Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics IGCSE - Electricity
Physics IGCSE - Electricity
Uploaded by
Xian Cong KoayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics IGCSE - Electricity
Physics IGCSE - Electricity
Uploaded by
Xian Cong KoayCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics IGCSE
Electricity
Charge & Current
There are two types of charges (bipolar).
- Positive charge
- Negative charge
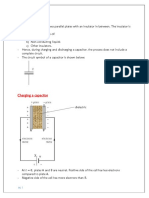
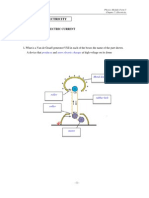
A Van de Graaff generator as shown in figure below is a machine that can be used to
produce and store charges.
When the Van de Graaff generator is switched on,
- It drives the rubber belt.
- This causes the rubber belt to rub against the roller and hence becomes charged.
- The charged is then carried by the moving belt up to the metal done where it is
collected.
- A large amount of charge is built up on the dome.
(Demo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmbhU_a7tjs&ab_channel=jordi3736)
The wires in an electric circuit are made of metal, because metal is a good conductor of
electric current. In the wires, the current is a flow of negatively charged electrons.
Prepared by: Xian Cong
SI Unit of charge is measured in Coulomb (C). Each electrons carries a negative charge
𝟏𝟏. 𝟔𝟔 × 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏−𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏 𝑪𝑪.
A charge ‘flow rate’ can be defined as Coulomb/second and we name it electric current.
Electric current is the rate of flow charge.
Hence, the relationship between electric current and charge is shown in formula below:
𝑄𝑄 = 𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼
Where:
𝑄𝑄 = charge measured in Coulombs (𝐶𝐶),
𝐼𝐼 = current measured in Ampere (𝐴𝐴),
𝑡𝑡 = time measured in seconds (𝑠𝑠).
Example
1. The current flowing through a resistor is 0.3A. What is the time required for 60C of
charge to flow through the resistor?
2. Find the number of electrons accumulated at the dome of a Van de Graff generator
when a current of 20mA flows through the galvanometer in 3s.
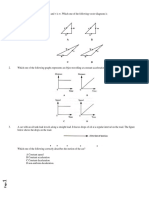
3. The diagram below shows light bulbs X and Y.
Q coulombs of charge flows through the light bulb X in t seconds and 2Q coulombs of
charge takes 3t seconds to flow through the light bulb Y. What is the ratio of current
flowing through X to the current flowing through Y?
Prepared by: Xian Cong
You might also like
- CHAPTER 2. Physics f5Document45 pagesCHAPTER 2. Physics f5Normawarni HasanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument25 pagesCurrent Electricitykistonmulemba13No ratings yet
- Van de Graff GeneratorDocument2 pagesVan de Graff GeneratorAlphy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDisha KatariaNo ratings yet
- Comm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1Document17 pagesComm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1anthdbaNo ratings yet
- 4 CapacitorsDocument16 pages4 CapacitorsDevNo ratings yet
- Physics Electricity Class 10Document12 pagesPhysics Electricity Class 10Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Homopolar MotorDocument7 pagesHomopolar MotorVĩ AoNo ratings yet
- Van de GraaffDocument8 pagesVan de Graaffnishantjain4No ratings yet
- Physice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFDocument7 pagesPhysice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFAbhilashaNo ratings yet
- S S E S: ElectricityDocument4 pagesS S E S: ElectricityRAJ STUDY WIZARDNo ratings yet
- Intro Voltage CurrentDocument30 pagesIntro Voltage CurrentlicramosaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and MagnetismDocument12 pagesElectrostatics and MagnetismkobeadjordanNo ratings yet
- Design DC and Ac Load Lines - Fall 2022Document5 pagesDesign DC and Ac Load Lines - Fall 2022Amera AdilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Electromagnetic Induction and Magnetic ForceDocument22 pagesLesson 3 - Electromagnetic Induction and Magnetic ForcehumayunNo ratings yet
- Van de GraaffDocument4 pagesVan de GraaffMaeka SanvictoresNo ratings yet
- 03 TheoryDocument8 pages03 TheoryRathankar RaoNo ratings yet
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDocument61 pagesBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 - Electric CircuitsDocument37 pagesLec 14 - Electric CircuitsNikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsDocument8 pagesCbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsShaam L VNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsDocument8 pagesCbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsShaam L VNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsDocument8 pagesCbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsShaam L VNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsDocument8 pagesCbse 12 Physics Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) Important Unsolved QuestionsShaam L VNo ratings yet
- CHT 10 Alternating CurrentDocument37 pagesCHT 10 Alternating Currentsaskiahnyoni18No ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H2 - COE - Notes Final PDFDocument18 pages14 - 15 - H2 - COE - Notes Final PDFeltytanNo ratings yet
- 2010 Physics Model YekaDocument9 pages2010 Physics Model YekaTizita EmanaNo ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument24 pagesPhysics PresentationGrace jereNo ratings yet
- 5.4 MagnetismDocument41 pages5.4 MagnetismEdward NealeNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument120 pagesTable of ContentsBonface Kenani100% (4)
- p1 FinalDocument9 pagesp1 FinalDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Basic Diodes and Basic Diode Applicatio NS: Report Submitted To The Electronic Engineering Lab Class 1Document7 pagesBasic Diodes and Basic Diode Applicatio NS: Report Submitted To The Electronic Engineering Lab Class 1Champika_MadhurabhashinNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Inductors in DC CircuitsDocument10 pagesCapacitors and Inductors in DC CircuitsLuka LasicNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Part 1Document21 pagesElectricity - Part 1Anonymous CommentatorNo ratings yet
- Phyf5 Chap2Document76 pagesPhyf5 Chap2Mohd AzlanNo ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Sure Short Question For Physics 3-Marks AnswerDocument16 pagesSure Short Question For Physics 3-Marks AnswerSantoshi PandeyNo ratings yet
- Gce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument26 pagesGce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 Solutionsjan12th2004No ratings yet
- Dynamometer Type Wattmeter WorkingDocument6 pagesDynamometer Type Wattmeter Workingsandeep rawatNo ratings yet
- Capacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An ExampleDocument15 pagesCapacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An Examplebeta akuiNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th AC Generator PDFDocument17 pagesPhysics 12th AC Generator PDFluckyNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th AC Generator PDFDocument17 pagesPhysics 12th AC Generator PDFlucky100% (2)
- Handout LISTRIK DINAMIS Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesHandout LISTRIK DINAMIS Bahasa Inggriscicha 25No ratings yet
- AC CurrentsDocument16 pagesAC CurrentsRoshan RajNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2SohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument67 pagesChapter OneWiz Nati XvNo ratings yet
- Nuclear LaboratoryDocument6 pagesNuclear LaboratoryMintesnot AbaynehNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: DC GeneratorDocument34 pagesElectrical Machines: DC GeneratorMarc Joshua MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document16 pagesLecture 17ririnyuNo ratings yet
- IAC Current Report 1Document7 pagesIAC Current Report 1ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- AS Trial - 2004 Mar - P1Document14 pagesAS Trial - 2004 Mar - P1Syafiq Shazwan100% (1)
- Current Electricity (Notes)Document27 pagesCurrent Electricity (Notes)cvgbhnjNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 Term 1 2015 - Y11Document17 pagesPhysics Paper 1 Term 1 2015 - Y11Ezra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideDocument60 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideLawrence HiewNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity TheoryDocument17 pagesCurrent Electricity TheoryChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL Quantities: Friction and ChargeDocument11 pagesELECTRICAL Quantities: Friction and ChargeNick MillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27-Current and ResistanceDocument21 pagesChapter 27-Current and ResistanceGled HysiNo ratings yet
- Generation of High DC Voltages: High Voltage Engineering ApplicationsDocument33 pagesGeneration of High DC Voltages: High Voltage Engineering ApplicationsMohammad Musa AbidNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet