Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RPA, AI and digital transformation
Uploaded by
Test accOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RPA, AI and digital transformation
Uploaded by
Test accCopyright:
Available Formats
e-ISSN: 2582-5208
International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science
Volume:03/Issue:01/January-2021 Impact Factor- 5.354 www.irjmets.com
A REVIEW- THE GOLDEN TRIANGLE OF RPA, AI AND
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
Sanket Daptardar*1
*1University of Petroleum and Energy Studies Research and Development, Dehradun,
Uttarakhand, India.
ABSTRACT
The use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is expanding rapidly across industry verticals, geographies, and
varied company sizes and business models, with companies chasing benefits including cost optimization,
operations optimization, enhanced customer experience, lower errors in repeatable tasks, seamless
management and control, and quick implementation turnaround and return of investment. That is promoting
consistently increasing spending in RPA space. Industry analysts predict spending on RPA software and tools to
rise between $1.3 billion and $2.9 billion in 2021. While it is possible to execute RPA without a comprehensive
digital transformation program, the success of these digital transformation programs will not see complete
success or serve its purpose without the inclusion of some automation capabilities. Evidently past few years
RPA has seen some of most welcoming and the best adaptability in the corporate world, the academic research
requires an enhanced and focused theoretical and synoptical analysis of RPA specifically empirical and start
generating data sets. Performing a literature review and lifecycle analysis, we propose – in a holistic and
structured way –traits that define success of RPA, providing preference as well as a focus for further research
and challenges.
Keywords: RPA, automation, digital transformation.
I. INTRODUCTION
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the term used for software tools that partially or fully automate human
activities that are manual, rule-based, and repetitive. They work by replicating the actions of a human
interacting with number of software applications to perform activities and tasks such as data entry, process
defined transactions, and respond to simple service queries. The “chatbot” which is one of the first adapted use
case of RPA enablement that has started to become pervasive on most interactive websites as a tool for
customer satisfaction, lead generation and basic interaction can handle the typical standard queries like “What
can I help you with today”, “What products are you searching for”, “Are you sure” and the like. Robotic process
automation (RPA) has become a digital changing agent in almost every industry by streamlining such
processes. Advancements in the field of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence is making businesses
ready for intelligent automation (IA), an extended output of RPA that concludes out how to execute gamut of
business processes with context, instead of as an increment of discrete tasks.
While RPA tools are not total replacements for the underlying business applications; instead, they simply
automate the existing manual tasks of human workers. The tools essentially scan at the screens that workers
today look at and tick, fill in and update the same boxes and fields within the user interface by pulling the
pertinent data from the defined location as well as it provides more time to the individuals to focus on work
that needs communication skills like developing client cooperation and solving the issues of the clients which
require complex emotional intelligence abilities of humans. The essential objectives of digital transformations
are numerous and can be utilized in different types of requirements and situations. Today many businesses are
using RPA and automated change systems together to see how these systems complement each other.
Nonetheless, RPA must be used in coordination with different AI systems, so that the client interactions are also
made more meaningful. Businesses can use RPA for bringing about rapid change in the capability of the
organization, hence increasing production and customer experience and satisfaction concurrently.
www.irjmets.com @International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering, Technology and Science
[887]
e-ISSN: 2582-5208
International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science
Volume:03/Issue:01/January-2021 Impact Factor- 5.354 www.irjmets.com
RPA tools are best suited for processes with repeatable, predictable interactions with IT applications. These
processes typically lack the scale or value to warrant automation via core systems transformation or if core
systems transformation is not due to be implemented soon. RPA tools can improve the efficiency of these
processes and the effectiveness of services without changing the underlining systems. RPA software ‘robots’
perform routine business processes by mimicking the way that people interact with applications through a user
interface and following simple rules to make decisions. Entire end-to-end processes can be performed by
software robots with little human interaction, typically to manage exception.
Fig.-1: Nature of Process Automation
II. DETAILS
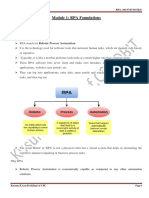
RPA IS AUGMENTING PEOPLE WITH AUTOMATION PROCEDURES
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the utilization of programming "robots" (i.e., digital programs) to
normalize and mechanize repeatable business measures. RPA robots can carry out similar tasks repeatedly
without any breaks. They will not change the method with which they complete the activities and task, the
coded instructions will be carried out precisely to the dot. Rather than making individuals excess, RPA robots
are more like menial helpers who let you offload tedious undertakings that are necessary and are very time-
consuming. In contrast to people, robots never get exhausted as they complete these assignments precisely as
educated and with the most extreme proficiency. Human-made reasoning (AI) and Robotic Process Automation
(RPA) are two of the best advances for businesses to accomplish the incongruent objectives of expanding
consumer loyalty and worker confidence while decreasing operational expenses.
RPA AND DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
RPA was developed from a few unique innovations. One was robotized apparatuses that recreated the way
individuals perform work to guarantee that the mechanized frameworks worked as usual. Another was the
venture content administration universe, organizations expected to separate information from approaching
structures, both filtered and in most cases, electronically conveyed. Like RPA, those devices dominated at taking
data from one framework and consequently moving it into another framework, quickly and dependably.
Today's RPA results are like macros in Excel, they liberate the process of bookkeeping. The most recent devices
permit individuals to record their activities without thinking about how to disclose to the RPA programming
precisely what steps to take. Clients can accordingly go in and tweak the recorded cycle as required.
www.irjmets.com @International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering, Technology and Science
[888]
e-ISSN: 2582-5208
International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science
Volume:03/Issue:01/January-2021 Impact Factor- 5.354 www.irjmets.com
The objective is straightforward: to dispose of tedious, manual errands. While sending RPA, organizations
should discover those assignments and computerize them. Numerous clients have announced a decrease in
mistakes and the time spent on the projects. Businesses can commonly acknowledge positive outcomes in
practically no time, opening assets quickly for different endeavors.
RPA IS ONE PORTION OF THE TOOLKIT OF DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
The business needs to drive computerized change. However, IT should be required to actualize the necessary
innovation changes. The test is that IT has restricted assets and cannot carefully change all business aspects
simultaneously. The IT division may have to refresh or supplant a vital framework before any RPA, and
advanced change exertion starts.
The initial step to completely mechanizing and carefully changing a cycle is to redesign the client's experience.
As that advances, the change exertion soothes out the information data sources and yields of the UI. The
progression of data progressively extends to downstream frameworks. IT can robotize extra guidelines in the
background over the long run, eliminating the requirement for individuals to start the legitimate
administration of the information.
RPA gets organizations past the halfway point. It permits the organization to mechanize undertakings without
waiting for each change to be finished. When done appropriately, RPA can help departments of the organization
gain interval ground while hanging tight for their chance on the need list.
An additional advantage to utilizing RPA happens when organizations permit staff to assemble bots themselves.
The subsequent robots rapidly uncover more about what individuals do every day. What are they mechanizing?
What are their problem areas? Like shadow IT revealed the unfulfilled staff requirements, RPA shows IT where
it needs to center its advanced change endeavors.
IA AND RPA INTEGRATING INTO AUTOMATION
RPA is utilized for work related to individuals via robotizing the monotonous cycles. AI is considered as a type
of innovation to supplant human work and computerize start to finish (unattended computerization). RPA
utilizes organized sources of info and rationale, while AI utilizes unstructured information sources and builds
up its reasoning. Joining both RPA and human-made brainpower can make an utterly self-ruling cycle. Since
businesses have organized information (e.g., structure fields) and unstructured information (e.g., free content,
everyday discourse), numerous cycles require both RPA and AI to completely robotize a process from start to
finish or to improve a mechanical cycle whenever it has been conveyed.
Start to finish robotization is critical to offering the self-assistance choices that such countless clients need.
Consider how opening another ledger online can be wholly robotized with RPA and AI's assistance, bringing
about fulfilled clients and cash-saving efficiencies for the bank. Our client needs to open another ledger on the
web. The chatbot checks the sort of record the client needs (a business account) and connects to the application
structure. The rounded-out structure is submitted and gave off to another robot who commences the cycle to
open another record. For example, the robot backs end assignments, checking the client FICO rating and
running a "know your client" confirmation measure on Google and informal communities.
Next, an intelligent OCR robot examines the checked reports the client transferred alongside the new record
structure. It recognizes a disparity in the client name as it shows up on the system and her driver's permit. This
exemption is sent for human mediation. The specialist affirms that John Doe and John Jane Doe are a similar
individual for sure because their Social Security Number is indistinguishable. Given human info, the robot
assesses how to react to comparable circumstances later. The robot approves the transferred archives utilizing
text examination and common language to decipher and classify critical information from inside the free
content. When all information is pieced together, the robot executes the arrangement of undertakings needed
to set up the new business account, interfacing with the bank's different back end frameworks. If the client's
information meets bank necessities, the robot sends an email to the client with a warm invite message, account
data, and access accreditations. At last, the robot reports back to the automated control live with a job well
done.
www.irjmets.com @International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering, Technology and Science
[889]
e-ISSN: 2582-5208
International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science
Volume:03/Issue:01/January-2021 Impact Factor- 5.354 www.irjmets.com
III. PREVIOUS WORK
As mentioned in the abstract there is limited literature review and lifecycle analysis available. However, there
are some OEM and services companies who have published good number of blogs and posts specific to
respective products and services with vertical and industry specific use cases.
IV. CONCLUSION
On the off chance that organizations see RPA as the last stage of computerized change, and not an unfortunate
obligation, they overlook what is important. Robots are delicate. They are reliant on things like the input data
and do not make decisions by themselves. A move up to the ERP, IA and Digital Transformation can break the
computerized tasks. More terrible, these sorts of changes can make a bot transfer incorrect data around the
processes. 9That is the reason computerized change is the drawn-out arrangement. Done right, it makes an
enduring interface that permits cycles to advance as the business changes.
Organizations that treat RPA as a break-fix along with computerized change endeavors continue will be
pioneers in the long haul. In addition, they will also rapidly outperform those that expect that their work is
finished when they send an RPA. We realize that for companies to be competitive, they must deliver on
customer commitments and expectations and to do so, they need remarkable procedures. Furthermore, to
arrive at process excellence, companies must comprehend the procedures, and focus on value-generating
activities first and then put resources into the tools that will enable identify, mitigate and solve problem
statements. This is termed as “Process Mining “. The innovation uses both business information (time-stamped
event logs) and user interaction data to deliver a genuine image of what standard operating procedures depict.
Reengineering of certain processes should be done by correcting, optimizing, or orchestrating differently over
numerous systems or functions, as opposed to just being automated.
The demand for open-source RPA software is going to increase. With taking everything into account, companies
tend to be skewed towards open-source solutions since they offer more transparency. These improvements
favor open-source RPA. We are seeing consistent growth in the open-source RPA ecosystem with new start-ups
being launched regularly. If a revenue-driven organization can build a competitive RPA product, it could
guarantee a huge portion of the RPA market.
Since 2020, the start of pandemic bigger organizations that are as of now utilizing RPA have started evaluating
alternate and additional approaches to utilize automation tools to be progressively more effective, with the
conventional act of outsourcing operational tasks to low-cost regions being ousted by a wealth of in-house RPA
developers. This practice, known as “Robo-sourcing”, will see programming robot developers automating work
and outsourcing tasks to robots to help improve employee efficiency and increase job satisfaction. It is a
section that should be orchestrated with regards to that broader vision, close by different tools that deliver
what RPA alone cannot: visibility, intelligent optimization, and a direct impact on central business outcomes.
Despite the rise of digital and robotics solutions, a significant challenge for businesses continues to be the
management of forms, correspondence, contracts, and other free text content. This is particularly the case with
external material such as customer or supplier contracts, which creates the need for highly manual case
management. To deploy these solutions within a business, we need a mechanism that that opens access to an
organization’s applications estate. An iceboat or chatbot is of course only as smart as the information it can
extract and relay to its user. The way this comes together, in this example, is by employing the robots to fetch
and deliver the data to our conversational interface, i.e., the chatbot, and thus answer the posed question. This
is achieved by the chatbot converting the abstract question into a series of queries that can be understood by
the RPA system. The robot then queries the system(s) of record to retrieve relevant data items, packages them
and hands the package back to the chatbot, enabling it to reconstruct these into a natural language response.
RPA is a crucial component in opening applications – particularly those that are difficult to integrate with – and
allows them 9to interact in the new world of conversational interfaces.
All businesses have some form of data pipeline feeding their supply chains and warehouses. They are designed
to try to provide 100% of the data needed on a regular basis. While it is usually adequate for reporting, it is not
a complete enough data set for analysis and insight generation. There is always a ‘last mile’ of supplementary
www.irjmets.com @International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering, Technology and Science
[890]
e-ISSN: 2582-5208
International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science
Volume:03/Issue:01/January-2021 Impact Factor- 5.354 www.irjmets.com
analysis required to capture a specific piece of insight. This augments the data set with data to support root
causes analysis of challenges such as month-end close for example.
V. REFERENCES
[1] Asatiani, A., & Penttinen, E, "Turning robotic process automation into commercial success-case
OpusCapita". Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases, 6, p. 67-74, 2016.
[2] Berruti, F., Nixon, G., Taglloni, G., & Whiteman, R "Intelligent process automation: The engine at the
core of the next-generation operating model"., 2017, pp.68-73.
[3] Vedder, R., & Guynes, C. S, "The challenge of bot sourcing. Review of Business Information Systems
(RBIS), 20(1)., 2016, https://doi. org/10.19030/rbis.v20i1.9677.
[4] Kroll, C., Bujak, A., Darius, V., Enders, W., & Esser, M, "Robotic process automation: Robots conquer
business processes in back offices.: Capgemini Consulting", 2016
[5] Sutherland, C., "). Framing a Constitution for Robotistan: Racing with the Machine of Robotic
Automation," Hfs Research, 2013
[6] Vom Brocke, J., Maaß, W., Buxmann, P., Maedche, A., Leimeister, J. M., & Pecht, G "Future work and
enterprise systems. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 60(4), p 357-366. https://doi.org/
10.1007/s12599-018-0544-2", 2018
[7] Bygstad, B. The coming of lightweight IT. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Conference on
Information Systems (ECIS) (pp. 1- 16). Münster, Germany, 2015
[8] Mendling, J., Decker, G., Hull, R., Reijers, H. A., & Weber, I." How do machine learning, robotic process
automation, and Blockchains affect the human factor in business process management?
Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 43, p 297-320
https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.04319. 2018
[9] KPMG," Transforming business models with robotic process automation: Fulfilling the vision of global
business services", 2016
[10] https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/robotic-process-automation-rpa
www.irjmets.com @International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering, Technology and Science
[891]
You might also like
- Understanding RPA - 1Document7 pagesUnderstanding RPA - 1Dwaraki DNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Robotic Process Automation (RPADocument19 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Robotic Process Automation (RPAJithinNo ratings yet
- RPA Automation Boosts Efficiency With BotsDocument3 pagesRPA Automation Boosts Efficiency With BotsMila TanNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide To RPA (Robotic Process Automation)Document15 pagesUltimate Guide To RPA (Robotic Process Automation)mrs dosadoNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument177 pagesNotesshashankgowdar02No ratings yet
- 182 Pages PDG - About RPADocument182 pages182 Pages PDG - About RPAjohanna100% (1)
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) : Kalinga Institute of Industrial TechnologyDocument25 pagesRobotic Process Automation (RPA) : Kalinga Institute of Industrial TechnologyShibam OjhaNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation: Bachelor of TechnologyDocument9 pagesRobotic Process Automation: Bachelor of TechnologyShivam Juneja0% (1)
- Ccs361 Rpa Unit 1 NotesDocument13 pagesCcs361 Rpa Unit 1 NotesSelva PriyaNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process AutomationDocument27 pagesRobotic Process AutomationMohitpandeNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation Design & Development 18CS745 Module 1Document61 pagesRobotic Process Automation Design & Development 18CS745 Module 1PavanNo ratings yet
- Beyond RPA How To Build Toward End-To-End Process AutomationDocument9 pagesBeyond RPA How To Build Toward End-To-End Process Automationpixie363No ratings yet
- Robotics Process AutomationDocument10 pagesRobotics Process AutomationPALLAVI KAMBLENo ratings yet
- RPA in Financial Services Infographic by RapidValueDocument1 pageRPA in Financial Services Infographic by RapidValuewawawa1No ratings yet
- Robotics Process Automation (RPA) : Impact of RPA On SocietyDocument10 pagesRobotics Process Automation (RPA) : Impact of RPA On SocietyXaundrae McDonaldNo ratings yet
- RPAide Presentation VFDocument10 pagesRPAide Presentation VFMandaleeka ShreeramNo ratings yet
- Intelligent RPA in the Oil & Gas SectorDocument15 pagesIntelligent RPA in the Oil & Gas Sectorbenny martadinataNo ratings yet
- Case Study Robotic Process Automation - 103822650Document14 pagesCase Study Robotic Process Automation - 103822650Abdullah ButtNo ratings yet
- RPA Interview KIT: Quality Thought PH: 9963486280, 9963799240 Location: Ameerpet / Kondapur Email IdDocument33 pagesRPA Interview KIT: Quality Thought PH: 9963486280, 9963799240 Location: Ameerpet / Kondapur Email IdRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst TrainingDocument6 pagesBusiness Analyst TrainingAhmed Mohamed SalihNo ratings yet
- What is RPA? Understanding Robotic Process AutomationDocument7 pagesWhat is RPA? Understanding Robotic Process Automationsadasiva001No ratings yet
- Intelligent Process Automation Ocr Whitepaper PDFDocument16 pagesIntelligent Process Automation Ocr Whitepaper PDFKang Apelah100% (1)
- Why Does AI MatterDocument1 pageWhy Does AI MatterGayathri KodakandlaNo ratings yet
- The Hyperautomation Revolution: Transforming Industries and WorkforcesFrom EverandThe Hyperautomation Revolution: Transforming Industries and WorkforcesNo ratings yet
- TOP 25 RPA Interview Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesTOP 25 RPA Interview Questions and AnswersTutorialsMateNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation Software Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandRobotic Process Automation Software Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- Discovering AI Application Across Value ChainDocument3 pagesDiscovering AI Application Across Value ChainSwarnendu BiswasNo ratings yet
- RPA Fundamentals: Robotic Process AutomationDocument8 pagesRPA Fundamentals: Robotic Process AutomationraviveNo ratings yet
- DI - Automation With IntelligenceDocument32 pagesDI - Automation With IntelligencepokalooNo ratings yet
- RPADocument18 pagesRPAQforQA100% (1)
- 8 Nasscom-Eri-Rpa Market Opportunity - NasscomDocument61 pages8 Nasscom-Eri-Rpa Market Opportunity - Nasscomnoestoypanadie2000No ratings yet
- The Imperatives For Automation SuccessDocument10 pagesThe Imperatives For Automation SuccessAnushree Pawanraj100% (1)
- Dont Get Left BehindDocument25 pagesDont Get Left BehindMarta GarcíaNo ratings yet
- FlowForma - 6 Step Digital Process Automation EGuideDocument20 pagesFlowForma - 6 Step Digital Process Automation EGuideOnur UyarNo ratings yet
- E-Guide The Ultimate Guide To RPADocument29 pagesE-Guide The Ultimate Guide To RPAAlpha Nikolai LaudenciaNo ratings yet
- Service-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureFrom EverandService-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- AE Ebook - The Art of Automation For Insurance IndustryDocument14 pagesAE Ebook - The Art of Automation For Insurance IndustryRupesh GuravNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Automation 101 Session1Document27 pagesIntelligent Automation 101 Session1Shreenidhi M RNo ratings yet
- RPA - RPA Center of Excellence - WhitepaperDocument12 pagesRPA - RPA Center of Excellence - WhitepaperSara CandeiasNo ratings yet
- WP StateOfProcessAutomation2022 FIN enDocument19 pagesWP StateOfProcessAutomation2022 FIN enayudingwani12No ratings yet
- Implementing Robotic Process Automation Standard RequirementsFrom EverandImplementing Robotic Process Automation Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- 5 WAYS AI BOOSTS WORKPLACE PRODUCTIVITYDocument4 pages5 WAYS AI BOOSTS WORKPLACE PRODUCTIVITYMarc Jeryl BotioNo ratings yet
- Uipath - Orchestrator QuestionsDocument7 pagesUipath - Orchestrator Questionssaubhagya ranjan mohapatraNo ratings yet
- Re Framework UiPathDocument13 pagesRe Framework UiPathAjit Kumar100% (1)
- Robotic Process Automation: A Straight-Forward ApproachDocument2 pagesRobotic Process Automation: A Straight-Forward ApproachcvacaNo ratings yet
- Hyper AutomationDocument2 pagesHyper Automationalejandro gonzalez100% (2)
- Automation Anywhere - Deployment Best PracticesDocument7 pagesAutomation Anywhere - Deployment Best PracticesparanjaliNo ratings yet
- Rpa & AiDocument14 pagesRpa & AiDeepika PamilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Business Process OutsourcingDocument35 pagesChapter 4 - Business Process OutsourcingBisrat FekedeNo ratings yet
- Use Case OverviewDocument29 pagesUse Case OverviewSatya YSNo ratings yet
- Ey Robotics in ClaimDocument9 pagesEy Robotics in ClaimCool ManNo ratings yet
- Rpa Report Asia 2017Document5 pagesRpa Report Asia 2017Thiago CostaNo ratings yet
- Rpa Super ImpDocument32 pagesRpa Super ImpthedNo ratings yet
- RPA GlossaryDocument5 pagesRPA GlossaryKatiyar RahulNo ratings yet
- Understanding RPA - 2Document6 pagesUnderstanding RPA - 2Dwaraki DNo ratings yet
- IPRM S01-ServiceOffer D4Document6 pagesIPRM S01-ServiceOffer D4Ali ClubistNo ratings yet
- AI Based Testing Brochure Dec 2019Document8 pagesAI Based Testing Brochure Dec 2019Sowmya PNo ratings yet
- Download AI Emotion Detection ProjectsDocument6 pagesDownload AI Emotion Detection ProjectsSanket Ghatte100% (1)
- Everest Group Peak Matrix Intelligent Document Processing Technology Vendors Focus On Abbyy 2020Document17 pagesEverest Group Peak Matrix Intelligent Document Processing Technology Vendors Focus On Abbyy 2020AmitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- STM Session 1Document15 pagesSTM Session 1Test accNo ratings yet
- Ethics ManualDocument7 pagesEthics ManualTest accNo ratings yet
- UM21283 - Value-Driven Digital Transformation Processes Through AutomationDocument1 pageUM21283 - Value-Driven Digital Transformation Processes Through AutomationTest accNo ratings yet
- UM21283 - Skills and Competencies For Digital Transformation - A Critical Analysis in The Context of RPADocument19 pagesUM21283 - Skills and Competencies For Digital Transformation - A Critical Analysis in The Context of RPATest accNo ratings yet
- Individual Project Report On Role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Digital TransformationDocument13 pagesIndividual Project Report On Role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Digital TransformationTest accNo ratings yet
- IB Urban Environments Option G (Latest 2024)Document154 pagesIB Urban Environments Option G (Latest 2024)Pasta SempaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Experience Report Lunar Module Landing Gear SubsystemDocument60 pagesApollo Experience Report Lunar Module Landing Gear SubsystemBob Andrepont100% (3)
- Template Research ProjectDocument13 pagesTemplate Research ProjectTuấn Anh Đoàn CôngNo ratings yet
- Hcin 543 Entity Relationship Diagram For Diabetes DataDocument4 pagesHcin 543 Entity Relationship Diagram For Diabetes Dataapi-534036919No ratings yet
- Ligot v. MathayDocument1 pageLigot v. MathayJoyce BaylonNo ratings yet
- Part 1 LEA 4 Law Enforcement Operations and Planning With Crime MappingDocument94 pagesPart 1 LEA 4 Law Enforcement Operations and Planning With Crime Mappingyomaeko CinkoNo ratings yet
- The Sssessential List of Microsoft Outlook Keyboard ShortcutsDocument3 pagesThe Sssessential List of Microsoft Outlook Keyboard Shortcutsabidaliabid1No ratings yet
- VATEUD Pilots ManualDocument32 pagesVATEUD Pilots ManualAndreas TzekasNo ratings yet
- PKG Materials Standards IIP A A JoshiDocument45 pagesPKG Materials Standards IIP A A JoshiDeepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Modern History Notes (Sample Notes For JPSC Mains Exam)Document21 pagesModern History Notes (Sample Notes For JPSC Mains Exam)Ijhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- 5 Short MustWatch Motivational Videos For TeachersrccymDocument4 pages5 Short MustWatch Motivational Videos For Teachersrccymfoxpeak8No ratings yet
- OptiLobe Rotary Lobe PumpDocument4 pagesOptiLobe Rotary Lobe PumpRemus-Mihai GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Workday Studio - Complex Integration Tool OverviewDocument3 pagesWorkday Studio - Complex Integration Tool OverviewHarithaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine 7-26-2016Document94 pagesElectrical Machine 7-26-2016Engr. Raheel khanNo ratings yet
- Missing Number Series Questions Specially For Sbi Po PrelimsDocument18 pagesMissing Number Series Questions Specially For Sbi Po PrelimsKriti SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- NY Long Island Group - Jun 2008Document8 pagesNY Long Island Group - Jun 2008CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Senate Bill 365Document5 pagesSenate Bill 365samtlevinNo ratings yet
- Genetic Modified FoodDocument16 pagesGenetic Modified FoodKishoNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Plasticity: Dong Phill Jang, Piemaan Fazily, Jeong Whan YoonDocument17 pagesInternational Journal of Plasticity: Dong Phill Jang, Piemaan Fazily, Jeong Whan YoonGURUDAS KARNo ratings yet
- Tribology Aspects in Angular Transmission Systems: Hypoid GearsDocument7 pagesTribology Aspects in Angular Transmission Systems: Hypoid GearspiruumainNo ratings yet
- CH 15 QuizDocument8 pagesCH 15 QuizNelano EastNo ratings yet
- To Register Your IGP Please Visit or Scan The QR Code Below To Register Your IGP Please Visit or Scan The QR Code BelowDocument1 pageTo Register Your IGP Please Visit or Scan The QR Code Below To Register Your IGP Please Visit or Scan The QR Code BelowLester Jao SegubanNo ratings yet
- TD102 Conductor - Standard ConductorsDocument2 pagesTD102 Conductor - Standard ConductorsHFandino1No ratings yet
- Proposed Rule: Employment: Adverse ActionsDocument4 pagesProposed Rule: Employment: Adverse ActionsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Instrument Landing SystemDocument35 pagesInstrument Landing SystemDena EugenioNo ratings yet
- George Washington's Presidency NotesDocument5 pagesGeorge Washington's Presidency Notesf kNo ratings yet
- RRB GR1Document2 pagesRRB GR1Eniyav DragneelNo ratings yet
- IC Release Management Checklist TemplateDocument5 pagesIC Release Management Checklist Templatepasc colcheteNo ratings yet
- Systemverilog Interview QuestionsDocument31 pagesSystemverilog Interview QuestionsDivya Dm100% (1)
- The Art of Comeback Donald TrumpDocument1 pageThe Art of Comeback Donald TrumpMoYagzud0% (2)