Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lakshya Rank Refinement Test No - 8: Jee Advance Pattern
Uploaded by
Jay Doshi ShashikantOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lakshya Rank Refinement Test No - 8: Jee Advance Pattern
Uploaded by
Jay Doshi ShashikantCopyright:
Available Formats
LAKSHYA RANK REFINEMENT TEST NO.
8
JEE ADVANCE PATTERN
TOPIC WISE TEST
Time: 02:00 PM to 05:00
T INDIA
Max.Marks:
PM
R 180
Name of the Student: ___________________ I.D. NO:
LR
MATHS:
Vectors: Addition of vectors, scalar multiplication, dot and cross products, scalar triple products and their
geometrical interpretations.
Three Dimensions: Direction cosines and direction ratios, equation of a straight line in space, equation of a
plane, distance of a point from a plane.
PHYSICS:
Electrostatics, Gauss law &Gravitation:
coulomb's law; electric field and potential; electrical potential energy of a system of point charges and of
electrical dipoles in a uniform electrostatic field; electric field lines; flux of electric field; gauss's law and its
application in simple cases, such as, to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged
infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell.
CHEMISTRY:
Group 17, Group 18, Metallurgy
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
JEE-ADVANCED-2014-P2-Model
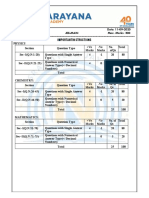
Time: 2.00 PM to 5.00 PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS Max Marks: 180
PHYSICS:
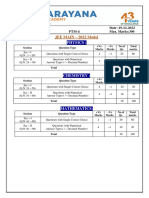
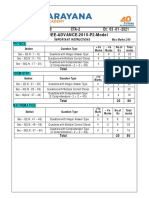
+Ve - Ve No.of Total
Section Question Type
Marks Marks Qs marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 1 – 10) Questions with Single Correct Choice 3 -1 10 30
Questions with Comprehension Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 11 – 16) (3 Comprehensions – 2 +2+2 = 6Q) 3 -1 6 18
Sec – III(Q.N : 17 – 20) Matrix Matching Type 3 -1 4 12
Total 20 60
CHEMISTRY:
+Ve - Ve No.of Total
Section Question Type
Marks Marks Qs marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 21 – 30) Questions with Single Correct Choice 3 -1 10 30
Questions with Comprehension Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 31 – 36) (3 Comprehensions – 2 +2+2 = 6Q) 3 -1 6 18
Sec – III(Q.N : 37 – 40) Matrix Matching Type 3 -1 4 12
T
Total 20 60
MATHEMATICS:
+Ve - Ve No.of Total
Section
R Question Type
Marks Marks Qs marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 41 – 50) Questions with Single Correct Choice 3 -1 10 30
Questions with Comprehension Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 51 – 56) (3 Comprehensions – 2 +2+2 = 6Q) 3 -1 6 18
LR
Sec – III(Q.N : 57 – 60) Matrix Matching Type 3 -1 4 12
Total 20 60
space for rough work Page 2
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
PART-I_PHYSICS Max Marks : 60
Section-1
(Only one Option correct Type)
This section contains 10 Multiple Choice questions. Each Question has Four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D). Out of Which
Only One is correct
1. Inside a satellite orbiting very close to earth’s surface, water does not fall out of
a glass when it is inverted. Which of the following is the best explanation for
above statement?
A) The earth does not exert any force on the water
B) The earth’s force of attraction on the water is exactly balanced by the force
created by satellites motion
C) The water & the glass have same acceleration towards the centre of the earth
& hence there is no relative motion between them
D) The gravitational attraction between the glass & the water balances the
earth’s attraction on the water
T
2. An uncharged conductor A is brought near a positively charged conductor B.
Then
R
A) the charge on B will increase but the potential of B will not change
B) the charge on B will not change but the potential of B will decrease
C) the charge on B will decrease but the potential of B will not change
LR
D) the charge on B will not change but the potential of B will increase
space for rough work Page 3
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
3. A point charge ‘q’ is placed at the apex of a Gaussian conical surface of semi
vertical angle 60o . Which of the following statements is not true ?
60
q
q
A) Electric flux magnitude through flat face of the cone is
4 o
q
B) Electric flux magnitude through the entire conical Gaussian surface is
4 o
q
C) Electric flux magnitude through the entire conical Gaussian surface is
3o
D) Electric flux magnitude function for the entire Gaussian surface is a
discontinuous function, when ‘q’ is moved along the axis near the apex.
4. What is the potential difference between the north pole(NP) and the centre(O) of
an inverted hemispherical conducting bowl of radius R carrying a uniform
T
surface density
N.P
R
O
R R R 2 R 2
LR
A)
2 o
B)
2 o
2 1 C)
2 o
D) 2( 2 1)
2 o
space for rough work Page 4
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
5. From a non-conducting sphere of uniform volume charge density and radius R, a
spherical cavity of radius R was made. Center of bigger sphere is origin (0,0,0)
4
R
and cavity is , 0 , 0 . Electric field inside the cavity is E o î . What is electric flux
2
linked with a Gaussian sphere of radius 3R centred at origin?
4
21 13 63 7
A) E o R 2 B) E o R 2 C) E o R 2 D) E o R 2
8 4 8 8
6. The figure shows electric field vectors at points A and B due to a point charge at
origin. All points A,B,C,D are in xy plane. Co-ordinates of A,B,D are (3,0), (3,4)
and (28,0) respectively. Length AD and BC represent the strength of these field
vectors at A and B respectively. The coordinates of point C are
C
T B
R A D
18 24 42 56 63 84
A) , B) , C) , D) 18 , 24
5 5 5 5 5 5
LR
space for rough work Page 5
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
7. The potential due to a conducting sphere of charge q at a point A outside the
sphere is 7V and electric field there is 3V / m . There is another point B such that
the electric field at this point smaller in magnitude than that of ‘A’. However, if
magnitude of the charge is tripled, the electric field at B becomes 3V/m. The
potential at B is now closest to (Assume potential at infinity is zero)
7
A) 21V B) 12V C) 7V D) V
3
8. Two small neutral metal spheres A and B each of radius r supported on
insulating stands located at a distance l from each other are connected by a thin
conducting wire. Near to the spheres is brought a point charge q at a distance
r on the line joining centers of the spheres. The charge net induced on
sphere B is
T A B
q
R
l l
qr qr qr 2
A) B) C) q D)
4 2
LR
2 4
space for rough work Page 6
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
9. A conducting sphere of radius R and surface charge density is given. An
imaginary infinitely large plane surface at a distance ‘x’ from centre of sphere
cuts the sphere as shown. What is the magnitude of the flux linked with one side
of plane surface area due to electric field due to sphere ( 0 x R )
2Rx 2 R 2 x 2 2x 2
A) B) C) D)
2 o o o o
10. Imagine a isolated uniform solid spherical rigid planet (ignore its rotation) of
mass M and radius R. A smaller sphere of radius R whose periphery coincides
2
T
with centre of original planet can be scooped out as shown. If the scooped out
portion somehow is slowly kept back in its place, then what is contact force
between this scooped out portion and rest of the planet ?
R R
M
O
LR
GM 2 GM 2 GM 2
A) B) C) D) zero
16R 2 8R 2 4R 2
space for rough work Page 7
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Section-2
(Paragraph Type)
This section contains 3 paragraphs each describing theory, experiment, data etc. Six questions relate to three
paragraphs with two questions on each paragraph. Each question pertaining to a particular paragraph
should have only one correct answer among the four choices A, B, C and D.
Paragraph for Questions 11 & 12:
On a certain planet which is a uniform solid sphere of mass M and Radius R, due
to rotation about its polar axis, ratio of maximum to minimum values of apparent
acceleration due to gravity at the surface is 3 : 2
T
11. What is the length of a Geostationary satellite which is a vertical rigid rod with
its one end suspended in air near earth’s surface?
3R
A) R B) 2( 3 1)R C) (2 2)R D)
R 2
12. If the rod is suddenly stopped and released, then immediately after release (Just
before collision with earth). What is the ratio of Tension in the rod at the points
LR
of trisection (closer point to earth to farther point to earth) ?
3 2 5
A) B) C) D) indeterminate
2 3 4
space for rough work Page 8
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Paragraph for Questions 13 & 14:
The electric potential varies in space according to the relation V = 3x + 4y. A
particle of mass 0.1 kg starts from rest from point (2, 3.2) under the influence of
this field. The charge on the particle is +1C. Assume V and (x, y) are in S.I.
units
13. The component of electric field in the x-direction (Ex) is
A) 3 Vm1 B) 4 Vm1 C) 5 Vm 1 D) 8 Vm 1
14. The velocity of the particle when it crosses the x-axis is
A) 20 × 10-3 ms-1 B) 40 × 10-3 ms-1
C) 30 × 10-3 ms-1 D) 50 × 10-3 ms-1
Paragraph for Questions 15 & 16:
T
In order to investigate the interaction between a point charge and a conducting
spherical shell, the method of spherical image charges can be applied. Firstly, we
R
can consider a simple situation of two point charges Q1 and Q 2 in space. In the
field produced by them the locus of points of zero potential is given by
1 Q1 Q2
LR
O
4 o r1 r2
space for rough work Page 9
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
r1 r2
Q1
Q2
r1
constant. According to Appollonios theorem, points with this property lie
r2
on a sphere called “Appollonios sphere”. Therefore zero potential surface is a
sphere.
If a spherical metal shell (of Radius R) is earthed (see diagram) and a point
charge ‘Q’ is placed inside it at a distance ‘d’ from centre (d<R), electric field
inside the shell (along with the points on the shell), due to the actual charge and
induced charge will be as if it were produced by the actual charge Q and a
negative point charge outside the spherical shell. The latter charge is what is
called a “spherical image charge”. The spherical shell, then can be considered
the “Appollonios’s sphere” mentioned above.
T
d
O Q
R
15. What is the force of interaction between grounded sphere and charge ‘Q’
mentioned in the paragraph? (K 1 )
4 o
LR
2
KQ Rd 2
KQ d KQ 2d KQ2
A) B) C) D)
(R 2 d 2 )2 R3 (R 2 d 2 )3/2 R 2 d2
space for rough work Page 10
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
16. The value and location of image charge will be
d
A) “ Q ” to the right of Q and outside the sphere
R
R
B) “ Q ” to the right of Q and outside the sphere
d
d
C) “ Q ” to the left of Q and inside the sphere
R
R
D) “ Q ” to the left of Q and outside the sphere
d
Section-3
(Matching List Type)
This section contains four questions, each having two matching lists (List-1 & List-II). The options for the correct match are
provided as (A), (B),(C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
17. Column-II describes uniform mass distribution with points A,B marked on the
material points of mass
distribution and P is a space point where direction of
gravitational field E is studied due to mass distribution in Column-I
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II
A) E has a component towards A
T B
P
A
R
P) Uniform circular ring. A,B are
diametrically opposite points. P is
LR
on diameter AB, closer to A
space for rough work Page 11
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
B) E is a null vector
B A
P
Axial view
Q) Uniform long hollow cylinder. APB
is a line perpendicular to axis of
cylinder passing through the axis
and far away from its ends. P is
closer to B
A
C) E has a component perpendicular
P
to AB
B
R) A,B are ends of two identical
uniform semi-infinite sheets. Line
APB is perpendicular to sheets
T
and P is midpoint of AB
A
P
B
R S) Similar description as option ‘r)’ but
the sheets’ indeterminate ends are
in opposite directions.
A) A- P ; B –Q,S ; C –R B) A- Q ; B –P,S ; C –R
LR
C) A- P ; B –Q,R,S ; C –doesn’t match
D) A- doesn’t match ; B –Q,R,S ; C – doesn’t match
space for rough work Page 12
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
18. Column I gives certain situation in which electric field is represented by electric
lines of forces in x-y plane. Column II gives corresponding representation of
equipotential lines in x-y plane. Match the figures in column I with the figures in
column II
Column-I Column-II
y y Higher potential
P) 1)
x x
Electric line
of forces
Lower potential
y y Lower potential
Q) 2)
x x
Electric line
of forces
Higher potential
y y
R) 3)
Lower potential
Higher potential
T
x x
Electric line
of forces
y y
S) 4)
Higher potential
Lower potential
R
x x
Electric line
of forces
LR
space for rough work Page 13
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
P Q R S P Q R S
A) 1 3 4 2 B) 2 4 3 1
C) 4 3 2 1 D) 3 1 4 2
19. In a free space, a thin rod (non-conducting) carrying uniformly distributed
negative charge ‘-q’ is placed symmetrically along the axis of a thin non-
conducting ring of radius R carrying uniformly distributed charge Q. Mass of the
rod is m and length is 2R . The ring is fixed and rod is free to move. The rod
is displaced slightly along the axis of the ring by a small distance x (x<<R) and
then released. Due to this displacement of rod by x from its symmetrically
position the electrostatic potential energy of ring-rod system changes by U . The
restoring force on rod immediately after release is F. The time period of small
oscillations of rod is T.
Column-I Column-II
(i) U for fixed values of Q ,q , R is (p) 2
proportional to x where n=
n
(ii) F for fixed values of Q,-q,R is (q) 1
T
proportional to x where r=
r
(iii) Un (where n as mentioned in (r) 3
x 2
option i) is where K=
R
K4 2 o R 3
(iv) T for fixed values of Q ,q , m is (s) 3
proportional to R where p=
p
A) i – p; ii – q; iii – p; iv – r B) i – p; ii – q; iii – q; iv – r
LR
C) i – p; ii – q; iii – r; iv – s D) i – p; ii – p; iii – p; iv - r
space for rough work Page 14
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
20. If a charge q is spread uniformly on a thin non-conducting square sheet, the
electric potential at its centre and corner are found to be v1 and v2 respectively. If
six such charged sheets are joined to make a hollow cube, the potential at the
centre of the cube is found be v3 . The potential at corner of this cube is v4 . In all
cases potential at infinitely distant points is assumed to be zero
Column – I Column – II
(A)
v1
= (P) -1
v2
(B) The number of points in the plane (Q) 4
of the isolated charged sheet mentioned
above having potential of v2 is
(C) v 3v v 3 where n= (R) 2
4 2
n
(D) Instead of potential at infinity, 1
T
(S)
potential at centre of isolated charged 2
sheet mentioned above is taken as zero,
then ratio of new value of v2 to old
R
value of v2 is
A) A-P, B-S, C-R, D-Q B) A-R, B-Q, C-R, D-P
LR
C) A-S, B-Q, C-R, D-P D) A-R, B-Q, C-Q, D-P
space for rough work Page 15
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
PART-II_CHEMISTRY Max Marks : 60
Section-1
(One or more options correct type)
This section contains 10 Multiple Choice questions. Each Question has Four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D). Out of Which
Only One is correct
21. HClO4 P4O10 A B . In ‘A’, the number of d p bonds are
A) 8 B) 4 C) 6 D) 7
22. ' p ' Au qCN H 2O O2 X OH . In the balanced stoichiometric equation
the ‘q’ value is
A) 8 B) 4 C) 2 D) 6
23.
KX . The true statement regarding the anion ‘ X ’ is
KI I 2
A) It has bent structure
T
B) The central iodine atom has sp3 hybridization
C) It has one d p bond
D) It has 9 lone-pairs
R
24. Which of the following is oxidized by Conc. H 2 SO4 ?
LR
A) HF B) HCl C) HI D) H 2 F2
space for rough work Page 16
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
25. The number of d p bonds in perxenate ion is
A) 4 B) 6 C) 8 D) 2
26. Which one of the following is not a carbonate mineral?
A) Cerrusite B) Anglesite C) Calamine D) Aragonite
27. (I) C s O2 g CO2 g
(II) 2CO g O2 g 2CO2 g
(III) 2C O2 g 2CO g
T
Match the graph with the above process
R
A) P-I, Q-II, R-III B) P-II, Q-I, R-III
C) P-III, Q-I,R-II D) P-III, Q-II, R-I
LR
28. The usual carbon content in steel is
A) 2 – 6% B) 2 – 0.2% C) 0.1 – 1% D) 0 – 6%
space for rough work Page 17
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
29. The chief slag formed in the Blast furnace during the extraction of iron is
A) FeSiO3 B) MgSiO3 C) Ca 3 PO4 2 D) CaSiO3
30. The slag formed during the Bessemer process in the extraction of copper is
A) FeSiO3 B) MgSiO3 C) Ca3 PO4 2 D) CaSiO3
Section-2
(Paragraph Type)
This section contains 3 paragraphs each describing theory, experiment, data etc. Six questions relate to three
paragraphs with two questions on each paragraph. Each question pertaining to a particular paragraph
should have only one correct answer among the four choices A, B, C and D.
Paragraph for Questions 31 and 32
Na2CO3 leached with water,
FeO.Cr2O3
Mass
evaporated, crystallized
P yellow compound
Blast of air
Conc.H 2 SO4
NH 4Cl
NaCl R Q Na2 SO4 .10 H 2O crystalized and
orange red orange red separated by filtration
31. R
T
A B H 2O . ' A ' and ' B ' are
R
A) Cr and N 2 B) Cr2O3 and N 2 C) Cr and NH 3 D) Cr2O3 and NH 3
32. ‘A’ can be best reduced to metal by using
LR
A) H 2 B) C C) Al D) Mg
space for rough work Page 18
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Paragraph for Question 33 and 34
3 AgNO
NaCl aqueous solution A
KI
B C
MnO2 Conc.H 2 SO4
D
K 2Cr2O7 Conc.H 2 SO4
33. The number of d p bonds in ‘D’ is
A)1 B)2 C)3 D) 4
34. The correct statement regarding A or B or C is
T
A) B gives blue color with starch
B) B does not react with water
R
C) A is insoluble in aqueous ammonia
LR
D) C is soluble in aqueous KI
space for rough work Page 19
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Paragraph for Question 35 and 36
(i) Cl2 reacts with water giving Cl2 H 2O HClO HCl
(ii) 2CuCl2
2CuCl Cl2
35. Which one of the following can behave like Cl2 ?
A) O2 B) N 2 C) CO2 D) CN 2
36. Cu CN 2
A B
CuI 2
C D
B & D are respectively
A) CuCN , CuI
T B) CuI , CuCN
C) I 2 , CN 2
R D) CN 2 , I 2
Section-3
(Matching List Type)
LR
This section contains four questions, each having two matching lists (List-1 & List-II). The options for the correct match are
provided as (A), (B),(C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
space for rough work Page 20
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
37. Match the column:
Column-I Column-II
P) ClO 1) Weakest base
Q) ClO2 2) Present of d p bonds
R) ClO3 3) Highest charge density on
oxygen
S) ClO4
4) Least delocalization of -
electrons
Code :
P Q R S P Q R S
T
A) 3,4 2 2 1,2 B) 3 1,2 3 1,3
C) 4 1,3 2,3 2 D) 1,2 2,3 3,4 1,3
R
LR
space for rough work Page 21
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
38. Match the element given in column-I with the property related to it given in
column-II
Column-I Column-II
P) Cl2 1) Forms stable Gas Hydrate
Q) Xe 2) Colored substance
R) I 2 3) Oxidizing agent
S) F2 4) Least reactive
P Q R S P Q R S
A) 1,3,4 2,4 2,3 1,4 B) 1,2,3 1,4 2,3 2,3
C) 1,4 2,3 2,4 1,2 D) 1,3 1,2 1,3 1,3
39. Match the metal given in column-I with the process related directly for the
extraction of metal or for the extraction of other metal
Column-I Column-II
T
P) Pb 1) Parkes process
Q) Ag 2) Pattinsons process
R) 3) Mc Arthur Forrest cyanide process
Zn
R
S) Au 4) Electrorefining
P Q R S P Q R S
LR
A) 1,2,3 1,3,4 1,2,4 2,3 B) 1,3 3,4 1,2 1,3
C) 3,4 2,3 1,4 3,4 D) 1,2,4 1,2,3,4 1,3,4 3,4
space for rough work Page 22
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
40. Match the product/s given in column-II with the reactive given in column-I
Column-I Column-II
P) ClO2 NaOH 1) NaClO2
Q) Cl2O6 NaOH 2) NaClO3
R) Cl2O NaOH cold 3) NaClO4
S) ClO2 NaOH H 2O2 4) NaClO
P Q R S P Q R S
A) 1,2 2,3 4 1 B) 2,3 1,3 1 4
C) 3 2 1
T 3 D) 1 2 3 4
R
LR
space for rough work Page 23
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
PART-III_MATHEMATICS Max Marks : 60
Section-1
(Only one Option correct Type)
This section contains 10 Multiple Choice questions. Each Question has Four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D). Out of Which
Only One is correct
41. Let a , b , c be three vectors given by a i j 2k , b 2i j k , c 5i 3 j and if
r is a unit vector then the maximum possible value of r a b r b c equals
A) 2 35 B) 3 7 C) 5 7 D) 10 7
2
42. If a b c p, a b q , b c r , a . p 1, b . p 1 and p 3 then which is false
1 1
A) a p 2p q p r B) b p pq pr
3 3
C) p q a b D) a b c p q r
T
43. Let a , b , c be unit vectors and are non-coplanar such that
a b c 2b c a 3c a b 3 a b c , is real, then number of
R
possible values of
A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3
LR
space for rough work Page 24
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
44. If A, B,C,D are four points in space and satisfying AB 3, BC 7, CD 11 and
DA 9 then the value of AC.BD
A) 0 B) 21 C) 15 D) 27
45. If the vectors i cj bk , ci j ak , bi aj k are coplanar vectors and a 1
2
then the maximum value of ai bj ck is
A) 3 B) 12 C) 18 D) 8
46. The resultant of the two vectors a and b is c . If c trisects the angle between a
and b and if a 6, b 4 then c equals (no two vectors are parallel)
A) 3 B) 4 C) 5 D) 6
a d c
T
47. If the vector r satisfies r a r .b c d be given by r a a 2
a .c a
then ( a, b, c, d are non – zero vectors and a is not perpendicular to c )
R
a .c a .b c .d r .a
A) 2 B) 2 C) 2 D) 2
a a a a
LR
space for rough work Page 25
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
48. The plane which contains the line 3 x y 1, z 4 and parallel to the line
x y z 1 0, y 2 z 1 cuts the x, y, z axes respectively at
,0,0 , 0, ,0 , 0,0, then 2 2 2 equals
A) 10 B) 14 C) 19 D) 21
49. Given a tetrahedran ABCD with AB=12, CD=6,. If the shortest distance between
the skew lines AB and CD is 8 and the angle between them is then the
6
volume of tetrahedran is
A) 12 B) 36 C) 48 D) 72
50.
T
If x and y be two unit vectors inclined at an angle 600 so that x y a and
R 1
x y b such that x a a b then the value of
2 is
A) 1 B) 2 C) 4 D) 5
LR
space for rough work Page 26
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Section-2
(Paragraph Type)
This section contains 3 paragraphs each describing theory, experiment, data etc. Six questions relate to three
paragraphs with two questions on each paragraph. Each question pertaining to a particular paragraph
should have only one correct answer among the four choices A, B, C and D.
Paragraph for Questions 51 & 52
y z
A plane P contains the line L1 : 1, x 0 and is parallel to the line
b c
x z
L2 : 1, y 0 then
a c
51. Equation of the plane P is
x y z x y z
A) 1 0 B) 1 0
a b c a b c
x y z x y z
C) 1 0 D) 1 0
a b c a b c
T
52. If the shortest distance between the lines L1 and L2 is ¼ then the shortest
x y z
distance from origin to the plane 1 is
a b c
R
A) ¼ B) ½ C) 1 D) 1/8
LR
space for rough work Page 27
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
Paragraph For Questions 53 & 54
y z x 1 y 1 z 1
If the three lines L1 : x y z, L2 : x , L3 : from a triangle
2 3 a b c
of area 6 square units
53. If , , is the point of intersection of L2 and L3 then equals
A) 4 B) 6 C) 0 D) 12
54. The possible acute angle between L2 and L3 is
22
A) B) C) cos 1 D)
3 6
7 10 2
Paragraph For Questions 55 & 56
The line of greatest slope on an inclined plane P1 is the line in the plane P1 which
T
is perpendicular to the line of intersection of the plane P1 and a horizontal plane
P2
55. Assuming the plane 2 x 3 y 4 z 0 to be horizontal, the direction cosines of the
R
line of greatest slope in the plane x 2 y 3 z 0 are
4 1 2 4 1 2 1 1 1 4 2 1
A) B) C) D)
LR
, , , , , , , ,
21 21 21 21 21 21 3 3 3 21 21 21
space for rough work Page 28
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
56. The coordinates of a point on the plane 2 x y 5 z 0 which is 2 11 units away
from the line of intersection of 2 x y 5 z 0 and 4 x 3 y 7 z 0 are
A) 6,2, 2 B) 3,1, 1 C) 6, 2,2 D) 1,3, 1
Section-3
(Matching List Type)
This section contains four questions, each having two matching lists (List-1 & List-II). The options for the correct match are
provided as (A), (B),(C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
57. Match the following
COLUMN – I COLUMN – II
(A) A line perpendicular to x 2 y 2 z 0 and passes (p) 3
through 0,1,0 . The perpendicular distance of this line
from origin is k then k equals ([] is GIF)
(B) The value of for which the plane x y z 1 0 , (q) 2
x 3 y 2 z 3 0,3 x y z 2 0 from a
triangular prism is
(C) If the circumcentre of the triangle whose vertices are (r) 4
T
3,2, 5 , 3,8, 5 and 3,2,1 is 1, , 3 then
equals
(D) If the four planes my nz 0, nz lx 0, lx my 0 (s) 0
R
and lx my nz p from a tetrahedran whose volume
p3
is then equals
3lmn
LR
A) A–s, B–r, C–r, D–q B) A–s, B–p, C–r, D–q
C) A–p, B–q, C–r, D–s D) A–p, B–r, C–s, D–q
space for rough work Page 29
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
58. Let L1 : x y z 4 0 2 x y z 3 , L2 : 3 x y z 4 0 x z 3
COLUMN – I COLUMN – II
(A) L1, L2 are coplanar then equals (p) 2
(B) If ( , , lies on both L1 and L2 then 3 (q) 1
equals
(C) If L1 is parallel to the plane x y pz 7 0 then p (r) 6
equals
(D) If L1, L2 are coplanar and if acute angle between L1, L2 (s) -1
7
T
is cos1 then k equals
k 3
A) A–s, B–r, C–q, D–p B) A–s, B–p, C–q, D–r
R
C) A–s, B–q, C–p, D–r D) A–s, B–p, C–r, D–q
LR
space for rough work Page 30
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
59. Match the following
COLUMN – I COLUMN – II
(A) ˆj (p) 1
If a b ˆj and 2a b 3iˆ , then cosine of the angle
2
between a and b is
(B) If a b c , angle between each pair of vectors is (q) 5 3
3
and a b c 6, then a
(C) Area of the parallelogram whose diagonals represent (r) 7
the vectors 3iˆ ˆj 2kˆ and iˆ 3 ˆj 4kˆ is
(D) If a is perpendicular to b c, b is perpendicular to (s) 3
5
c a , c is perpendicular to a b , a 2, b 3 and c 6
T
then a b c is
A) A–s, B–p, C–q, D–r B) A–s, B–q, C–p, D–r
R
C) A–s, B–r, C–p, D–q D) A–r, B–q, C–p, D–s
LR
space for rough work Page 31
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
60.
COLUMN – I COLUMN – II
(A) The line r i j t i k where ' t ' is scalar passes (p) i j 2 k
through the point
(B) The line r i j t i k where ' t ' is scalar and the (q) i j 2 k
plane r. 2 i j k 2 intersect at the point
(C) The point on the line r i j t i k where ' t ' is (r) 2 i j 3 k
scalar, which is at a distance of 3 units from the point
having position vector i is/are
(D) The volume of the parallelepiped having adjacent (s) j k
sides i k , 2 i j k and c is 4 cubic units then c may be
A) A–qrs, B–s, C–q, D–q
C) A–qrs, B–p, C–s, D–r
T B) A–qrs, B–q, C–s, D–q
D) A–qrs, B–prs, C–qs, D–q
R
LR
space for rough work Page 32
TOPIC WISE TEST-8 PAPER-2
You might also like
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- Lakshya Rank Refinement Test No - 8: Paper-IDocument22 pagesLakshya Rank Refinement Test No - 8: Paper-IJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- 01 11 14 SR IPLCO Jee Adv PTA 10 2014 P2 Q'PaperDocument13 pages01 11 14 SR IPLCO Jee Adv PTA 10 2014 P2 Q'PaperT.n Charith100% (1)
- 12.07.20 Sr.n-Superchaina Jee Adv 2014 p1 Gta-1 P-I QPDocument17 pages12.07.20 Sr.n-Superchaina Jee Adv 2014 p1 Gta-1 P-I QPsaloni guptaNo ratings yet
- Assessment # 33 (P - I) Question PaperDocument14 pagesAssessment # 33 (P - I) Question PaperAshwin KoradeNo ratings yet
- 14.05.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2014 P2 GUT-2 P-II QPDocument23 pages14.05.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2014 P2 GUT-2 P-II QPswarupNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Advanced Paper 15 PDFDocument44 pagesIit Jee Advanced Paper 15 PDFJatin Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- 12.07.20 Sr.n-Superchaina Jee Adv 2014 p2 Gta-1 P-II QPDocument23 pages12.07.20 Sr.n-Superchaina Jee Adv 2014 p2 Gta-1 P-II QPsaloni guptaNo ratings yet
- Model A QP WATDocument18 pagesModel A QP WATasdfNo ratings yet
- TWT-2 Paper2Document31 pagesTWT-2 Paper2Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2015 - PAPER-IIDocument17 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2015 - PAPER-IISamarth ThakurNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit - Wta-29 - (2020-P1) - Q.P - 01-05-2022Document14 pagesXi Iit - Wta-29 - (2020-P1) - Q.P - 01-05-2022Dinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- TWT-2 Paper1Document24 pagesTWT-2 Paper1Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Xii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Document13 pagesXii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Stephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced 2019 Physics Quick Rivision Test-5 QuesitonsDocument13 pagesJee Advanced 2019 Physics Quick Rivision Test-5 QuesitonsSky SirNo ratings yet
- Master Jee Classes: JEE-ADVANCE-2014-P2-ModelDocument42 pagesMaster Jee Classes: JEE-ADVANCE-2014-P2-ModelkamalNo ratings yet
- 08-08-19 Sri Chaitanya-Jr - Chaina-I Jee-Adv (2014 P2) WTA-13 Q.PDocument28 pages08-08-19 Sri Chaitanya-Jr - Chaina-I Jee-Adv (2014 P2) WTA-13 Q.PPRANITH REDDYNo ratings yet
- 07 12 16 - SR - IIT IZ CO SPARK - RPTA 13 - 2015 - P1 - Q.PDocument31 pages07 12 16 - SR - IIT IZ CO SPARK - RPTA 13 - 2015 - P1 - Q.PfocusonyourgoaldreamiitbombayNo ratings yet
- Xii CF Iit - 16.05.2022 WTM-04 (Jee Mains Model)Document16 pagesXii CF Iit - 16.05.2022 WTM-04 (Jee Mains Model)Kripanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- 06-02-2022 SR - Iit Star Batch II Jee-Adv 2011-p1 Pta-14 Q.P FinalDocument11 pages06-02-2022 SR - Iit Star Batch II Jee-Adv 2011-p1 Pta-14 Q.P FinalCE-026 BharadwajaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola AssignmentDocument25 pagesHyperbola AssignmentPrathamesh NavaleNo ratings yet
- 03 01 2020 SR Iit N Chaina N120 Jee Adv2015 P2 Cta 2 QP Final1Document14 pages03 01 2020 SR Iit N Chaina N120 Jee Adv2015 P2 Cta 2 QP Final1Tejas MagguNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Adv Mock Test - 32Document19 pagesFiitjee: Adv Mock Test - 32Jijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- 07-06-20 - Cat-43 - 2014-P2 - QP - KeyDocument26 pages07-06-20 - Cat-43 - 2014-P2 - QP - KeyPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- GT 2 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument26 pagesGT 2 Paper 1 SolutionsAnand MurugananthamNo ratings yet
- 22-12-18 JR - IIT-IZ-N120 Jee Adv 2014 P1 WAT-28 QP PDFDocument19 pages22-12-18 JR - IIT-IZ-N120 Jee Adv 2014 P1 WAT-28 QP PDFM jhansiNo ratings yet
- 30-05-21 Inc - Sr.iit Star Co-Sc Jee Adv 2015 P-II Cat-20 QPDocument18 pages30-05-21 Inc - Sr.iit Star Co-Sc Jee Adv 2015 P-II Cat-20 QPVijay RaghavaNo ratings yet
- Xii Pass Ic Iit FTM-06 18-09-2023 QPDocument16 pagesXii Pass Ic Iit FTM-06 18-09-2023 QPnoshit00100No ratings yet
- 23 05 16 JR - Iit Iz Co Spark (Incoming) Jee Adv (2012 p1) Wta 4 Q.P F NDocument18 pages23 05 16 JR - Iit Iz Co Spark (Incoming) Jee Adv (2012 p1) Wta 4 Q.P F NrahulNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2012 - PAPER-IDocument18 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2012 - PAPER-ISridhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 08-01-22 - JR - Iit - (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2014 (P-Ii) - Wat-35 - QPDocument23 pages08-01-22 - JR - Iit - (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2014 (P-Ii) - Wat-35 - QPMike WazowskiNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: SyllabusDocument16 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: SyllabusPrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2016 - PAPER-IDocument16 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: 2016 - PAPER-IAditya Raj SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cat 2Document25 pagesCat 2Raghav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 16 05 16 - JR - IIT IZ CO SPARK (Incoming) - Jee Adv (2014 P1) - WTA 3 - Q.PAPER - F - N PDFDocument17 pages16 05 16 - JR - IIT IZ CO SPARK (Incoming) - Jee Adv (2014 P1) - WTA 3 - Q.PAPER - F - N PDFCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- 11-09-2020 - Inc SR Iit Co Spark & Spark, Ic Jee Main Model QPDocument8 pages11-09-2020 - Inc SR Iit Co Spark & Spark, Ic Jee Main Model QPNarayana GIRLS CAMPUSNo ratings yet
- 29.05.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2016 - P1 - GTA-1 - QPDocument17 pages29.05.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2016 - P1 - GTA-1 - QPPhani PadmasriNo ratings yet
- 03-05-20 - SR - IIT - N-SUPER CHAINA&N-CHAINA - Jee-Adv - 2017 - P1 - GTA-13 - P-I - QPDocument19 pages03-05-20 - SR - IIT - N-SUPER CHAINA&N-CHAINA - Jee-Adv - 2017 - P1 - GTA-13 - P-I - QPsaloni guptaNo ratings yet
- 08-01-22 - JR - Iit - (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2014 (P-Ii) - Wat-35 - QP PDFDocument21 pages08-01-22 - JR - Iit - (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2014 (P-Ii) - Wat-35 - QP PDFMike WazowskiNo ratings yet
- 01.11.20-Pta 10Document30 pages01.11.20-Pta 10Tejas MagguNo ratings yet
- 21-06-20 - Jee-Adv - CAT-44 - QP - KEYDocument23 pages21-06-20 - Jee-Adv - CAT-44 - QP - KEYPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: RPTA-12Document18 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: RPTA-12Sridhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 01 12 19 - SR - Chaina II - SR.C IPL - SR - IPL IC - BT 1 - Jee Adv (2014 P2) - RPTA 12 - Q.PAPER PDFDocument18 pages01 12 19 - SR - Chaina II - SR.C IPL - SR - IPL IC - BT 1 - Jee Adv (2014 P2) - RPTA 12 - Q.PAPER PDFSridhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up Xii Ic Iit (Cta-01) 22-05-2023-Adv - 2022 P-1-q. Paper FinalDocument9 pagesWarm-Up Xii Ic Iit (Cta-01) 22-05-2023-Adv - 2022 P-1-q. Paper FinalPavika KaurNo ratings yet
- 16 04 15 SR COIPL Jee Adv GTA 3 2011 P2 Q'PaperDocument11 pages16 04 15 SR COIPL Jee Adv GTA 3 2011 P2 Q'PaperYogesh BansalNo ratings yet
- 01-05-21 - SR.N-SUPER CHAINA - Jee-Adv - UTA-1 - SYLLABUS: Sec: OSR - IIT - N-SC Date: 01-05-21 Time: 03:00 Hrs Max. Marks: 180Document19 pages01-05-21 - SR.N-SUPER CHAINA - Jee-Adv - UTA-1 - SYLLABUS: Sec: OSR - IIT - N-SC Date: 01-05-21 Time: 03:00 Hrs Max. Marks: 180Kanishk mishraNo ratings yet
- 07062020Document19 pages07062020Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- CPT 3Document9 pagesCPT 3ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- 17 05 20 - Cat 42 - QPDocument19 pages17 05 20 - Cat 42 - QPPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- 16 12 18 - JR - IPL.IC - Jee Adv 2013 (P2) - Q.PaperDocument20 pages16 12 18 - JR - IPL.IC - Jee Adv 2013 (P2) - Q.PaperZhugzhuang ZuryNo ratings yet
- Xii Stud Iit - FTM-10 - 23.10.2023 - QPDocument18 pagesXii Stud Iit - FTM-10 - 23.10.2023 - QPhemab30851No ratings yet
- Test SeriesDocument23 pagesTest Seriespass6117stbdNo ratings yet
- 11 05 23 SR OUTGOING Jee AdvP2 SGTA 3PAPER 2 QP FINALDocument17 pages11 05 23 SR OUTGOING Jee AdvP2 SGTA 3PAPER 2 QP FINALVallabhNo ratings yet
- Jee Adv Mp7 Paper1Document19 pagesJee Adv Mp7 Paper1kvg3venu7329No ratings yet
- 02-08-20 - Incoming - Jr.iit - Star Co-Sc - Iit Jee Adv - 2017 - P-I - Wat-10 - QPDocument17 pages02-08-20 - Incoming - Jr.iit - Star Co-Sc - Iit Jee Adv - 2017 - P-I - Wat-10 - QPASHUTOSH PATNAIKNo ratings yet
- 18-12-2022 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS - BT - Jee-Adv (2020-P - PTA-14 - Q.PaperDocument23 pages18-12-2022 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS - BT - Jee-Adv (2020-P - PTA-14 - Q.PaperKrishnamohanNo ratings yet
- 16-04-2022 Xi Iit WTM - QPDocument13 pages16-04-2022 Xi Iit WTM - QPDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 43Document8 pagesPhysics Assignment 43Param shahNo ratings yet
- REVISED.02.07.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2015 P1 PTA-7 QPDocument17 pagesREVISED.02.07.20 Sr.N-SUPERCHAINA Jee Adv 2015 P1 PTA-7 QPsaloni guptaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towergad B-218Document1 pageCooling Towergad B-218Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Selection Chart Worm GearsDocument1 pageSelection Chart Worm GearsJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Maths (Question Paper)Document7 pagesMaths (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Physics (Question Paper)Document7 pagesPhysics (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Adaptable Gear CatalogueDocument8 pagesAdaptable Gear CatalogueJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Question Paper)Document5 pagesChemistry (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- TWT-2 Paper2Document31 pagesTWT-2 Paper2Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- TWT-2 Paper1Document24 pagesTWT-2 Paper1Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Form For VendorDocument20 pagesForm For VendorJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- TWT-3 Paper-2Document31 pagesTWT-3 Paper-2Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Wholesale Customers DataDocument14 pagesWholesale Customers DataJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- LFL HK New Vendor Registration Form-20190920Document2 pagesLFL HK New Vendor Registration Form-20190920Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Org ChartDocument1 pageOrg ChartJay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- v4n3 PDFDocument168 pagesv4n3 PDFJorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Amp-Eng Anger Management ProfileDocument6 pagesAmp-Eng Anger Management Profileminodora100% (1)
- Nutrition AssessmentDocument7 pagesNutrition AssessmentJoyce VitalNo ratings yet
- Finalllllll BPDocument46 pagesFinalllllll BPSheypia Agustin JacintoNo ratings yet
- Slender Quest DetailsDocument1 pageSlender Quest Detailsparents021No ratings yet
- Directory of Acredited Medical Testing LaboratoriesDocument93 pagesDirectory of Acredited Medical Testing LaboratoriesCALIDAD METROMEDICA E.UNo ratings yet
- MBBS Cafeteria TEST 1Document7 pagesMBBS Cafeteria TEST 1aalishba6a2b9cNo ratings yet
- E560 PSR00 DSDocument4 pagesE560 PSR00 DSSalvador FayssalNo ratings yet
- CORONADocument25 pagesCORONAMohammedNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Capacitive ReactanceDocument4 pagesLab 2 - Capacitive Reactanceali basitNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Module Compilation FinalsDocument107 pagesIncome Taxation Module Compilation FinalsJasmine CardinalNo ratings yet
- Formulating A Dental Treatment Plan: DR Tashnim BagusDocument33 pagesFormulating A Dental Treatment Plan: DR Tashnim BagustarekrabiNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine + OndansetronDocument7 pagesRanitidine + OndansetronAllicia PutriNo ratings yet
- Manual Fritadeira PDFDocument136 pagesManual Fritadeira PDFtherasiaNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 - Toothache Drugs and MedicationsDocument10 pagesPBL 3 - Toothache Drugs and MedicationsAlbert LawNo ratings yet
- Comparison FM Vs ATEX Flow Chart PDFDocument1 pageComparison FM Vs ATEX Flow Chart PDFGoogool YNo ratings yet
- Siklus Biogeokimia - Retensi NutrienDocument24 pagesSiklus Biogeokimia - Retensi NutrienPutri Nur Fadhilah YasharNo ratings yet
- Interpretacion Curso Cat CoolantDocument39 pagesInterpretacion Curso Cat Coolanthouston machacaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Wassce Integrated Science 1Document6 pages2018 Wassce Integrated Science 1Theophilus Asante-TannorNo ratings yet
- Bio-Fertilizer Data SheetDocument1 pageBio-Fertilizer Data SheetOnyekachi MacaulayNo ratings yet
- Mini Dental ImplantsDocument11 pagesMini Dental ImplantsDario PuljićNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineDocument7 pagesBuoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineEmmanuel LawrenceNo ratings yet
- CyberPunk 2020 - Unofficial - Reference Book - Ammo and Add-OnsDocument6 pagesCyberPunk 2020 - Unofficial - Reference Book - Ammo and Add-Onsllokuniyahooes100% (1)
- Pressure Relief Valve, Poppet-Type, Direct-Acting: M28x1.5 - Q 50 L/min (13 GPM) - P 320 Bar (4600 PSI)Document2 pagesPressure Relief Valve, Poppet-Type, Direct-Acting: M28x1.5 - Q 50 L/min (13 GPM) - P 320 Bar (4600 PSI)Richam HamzeNo ratings yet
- JSLHR Author InstructionsDocument14 pagesJSLHR Author InstructionsChanyanit CharoenpholNo ratings yet
- The Internet Test 9th Grade A2b1 Tests 105573Document5 pagesThe Internet Test 9th Grade A2b1 Tests 105573Daniil CozmicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Assessment of PostureDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Assessment of Posturehis.thunder122No ratings yet
- 10 Achievement ChartDocument3 pages10 Achievement ChartLyka ollerasNo ratings yet
- Master of International HealthDocument5 pagesMaster of International HealthJesper Domincil BayauaNo ratings yet
- Fleming Trio-E Promotional SheetDocument2 pagesFleming Trio-E Promotional SheetRed BarnNo ratings yet