Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2022 Tutorial 12 Differential Equations - QN
Uploaded by
PROgamer GTOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2022 Tutorial 12 Differential Equations - QN
Uploaded by
PROgamer GTCopyright:
Available Formats
Jurong Pioneer Junior College
H2 Mathematics (9758) JC2-2022
Tutorial 12: Differential Equations
1. Solve the following differential equations giving y in terms of x:
(a) 2 x 2 1 x ,
dy
dx
(b)
9 4 x2
dy
dx
2, (c)
1 dy
x dx
ex ,
2
3x 1 x 2 .
dy 5
(d) [3,3,3,3]
dx
2. Solve the following differential equations:
dy dy dy
(a) cos 2 2 y , (b) y 2 y2 4 , (c) sec3 y cosec y . [4,4,3]
dx dx dx
d2 y
3. Solve the differential equation e x 1 e2 x , giving y in terms of x. [3]
dx 2
d2 y dy
4. Solve the differential equation cos x 2 1, given that y 0 and
2
1 when x 0 . [5]
dx dx
5. N1987/P2/14
dy 1 x y
The variables x and y are connected by the differential equation . Show that the
dx 1 x y
du 2
substitution u x y reduces the equation to , and solve this differential equation.
dx 1 u
Deduce that x y 2( x y ) A, where A is an arbitrary constant.
2
[7]
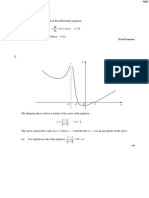
6. N1991/P2/14b (modified)
dy
Show that the differential equation x 2 2 xy 3 0 may be reduced by means of the
dx
du 3
substitution y ux 2 to 4 . Hence, or otherwise, show that the general solution for y in
dx x
1
terms of x is y Cx 2 , where C is an arbitrary constant. Sketch the curve for which C 1 . [7]
x
Tutorial 12 Differential Equations (Questions) / Pg 1
Jurong Pioneer Junior College
H2 Mathematics (9758) JC2-2022
7. Newton’s law of cooling states that the rate at which an object cools is proportional to the
difference between its temperature and that of its surroundings.
Assuming that the room temperature remains constant at 25 C and that the object has an initial
temperature of 105 C , show that 25 80e kt where C is the temperature of the object at
time t minutes after cooling commences and k is an arbitrary constant.
Given that it takes 10 minutes for the object to reach a temperature of 65 C , determine how
much more time is needed for the object to cool to 30 C .
Comment on the appropriateness of the model for a cooling time of 12 hours. [7]
8. The rate at which a substance evaporates is k times the amount of substance which has not yet
evaporated, where k is a constant.
If the initial amount of substance was A and the amount which has evaporated at time t is x, write
down a differential equation involving x, and solve it to give x in terms of A, k and t.
1
Show that the time taken for half the substance to evaporate is ln 2 . [6]
k
9. A rectangular tank with its base horizontal is filled with water to a depth h at time t = 0. Water
leaks out of the tank from a small hole in the base at a rate proportional to the square root of the
1
depth of the water. If the depth of water is h at time T, find the further time, in terms of T, it will
2
take before the tank is empty. [7]
10. The amount of water contained in a certain leaf at time t hr is denoted by x mm3 . The leaf absorbs
water from the plant at a constant rate and loses water by evaporation at a rate mm3 / hr is
proportional to the amount of water it contains. Show that the rate of change of amount of water in
dx
the leaf can be represented by the differential equation a bx where a and b are
dt
a
positive constants. Solve this equation, given that, when t 0, x . Hence express x in terms
2b
Tutorial 12 Differential Equations (Questions) / Pg 2
Jurong Pioneer Junior College
H2 Mathematics (9758) JC2-2022
of a, b and t and deduce that the amount of water contained in the leaf never exceeds the value of
a
. [6]
b
11. N2014/P1/Q10
Answers:
1(a) y ln 2 x 2 1 C ,
1 2x 1 2 1
(b) y sin 1 ( )C , (c) y e x c , (d) y (1 x 2 )6 c
4 3 2 4
1 y
2(a) y tan 1[2( x C )] , (b) y 2 tan 1 x C , (c) cos4 y 4 x c
2 2
x
3) y e e x Cx D ; 4) y ln sec x x ; 7) 30 more minutes;
a ae kt
10) x 2 e
kt a bt
8) x A Be ; 9) (1 2)T ; ;
2b b 2b
5 2x 1 2 5 1
11 (ii) t 5 ln , 11(iii)(a) 5 ln , 11(iii)(b) 2.152 ,
5 2x 1 2 5 1
( 5 1)et / 5
1 5
11(iv) x
t / 5
2(1 e )
Note : Supplementary Exercise is available on KM Portal.
Tutorial 12 Differential Equations (Questions) / Pg 3
You might also like
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)From EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)No ratings yet
- DE TutorialDocument5 pagesDE TutorialXin XinNo ratings yet
- Area Vol and DE PracticeDocument28 pagesArea Vol and DE Practiceaditya.khandelwal.2020No ratings yet
- 43 Ext 14Document2 pages43 Ext 14api-3706821No ratings yet
- A4P-Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesA4P-Differential EquationsAimbotNo ratings yet
- MM ODL 5Document16 pagesMM ODL 5Shakeb RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesChapter 10 - Differential EquationsSelvarani NadarajahNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Harni: Academic Session 2023 - 2024 Practice WorksheetDocument1 pageDelhi Public School Harni: Academic Session 2023 - 2024 Practice Worksheetsriramsonic007No ratings yet
- De Notes Higher Order NonhomogeneousDocument9 pagesDe Notes Higher Order NonhomogeneousRichard Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 6.1 - 6.3a PracticeDocument1 page6.1 - 6.3a PracticeBOBNo ratings yet
- Test 24B First Order Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesTest 24B First Order Differential EquationsHa MinhNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationDocument7 pagesDifferential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationGlennmark RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: Edexcel GCEDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations: Edexcel GCEGamer ConNo ratings yet
- First-Order Differential EquationDocument10 pagesFirst-Order Differential EquationURMILA BAUNo ratings yet
- First-Order Differential EquationDocument10 pagesFirst-Order Differential EquationNurathirahNo ratings yet
- First-Order Differential EquationDocument10 pagesFirst-Order Differential EquationNurathirahNo ratings yet
- Mat314 PDFDocument4 pagesMat314 PDFKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- 2023 Differential Equations Discussion Solution (CSL)Document15 pages2023 Differential Equations Discussion Solution (CSL)Xin XinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Differential Equationssyamimi balkhisNo ratings yet
- Integration Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesIntegration Its ApplicationJohn GohNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations MTH 242 Lecture # 03 Dr. Manshoor AhmedDocument28 pagesDifferential Equations MTH 242 Lecture # 03 Dr. Manshoor AhmedMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- 29 Ext 10Document2 pages29 Ext 10api-3706821No ratings yet
- University of Ghana: Second Semester Examinations, 2013/2014 Bsc/BaDocument5 pagesUniversity of Ghana: Second Semester Examinations, 2013/2014 Bsc/BaDavidNo ratings yet
- Defslt Lec # 04 15-01-21Document5 pagesDefslt Lec # 04 15-01-21AkashNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Indefinite Integrals (With Solutions)Document8 pagesTopic 1 Indefinite Integrals (With Solutions)Syed Shahzaib AsgharNo ratings yet
- Calculus (104) 09Document4 pagesCalculus (104) 09蕭卉妤No ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Diffusion: Fick's Second Law: DX X DC) ADocument7 pagesLecture 4: Diffusion: Fick's Second Law: DX X DC) ALloyd R. PonceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (1st ODE)Document35 pagesChapter 2 (1st ODE)一鸿No ratings yet
- 2014 2 Selangor Bandarutama PJ Maths QaDocument6 pages2014 2 Selangor Bandarutama PJ Maths QaXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Sudoder Integral Calculus WorksheetDocument6 pagesSudoder Integral Calculus WorksheetDaniel BrownNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- 2 DifferatiationDocument15 pages2 DifferatiationNamoonde MalamboNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Iii (Transform & Discrete Mathematics) : R Xiyjzk R R RDocument2 pagesMathematics-Iii (Transform & Discrete Mathematics) : R Xiyjzk R R RMortaza HaidarriNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 D.E 2nd Order NCB 10303Document7 pagesTutorial 3 D.E 2nd Order NCB 10303Ibrahim YahyaNo ratings yet
- 9 3Document13 pages9 3komarovischool8No ratings yet
- Tutorial 8BDocument10 pagesTutorial 8BaNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document36 pagesPart 4gvmanojkumarrNo ratings yet
- Math 3342 HS03Document2 pagesMath 3342 HS03Andrew AlarconNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 IntegrationDocument1 pageTutorial 1 Integrationrosmawati_kadirNo ratings yet
- Laode Unit IIDocument58 pagesLaode Unit IIasfvkjsv asgbaegbNo ratings yet
- MATH 115: Lecture XII NotesDocument5 pagesMATH 115: Lecture XII NotesDylan C. BeckNo ratings yet
- De NotesDocument8 pagesDe Notesjistoni tanNo ratings yet
- Integration 2 PDFDocument5 pagesIntegration 2 PDFAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, H. P. India Engineering Mathematics - IC 110 Tutorial-8 Odd Semester (2019-20)Document1 pageIndian Institute of Technology Mandi, H. P. India Engineering Mathematics - IC 110 Tutorial-8 Odd Semester (2019-20)Amit ProNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document3 pagesExercise 3Anant DwivediNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Ii Ras203Document2 pagesEngineering Mathematics Ii Ras203Dhananjay ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- TKSSDocument22 pagesTKSSsignboonsgslNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Second-Order Differential EquationsDocument51 pagesChapter 4 - Second-Order Differential EquationsLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Faculty - Computer Sciences and Mathematic - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Mat522Document5 pagesFaculty - Computer Sciences and Mathematic - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Mat522M. Arief Fiqrie MuryadiNo ratings yet
- 02 Differential Equations (Order Degree & Formation)Document2 pages02 Differential Equations (Order Degree & Formation)Vocab GuruNo ratings yet
- Mathst 29909Document32 pagesMathst 29909Adrian 猪是的 念来过倒No ratings yet
- Homework8.2 - Ans Diferencial EquationDocument5 pagesHomework8.2 - Ans Diferencial EquationYVES GARNARD IRILANNo ratings yet
- 2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsDocument3 pages2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- 7.8 Implicit Differentiation 5 PDFDocument7 pages7.8 Implicit Differentiation 5 PDFHin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 2019 H2 JC2 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document15 pages2019 H2 JC2 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- Ode PDFDocument81 pagesOde PDFHindi Hindi100% (1)
- Reducing Second Order Linear Differential Equations Using A SubstitutionDocument1 pageReducing Second Order Linear Differential Equations Using A SubstitutionKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Previous Years Questions (2017-) Segment-Wise: Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument14 pagesPrevious Years Questions (2017-) Segment-Wise: Ordinary Differential EquationsakashNo ratings yet
- June 2007 QPDocument6 pagesJune 2007 QPdaimon6407No ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument9 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationsAnonymous gViEc4100% (1)
- Oral Communication - Reading AloudDocument21 pagesOral Communication - Reading AloudPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication - Spoken InteractionDocument16 pagesOral Communication - Spoken InteractionPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Advance Your Potential. Shape Our NationDocument2 pagesAdvance Your Potential. Shape Our NationPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Jun Hol H1 Annotated QP and Suggested Answers Rapeseed Dilemma (2018 PJC J2 MYE H1 P1 Q1)Document15 pagesJun Hol H1 Annotated QP and Suggested Answers Rapeseed Dilemma (2018 PJC J2 MYE H1 P1 Q1)PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 JPJC J2 H1 EC MYE (Annotated QP)Document8 pages2021 JPJC J2 H1 EC MYE (Annotated QP)PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2022 Term 2 JC 2 H1 Economics SOW (Final) - Students'Document5 pages2022 Term 2 JC 2 H1 Economics SOW (Final) - Students'PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- P3 2020 - 4E5N Science (Chemistry) - Holiday AssignmentDocument15 pagesP3 2020 - 4E5N Science (Chemistry) - Holiday AssignmentPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2022 JC2 Mid Year Exam Timetable (Final)Document1 page2022 JC2 Mid Year Exam Timetable (Final)PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- JC2 Mid Year Examination 2022: Subject: Date Paper No. TimeDocument1 pageJC2 Mid Year Examination 2022: Subject: Date Paper No. TimePROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 21A01 Jun Holiday Extended Curriculum Timetable: Mon 30 MayDocument31 pages21A01 Jun Holiday Extended Curriculum Timetable: Mon 30 MayPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- JPJC 2019 Prelim - P2 - AnsBooklet - FinalDocument9 pagesJPJC 2019 Prelim - P2 - AnsBooklet - FinalPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 Year End Holiday SQ2 Graphing Techniques (Solutions) 4 Dec 21Document5 pages2021 Year End Holiday SQ2 Graphing Techniques (Solutions) 4 Dec 21PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- J2 MYE Venue (Thu 26 May)Document1 pageJ2 MYE Venue (Thu 26 May)PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 GP P2 Skills - AQDocument39 pages2021 JC1 GP P2 Skills - AQPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2022 Term 1 JC2 H1 Economics SOW Students'Document3 pages2022 Term 1 JC2 H1 Economics SOW Students'PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 Year End Exam TimetableDocument1 page2021 JC1 Year End Exam TimetablePROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- SOR Qns AllDocument17 pagesSOR Qns AllPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Cambridge 2011Document8 pagesCambridge 2011PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2019 JPJC JC2 GP Prelim P2 InsertDocument2 pages2019 JPJC JC2 GP Prelim P2 InsertPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsDocument3 pages2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 H2 Chemistry (9729) Volumetric Analysis Practical NotesDocument13 pages2021 JC1 H2 Chemistry (9729) Volumetric Analysis Practical NotesPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- The Gaseous State Notes - Fully AnnotatedDocument17 pagesThe Gaseous State Notes - Fully AnnotatedPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- 2021 Intro To Organic - Lecture Notes - AnnotatedDocument29 pages2021 Intro To Organic - Lecture Notes - AnnotatedPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans 1-26 Through 1-30Document5 pagesLesson Plans 1-26 Through 1-30api-246024051No ratings yet
- Response To Arbitrary, Step, and Pulse Excitations: Part A: Response To Arbitrarily Time-Varying ForcesDocument40 pagesResponse To Arbitrary, Step, and Pulse Excitations: Part A: Response To Arbitrarily Time-Varying ForcesMakaraSoyNo ratings yet
- Continuum Micro-Mechanics of Elastoplastic Polycrystals PDFDocument13 pagesContinuum Micro-Mechanics of Elastoplastic Polycrystals PDFChandra ClarkNo ratings yet
- 2009 Maths MC SolutionDocument18 pages2009 Maths MC SolutionyshunmingNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument269 pagesDesignTharusha MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Matrix Chain MultiplicationDocument13 pagesMatrix Chain MultiplicationAbdallahi SidiNo ratings yet
- Math104s09 Hw3solDocument3 pagesMath104s09 Hw3solPriyanka MuraliNo ratings yet
- Teacher Made Learner Home Task - TemplateDocument3 pagesTeacher Made Learner Home Task - Templatedaneca teogancoNo ratings yet
- MHS11 Z TransformDocument16 pagesMHS11 Z TransformHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations Handout WorksheetDocument2 pagesBalancing Equations Handout WorksheetnaveenNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis Using FEMDocument7 pagesModal Analysis Using FEM2gangadharaNo ratings yet
- C3 Differentiation Topic AssessmentDocument6 pagesC3 Differentiation Topic AssessmentFaridOraha100% (1)
- Integration by PartsDocument20 pagesIntegration by PartsSandun WanaguruNo ratings yet
- 9709 2007 Syllabus PDFDocument30 pages9709 2007 Syllabus PDFAhmet ArduçNo ratings yet
- Revision Paper For Math Test 1 Name: 7C/7D/7E/7N DateDocument10 pagesRevision Paper For Math Test 1 Name: 7C/7D/7E/7N DateHarris SuhardjaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Elliptic Partial Differential Equations by Haar Wavelet Operational Matrix MethodDocument100 pagesNumerical Solution of Elliptic Partial Differential Equations by Haar Wavelet Operational Matrix Methodsashankchappidigmail100% (1)
- GM The Domain, Range, Intercepts, ZeroesDocument35 pagesGM The Domain, Range, Intercepts, ZeroesKaizel BritosNo ratings yet
- Questions - Homework - 9th - Maths - 2023-12-09T2328Document5 pagesQuestions - Homework - 9th - Maths - 2023-12-09T2328ramanyadav3150No ratings yet
- I Pu Maths 1Document2 pagesI Pu Maths 1Komal GowdaNo ratings yet
- 2.quadratic EquationsDocument17 pages2.quadratic EquationsHarith HanifNo ratings yet
- OF Bisects CD. Thus, FD CD and FD 1: A. RadiusDocument2 pagesOF Bisects CD. Thus, FD CD and FD 1: A. RadiusRondex PabloNo ratings yet
- CDS Exam PatternDocument5 pagesCDS Exam PatternAchal MeshramNo ratings yet
- Quadrature ParabolaDocument6 pagesQuadrature ParabolaThomas RoumeliotisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matlab: AppendixDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Matlab: Appendixtdk13No ratings yet
- 3.5 Problems: 3.4.2 Principal Values of Euler AnglesDocument3 pages3.5 Problems: 3.4.2 Principal Values of Euler AnglesPetar Juric0% (1)
- Course WorkDocument20 pagesCourse WorkKonesi RonaldNo ratings yet
- PAST YEAR CALCULUS 2 (MAT 235) (Suggested Answer)Document10 pagesPAST YEAR CALCULUS 2 (MAT 235) (Suggested Answer)mohdhafizmohdlokmanNo ratings yet
- Linear CombinationDocument5 pagesLinear CombinationEka YaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document154 pagesChapter 3Lucas WeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusFrom EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet