Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differentiate Between Sludge & Scale Sludge Scale
Uploaded by
Sankalp ShandilyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differentiate Between Sludge & Scale Sludge Scale
Uploaded by
Sankalp ShandilyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Differentiate between Sludge & Scale
Sludge Scale
1 Due to heating, the salt containing water will get 1 When these precipitates becomes hard and
concentrated and changes into loose and slimy adherent called scales.
precipitates called sludge.
2 Sludge is not harmful for boiler. 2 Scales is harmful for boiler.
3 Sludge can be removed from the bottom of the 3 Scale can be removed by either external or internal
boiler time to time. treatment or hammering.
4 Sludge doesn’t cause clogging and corrosion. 4 Scale causes clogging and corrosion.
5 Sludge increases the discarding cost of waste. 5 Scale increases the maintenance and operation
cost.
Differentiate between Priming & Foaming
Priming Foaming
1 When boiler is producing steam very rapidly some 1 Foaming is the persistent formation of bubbles or
particles of the water carried along with the steam. foam in the boiler.
This process of “Wet Steam” formation is called
priming.
2 Priming is caused by dissolved salts, high steam 2 Foaming is caused by the presence of oily
velocity, sudden heating, improper design etc. substances in water.
3 Priming can be prevented by improving the boiler 3 Foaming can be prevented by addition of anti-
design, adding mechanical purifier, maintaining foaming agents such as castor oil, Gallic acid,
low water level and decreasing the salt Tannic acid, sodium aluminate etc.
concentration.
4 Priming reduces the boiler efficiency, life of 4 Foaming reduces the boiler efficiency and
machinery parts. damages machinery parts.
5 Due to priming one can’t judge the water level 5 Due to foaming boiler pressure can’t be
properly. maintained and water level also can’t be judged.
Differentiate between Proximate analysis & Ultimate analysis
Proximate analysis Ultimate analysis
1 Proximate analysis is an empirical analysis. 1 Ultimate analysis is an absolute analysis.
2 In Proximate analysis, the values are not accurate 2 In Ultimate analysis, the values are accurate.
but approximate as the data varies with the
procedure adopted.
3 The analysis performed are: Moisture content, 3 The analysis performed are: Percentage of C, H,
Volatile matter content, Ash content and Fixed N, S, O elements.
carbon content.
4 Proximate analysis is more physical analysis. 4 Ultimate analysis is more chemical analysis.
5 Proximate analysis is bulk analysis. 5 Ultimate analysis is an elemental analysis.
6 Sequence of analysis must be maintained. 6 No need to maintain the sequence of analysis.
Differentiate between Aniline point & Steam emulsion number (SEN)
Aniline point Steam emulsion number (SEN)
1 The minimum equilibrium solution temperature 1 The number of seconds required for oil to separate
for equal volumes of aniline and oil sample is when it is emulsified and separated under
called aniline point. specified conditions is called Steam emulsion
number (SEN).
2 Aniline point gives an idea about the quality of 2 SEN gives an idea of stability of emulsion.
lubricating oil.
3 Aniline point should be high for a good quality of 3 SEN should be low for a good quality of
lubricating oil. lubricating oil.
4 The unit of Aniline point is degree Celsius (°C) 4 The unit of SEN is time (sec).
5 Higher Aniline point indicates the lower 5 Higher SEN indicates the high stability of
percentage of aromatic hydrocarbons in emulsion.
lubricating oil.
Differentiate between Viscosity & Viscosity index
Viscosity Viscosity index (VI)
1 The property of a liquid by virtue of which it 1 Viscosity index is an empirical number indicating
opposes relative motion between its difference the effect of change of temperature on viscosity of
layers is known as viscosity or internal friction of oil.
liquid.
2 Viscosity is the property of liquid. 2 Viscosity index is the property of lubricants.
3 The unit of viscosity is centipoise or centistokes. 3 Viscosity index is unit less property.
4 Viscosity should be moderate (neither too high nor 4 Viscosity index should be higher for a good
too low) for a good quality of lubricating oil. quality of lubricating oil.
5 Viscosity can be measured by Redwood, Engler or 5 Viscosity index can be determined graphically.
Saybolt viscometers.
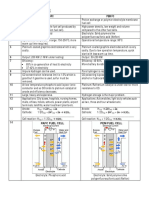
Differentiate between LDP & HDP
LDP HDP
1 Full form: Low density polythene 1 Full form: High density polythene
2 Temperature require for the synthesis is about 2 Temperature require for the synthesis is about
350-570 K. 330-350 K.
3 Pressure require for the synthesis is about 1000- 3 Pressure require for the synthesis is about 1 atm.
2000 atm.
4 Chain initiator required for the synthesis is traces 4 Catalyst required for the synthesis is Zeigler-Natta
of Oxygen or a Peroxide which initiate the catalyst (ZNC).
polymerization.
5 LDPs are branched polymers. 5 HDPs are linear polymers.
6 LDP is chemically inert tough but flexible and 6 HDP is chemically inert but relatively tough and
poor conductor of electricity. hard with high tensile strength.
7 LDP is used in manufacturing of squeeze bottles, 7 HDP is used in manufacturing of containers,
toys, flexible pipes etc. drums, durable pipes, water tanks, bottles etc.
Differentiate between Starch & Cellulose
Starch Cellulose
1 Molecular formula: (C6H10O5)n 1 Molecular formula: (C6H10O5)n
2 Source: Wheat, Corn, Rice, Potatoes etc. 2 Source: Wood, Plant fibers, Cotton etc.
3 Starch is a condensation polymer. 3 Cellulose is condensation polymer.
4 Monomer: -D (+) Glucose 4 Monomer: -D (+) Glucose
5 Starch contains 20% Amylose (water soluble) and 5 There is a single component only as cellulose
80% Amylopectin (water insoluble) (water insoluble).
6 Starch is a mixture of linear (Amylose) and 6 Cellulose is a linear polymer.
branched-helix (Amylopectin) polymers.
7 In Amylose C1-C4 and in Amylopectin C1-C4 as 7 C1-C4 glycosidic linkage present.
well as C1-C6 glycosidic linkages present.
8 The shape of glycosidic linkage is “U” shape in 8 The shape of glycosidic linkage is “Z” shape.
Amylose and “Zigzag” shape in Amylopectin.
Differentiate between Graphite & Molybdenum disulphide
Graphite Molybdenum dishulphide (MoS2)
1 Graphite is a planner structure. 1 MoS2 is a sandwich structure.
2 It is a network structure. 2 It is a network structure.
3 The distance between two layers is 3.4 °A. 3 The distance between two layers of Mo is 6.26 °A.
4 C-C bond length is 1.42 °A. (SP2 hybridization) 4 Mo-Mo bond length is 3.08 °A and S-S bond
length is 3.15 °A.
5 In air, it can be used up to 375 °C. 5 In air, it can be used up to 400 °C.
6 Graphite is being used as solid as well as Oil dag MoS2 is being used as a mixture of 70% MoS2, 7%
and Aqua dag (mixture with oil and water as semi Graphite and 23% Silicates.
solid lubricant).
7 Application: Railway tracks joints, Printer roller, 7 Applications: Nuclear reactors, Low pressure and
Internal combustion engines, Cast iron bearings, extreme temperature applications, Space vehicles
Heavy chains, Air compressors etc. etc.
You might also like
- Examination of LipidsDocument3 pagesExamination of LipidsJannah IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Emulsion (CORE - 3 in 1) Lecture3Document186 pagesEmulsion (CORE - 3 in 1) Lecture3Baham TamyNo ratings yet
- D 1994 - 95 R00 Rde5otq - PDFDocument2 pagesD 1994 - 95 R00 Rde5otq - PDFMarceloNo ratings yet
- Classification of Insulating Materials As Per ISIDocument6 pagesClassification of Insulating Materials As Per ISIindranil das100% (2)
- Chapter 1-4 WorksheetsDocument13 pagesChapter 1-4 Worksheetskrishmadaan100No ratings yet
- Styrene Butadiene RubberDocument27 pagesStyrene Butadiene RubberabdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Principles and Black Liquor Properties: David T. Clay, PH.DDocument6 pagesEvaporation Principles and Black Liquor Properties: David T. Clay, PH.DJKKNo ratings yet
- Black Liquor Properties EquationsDocument6 pagesBlack Liquor Properties EquationsavgpaulNo ratings yet
- Oil Analysis Variout TestsDocument3 pagesOil Analysis Variout TestsHiren VasaniNo ratings yet
- GD-264 Manual PDFDocument9 pagesGD-264 Manual PDFAnonymous srwHCpANo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure PDFDocument10 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure PDFAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Presentation DGADocument63 pagesPresentation DGAMuhammad Ahmed100% (2)
- Question Bank - 1703847805Document7 pagesQuestion Bank - 1703847805yawalo4821No ratings yet
- Exp 3Document9 pagesExp 3tamanranya234No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (NIVETHA)Document22 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project (NIVETHA)lakmi260107No ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry THEORYDocument16 pagesSurface Chemistry THEORYSantosh GulechhaNo ratings yet
- Class9 TH Chapter 2Document7 pagesClass9 TH Chapter 2knramya18No ratings yet
- Internal Exam Que Ans - BT 101 - 1613801471Document9 pagesInternal Exam Que Ans - BT 101 - 1613801471sid mankarNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petrochemicals Technology LabDocument18 pagesPetroleum and Petrochemicals Technology LabMaham FatimaNo ratings yet
- ASTM Method For Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric PressureDocument7 pagesASTM Method For Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric PressureSaiVenkatNo ratings yet
- Aashul Heda (BT10MME042) Akashy Toradmal (BT10MME021) Hetasha Vaidya (BT10MME043) Varun Pande (BT10MME065)Document7 pagesAashul Heda (BT10MME042) Akashy Toradmal (BT10MME021) Hetasha Vaidya (BT10MME043) Varun Pande (BT10MME065)Prashant ParshivnikarNo ratings yet
- Ssino 5Document14 pagesSsino 5shuaibu abdullahiNo ratings yet
- Water Softening IndustryDocument4 pagesWater Softening IndustryArslanAliNo ratings yet
- Re CrystallizationDocument18 pagesRe CrystallizationSeema SuranjikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. (5) : Classification of Crude OilDocument17 pagesLecture No. (5) : Classification of Crude OilKurdish DriverNo ratings yet
- 1.distinguish Between Sludge and Scale With An Example: Part - ADocument17 pages1.distinguish Between Sludge and Scale With An Example: Part - ADinesh Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Conditions Unit3l2Document17 pagesFluids and Conditions Unit3l2KJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practicals VivaDocument17 pagesChemistry Practicals VivaPriyanshu BajajNo ratings yet
- Completion - Reservoir Drill in FluidsDocument45 pagesCompletion - Reservoir Drill in FluidsFauzan Rahman Haq100% (1)
- Water ChemistryDocument3 pagesWater ChemistrySaki MonteroNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 6470-99 Salt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) 1 PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D 6470-99 Salt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) 1 PDFsofiane ouchaouaNo ratings yet
- KF Titration BasicsDocument4 pagesKF Titration Basicsammuluhai333No ratings yet
- Revised Book in Chem1202Document78 pagesRevised Book in Chem1202imanNo ratings yet
- 2019 DryKeep PresentationDocument73 pages2019 DryKeep PresentationEunsung QANo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Emulsion Polymerization of StyreneDocument11 pagesExperiment 1: Emulsion Polymerization of StyreneNurshahanimNo ratings yet
- Adipic Acid & NylonDocument28 pagesAdipic Acid & NylonjanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Pre-LabDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Pre-LabMollyNo ratings yet
- O'Level Chemistry (5070) Quick RevisionDocument19 pagesO'Level Chemistry (5070) Quick RevisionLil Puhpu100% (1)
- Kandhari Beverages Private Limited: SAMBA, J & K, IndiaDocument20 pagesKandhari Beverages Private Limited: SAMBA, J & K, IndiaVeeraprasad CGNo ratings yet
- Art IntegrationDocument12 pagesArt IntegrationSimhadri MohithNo ratings yet
- Jar Test Lab ReportDocument14 pagesJar Test Lab ReportShaun KerouacNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil&DgaDocument70 pagesTransformer Oil&DgaBasudev PatraNo ratings yet
- Chem - Lab ManualDocument53 pagesChem - Lab ManualHarshit JainNo ratings yet
- Determination of Acid Numbers of Hot-Melt Adhesives: Standard Test Method ForDocument2 pagesDetermination of Acid Numbers of Hot-Melt Adhesives: Standard Test Method Fordavid dawoudNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Rubber Lec-1 - 2Document51 pagesSynthetic Rubber Lec-1 - 2reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Dieselpower Enhancer 25 LTRDocument2 pagesDieselpower Enhancer 25 LTRGohNo ratings yet
- 9701 s06 QP 2Document12 pages9701 s06 QP 2Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Treament of LubesDocument35 pagesTreament of LubesAnand kesanakurtiNo ratings yet
- Merit Science Academy FSD: Chemistry 1 YearDocument1 pageMerit Science Academy FSD: Chemistry 1 YearShakaibNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual ChemistryDocument48 pagesLab Manual ChemistryRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 STDocument15 pagesAss 2 STraunNo ratings yet
- Book ReportDocument14 pagesBook ReportNandita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solid Surface HandbookDocument7 pagesSolid Surface HandbookMohamed Amin MazenNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science - Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure PDFDocument6 pagesClass 9 Science - Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure PDFGaurav SethiNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument29 pagesEngineering Materialssolomonsanjiv883No ratings yet
- Crystallisation Lec 38,39Document23 pagesCrystallisation Lec 38,39Adheep DasNo ratings yet
- Polymers - Hand Written NotesDocument24 pagesPolymers - Hand Written NotesSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment - Class NotesDocument84 pagesWater Treatment - Class NotesSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Fulleren - Engineering Materials - ADDocument8 pagesFulleren - Engineering Materials - ADSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Green Chemistry Presentation - ADDocument25 pagesGreen Chemistry Presentation - ADSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Polymers and Composite Materials: Shibu G. PillaiDocument32 pagesPolymers and Composite Materials: Shibu G. PillaiSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Explosives: - Prof. Neha PatniDocument23 pagesExplosives: - Prof. Neha PatniSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PAFC & PEMFCDocument1 pageDifference Between PAFC & PEMFCSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- What Defines Critical Thinking and How Do We Start Thinking Critically?Document33 pagesWhat Defines Critical Thinking and How Do We Start Thinking Critically?Sankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Session 5A Bounded Rationality Dec 2020Document21 pagesSession 5A Bounded Rationality Dec 2020Sankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Critical Thinking July 2020Document18 pagesSession 1 Critical Thinking July 2020Sankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Types of Thinking July 2020Document23 pagesSession 2 Types of Thinking July 2020Sankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- 2SP103 Critical Thinking Special Assignment February 2021 1Document8 pages2SP103 Critical Thinking Special Assignment February 2021 1Sankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Thorplas Engineering ManualDocument32 pagesThorplas Engineering ManualNguyen JohnNo ratings yet
- 10th Science I SemiENG QueBank MSCERTDocument55 pages10th Science I SemiENG QueBank MSCERTyash shindeNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Chap. 2Document53 pagesCorrosion: Chap. 2Daniel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Studies in Polyelectrolytes. Ii. Gum Arabate Sadhan Basu, Pares Ch. Dasgupta and Anil K. SircarDocument10 pagesStudies in Polyelectrolytes. Ii. Gum Arabate Sadhan Basu, Pares Ch. Dasgupta and Anil K. SircarAmalia WardatulNo ratings yet
- Aci 221R-96Document3 pagesAci 221R-96farhadamNo ratings yet
- Resin DefoulingDocument4 pagesResin DefoulingTim KuNo ratings yet
- 1CH0 2H Que 20211130Document32 pages1CH0 2H Que 20211130Jordan DanielNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates Are The Most Abundant of All Organic Compounds in NatureDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates: Carbohydrates Are The Most Abundant of All Organic Compounds in NatureMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- Enzymes RegulationDocument87 pagesEnzymes RegulationWahyu KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Part 1Document49 pagesToxicology Part 1Sapana YadavNo ratings yet
- CH203 Fall 2014 NMR Practice Quiz 1 Answers PDFDocument8 pagesCH203 Fall 2014 NMR Practice Quiz 1 Answers PDFBUCH20350% (2)
- Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIDocument1,209 pagesComprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIHello World100% (1)
- Metallographic Laboratory Safety: Standard Guide OnDocument9 pagesMetallographic Laboratory Safety: Standard Guide OnNebu Mathew RoyNo ratings yet
- Peracetic Acid in Cooling Water CircuitsDocument33 pagesPeracetic Acid in Cooling Water CircuitsUttam JaipuriaNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Moringa StenopetalaDocument50 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Moringa Stenopetalaimran shaukatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: Dr. Norma B. Muyot, Che, EddDocument22 pagesChemistry For Engineers: Dr. Norma B. Muyot, Che, EddRyan J ArsagaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument22 pagesAcids Bases and Saltsd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Allied School, Lahore 3-11-23Document6 pagesAllied School, Lahore 3-11-23advancesci60No ratings yet
- 01 Atomic Structures WSDocument34 pages01 Atomic Structures WSAreeba EjazNo ratings yet
- Use of Modified Tapioca Starches As Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument10 pagesUse of Modified Tapioca Starches As Pharmaceutical ExcipientsFabiana OlenaNo ratings yet
- A Survey Report On PreservativesDocument46 pagesA Survey Report On Preservatives0921pyNo ratings yet
- Histopath LectureDocument15 pagesHistopath LectureAhnorrei PavlaskaNo ratings yet
- Sri Mulyati Jurnal 1Document10 pagesSri Mulyati Jurnal 1Hery Aceh OfficialNo ratings yet
- EPA Method 1657 AccuStandardDocument39 pagesEPA Method 1657 AccuStandardduygu9merve100% (1)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 Crash CourseDocument75 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 2 Crash CourseKewi Love100% (3)
- Gold Plating: Alan BlairDocument2 pagesGold Plating: Alan BlairHiden HidenNo ratings yet
- 0653 m19 QP 42 PDFDocument24 pages0653 m19 QP 42 PDFmaria paula peña narvaezNo ratings yet
- 04 - StoichiometryDocument6 pages04 - StoichiometryMj LizardoNo ratings yet
- E 59a Product Data 10 15Document2 pagesE 59a Product Data 10 15marcos crisostoNo ratings yet
- Project Report Soap ManufacturingDocument6 pagesProject Report Soap ManufacturingSuleman Mossa80% (5)