by the following function of time ( in seconds ). 21. A projectile has an initial velocity of 110 m/s and a launch angle
20 from the horizontal. The surrounding terrain is level, and air
( t ) = t - 2t - 4t + 10. What is the angular acceleration at
3 2
friction is to be disregarded. What is the maximum elevation
t = 5 s? achieved by the projectile?
A. 4 rad / s2 C. 26 rad / s2 * A. 72 m * C. 350 m
B. 6 rad / s2 D. 30 rad / s2 B. 140 m D. 620 m
Answer: A
Answer: C
17. The rotor of a steam turbine is rotating at 7200 rpm when the
steam supply is suddenly cut off. The rotor deceleration at a 22. The velocity (in m/s) of a falling ball is described by the
constant rate and come to rest after 5 min. What was the equation v = 32 + t + 6t2. What is the acceleration at time t = 2
angular deceleration of the rotor? s?
A. 0.40 rad / s2 C. 8.5 rad / s2 A. 9.8 m/s2 C. 32 m/s2
2
2
B. 2.5 rad / s * D. 16 rad / s2 B. 25 m/s * D. 58 m/s2
Answer: B
Answer: B
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
4
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
25. A projectile whose mass is 10 g is fired directly upward from
ground level with an initial velocity of 1000 m/s. Neglecting the
effects of air resistance, What will be the speed of the projectile
when it impacts the ground?
A. 707 m/s C. 1000 m/s *
B. 981 m/s D. 1414 m/s
Answer: C
23. A particle starting from rest experienced an acceleration of 3
m/s2 for 2 s. The particle then returned to rest in an additional
distance of 8 m. assuming all acceleration were uniform what
was the total time elapsed for the particle’s motion?
A. 2.67 s C. 4.67 s *
B. 4.00 s D. 5.33 s
Answer: C
26. A fisherman cuts his boat’s engine as it is entering a harbor. The
boat comes to a dead stop with its front end touching the dock.
The fisherman’s mass is 80 kg. He moves 5 m from his set at
the back to the front of the boat in 5 s, expecting to be able to
reach the dock. If the empty boat has mass of 300 kg, how far
will the fisherman have to jump to reach the dock?
A. 1.1 m * C. 1.9 m
B. 1.3 m D. 5.0 m
Answer: A
24. The location of a particle moving in the x – y plane is given by
the parametric equation x = t2 + 4t and y = (1/4) t4 – 60 t,
where x and y are in meters and t is in seconds. What is the
particle’s velocity at t = 4 s?
A. 8.95 m/s C. 12.6 m/s *
B. 11.3 m/s D. 16.0 m/s
Answer: C
27. The elevator in a 12- story building has a mass of 1000 kg. Its
maximum velocity and maximum acceleration are 2 m/s and 1
m/s2, respectively. A passenger with a mass of 75 kg stands on
a bathroom scale in the elevator as the elevator ascends at the
maximum acceleration. What is the scale reading just as the
elevator reaches its maximum acceleration?
A. 75 N C. 811 N *
B. 150 N D. 886 N
Answer: C
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
5
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
28. A 100 kg block is pulled along a smooth, flat surface by an 31. A hallow cylinder has a mass of 2 kg, a height of 1 m, an outer
external 500 N force. If the coefficient of friction between the diameter of 1 m, an inner diameter of 0.8 m. What is the
block and the surface is 0.15, What acceleration is experience cylinder’s mass moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to
by the block due to the external force? the cylinder’s longitudinal axis and located at the cylinder’s end?
A. 3.23 m/s2 * C. 4.33 m/s2 A. 0.41 kg.m2 C. 0.87 kg.m2 *
B. 3.80 m/s2 D. 5.00 m/s2 B. 0.79 kg.m2 D. 1.49 kg.m2
Answer: A Answer: C
29. A 2000 kg car pulls a 500 kg trailer. The car and trailer
accelerates from 520 km/h to 75 km/h at a rate of 1 m/s2. What
linear impulse does the car impact on the trailer?
A. 3470 N.s * C. 12 500 N.s
B. 8680 N.s D. 17 400 N.s
Answer: A 32. A wheel with a radius of 80 cm rolls along a flat surface at 3
m/s. if arc AB on the wheel’s parameter measure 90, What is
the velocity of point A when point B contact the ground?
A. 3.00 m/s C. 3.75 m/s
B. 3.39 m/s D. 4.24 m/s *
Answer: D
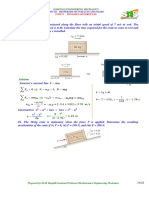
30. The block –spring system shown oscillates once every 3 s. There
is no friction between the block and the surface. If the spring
constant is 6 N/m, What is the approximate mass of the block.
A. 1.37 kg* C. 26.3 kg
B. 5.47 kg D. 72.00 kg
Answer: A
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
6
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
33. A 10 kg block is resting on a horizontal circular dish (e.g.,
turntable) at a radius of 0.5 m from the center. The coefficient
of friction between the block and disk is 0.2. The disk rotates
with a uniform angular velocity. What is the minimum angular
velocity of the disk that will cause the block to slip?
A. 1.40 rad/s C. 3.92 rad/s
B. 1.98 rad/s * D. 4.43 rad/s
Answer: B
35. A 6 kg sphere moving at 3 m/s collides with a 10 kg sphere
travelling 2.5 m/s in the same direction. The 6 kg ball comes to
a complete stop after the collision. What is the new velocity of
the 10 kg ball immediately after collision?
A. 0.5 m/s C. 4.3 m/s *
B. 2.8 m/s D. 5.5 m/s
Answer: C
34. A ball is dropped from rest a point 12 m above the ground into
a smooth, frictionless chute. The ball exits the chute 2 m above
the ground and at an angle 45 from the horizontal. Air resistant
is negligible. Approximately how far will the ball travel in the
horizontal direction before hitting the ground?
A. 12 m C. 22 m * 36. A vessel is initially connected to a reservoir open to the
B. 20 m D. 24 m atmosphere. The connecting valve is then closed, and a
Answer: C vacuum of 65.5 kPa is applied to the vessel. What is the
absolute pressure in the vessel? Assume standard atmospheric
pressure.
A. 36 kPa * C. 86 kPa
B. 66 kPa D. 110 kPa
Answer: A
37. At a particular temperature, the surface tension of water is
0.073 N/m. Under ideal conditions, the contact angle between
glass and water is zero. A student in a laboratory observes
water in a glass capillary tube with a diameter of 0.10 mm.
What is the theoretical height of the capillary rise?
A. 0.00020 m C. 0.045 m
B. 0.013 m D. 0.30 m *
Answer: D
38. What is the atmospheric pressure on a planet if the absolute
pressure is 100 kPa and the gage pressure is 10 kPa ?
A. 10 kPa C. 90 kPa *
B. 80 kPa D. 100 kPa
Answer: C
39. A 100 g of water are mixed with 150 g of another fluid ( density
= 790 kg/m3). What is the specific volume of the resulting
mixture, assuming that the volumes are additive and the
mixture is homogeneous?
A. 0.63 cm3/g C. 0.88 cm3/g
3
B. 0.82 cm /g D. 1.20 cm3/g *
Answer: D
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
7
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
44. A fluid with a vapor pressure of 0.20 Pa and a specific gravity of
12 is used in a barometer. If the fluid’s column height is 1 m,
what is the atmospheric pressure?
A. 9.80 kPa C. 101 kPa
B. 11.8 kPa D. 118 kPa *
Answer: D
45. What is the height of mercury column is equivalent to a
pressure of 700 kPa? The density of mercury is 13,500 kg/m 3.
40. A 100 g of water are mixed with 150 g of another fluid ( density A. 0.75 m C. 3.4 m
= 790 kg/m3). What is the specific gravity of the resulting B. 1.5 m D. 5.3 m *
mixture, assuming that the volumes are additive and the Answer: D
mixture is homogeneous?
A. 0.63 C. 0.86 *
B. 0.82 D. 0.95
Answer: C
Density of mixture from above problem is 0.862 g/cm3
46. What is the resultant hydrostatic force on one side of a 25 cm
diameter vertical circular plate standing at the bottom of a 3 m
pool of water?
A. 1.38 kN * C. 1.92 kN
41. The film width in a surface tension experiment is 10 cm/. If B. 1.63 kN D. 2.72 kN
mercury is the fluid ( surface tension = 0.52 cm/s ), what is the Answer: A
maximum force that can be applied without breaking the
membrane ? Neglect gravitational force.
A. 0.10 N * C. 2.0 N
B. 1.0 N D. 3.4 N
Answer: A
42. The average specific gravity of seawater is 1.15. What is the
absolute pressure at the bottom of 3000 m of sea?
A. 2.1 Mpa C. 28 Mpa
B. 2.5 Mpa D. 34 Mpa *
Answer: D
47. Water flows through a multisectional pipe placed horizontally on
the ground. The velocity is 3 m/s at the entrance and 2.1 m/s at
the exit. What is the pressure difference between these two
points.
A. 0.2 kPa C. 28 kPa
B. 2.3 kPa * D. 119 kPa
Answer: B
43. What is the depth of the center pressure on the vertical plate
(width = 1.5 m and height = 2 m) if the upper edge is 1.5 m
below the water surface?
A. 2.12 m C. 2.50 m
B. 2.32 m D. 2.63 m *
Answer: D
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
8
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
48. What is the mass flow rate of a liquid with density 0.690 gm/cc 52. A pitot-tube is used to measure the flow of an incompressible
flowing through a 5 cm ( inside diameter) pipe at 8.3 m/s. fluid ( = 926 kg/m3 ). If the velocity is measured as 2 m/s and
A. 11 kg/s * C. 140 kg/s the stagnation pressure is 14.1 kPa, what is the static pressure
B. 69 kg/s D. 340 kg/s of the fluid where the measurement is taken?
Answer: A A. 10.4 kPa C. 12.2 kPa *
B. 11.7 kPa D. 13.5 kPa
49. The mean velocity of 40ºC water in a 44.7 mm (inside diameter)
tube is 1.5 m/s. The kinematic viscosity is 6.58 x 10 -7 m2/s.
What is the Reynolds number?
A. 9.06 x 104 C. 1.02 x 105 *
B. 8.54 x 10 3
D. 8.13 x 104 53. A sharp-edge orifice with a 50 mm diameter opening in the
Answer: C vertical side of a large tank discharges under a head of 5 m. If
the coefficient of contraction is 0.62 and the coefficient of
velocity is 0.98, what is the discharge?
A. 0.003 m3/s C. 0.010 m3/s
B. 0.004 m3/s D. 0.012 m3/s *
50. What is the head loss for water flowing through a horizontal
pipe if the gage pressure at point 1 is 1.03 kPa, the gage
pressure at point 2 downstream is 1.00 kPa, and the velocity is
constant?
A. 3.1 x 10-3 m * C. 2.3 x 10-2 m
-2
B. 3.1 x 10 m D. 2.3 m
Answer: A
54. The velocity of the water in the stream is 1.2 m/s. What is the
height of water in the pitot tube?
A. 3.7 cm C. 7.3 cm *
B. 4.6 cm D. 9.2 cm
51. What horizontal force is required to hold the plate stationary
against the water jet? (All the water leaves parallel to the plate).
Diameter is 30 cm and volume flow rate is 0.05 m 3/s
A. 17.7 N C. 35.4 N *
B. 42.2 N D. 67.5 N
55. What is the velocity of water under an 18 m head discharging
freely into the atmosphere through a 25 mm diameter round-
edged orifice?
A. 1.18 m/s C. 18.4 m/s *
B. 3.22 m/s D. 8.21 m/s
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
9
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
59. A large pump for a metropolitan water system transfers water
from a lower reservoir to an upper reservation 350 m above.
The flow rate is 8.5 m3/min. The water is discharged freely to
the upper reservoir. A gas turbine drives the pump, and
effective hydraulic power is 625 kW after losses. What is the
approximate theoretical hydraulic head developed across the
pump ?
A. 20 m C. 180 m
B. 90 m D. 450 m
56. A 1:1 model of a torpedo is tested in a wind tunnel according to
the Reynolds number criterion. At the testing temperature, the
kinematic viscosity of air is 1.41 x 10-5 m2/ s and the kinematic
viscosity of water is 1.31 x 10-6 m2/s. If the velocity of the
torpedo in water is 7 m/s, what should be the air velocity in the 60. A large pump for a metropolitan water system transfers water
wind tunnel? from a lower reservoir to an upper reservation 350 m above.
A. 0.6 m/s C. 18 m/s The flow rate is 8.5 m3/min. The water is discharged freely to
B. 7.0 m/s D. 75 m/s * the upper reservoir. A gas turbine drives the pump, and
effective hydraulic power is 625 kW after losses. What is the
friction loss in the pipe between the two reservoirs?
A. 6 m C. 52 m
B. 14 m D. 100 m *
61. Air flowing through cylindrical duct encounters a constricted
flow area. The initial flow area is 2.5 m 2. The air entering the
constriction has a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 97
kPa. The constricted area is 0.10 m 2. The air in the constriction
has a density of 1.416 kg/m3. The differences in pressure across
the constriction is relatively low, and the air velocity through
constriction is 10 m/s. What is the density of the air before it
encounters the constriction?
A. 1.13 kg/m3 * C. 1.18 kg/m3
3
B. 1.0 kg/m D. 0.0389 kg/m3
57. A sharp-edge orifice with a 50 mm diameter opening is located
in the vertical side of a large tank. The coefficient of contraction
for the orifice is 0.62 and the coefficient of velocity if 0.98. The
orifice discharges under a hydraulic head of 5 m.
A. 31 mm C. 50 mm
B. 39 mm * D. 64 mm
58. A sharp-edge orifice with a 50 mm diameter opening is located 62. Air flowing through cylindrical duct encounters a constricted
in the vertical side of a large tank. The coefficient of contraction flow area. The initial flow area is 2.5 m2. The air entering the
for the orifice is 0.62 and the coefficient of velocity if 0.98. The constriction has a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 97
orifice discharges under a hydraulic head of 5 m. What is the kPa. The constricted area is 0.10 m 2. The air in the constriction
velocity at the vena contracta? has a density of 1.416 kg/m3. The differences in pressure across
A. 9.7 m/s * C. 5.4 m/s the constriction is relatively low, and the air velocity through
B. 1.7 m/s D. 3.3 m/s constriction is 10 m/s. What is the velocity of air approaching
the constriction?
A. 0.40 m/s C. 2.1 m/s
B. 0.50 m/s * D. 3.3 m/s
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|15539678
10
MATHEMATICS, ECONOMICS, SCIENCES FINAL COACHING EXAM 03 – MESL PROBS
65. A 70% efficient pump pumps water from the ground level to a
height of 5 m. How much power is used if the flow rate is 10
m3/s ?
A. 80 kW C. 700 kW *
B. 220 kW D. 950 kW
63. Air flowing through cylindrical duct encounters a constricted …END…
flow area. The initial flow area is 2.5 m2. The air entering the
constriction has a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 97
kPa. The constricted area is 0.10 m 2. The air in the constriction SUBMIT THIS TEST QUESTION SET TO YOUR WATCHERS.
has a density of 1.416 kg/m3. The differences in pressure across BRINGING THE TEST QUESTION SET OUT OF THE ROOM
the constriction is relatively low, and the air velocity through WILL BE A GROUND FOR DISCIPLINARY ACTION.
constriction is 10 m/s. What is the Mach number at that point?
A. 0.014 C. 0.0029*
B. 0.29 D. 1.0
64. A rectangular flume is 13 cm wide and 7 cm high. The freeboard
is 25% of the flume height. What is the hydraulic radius?
A. 2.3 cm C. 3.2 cm
B. 2.9 cm * D. 3.4 cm
Downloaded by Ff Eleven (ffeleven01@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Final Pre-Board (Mathematics, Power Plant & Machine Design)Document2 pagesFinal Pre-Board (Mathematics, Power Plant & Machine Design)Dominic LibradillaNo ratings yet
- 1st MATH CoachingDocument8 pages1st MATH CoachingJaypee BucatcatNo ratings yet
- Coaching Machine DesgnDocument4 pagesCoaching Machine DesgnJerome Isaac KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Deophantine 6Document169 pagesDeophantine 6Caro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS (INTEGRAL CALUCULUS) – DAY 10 MAXIMA AND MINIMADocument14 pagesMATHEMATICS (INTEGRAL CALUCULUS) – DAY 10 MAXIMA AND MINIMARALPH JEAN CA�AREJONo ratings yet
- WakakaDocument3 pagesWakakaNino Monta100% (1)
- Coaching 150 Pipe UpDocument150 pagesCoaching 150 Pipe Uprobert carbungco100% (1)
- Vip 02 Pipe Looks FamDocument65 pagesVip 02 Pipe Looks FamUllyses SebialNo ratings yet
- Gear PrimeDocument7 pagesGear PrimeEjNo ratings yet
- Strain Stress Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesStrain Stress Sample ProblemsPaul CatayongNo ratings yet
- Coaching Discussion 04 (Economics Problems) : R S R S R S R SDocument5 pagesCoaching Discussion 04 (Economics Problems) : R S R S R S R SLao GeneNo ratings yet
- Shaft Diameter and Torsional Deflection CalculationDocument4 pagesShaft Diameter and Torsional Deflection CalculationMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- PDF Machine Design Final Coaching ComprDocument17 pagesPDF Machine Design Final Coaching ComprkilluaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and HVAC systems guideDocument53 pagesRefrigeration and HVAC systems guideCharles NunezNo ratings yet
- 10 Thermodynamics 01Document1 page10 Thermodynamics 01Jhun BrionesNo ratings yet
- N Une: INSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Following ProblemsDocument7 pagesN Une: INSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Following ProblemsAaron Elijah RabayaNo ratings yet
- ME198D Applied Mechanics ProblemsDocument5 pagesME198D Applied Mechanics ProblemsKlydeJoseNo ratings yet
- Mehanics - Statics and DynamicsDocument4 pagesMehanics - Statics and DynamicsVictor John PingkianNo ratings yet
- Donguiz, Shiela MareDocument12 pagesDonguiz, Shiela Mareyeng botzNo ratings yet
- USA Heat Transfer EtcDocument9 pagesUSA Heat Transfer EtcFernan Macusi0% (1)
- Thermodynamics: Answer: ADocument5 pagesThermodynamics: Answer: AKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Best Mesl StudoDocument15 pagesBest Mesl StudoJoenielNo ratings yet
- Machine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009Document9 pagesMachine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009maria katherine pantojaNo ratings yet
- FLYWHEELDocument5 pagesFLYWHEELEj0% (1)
- Booklet 2Document7 pagesBooklet 2Jherico Jay SantosNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt (Pipe 7)Document22 pagesIbong Tiririt (Pipe 7)PANZY GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Mesl 2019 PDFDocument10 pagesMesl 2019 PDFSolayao, Jan Marvin J.No ratings yet
- 19 21Document6 pages19 21Aub Enriquez100% (1)
- PRIME Diagnostic Test 5 MESL Elements and Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesPRIME Diagnostic Test 5 MESL Elements and Problem SolvingFrankie NovelaNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Stresses 2016Document2 pagesExercises On Stresses 2016Santos JustinNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument8 pagesMathematicsGeorge Isaac McQuilesNo ratings yet
- ME 601 Trigonometry Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesME 601 Trigonometry Practice Problems and Solutionslance galorportNo ratings yet
- USA Nozzle 01Document2 pagesUSA Nozzle 01Justin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Linx JCSF Mathematics (Problems and Elements)Document38 pagesLinx JCSF Mathematics (Problems and Elements)cledcel15No ratings yet
- 29.1 Belts, Chain - Sprockets, - Threaded Members SolutionsDocument11 pages29.1 Belts, Chain - Sprockets, - Threaded Members SolutionsMarcelo AmandoronNo ratings yet
- 42 49 MDDocument11 pages42 49 MDRyan TogononNo ratings yet
- Me Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsDocument9 pagesMe Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsGerald EspanillaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lubrication & Journal Bearings: Isat U Me - Me 413A Machine Design 2 - Lecture Notes OnlyDocument6 pagesModule 3 - Lubrication & Journal Bearings: Isat U Me - Me 413A Machine Design 2 - Lecture Notes OnlyGeoffrey GolbequeNo ratings yet
- Pipe PreboardDocument3 pagesPipe Preboardlawrence catipayNo ratings yet
- PIPE20 PREBOARD202 PDFDocument15 pagesPIPE20 PREBOARD202 PDFJimwell Bobadilla100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips - Machine Problem With AnswerDocument7 pagesDokumen - Tips - Machine Problem With AnswerLanz CruzatNo ratings yet
- Preboard Examination in Machine DesignDocument4 pagesPreboard Examination in Machine Designlawrence catipayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design and Construction Code ReviewDocument14 pagesEngineering Design and Construction Code ReviewLister NambatacNo ratings yet
- BRC - Bananaman Review Center Set2Document16 pagesBRC - Bananaman Review Center Set2Paul AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1vinard milanoNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument25 pagesQuiz LetChristopher Lennon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MD in House Set 1 4 1Document12 pagesMD in House Set 1 4 1Mark Juren AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Helium Gas Compression Problem SolvedDocument37 pagesHelium Gas Compression Problem SolvedYato QtNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesProbability and Statistics Lecture NotesArsenio OvillaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Differential Equations 01 SolutionsDocument5 pages8.1 Differential Equations 01 SolutionsmaverNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 PDFDocument7 pagesQuiz 2 PDFRuth Montebon0% (1)
- Pipe Preboard 1Document10 pagesPipe Preboard 1Chyno Kang100% (1)
- HGFHFGHFGDocument24 pagesHGFHFGHFGAljhon BautistaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Mechanical Properties of Structural ComponentsDocument9 pagesCalculating Mechanical Properties of Structural Componentsrenz magatNo ratings yet
- MD PPT For Review-1Document78 pagesMD PPT For Review-1Victor CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Rectangular key force calculationDocument5 pagesRectangular key force calculationAdrian Kim MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Economics, Sciences: Final Coaching Exam 03 - Mesl ProbsDocument10 pagesMathematics, Economics, Sciences: Final Coaching Exam 03 - Mesl ProbsManoy Bermeo60% (5)
- Eval Exam 4 Review Nov 2021Document5 pagesEval Exam 4 Review Nov 2021Iris FloresNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1167419644168481477Document11 pagesInbound 1167419644168481477Clint Ford PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Practice Final ExamDocument7 pagesPractice Final ExamChetanya SinglaNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 088Document8 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 088Ff ElevenNo ratings yet
- Sol5 6Document5 pagesSol5 6Ff ElevenNo ratings yet
- Week 10Document12 pagesWeek 10Ff ElevenNo ratings yet
- 19met102 Engineering Mechanics: Unit Iii Properties of Surfaces and SolidsDocument2 pages19met102 Engineering Mechanics: Unit Iii Properties of Surfaces and SolidsFf ElevenNo ratings yet
- This Is Chapter 43, Problem 8.: Question DataDocument13 pagesThis Is Chapter 43, Problem 8.: Question DataFf ElevenNo ratings yet
- Problems Fluidmechanics300507Document35 pagesProblems Fluidmechanics300507Noh Ellie60% (5)
- 2023-Prise List Pan India All ProductDocument12 pages2023-Prise List Pan India All ProductHiren PatelNo ratings yet
- Tertiary Oil Recovery Methods ExplainedDocument12 pagesTertiary Oil Recovery Methods ExplainedDing J. LimNo ratings yet
- HONEYWELL, Valve SelectionDocument27 pagesHONEYWELL, Valve Selectionmohamed nizmyNo ratings yet
- Irrigation NotesDocument18 pagesIrrigation NotesFaisal RasoolNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAhmedalaal LotfyNo ratings yet
- 230L2M551 - Cement Mixing EquipmentDocument43 pages230L2M551 - Cement Mixing Equipmentyao nestorNo ratings yet
- Pump Reliability - Correct Hydaulic SelectionDocument3 pagesPump Reliability - Correct Hydaulic SelectionRafaelNo ratings yet
- Tarea de Termo 1Document4 pagesTarea de Termo 1Mileny Mileny Q PeñaNo ratings yet
- RVT Liquid DistributorDocument5 pagesRVT Liquid DistributorimeagorNo ratings yet
- Assignment With AnswersDocument4 pagesAssignment With AnswersJasdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles for Sizing Grease InterceptorsDocument5 pagesBasic Principles for Sizing Grease InterceptorsSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Pipe Friction LossDocument6 pagesPipe Friction LossHoongNo ratings yet
- Shell Lubricants Albida Alvania Multiservice GreasesDocument1 pageShell Lubricants Albida Alvania Multiservice GreasesvinothNo ratings yet
- CSP0000160-01 Accessory Equipment-Tab 1-14 PDFDocument531 pagesCSP0000160-01 Accessory Equipment-Tab 1-14 PDFDavid Saico CuracaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery Sixth EditionDocument654 pagesFluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery Sixth EditionRohit Panthi100% (4)
- CE 023 3 Hydrostatic Forces-2Document66 pagesCE 023 3 Hydrostatic Forces-2ANGELA BALAISNo ratings yet
- Buoyant Force ExplainedDocument27 pagesBuoyant Force ExplainedMukul Ganwal 18BME0628No ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Avoidance of Vibration Induced Fatigue Failure in Process PDocument5 pagesGuidelines For The Avoidance of Vibration Induced Fatigue Failure in Process PFSAAVEDRAFNo ratings yet
- NPSH Calculator Single Pump ApplicationDocument10 pagesNPSH Calculator Single Pump ApplicationKali Dass KMNo ratings yet
- Absolute Volume CalculationsDocument24 pagesAbsolute Volume CalculationsAngelo Danny VelascoNo ratings yet
- TA1664-5213-5001 Equipment List and Electrical Loads MEP OSBL ISBLDocument2 pagesTA1664-5213-5001 Equipment List and Electrical Loads MEP OSBL ISBLIskandar HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document24 pagesLecture 21jnmanivannanNo ratings yet
- Udaipur LakesDocument9 pagesUdaipur Lakesabhay guptaNo ratings yet
- Surface Aerators: (Fixed and Floating Types)Document3 pagesSurface Aerators: (Fixed and Floating Types)ganeshNo ratings yet
- Cementing ProgrammeDocument11 pagesCementing ProgrammeAutumn Assirem TrefoilNo ratings yet
- How To Classify Oil TanksDocument4 pagesHow To Classify Oil TanksDineshkumar SNo ratings yet
- ME8694 HydraulicsandPneumaticsQuestionBank PDFDocument15 pagesME8694 HydraulicsandPneumaticsQuestionBank PDFVikram mNo ratings yet
- HEC-RAS 5.1 Mud and Debris FlowDocument34 pagesHEC-RAS 5.1 Mud and Debris FlowFranco VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Delta Wing AerodynamicsDocument26 pagesDelta Wing AerodynamicsJohnNo ratings yet