Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022
Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022
Uploaded by
Aayush ShuklaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022
Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022
Uploaded by
Aayush ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
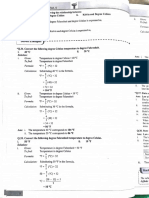
Std. X1 Sci.: Perfect Chemistry (Vol.
)
13 Properties of matter and their measurement
9.13, plain:
Ans:
Physical and chemical properties
Physical properties: These are
or
properties which
the composition of the substance.
can be measured or observed without changing the
identity
c.g Colour, odour, melting point, boiling point, density, etc.
. Chemical properties: These properties in which substances undergo change in chemical composition.
are
Coal bums in air to
produce carbon dioxide, magnesium wire burns in air in the presencc of oxygen to
form magnesium oxide, etc.
Q.14. How are properties of matter measured?
Ans:
Measurcment involves comparing a property of matter with some ixed standard which is reproducible and
unchanging.
Properties such as mass, length, area, volume, time, etc. are quantitative in nate can be measured.
ii. A quantitative measurement is represented by a number followed by units in which it is measured.
These units are arbitrarily chosen on the basis of universally accepted standards.
e.g. Length of class room can be expressed as 10 m. Here, 10 is the number and 'm' is the unit 'metre' in
which the length is measured.
Q.15. Define: Units
Ans: The arbitrarily decided and universally accepted standards are called units.
e.g. Metre (m), kilogram (kg).
Q.16. What are the various
systems in which units are expressed?
Ans: Units are expressed in various systems like CGS
(centimetre for length, gram for mass and second for time),
FPS (foot, pound, second) and MKS (metre, kilogram, second) systems, etc.
GG-Gyan Guru
Why are units important?
During calculations, confinement to one single system of unit
is advisable. NASA's Mars climate orbiter (first weather
satellite for mars) was destroyed due to heat. The mission
failed as there was a confusion while estimating the distance
between earth and mars in miles and kilometres.
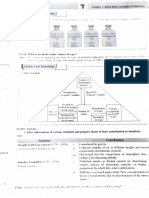
2.17. What are SI units? Name the fundamental SI units.
Ans: SI Units: In 1960, the general conference of weights and measures proposed revised metric system, called
International system of Units i.e. SI system (abbreviated from its French name).
The seven fundamental SI units are as given below:
No. Base physical quantity SI unit
Symbol
Length Metre m
. Mass Kilogram kg
ii. Time Second
iv. Temperature Kelvin K
Amount of substance Mole mol
vi. Electric current Ampere A
vii. Luminous intensity Candela cd
INote: Units for other quantities such as speed, volume, density, etc. can be derived from fiumdamental SI
units.
You might also like
- Anthony Robert Booth - Darrell P. Rowbottom - Intuitions-Oxford University Press, USA (2014) PDFDocument300 pagesAnthony Robert Booth - Darrell P. Rowbottom - Intuitions-Oxford University Press, USA (2014) PDFKároly PálNo ratings yet
- GKDocument155 pagesGKindrajeet palNo ratings yet
- 2.units and Measurements 4 37Document34 pages2.units and Measurements 4 37Rajesh PinjarlaNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron: Physical and Engineering PropertiesFrom EverandCast Iron: Physical and Engineering PropertiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Units and DimensionsDocument11 pagesUnits and DimensionsNurAliaArisya100% (1)
- Physics Learning MaterialDocument128 pagesPhysics Learning MaterialMukesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Diension - AnalysisDocument7 pagesDiension - Analysisarun joshiNo ratings yet
- Scientific Management TheoryDocument4 pagesScientific Management TheoryMd Sazzad HossainNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument11 pagesUnits and MeasurementsMohammad EhteramuddinNo ratings yet
- P-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFDocument32 pagesP-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFriddhiNo ratings yet
- ME3351 - Engineering Mechanics - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inDocument161 pagesME3351 - Engineering Mechanics - 02 - by WWW - Notesfree.inMd. Zishanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Unit & Dimension Intro - Theory & CET withOUTDocument6 pagesLec 1 - Unit & Dimension Intro - Theory & CET withOUTAnsh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities Hands OutsDocument19 pagesPhysical Quantities Hands OutsIkshya kcNo ratings yet
- Physics Learning Material 1 13Document13 pagesPhysics Learning Material 1 13Rehab RamadanNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts Applied in ChemistryDocument7 pagesSome Basic Concepts Applied in ChemistryRidham GoyalNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesUnits and MeasurementsNITHISH KUMAR.GNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Some Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageMeasurement of Some Physical PropertiestoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Units and Dimensions - Dimensional FormulaDocument13 pagesUnits and Dimensions - Dimensional Formulaabhi singhNo ratings yet
- Units and Measure MentsDocument17 pagesUnits and Measure MentsRezin ChNo ratings yet
- Physics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24Document45 pagesPhysics Teacher's Copy VI Screening Material 2023-24govind_galamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsHu XiaoNo ratings yet
- Units and DimensionsDocument11 pagesUnits and DimensionsSamyak RoteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1TanishqNo ratings yet
- Unit Dimension Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesUnit Dimension Chapter PDFAbhishek100% (1)
- UD Kinamatics NLMDocument45 pagesUD Kinamatics NLMSancia SamNo ratings yet
- 25 Apr 2022 PhysicsDocument55 pages25 Apr 2022 PhysicsA. SANDESHNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics 2020Document111 pagesMedical Physics 2020Sweet manNo ratings yet
- AnIntroductiontoPhysicsbyDr A U BajpeyeeDocument68 pagesAnIntroductiontoPhysicsbyDr A U BajpeyeeSeif Aldin KhamisNo ratings yet
- Units Dimensions and Error AnalysisDocument25 pagesUnits Dimensions and Error Analysisaustinfru7No ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics Notesredz45No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1satarupa BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PDFDocument9 pagesUnit1 PDFAnkit KambleNo ratings yet
- Che 4 BookDocument423 pagesChe 4 BookAnonymous PMF8IpBtfNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document74 pagesBlock 1joshua iwujiNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Basics of MeasurementDocument36 pagesCH - 1 Basics of MeasurementSusovan SensharmaNo ratings yet
- System of UnitsDocument9 pagesSystem of UnitsHoney AliNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics CH 1Document8 pages11th Physics CH 1KamranNo ratings yet
- Quantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pagesQuantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDane BosevNo ratings yet
- Unit, Dimension & MeasurementDocument21 pagesUnit, Dimension & MeasurementgginrearrangeitproperlyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 For WebDocument26 pagesCH 1 For WebTwinkle GirlNo ratings yet
- Unit + MeasurementDocument12 pagesUnit + MeasurementSombir AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Units and MeasurementsAshwini PramodNo ratings yet
- Phys 110 CH 1Document17 pagesPhys 110 CH 1Mamdoh Al-QuthamiNo ratings yet
- GP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementDocument6 pagesGP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementKatlo MokgethiNo ratings yet
- Physics XIsDocument52 pagesPhysics XIsAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic Concepts of ChemistryAtanu SarkarNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurement (Notes)Document12 pagesUnits and Measurement (Notes)ruchihonaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and Units F6Document37 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Units F6little book loungeNo ratings yet
- Arjuna NEET PhysicsDocument39 pagesArjuna NEET PhysicsSarita PrasadNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade VIIIDocument1 pagePhysics Grade VIIIخالد محمدNo ratings yet
- DimensionsDocument39 pagesDimensionsಶ್ರೀಕಾಂತ್ ತಿಪ್ಪೇರುದ್ರಪ್ಪNo ratings yet
- L1 - Units and Dimensions PDFDocument74 pagesL1 - Units and Dimensions PDFविभूति गर्गNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Physical Quantities and Units PDFDocument2 pages1.1.1 Physical Quantities and Units PDFAmber100% (2)
- 1.1.1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pages1.1.1 Physical Quantities and UnitsNikitha SomaratneNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch-1 For Class 11thDocument46 pagesPhysics Ch-1 For Class 11thkapil sharmaNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Notes-AyyappanDocument46 pagesHSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Notes-AyyappanDebater DudeNo ratings yet
- 1.units and MeasurementsDocument27 pages1.units and Measurementsahmed khanNo ratings yet
- International System of Units (SI)Document14 pagesInternational System of Units (SI)Luka TikveshanskiNo ratings yet
- PW 01 - 25.02-1.03.2019 - Physical Quantities and Error Calculations PDFDocument53 pagesPW 01 - 25.02-1.03.2019 - Physical Quantities and Error Calculations PDFLiviu LucaNo ratings yet
- Chem-1 Data Analysis 2022-23Document40 pagesChem-1 Data Analysis 2022-23maddie.jngNo ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Units & Dimensions - 8th April.Document16 pages(L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Units & Dimensions - 8th April.AnanayNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 Trignometry 2Document5 pagesCHP 3 Trignometry 2Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Theory FYJC Question Bank For CSDocument1 pageTheory FYJC Question Bank For CSAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- AITS 2223 FT IV JEEA Paper 2 OFFLINE PDFDocument13 pagesAITS 2223 FT IV JEEA Paper 2 OFFLINE PDFAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 Complex NumbersDocument7 pagesCHP 10 Complex NumbersAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- FYJC NetworkingDocument8 pagesFYJC NetworkingAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Fyjc Science Online Lectures Time TableDocument1 pageFyjc Science Online Lectures Time TableAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Pair of Lines Assignment - 2024 BatchDocument2 pagesPair of Lines Assignment - 2024 BatchAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Fyjc Science Second Term Examination 2023 (Mira Road) - 1Document2 pagesFyjc Science Second Term Examination 2023 (Mira Road) - 1Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Name Aayush Shukla Class 10 Div B Roll. No. 57 Subject Science 2 Paper - 1Document6 pagesName Aayush Shukla Class 10 Div B Roll. No. 57 Subject Science 2 Paper - 1Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Input & Output DevicesDocument27 pagesInput & Output DevicesAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Memories 1Document7 pagesMemories 1Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Aayush English.Document15 pagesAayush English.Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 21 Sept 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Std. Xi SCL.: Perfect Chemistry (Vol.: GivenDocument1 pageStd. Xi SCL.: Perfect Chemistry (Vol.: GivenAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Au 2022 9Document1 pageAdobe Scan 01 Au 2022 9Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- The Shhastat Gúsl in The Class: Can Ge H Aamauning DegltDocument4 pagesThe Shhastat Gúsl in The Class: Can Ge H Aamauning DegltAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Au 2022 6Document1 pageAdobe Scan 01 Au 2022 6Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Std. XI Sci.: Perfect Chemistry (Vol. 1) : of SolutionDocument1 pageStd. XI Sci.: Perfect Chemistry (Vol. 1) : of SolutionAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Aayush AlgebraDocument12 pagesAayush AlgebraAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Maliple Cholkce Questions: T H e Eesthe A ErDocument1 pageMaliple Cholkce Questions: T H e Eesthe A ErAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Aug 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 01 Aug 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Concepts: Answers To Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageConcepts: Answers To Multiple Choice QuestionsAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Ii. H:S0 Average (1 AverageDocument1 pageChapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Ii. H:S0 Average (1 AverageAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sed. 1 Se Perfect Chemistry (Vo.) : CalcuDocument1 pageSed. 1 Se Perfect Chemistry (Vo.) : CalcuAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 31 Jul 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- VI Sem BSC B Consolidated IA MarksDocument3 pagesVI Sem BSC B Consolidated IA MarksShireen NedungadiNo ratings yet
- Unit Three - Planning and Evaluating Teacher Made TestsDocument25 pagesUnit Three - Planning and Evaluating Teacher Made Testskhadar Abdi BuuxNo ratings yet
- Mcnemars TestDocument20 pagesMcnemars TestMiaNo ratings yet
- Mid Test Revision Revision Lecture: AF301 Theories of Regulation 1Document5 pagesMid Test Revision Revision Lecture: AF301 Theories of Regulation 1Shivneel Naidu100% (1)
- Activity3 Bce211Document5 pagesActivity3 Bce211Icy IzzyNo ratings yet
- Canada Gender Based ResearchDocument11 pagesCanada Gender Based ResearchSamNo ratings yet
- 490 (4) Nagel Bat PDFDocument4 pages490 (4) Nagel Bat PDFFriedrich SchlegelNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and Studies Online Reservation SystemDocument7 pagesReview of Related Literature and Studies Online Reservation SystemafmzrvaxhdzxjsNo ratings yet
- Poultry InspectionDocument178 pagesPoultry InspectionEverton OliveiraNo ratings yet
- JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist For Analytical Cross Sectional StudiesDocument4 pagesJBI Critical Appraisal Checklist For Analytical Cross Sectional StudieswennijuniarniNo ratings yet
- STS Report Group 1Document37 pagesSTS Report Group 1keen vNo ratings yet
- Basics of Science CommunicationDocument18 pagesBasics of Science CommunicationChamaraNo ratings yet
- STS LESSON 1 - Time of TechnologyDocument42 pagesSTS LESSON 1 - Time of Technology12 ABM 2A-BORRES, JEAN ROSENo ratings yet
- Alba Ve Hasher, 1983Document29 pagesAlba Ve Hasher, 1983Sumeyye ArkanNo ratings yet
- DMJ Word TemplateDocument7 pagesDMJ Word TemplateFIKOPEEA PEEANo ratings yet
- Ch.4 - Experimental Research DesignsDocument19 pagesCh.4 - Experimental Research DesignsMeghna ShettyNo ratings yet
- STS MODULE 3 Science, Technology, and Nation-BuildingDocument12 pagesSTS MODULE 3 Science, Technology, and Nation-BuildingChristine Joyce EnriquezNo ratings yet
- MSC HandbookDocument27 pagesMSC HandbooknatzenNo ratings yet
- Prize List 2017Document6 pagesPrize List 2017magmileNo ratings yet
- RubrikDocument1 pageRubrikRoy Desusa IINo ratings yet
- Recognition of Patterns With Fractal Structure in Time SeriesDocument5 pagesRecognition of Patterns With Fractal Structure in Time Serieskarim salimiNo ratings yet
- QM t4Document1 pageQM t4Vishal NarnauliaNo ratings yet
- Lydia HallDocument24 pagesLydia HallElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Purya Proj ONDocument65 pagesPurya Proj ONOmkar joshi gurujiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education W/ FP: (MWF 12:00-1:00 PM)Document4 pagesEnvironmental Education W/ FP: (MWF 12:00-1:00 PM)Arlyn MansabparNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 First Period Physics NotesDocument20 pagesGrade 10 First Period Physics NotesAlphonso Tulay100% (2)
- Wolfgram 1Document261 pagesWolfgram 1Rajiv Singh ManhasNo ratings yet
- Definition, Scope, Importance and Limitations of StatisticsDocument8 pagesDefinition, Scope, Importance and Limitations of StatisticsVNo ratings yet